Chlorine supplementing method for guaranteeing biological stability of water quality of long-distance water delivery pipe network
A technology of biological stability and water delivery pipes, applied in chemical instruments and methods, oxidized water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of low residual chlorine concentration and high number of heterotrophic colonies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0235] Specific embodiment 1: The chlorine supplement method for ensuring the biological stability of the water quality of the long-distance water pipeline network in this embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
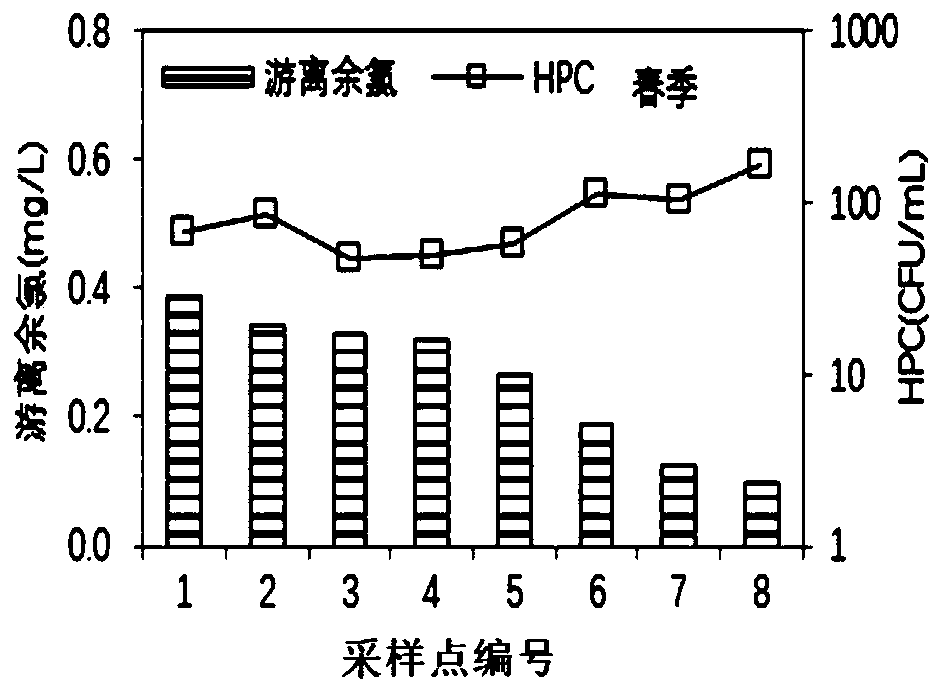
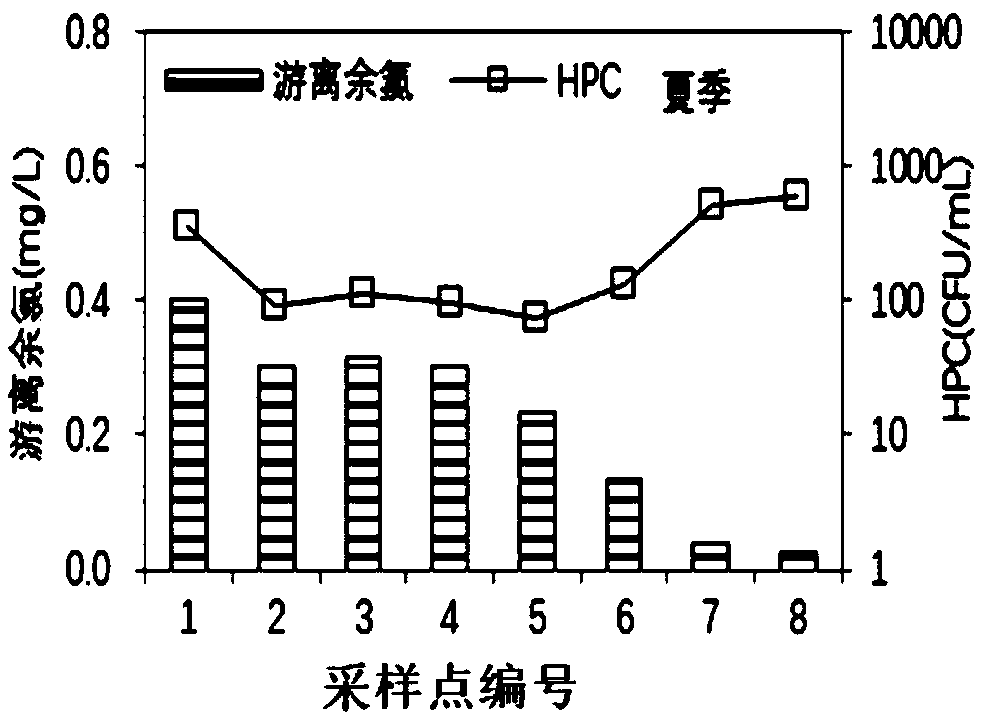
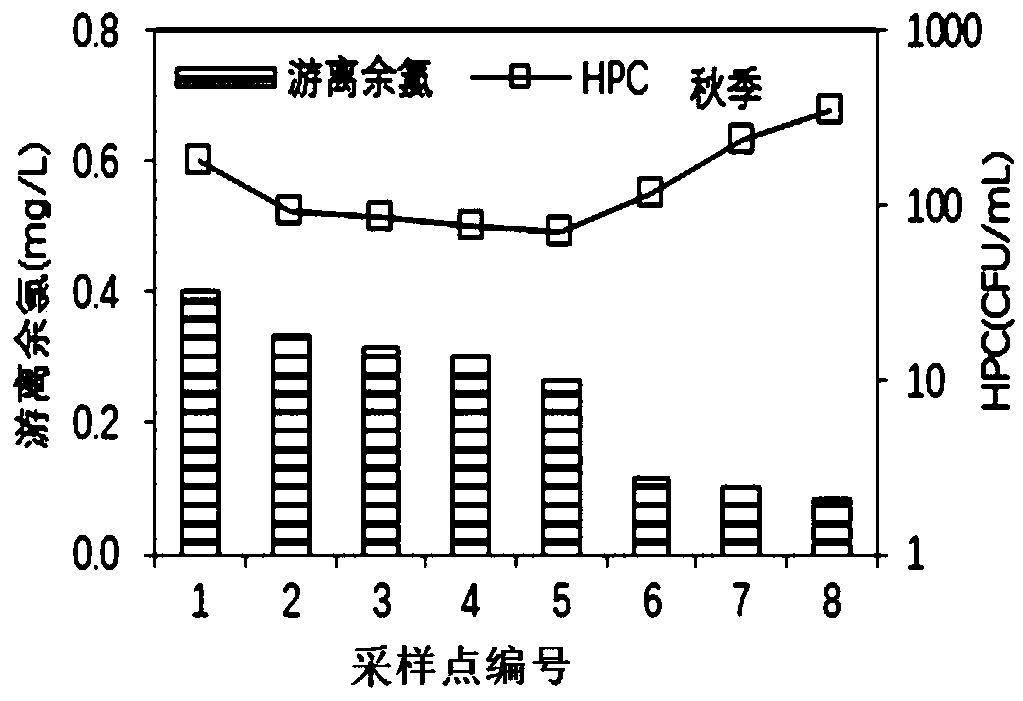
[0236] 1. Select the target water distribution network in the area, analyze the correlation between residual chlorine in the water and HPC, and determine the minimum concentration of residual chlorine in the water for the water distribution network to ensure the biological stability of the water quality;
[0237] 2. Take the effluent from the clean pool of the water plant, establish a residual chlorine attenuation model and a DBPs generation and consumption model, and take a sample at the water distribution main sampling port to detect the water quality to verify and optimize the water quality model;
[0238] 3. With the filtered water of the water plant as the object, the ammonia nitrogen concentration of the filtered water is measured and verified by th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0241] Specific embodiment two: This embodiment is different from the specific embodiment one in that the method for establishing the residual chlorine attenuation model described in step two is as follows:
[0242] Take the effluent from the clean pool of the water plant, measure 50mL and add it to a 50mL colorimetric tube with a stopper to obtain multiple samples, process different samples to determine the residual chlorine concentration, and tt represents the hydraulic retention time of the clean pool, because when water is taken from the outlet of the clean pool , The water sample already exists tt's water age,
[0243] The following four assumptions were put forward in establishing the residual chlorine attenuation model:
[0244] (1) The attenuation reaction of residual chlorine and the formation of DBPs during actual disinfection are first-order reactions based on residual chlorine concentration;
[0245] (2) There is a fixed ratio s (DBPs) between the amount of generated DBPs ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0257] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment is different from specific embodiment one or two in that the method for establishing the DBPs generation and consumption model described in step two is as follows:
[0258] Take the effluent from the clean pool of the water plant, accurately measure 50mL and add it to a 50mL colorimetric tube with stopper to obtain multiple samples, and accurately measure 30mL of water samples and add them to a 40mL Agilent screw-top sample bottle to obtain multiple samples. Add ascorbic acid to the bottle to quench the formation reaction of DBPs, and then measure the concentration of various DBPs to obtain the concentration of DBPs in water samples of different water ages. tt represents the hydraulic residence time of the clear pool, because when the water is taken from the water outlet of the clear pool, the water sample already exists tt Water age
[0259] The following four hypotheses were put forward in establishing the model:
[0260] (1) The a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com