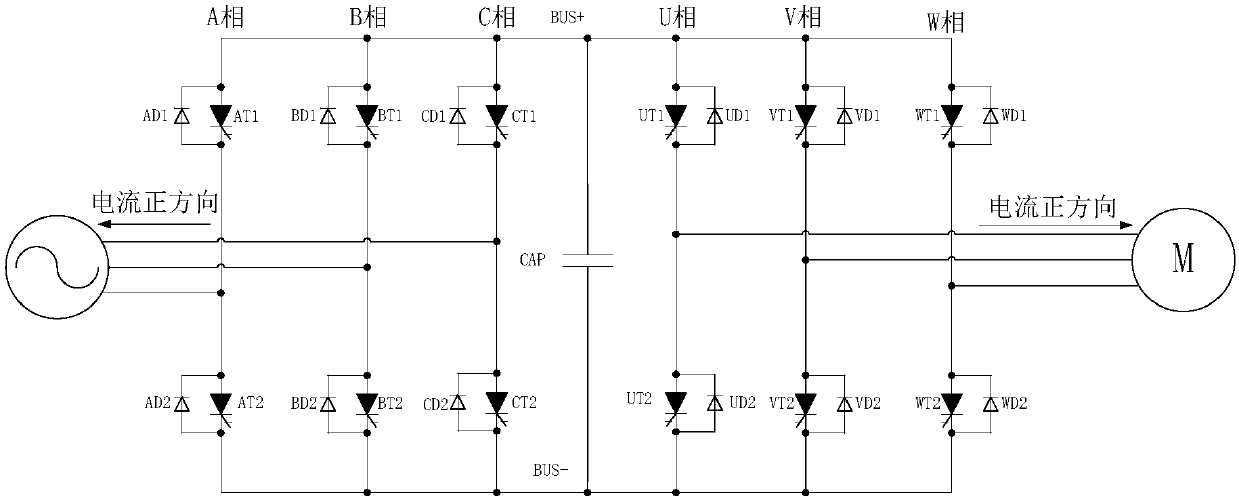
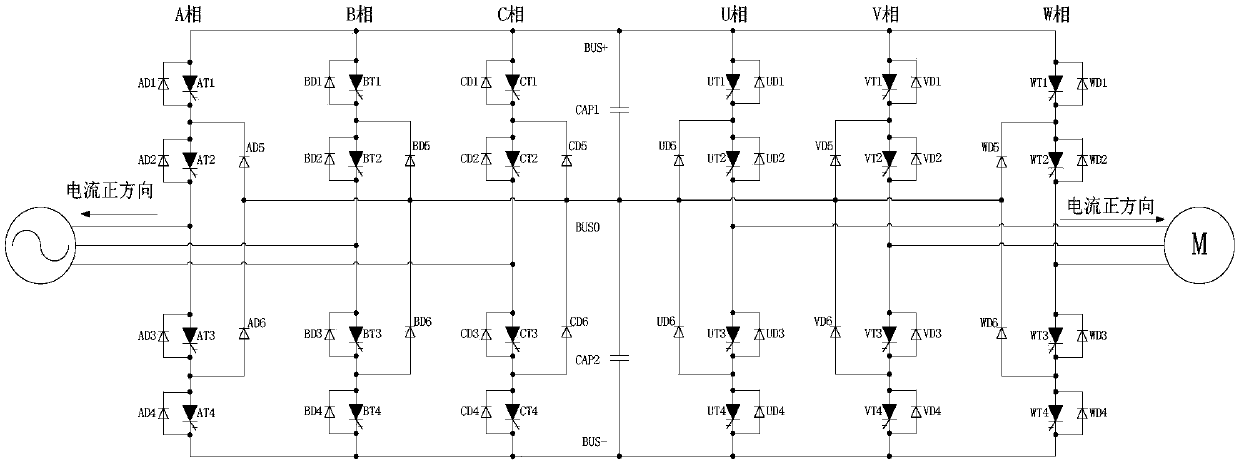
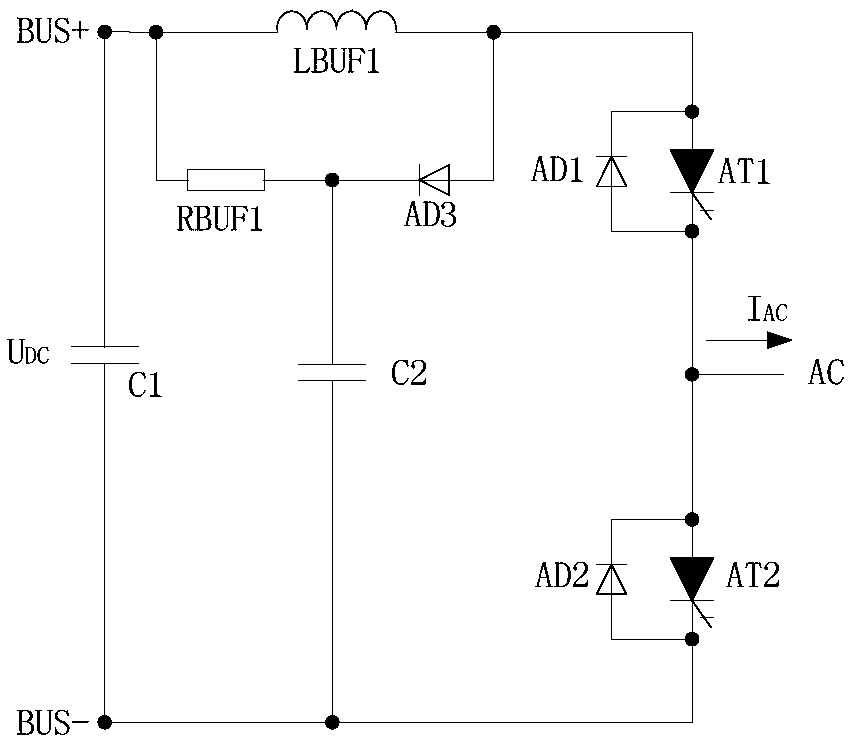
Converter fault processing method, readable storage medium and converter
A fault handling method and converter technology, applied in the direction of converting AC power input to AC power output, output power conversion devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of damage and damage of fully controlled switching devices, and avoid failure magnifying effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the converter fault handling method of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0088] Step 1, the controller U3 runs the main program, that is, detects the main circuit U1 of the converter, and determines whether the main circuit U1 is faulty.
[0089] Step 2: When the controller U3 judges that the main circuit U1 is not faulty, return to step 1; when the controller judges that the main circuit U1 is faulty, enter the next step.
[0090] Step 3: The controller U3 determines the faulty phase unit and the non-faulty phase unit of the main circuit U1 of the converter.
[0091] Step 4: The controller U3 sends a control command to turn off the fully-controlled switching device of the non-faulty phase unit of the main circuit U1 of the converter, and keeps the switching state of the fully-controlled switching device of the faulty phase unit of the main circuit U1 of the converter. Change.
Embodiment 2
[0093] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the converter fault handling method of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0094] Steps 1 to 4 of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 1.
[0095] The "fault" in step 1 includes direct faults and non-direct faults, and "judging whether the main circuit U1 has a fault" refers to judging whether the main circuit U1 has a direct fault or a non-direct fault. The failed phase unit is called the faulted phase unit, and the remaining unfaulted phase units are called non-faulted phase units, the same below.
[0096] Step 5: When a non-shoot-through fault is detected but a shoot-through fault is not detected, within the delay time Tdelay, the controller U3 detects the faulty phase unit and determines whether a shoot-through fault occurs in the faulty phase unit.
[0097] Step 6. When the controller U3 detects that the faulty phase unit has a through fault, the controller U3 issues a command to continue to maintain th...
Embodiment 3
[0101] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the converter fault handling method of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0102] Steps 1 to 4 of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 1.
[0103]The "fault" in step 1 includes direct faults and non-direct faults, and "judging whether the main circuit U1 has a fault" refers to judging whether the main circuit U1 has a direct fault or a non-direct fault.
[0104] Step 5: When a non-shoot-through fault is detected but a shoot-through fault is not detected, within the delay time Tdelay, the controller U3 detects the faulty phase unit and determines whether a shoot-through fault occurs in the faulty phase unit.
[0105] Step 6: When the controller U3 does not detect the through fault of the faulty phase unit, the controller U3 issues a command to turn off the full-control switching device of the faulty phase unit of the converter.
[0106] When the controller U3 detects the through fault of the faulty phase unit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com