A high-stretch, high-viscosity, self-healing double-network hydrogel for tissue adhesion and its preparation method and application
A hydrogel and double network technology, applied in general culture methods, biochemical equipment and methods, applications, etc., can solve the problems of inability to achieve high strength, high toughness mechanical properties, inability to rebuild extracellular matrix, and low cell mass transfer efficiency and other issues, to achieve good cell compatibility, excellent tissue adhesion performance, and high self-healing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
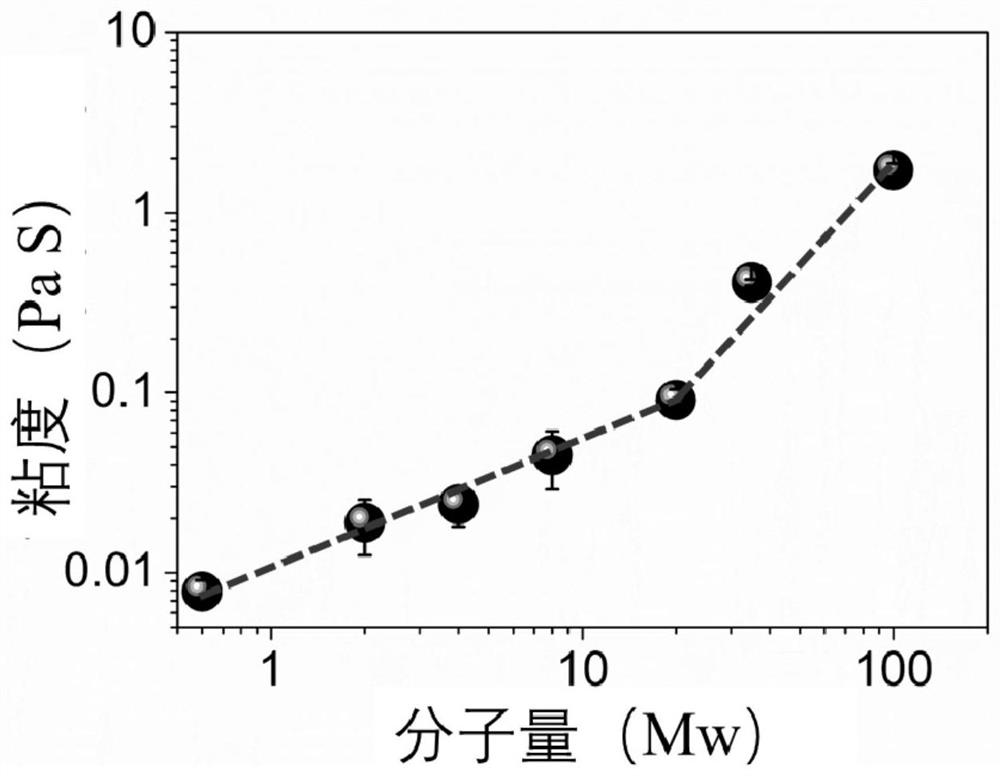
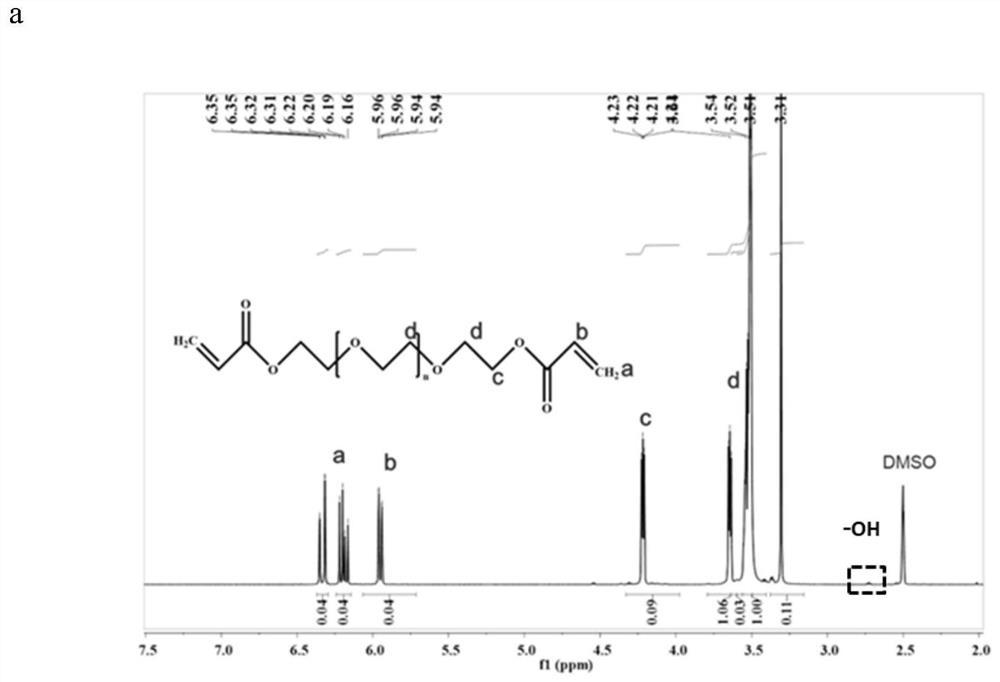
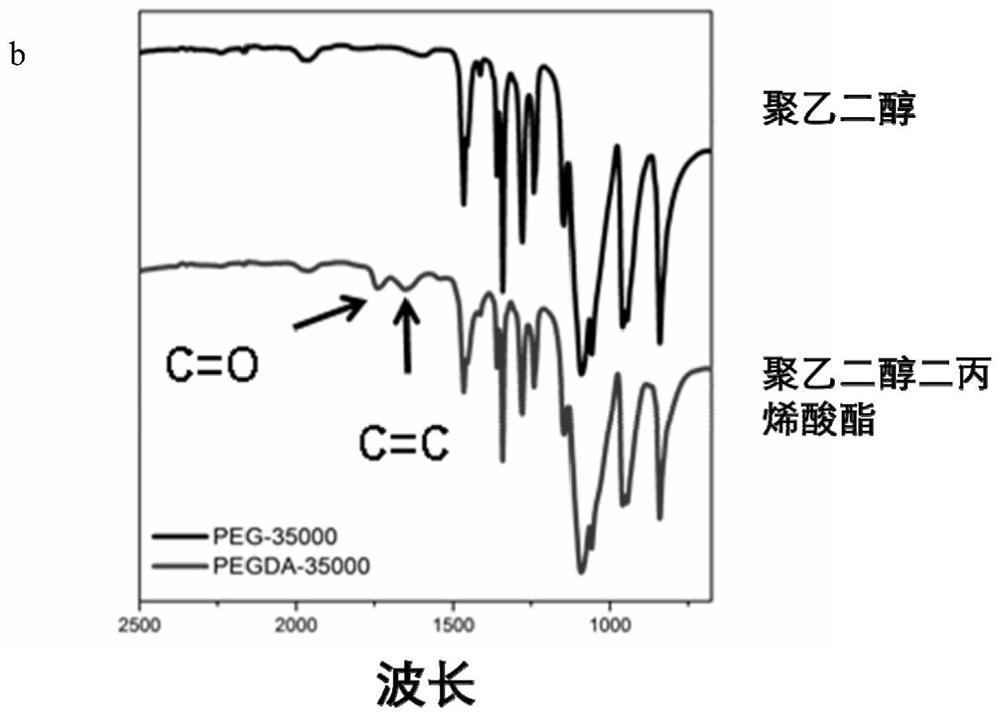
[0056] In this example, polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA) was prepared by a one-step method. 35 g of polyethylene glycol (PEG) with a molecular weight of 35 kDa was dissolved in 80 mL of anhydrous dichloromethane, and 0.74 mL of triethylamine and 1 mL of acryloyl chloride was reacted at room temperature for 24 hours. After the reaction, the impurities were washed with anhydrous magnesium carbonate solution, extracted and separated, precipitated in ether, and then freeze-dried to obtain polyethylene glycol diacrylate with a molecular weight of 35 kDa. Carry out hydrogen NMR spectrum analysis to polyethylene glycol diacrylate ( figure 2 a) It can be seen that a double bond characteristic peak has appeared at 5.80ppm, and infrared spectroscopic analysis ( figure 2 b) at 1730cm -1 The peak corresponding to the C=O bond indicates the successful grafting of acrylate on the polyethylene glycol, and the unreacted polyethylene glycol content and the double bond peak area are d...
Embodiment 2
[0069] According to the data calculated in Example 1, polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight of 35 kDa is selected as the physical network, and 35 kDa is higher than the critical molecular weight of polyethylene glycol.
[0070] Dissolve 0.4 g of polyethylene glycol diacrylate with a molecular weight of 35 kDa and 0.4 g of polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight of 35 kDa in 1 mL of deionized water, and add 0.005 g of 2-hydroxy-4′-(2-hydroxyethoxy Base)-2-methylpropiophenone was mixed at 60° C. for 30 min to form a homogeneous solution to obtain a pre-polymerization solution (pre-polymerization liquid) of a double network hydrogel. Put the pre-polymerization solution at 365nm, 50mw / cm 2 The double network hydrogel was cross-linked under ultraviolet light for 30s, and its viscoelastic data, self-healing efficiency and lap bonding strength are listed in Table 3. Freeze the double-network hydrogel in the -80°C refrigerator for 1 hour and take it out. The cross-section o...
Embodiment 3
[0072] According to the data calculated in Example 1, polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight of 35 kDa is selected as the physical network, and 35 kDa is higher than the critical molecular weight of polyethylene glycol.
[0073] Dissolve 0.4 g of polyethylene glycol diacrylate with a molecular weight of 35 kDa in 1 mL of deionized water, and add 0.005 g of 2-hydroxy-4′-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-2-methylpropiophenone at 60 °C for 30 min to form a uniform solution to obtain a polyethylene glycol diacrylate hydrogel pre-polymerization solution (pre-polymerization solution). Put the pre-polymerization solution at 365nm, 50mW / cm 2 Crosslink under ultraviolet light for 30s to obtain polyethylene glycol diacrylate hydrogel. Dissolve 4 g of polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight of 35 kDa in 10 mL of aqueous solution to obtain a uniform polyethylene glycol solution. The acrylate hydrogel was soaked in polyethylene glycol solution for 24 hours until the polyethylene glycol molecules...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com