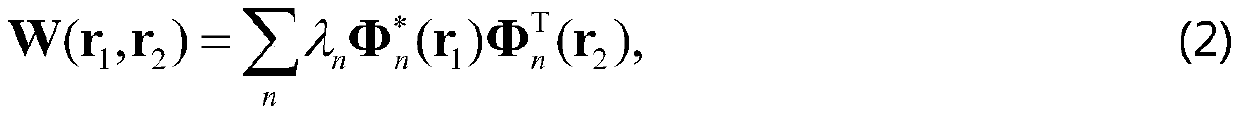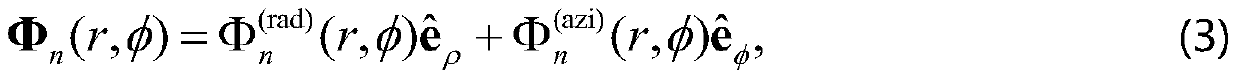Rapid calculation method for realizing tight focusing of partially coherent light
A fast calculation and tight focusing technology, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of restricting the research of tight focusing characteristics, increasing calculation time, and consuming calculation time, so as to shorten calculation time, reduce distortion, and reduce calculation. Distortion effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments, so that those skilled in the art can better understand the present invention and implement it, but the examples given are not intended to limit the present invention.
[0025] The fast calculation method for realizing the tight focusing of partially coherent light in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0026] S10. Expand the partially coherent light beam into multiple fully coherent sub-light sources, and the multiple fully coherent sub-light sources are independent of each other;
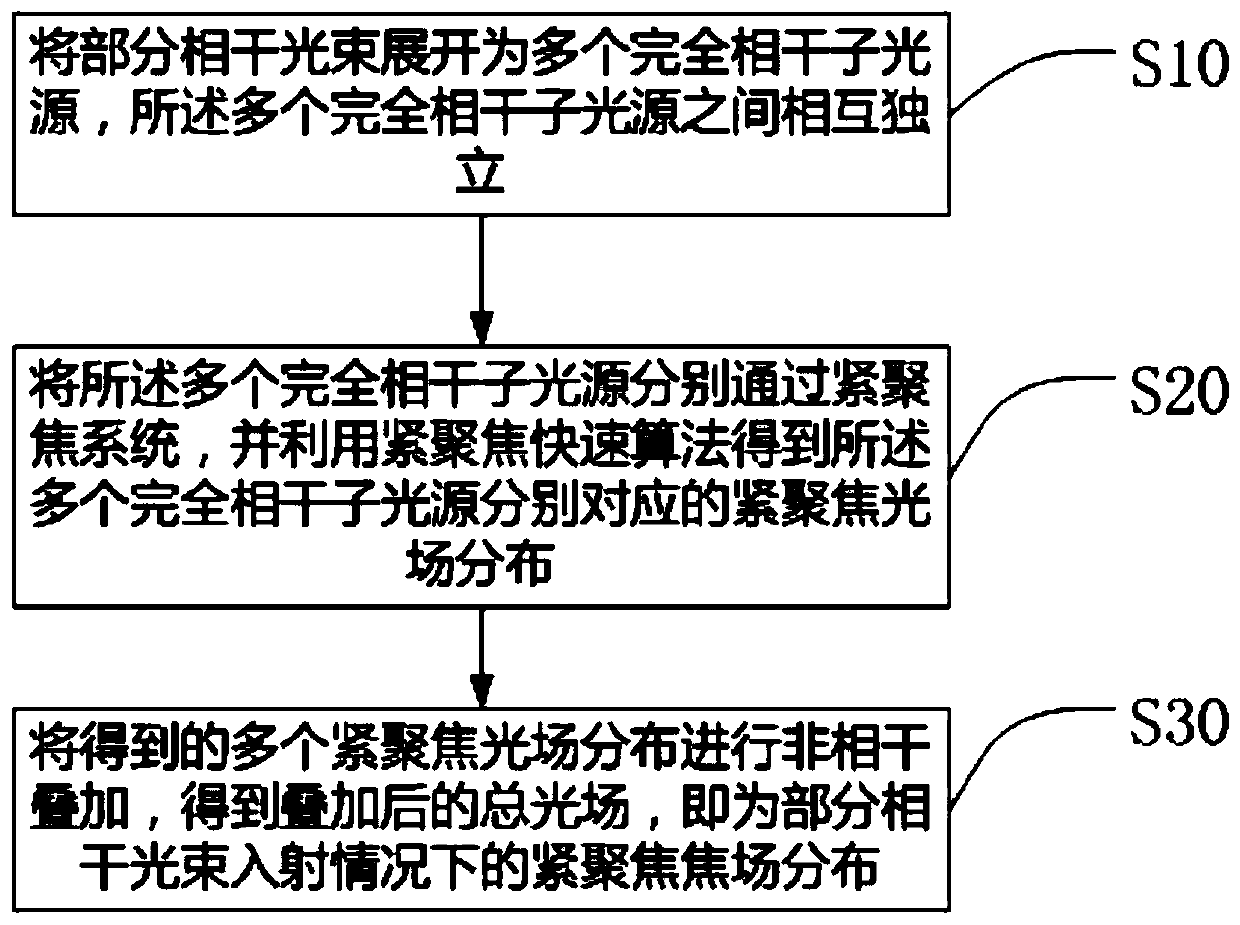
[0027] Among them, when the incident beam in the tightly focused system is a partially coherent beam, its second-order statistical properties can be expressed by the following coherence matrix:
[0028] W(r 1 , r 2 )=* (r 1 )E T (r 2 )>, (1)
[0029] Among them, E(r) represents the random electric field at point r in space, * represents the complex c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com