Dynamic Extraction Method of Software Genes in Memory Based on Markov Model
A Markov model and dynamic extraction technology, applied in the field of malicious code detection, can solve the problems of low extraction efficiency, achieve the effect of reducing the analysis scale, increasing the complexity of data processing, and improving work efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
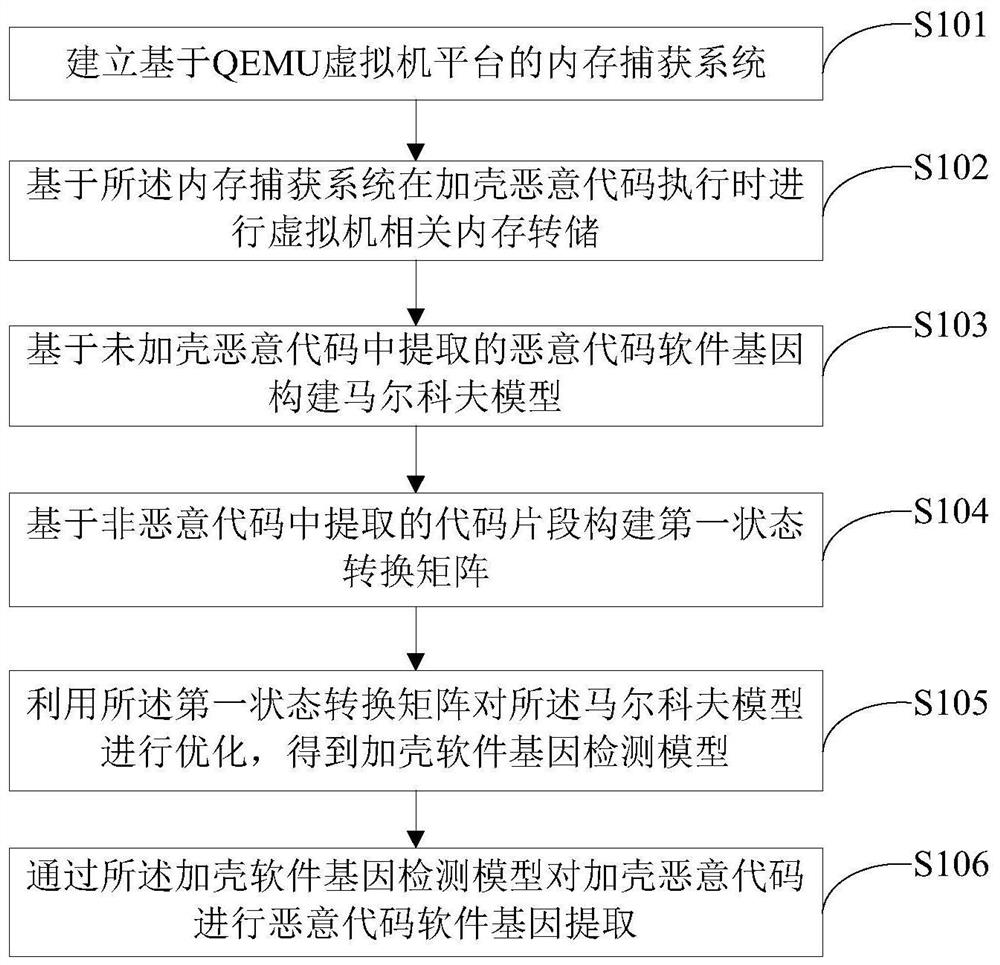
[0043] like figure 1 As shown, a Markov model-based software gene dynamic extraction method in memory, including:
[0044] Step S101: establishing a memory capture system based on the QEMU virtual machine platform;
[0045] Step S102: Based on the memory capture system, the virtual machine-related memory dump is performed when the packed malicious code is executed;
[0046] Step S103: constructing a Markov model based on the malware gene extracted from the unpacked malicious code;
[0047] Step S104: constructing a first state transition matrix based on code fragments extracted from non-malicious codes;
[0048] Step S105: using the first state transition matrix to optimize the Markov model to obtain a packer software gene detection model;
[0049]Step S106: Using the packer software gene detection model to extract the packer malicious code software gene.
[0050] The invention dynamically runs samples in a virtual environment by constructing a memory capture system based ...
Embodiment 2
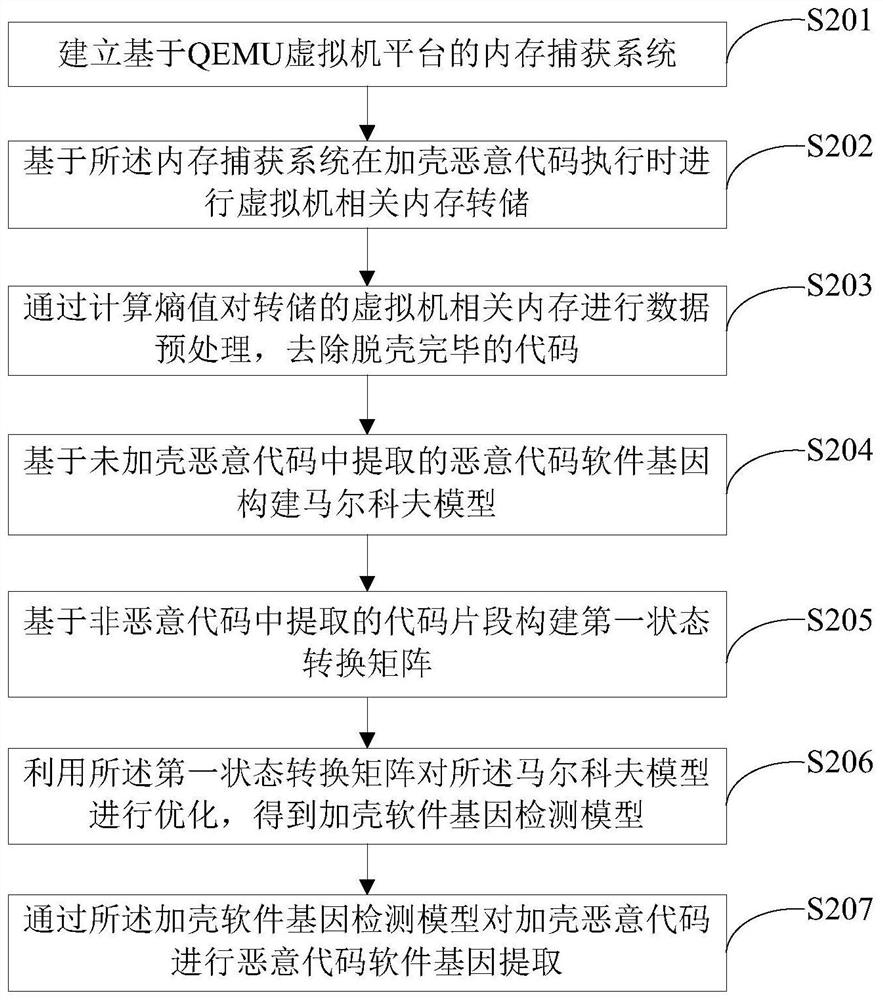
[0052] like figure 2 As shown, another Markov model-based in-memory software gene dynamic extraction method includes:
[0053] Step S201: Establish a memory capture system based on the QEMU virtual machine platform;
[0054] Specifically, a virtual machine is built on the QEMU virtual machine platform, and a control server and a file server are built on the periphery of the QEMU virtual machine platform to form a memory capture system; the control server communicates and controls the QEMU virtual machine platform to control the snapshot of the virtual machine Reply, run, suspend and memory dump; the file server transmits the files of the packed malicious code between the client and the virtual machine; the virtual machine unpacks the packed malicious code.
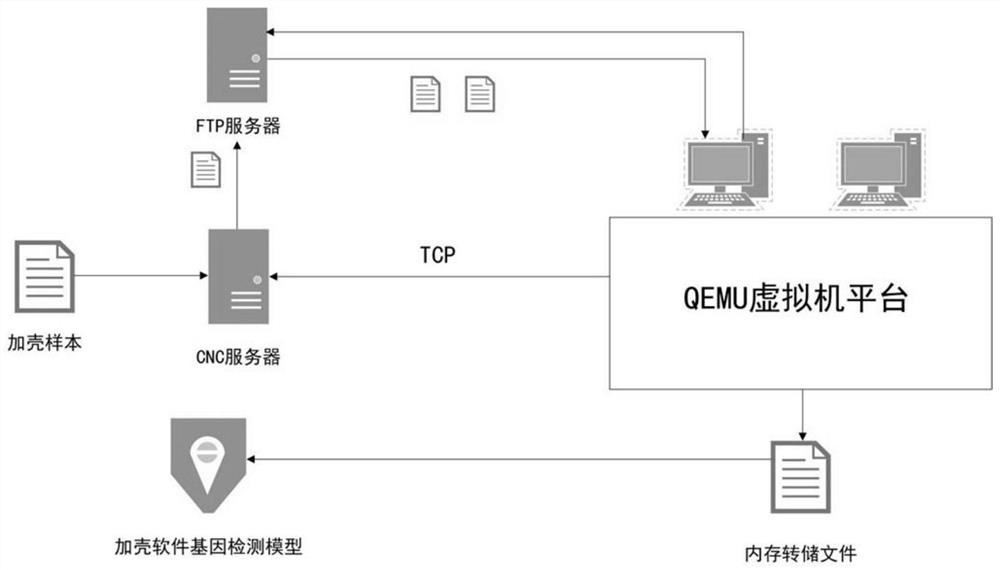
[0055] As a possible implementation, such as image 3 As shown, Qemu is selected as the virtual machine platform, a CNC real-time control server and an FTP file server are built around the virtual environment, and two v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com