A method for multiplexing network packet headers at the application layer
A technology of network message and application layer, which is applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems that the mark cannot be obtained and can only be used by the Linux kernel protocol stack, etc., to achieve the effect of improving data processing performance, easy tracking, and improving performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
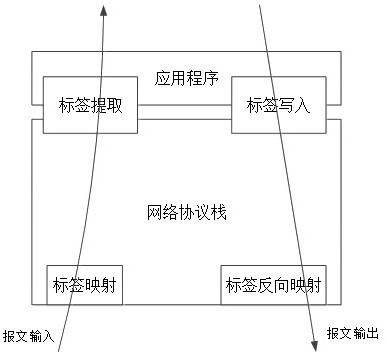
[0037] A method for multiplexing network packet headers at the application layer, which performs custom mapping on the header fields of each layer of the IP network, converts them into application layer labels, and sends the converted labels to the application layer through the protocol stack, and the application layer Directly use the tag sent as the session ID to process the data instead of generating a set of session tags by itself. The key point is that the application layer maps and multiplexes the header labels at the bottom layer of the network to reduce redundancy and improve the data processing performance of the entire network. At the same time, the unification of labels can reduce the difficulty of diagnosing network problems.
[0038] like figure 1 As shown, the input direction: the message passes through several data processing modules of "label mapping->network protocol stack->label extraction->application program" in sequence. Output direction: The message pas...
Embodiment 2
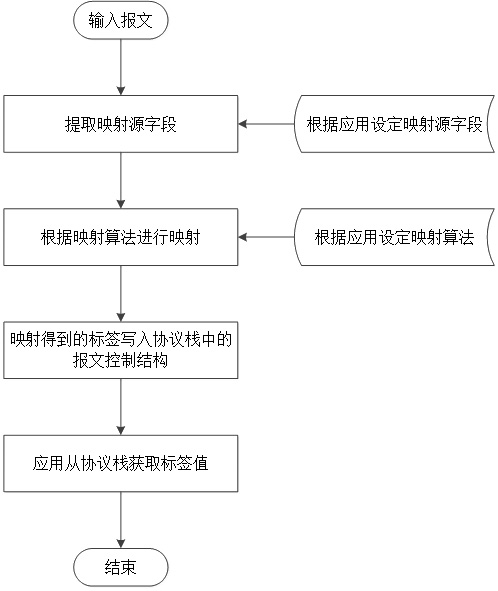
[0040] This embodiment is optimized on the basis of embodiment 1, such as figure 2 As shown in , the packets in the input direction go through the following processing steps in sequence:
[0041] 1. Extract the mapping source field. The extraction basis is set by the application program, and the optional fields include Mac address, Ethernet protocol number, VLAN Tag, VXLAN ID, IP address, IP protocol number, IP port number, etc. It can be a single field or a combination of multiple fields.
[0042] 2. Perform mapping according to the mapping algorithm to obtain the application tag value. The mapping algorithm is set by the application. It can be a simple one-to-one mapping, or hash calculation based on the combination of multiple fields. The optional calculation hash algorithm includes CRC16, CRC32, MD5, etc. One-to-one mapping directly uses a message field such as a Mac address as the application label, and hash mapping uses the hash result as the application label.
[0...
Embodiment 3
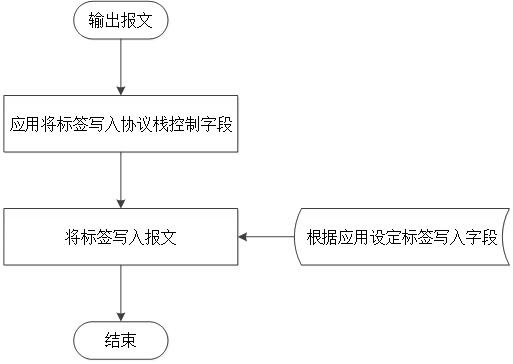
[0050] This embodiment is optimized on the basis of embodiment 1 or 2, as figure 2 As shown in , packets in the output direction go through the following steps in sequence:
[0051]1. The application writes the label into the protocol stack message control field. Similar to the input direction, the implementation of this step may be slightly different for different protocol stack implementations. Some can reuse existing fields in the message control structure, while others need to add a new field.
[0052] 2. Write the tag into the message. Unlike the packet input direction, the label reverse mapping in the output direction does not support hash mapping. The reason is that due to the limitation of traditional network equipment, the network layer packet header cannot be modified arbitrarily. However, in some scenarios, the network layer still allows modification of the header. For example, the network layer uses a user-defined SDN network. In this solution, the application...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com