Offset modeling method of 3D mesh surface with variable thickness based on laplacian differential domain deformation
A three-dimensional mesh, variable thickness technology, applied in the field of additive manufacturing, can solve problems such as stress concentration, difference in detail features, and inability to guarantee mechanical properties, and achieve the effect of improving stress concentration and increasing bearing capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
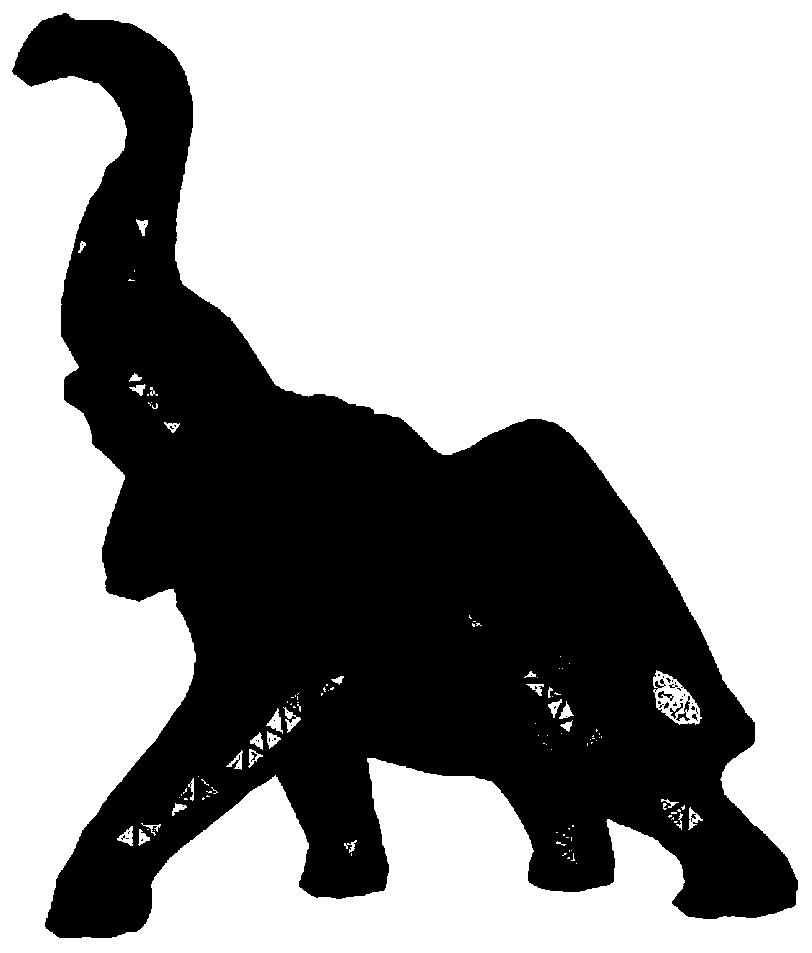
[0075] A variable thickness offset modeling method for a three-dimensional mesh surface based on Laplacian differential domain deformation, comprising the following steps:
[0076] Step 1. Read the 3D discrete surface model and extract Morse's significant feature points, such as figure 2 shown;
[0077] (1) Calculate the Morse function value f(v) of all vertices v of the original mesh surface with the average curvature:
[0078]
[0079] where the maximum and minimum principal curvature k of each vertex max 、k min , this kind of feature information can be solved by fitting the surface. The cubic polynomial used to fit the surface can be expressed as follows:
[0080] z=Ax 3 +Bx 2 y+Cxy 2 +Dy 3 +Ex 2 +Fxy+Gy 2 +Hx+ly
[0081] (2) Using the Gaussian filter function W c and feature preserving function W s , calculate the bilateral filter value B(f(v),r) of f(v):
[0082]
[0083] Where r represents the neighborhood radius of the vertex of the grid, N(v, 2r) r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com