Shear wave imaging based on ultrasound with increased pulse repetition interval
An ultrasonic imaging system and shear wave technology, applied in ultrasonic/sonic/infrasound image/data processing, ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosis, ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic equipment control, etc., can solve problems such as errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
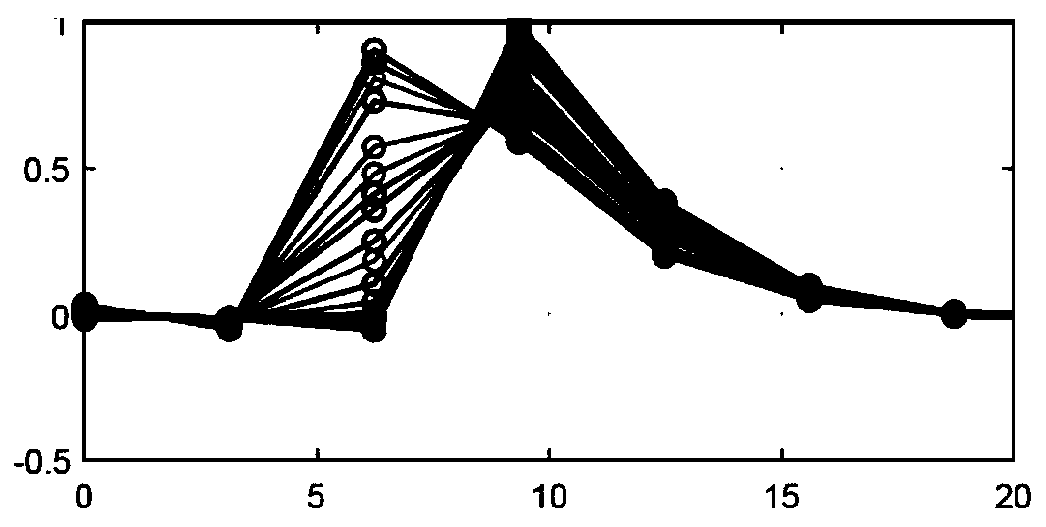
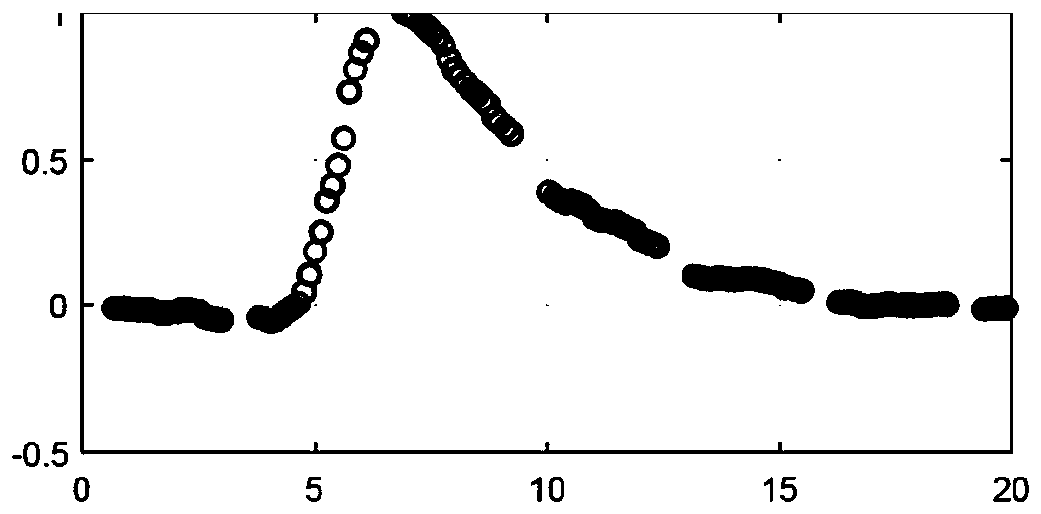
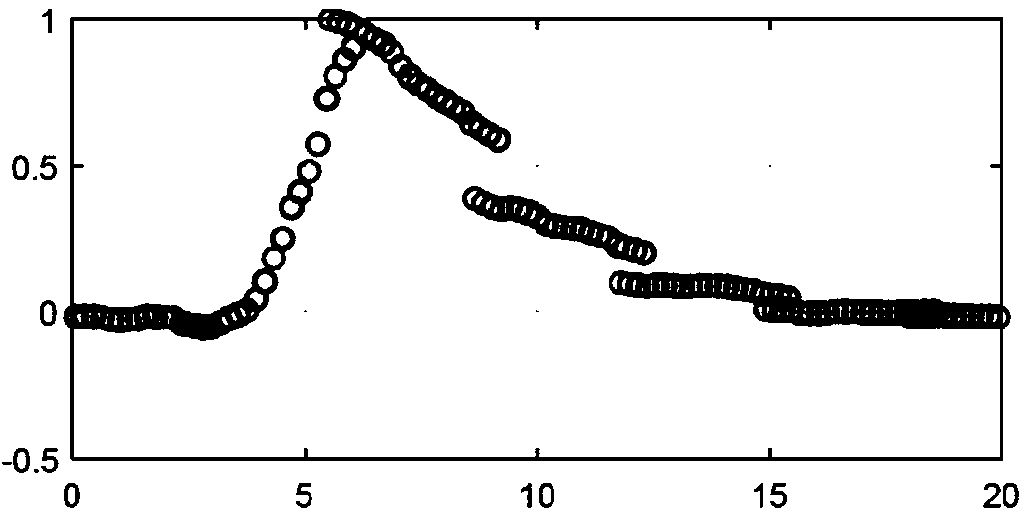
[0013] Provides shear wave imaging with ultrasound in highly rigid media. Examples of such rigid media in medical imaging include musculoskeletal (MSK) (e.g. tendon), prostate, and focal lesions of the liver. By increasing the apparent PRF, shear wave velocity can be estimated more accurately even if the ultrasonic round-trip travel time results in undersampling of a given location. The same approach can be used in less rigid media where tracking frequency is not an issue. This approach increases the effective PRF, leading to potentially more accurate shear wave velocity estimates.
[0014] Displacement profiles from multiple lateral positions are combined. Displacement profiles from different lateral locations are time-shifted and scaled based on possible shear-wave velocities and attenuations. The time shifted and scaled distributions are combined to form a displacement distribution with a higher effective PRF. Shear wave velocity is calculated by finding the time offset...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com