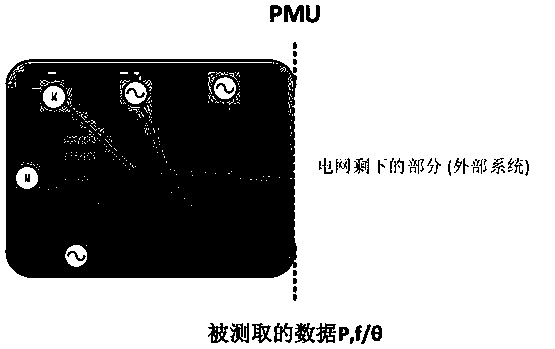
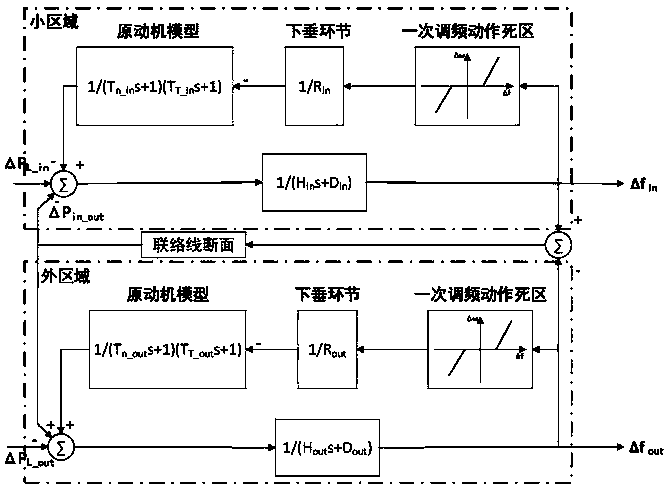
Quantitative calculation method for power grid inertia weakening in wind power plant grid connection
A technology for wind farms and power grids, which is applied in the field of quantitative calculation of grid-connected wind farms to weaken grid inertia. The effect of objective, continuous real-time estimation of estimation results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0063] In Matlab / simulink environment, established Figure 4 The simulation system is the New England 10-machine 39-node standard test system. Among them, the fan is used instead of G10 to connect to the system, the motor is used to replace the conventional load on the 39 bus, and the slip rate of the motor is changed to simulate the load disturbance in the system.
[0064] Among them, the simulation parameters are as follows: 1) Double-fed fan parameters: rated voltage Vn = 575V, rated power Pn = 250MW, stator resistance Rs = 0.023pu, stator inductance Ls = 0.18pu, rotor resistance Rr = 0.016pu, rotor inductance Lr = 0.16pu, excitation inductance Lm=2.9pu, inherent inertia time constant HDFIG=5.29s, speed controller integral coefficient Ki=0.6. Rated angular velocity ωnom=157.08rad / s, rated wind speed VwN=11.7m / s, converter time constant τ=0.02s. 2) The generator, line and load simulation parameters are shown in Table 1, 2 and 3 respectively. All per unit values are base...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com