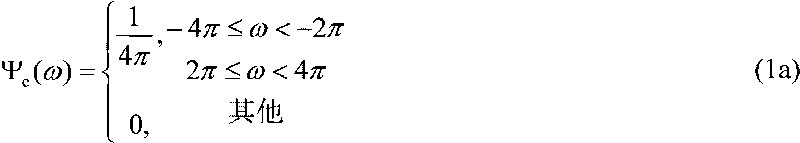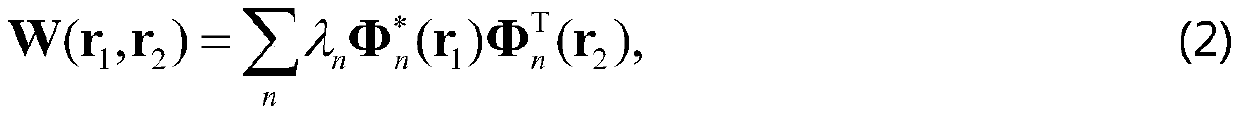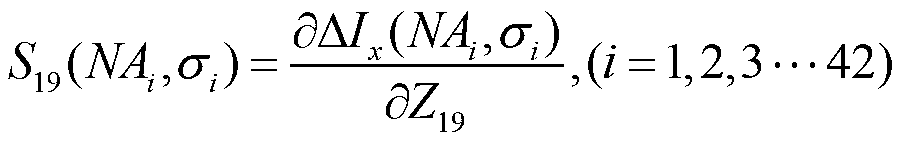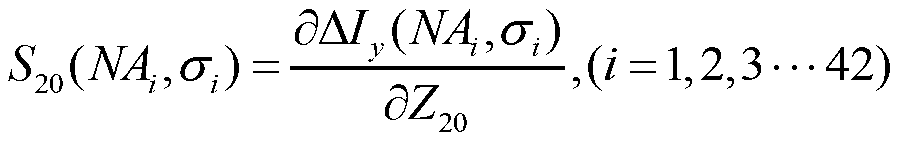Patents
Literature
43 results about "Partial coherence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
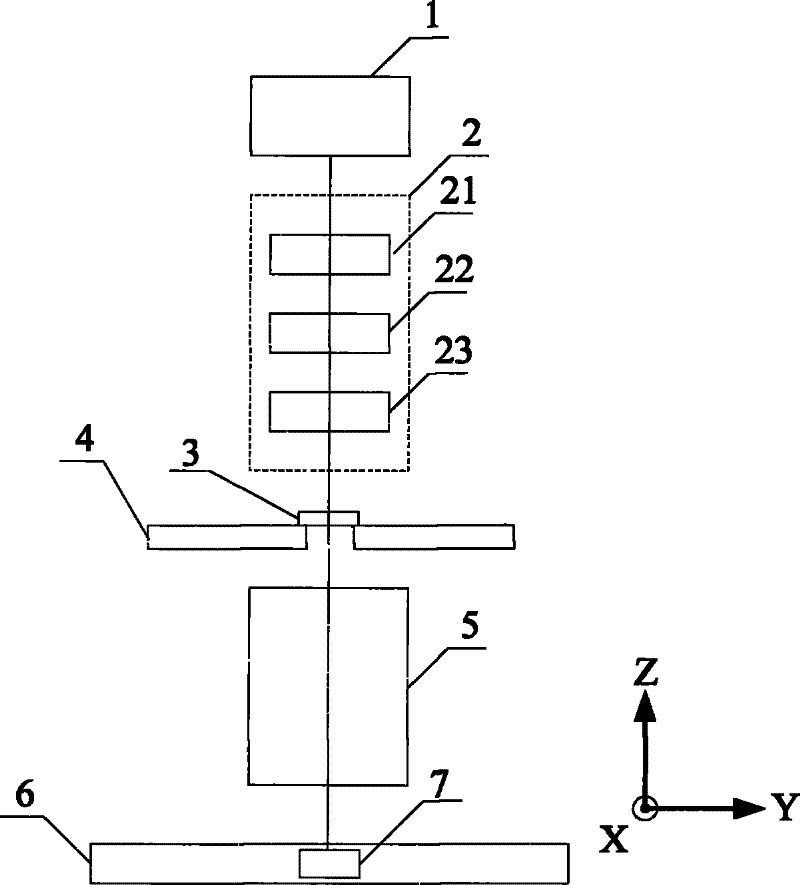
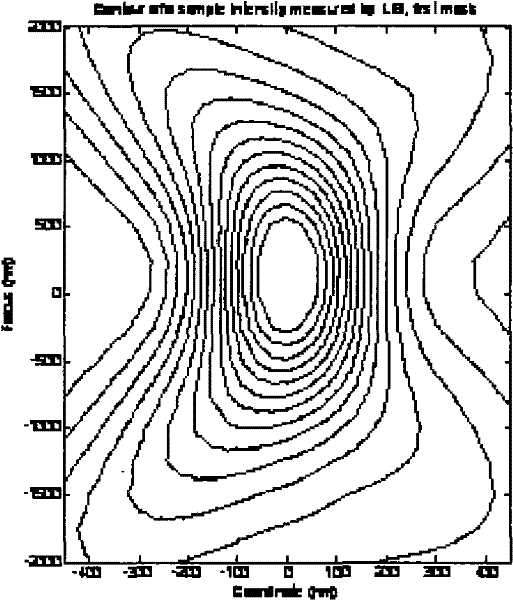
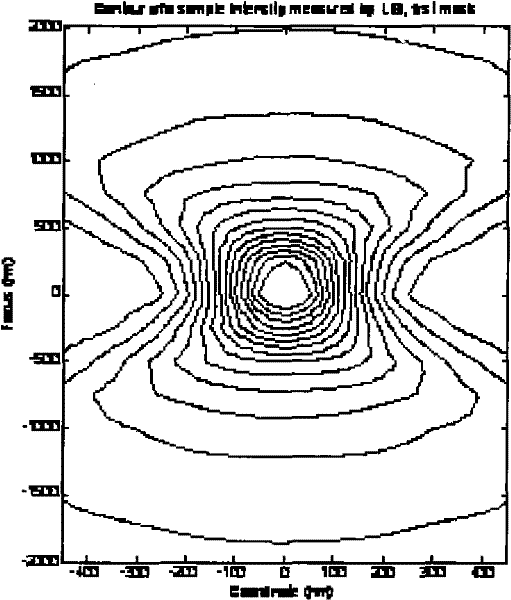
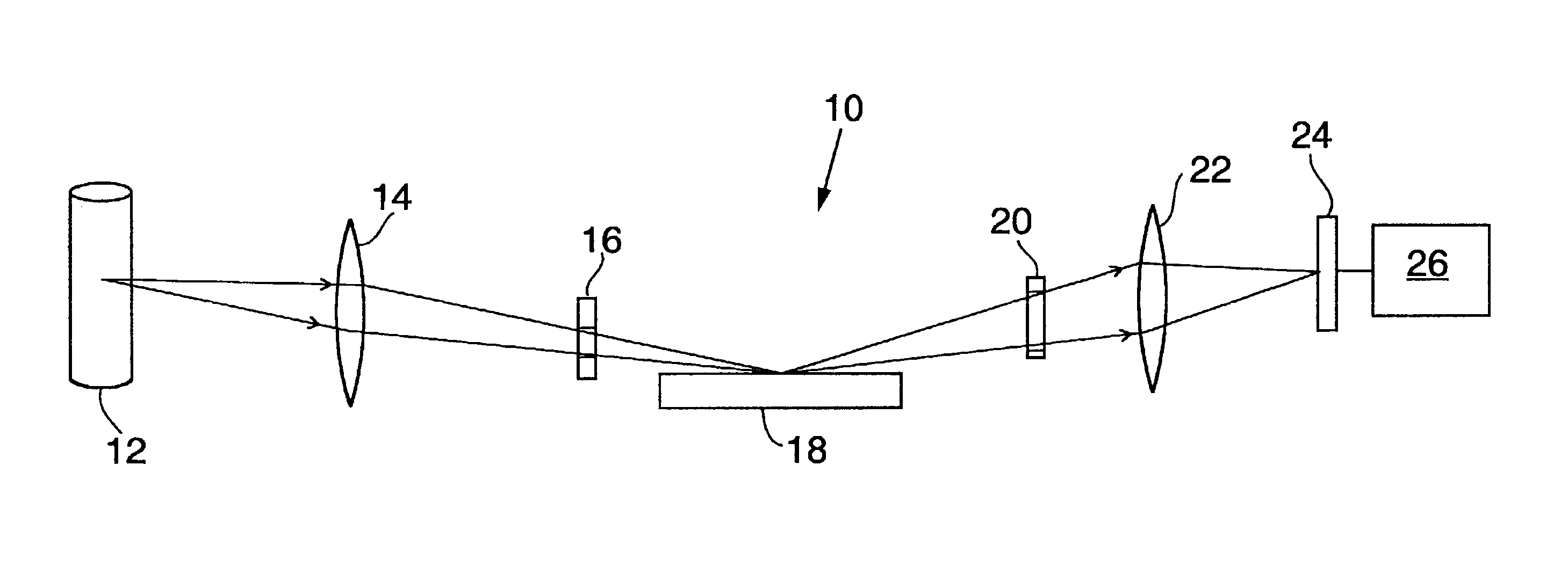
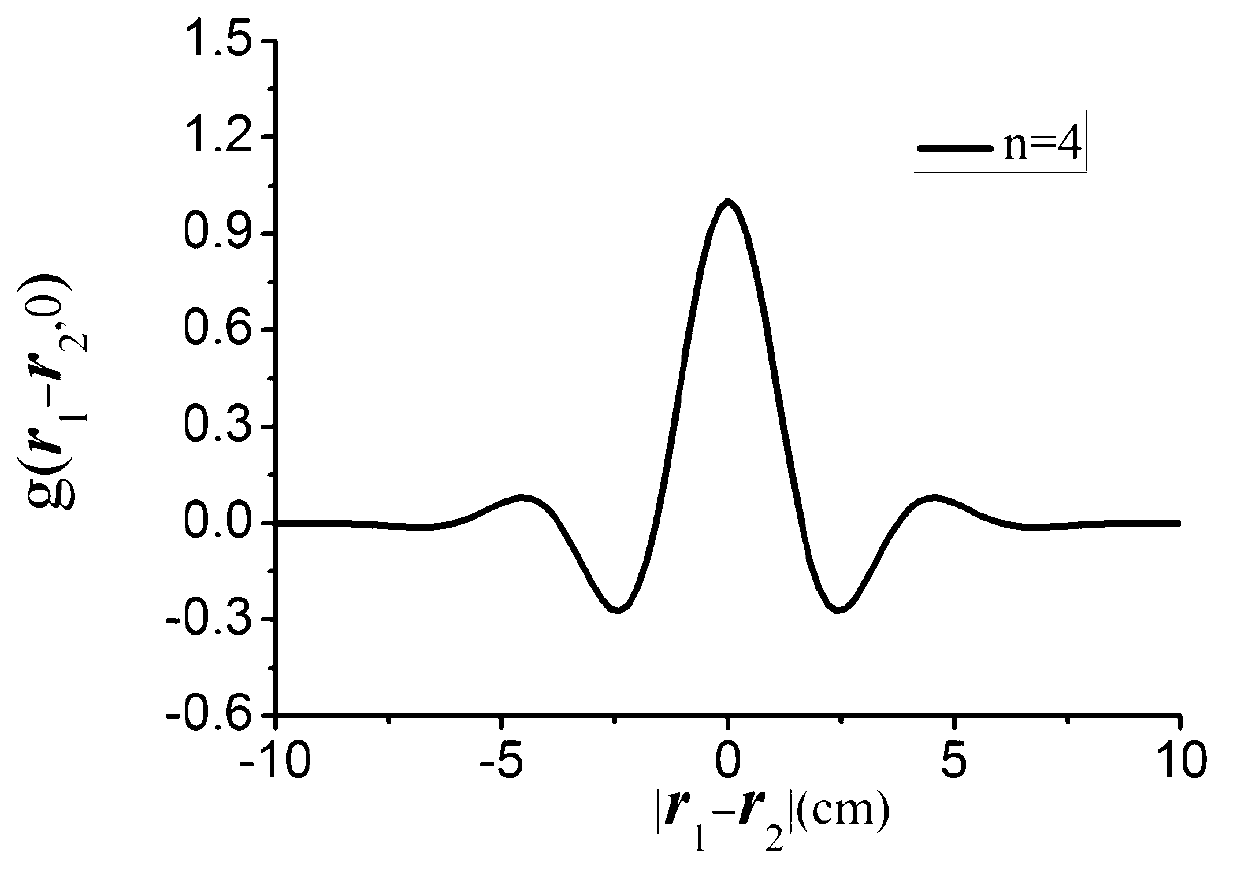
Partial coherence (generally represented by ) is one of the important parameters of lithographic tool to assess the performance of pupil fill. In this paper, a novel method of partial coherence measurement for the illumination system is proposed.
Partial coherence interferometer with measurement ambiguity resolution
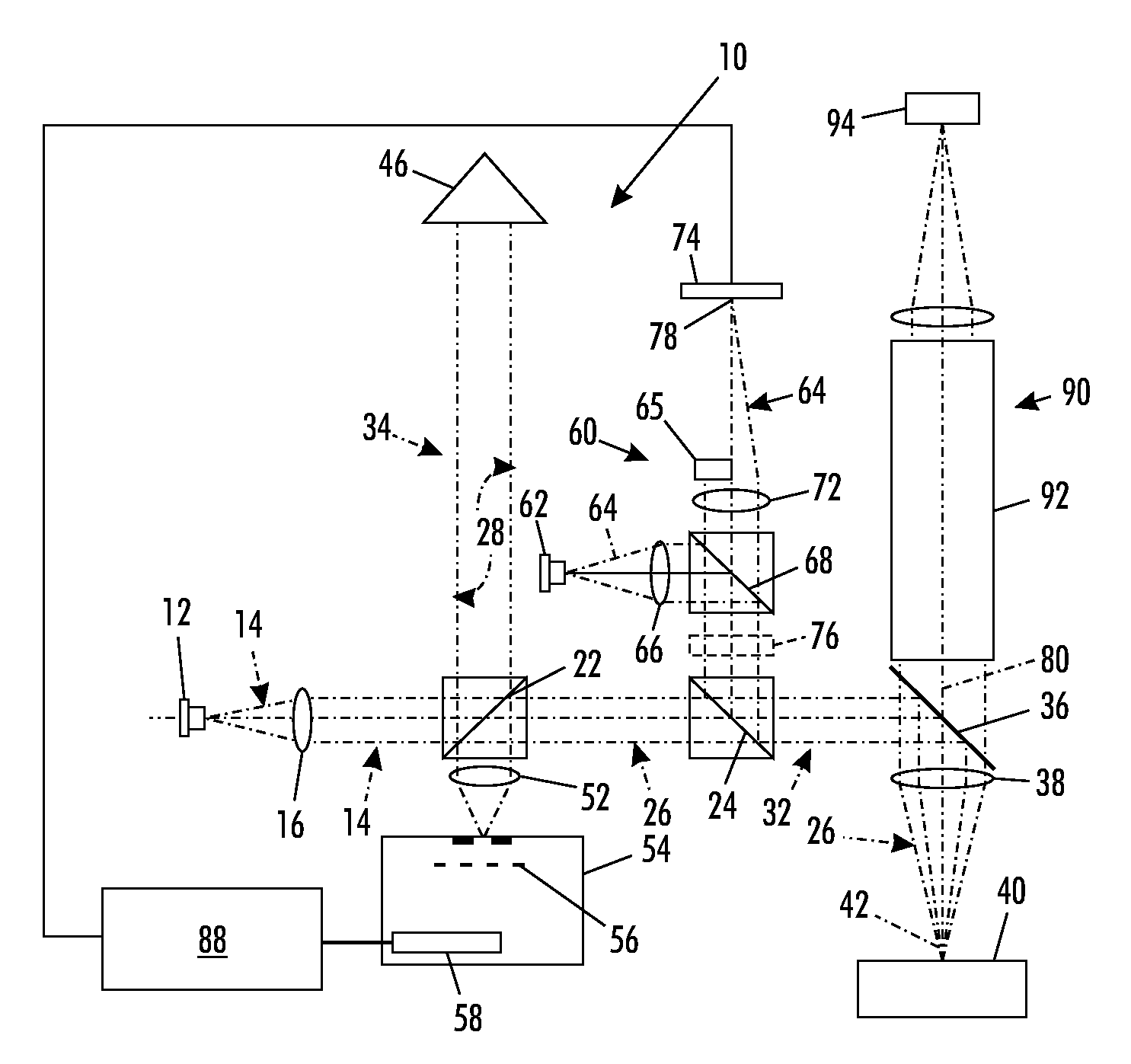
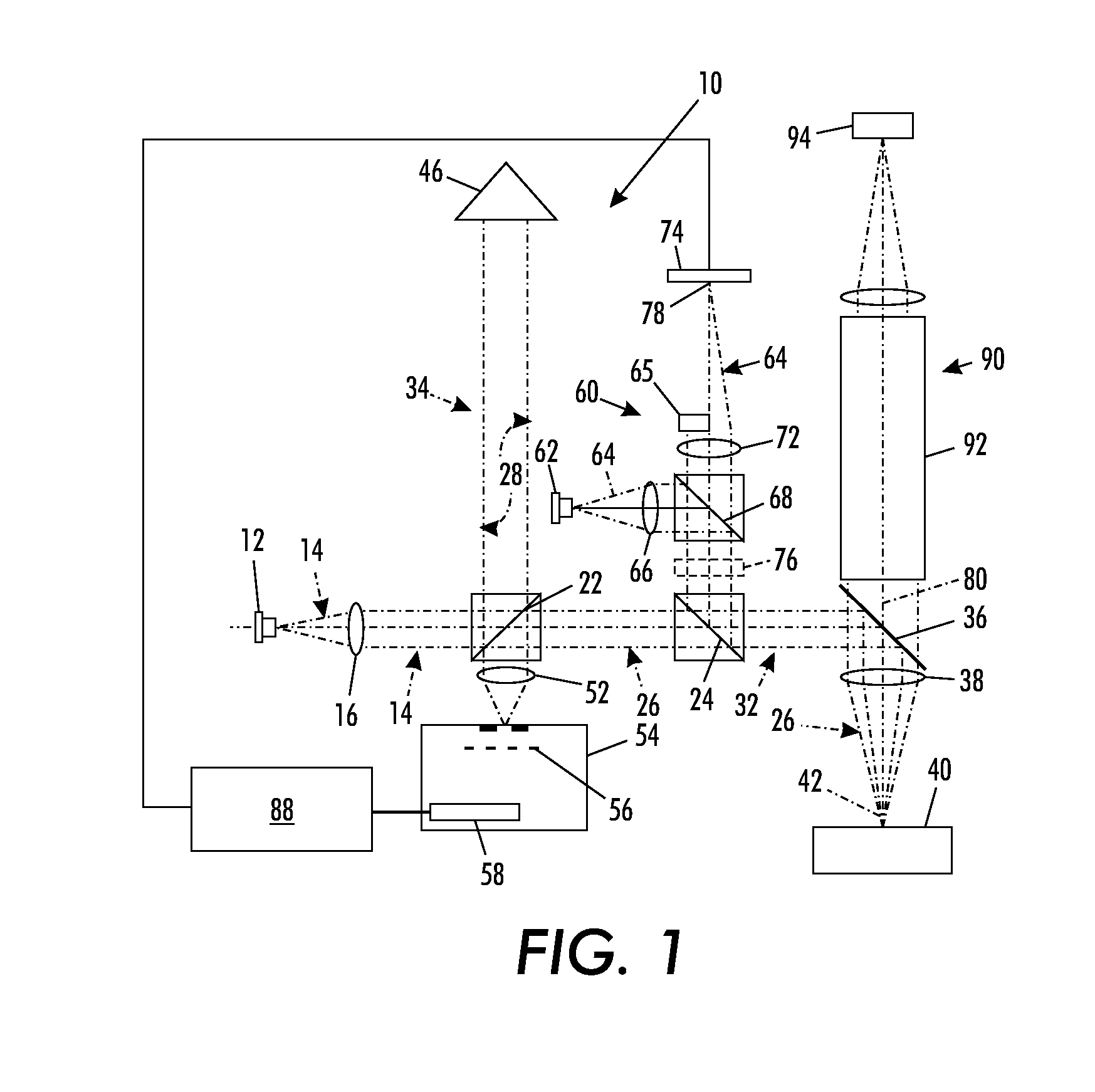
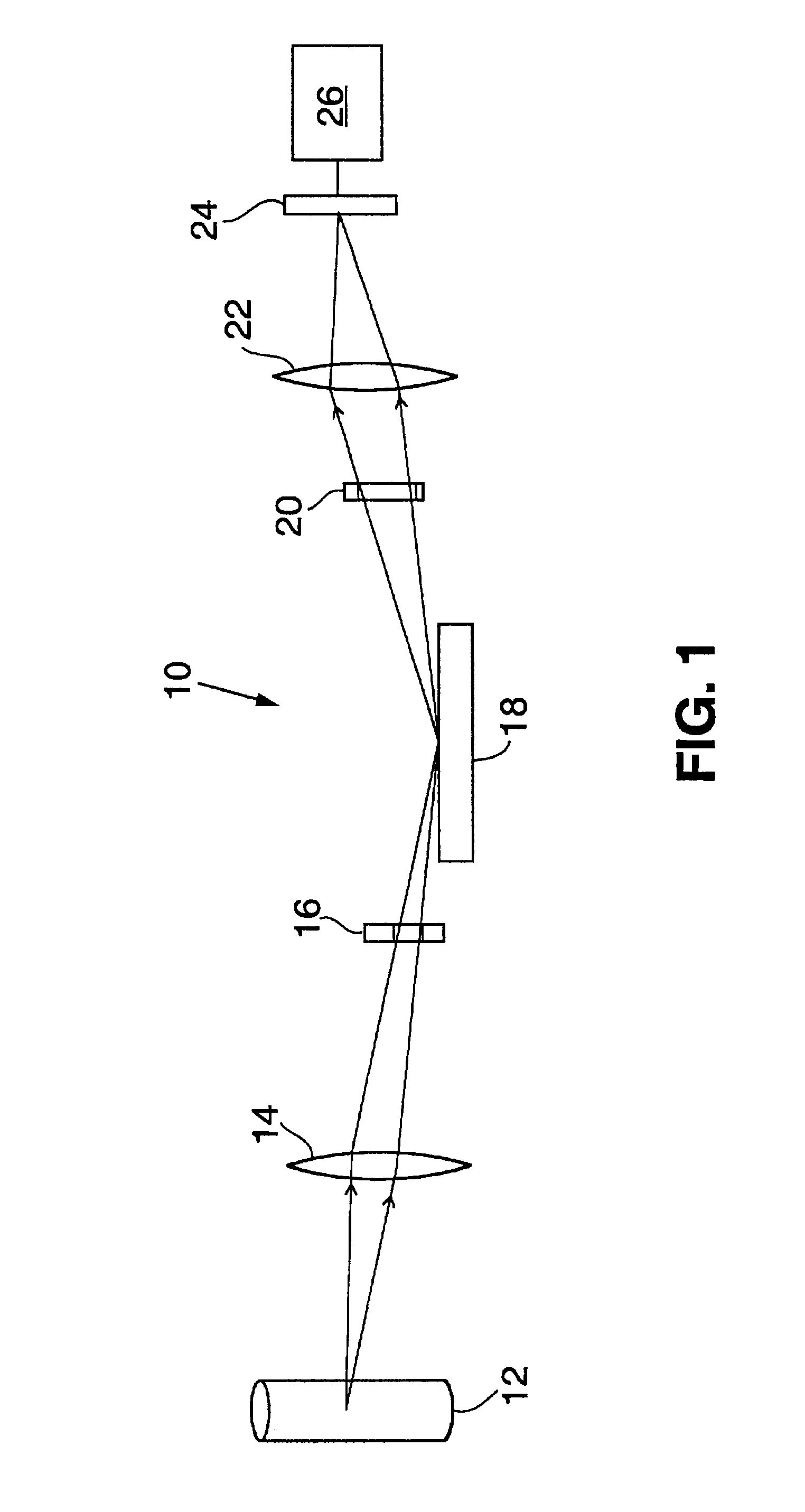
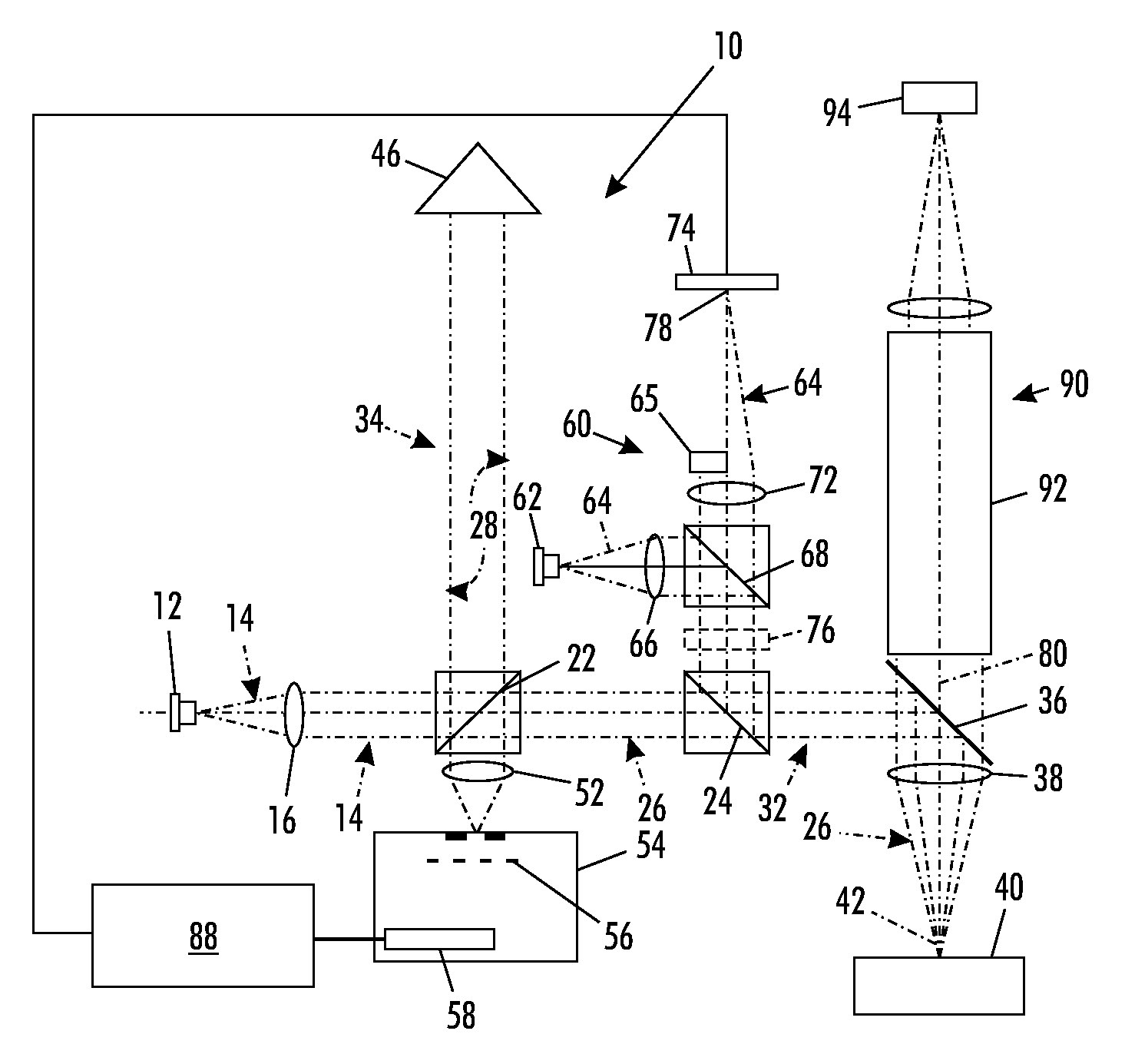
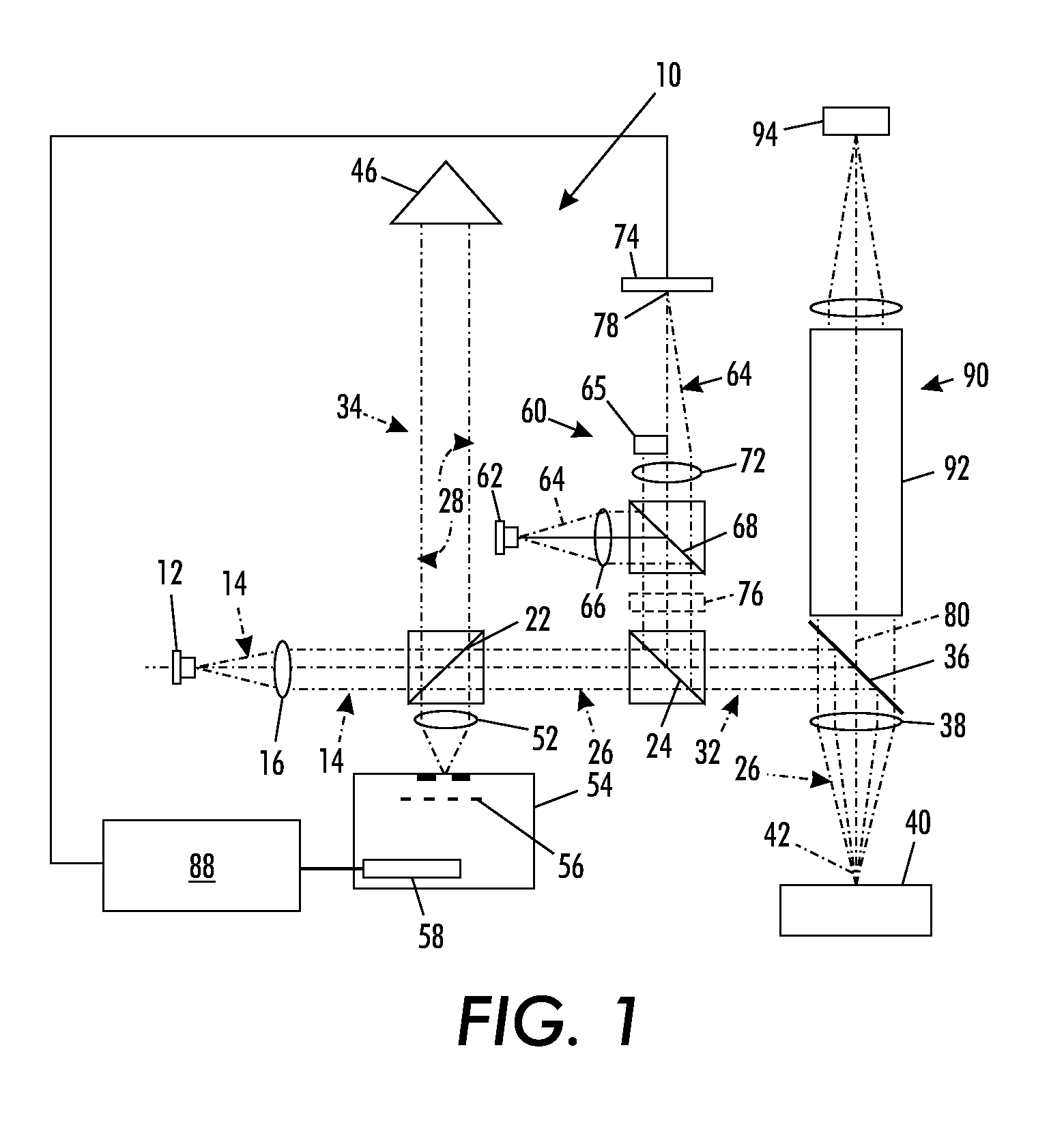
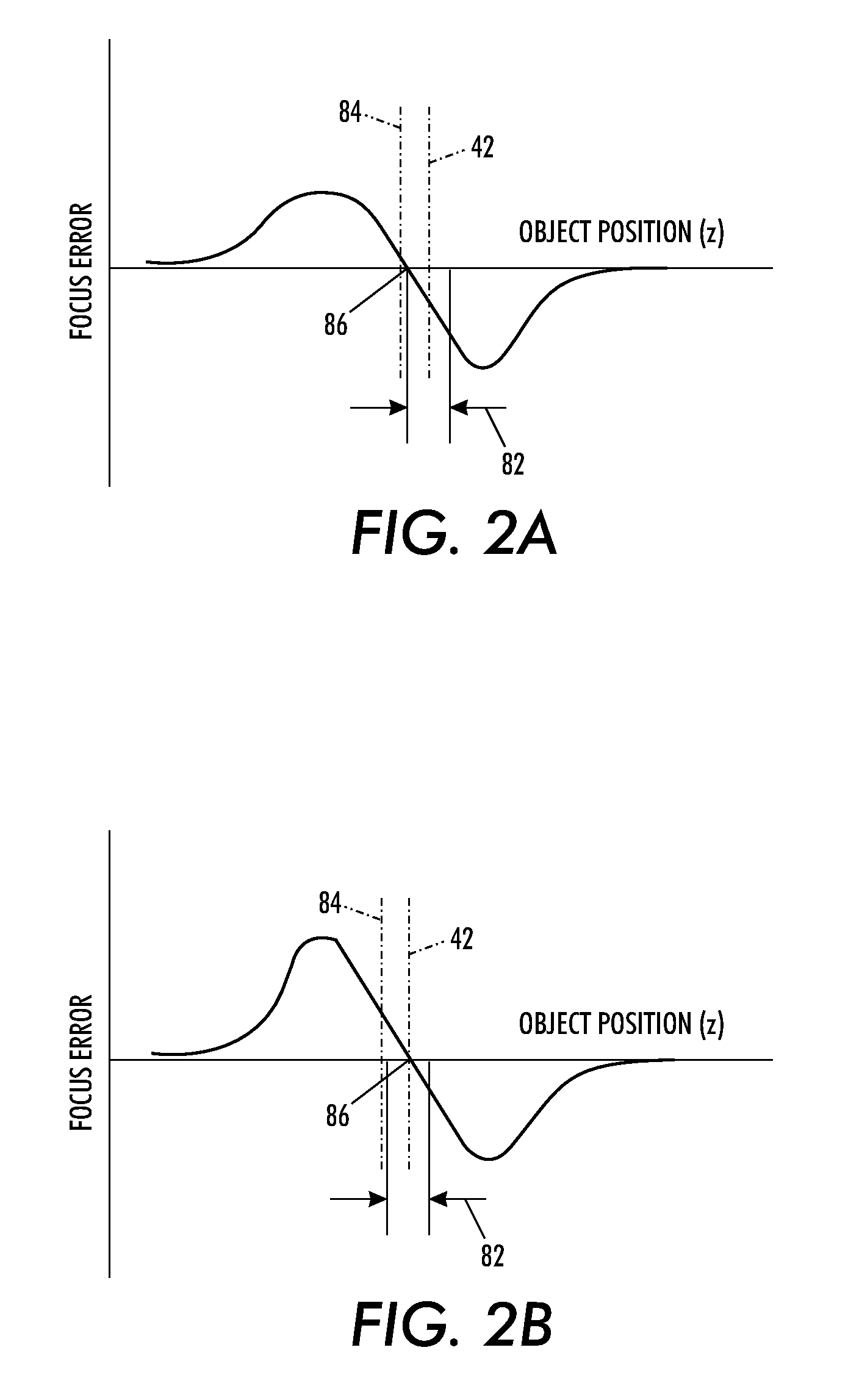
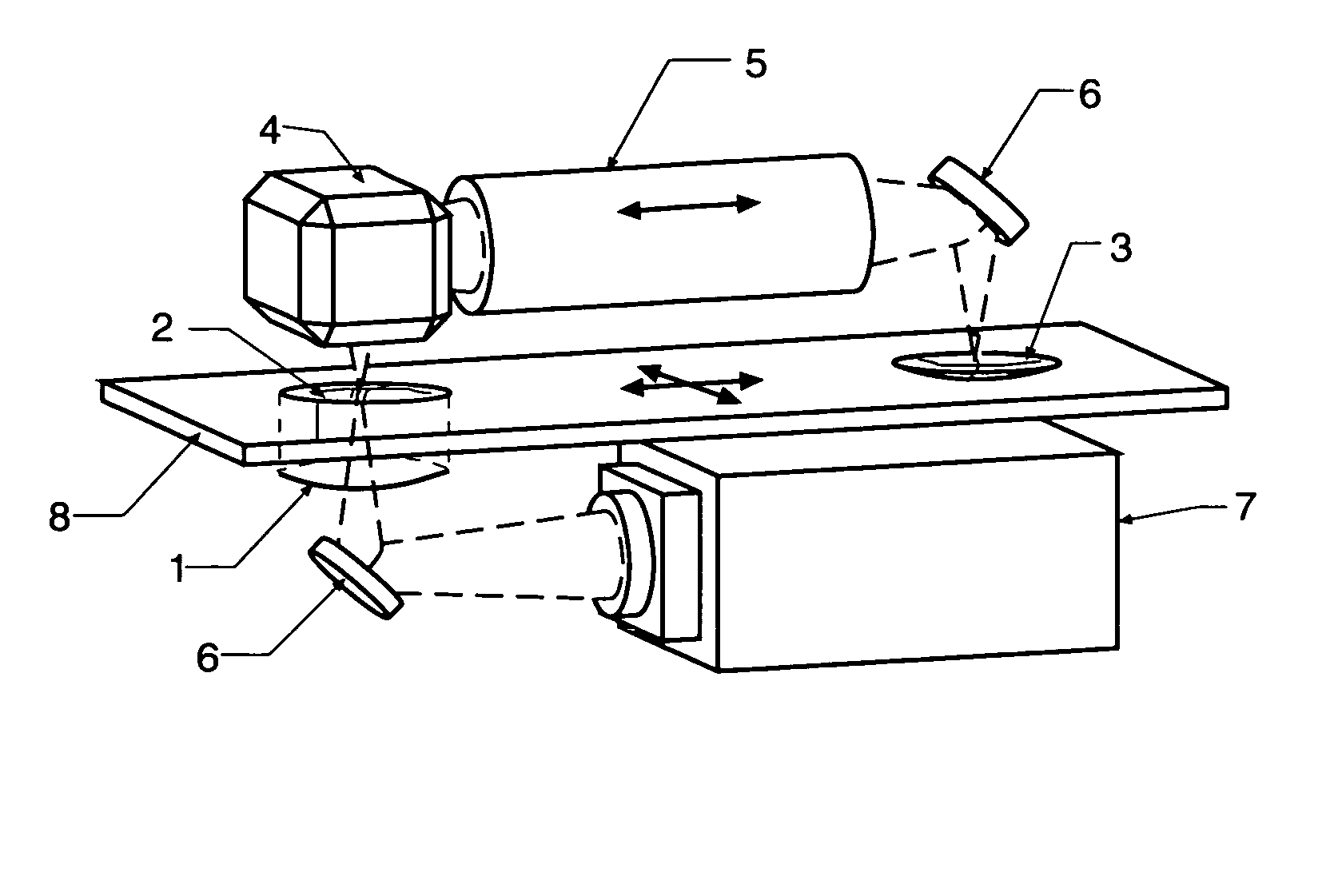
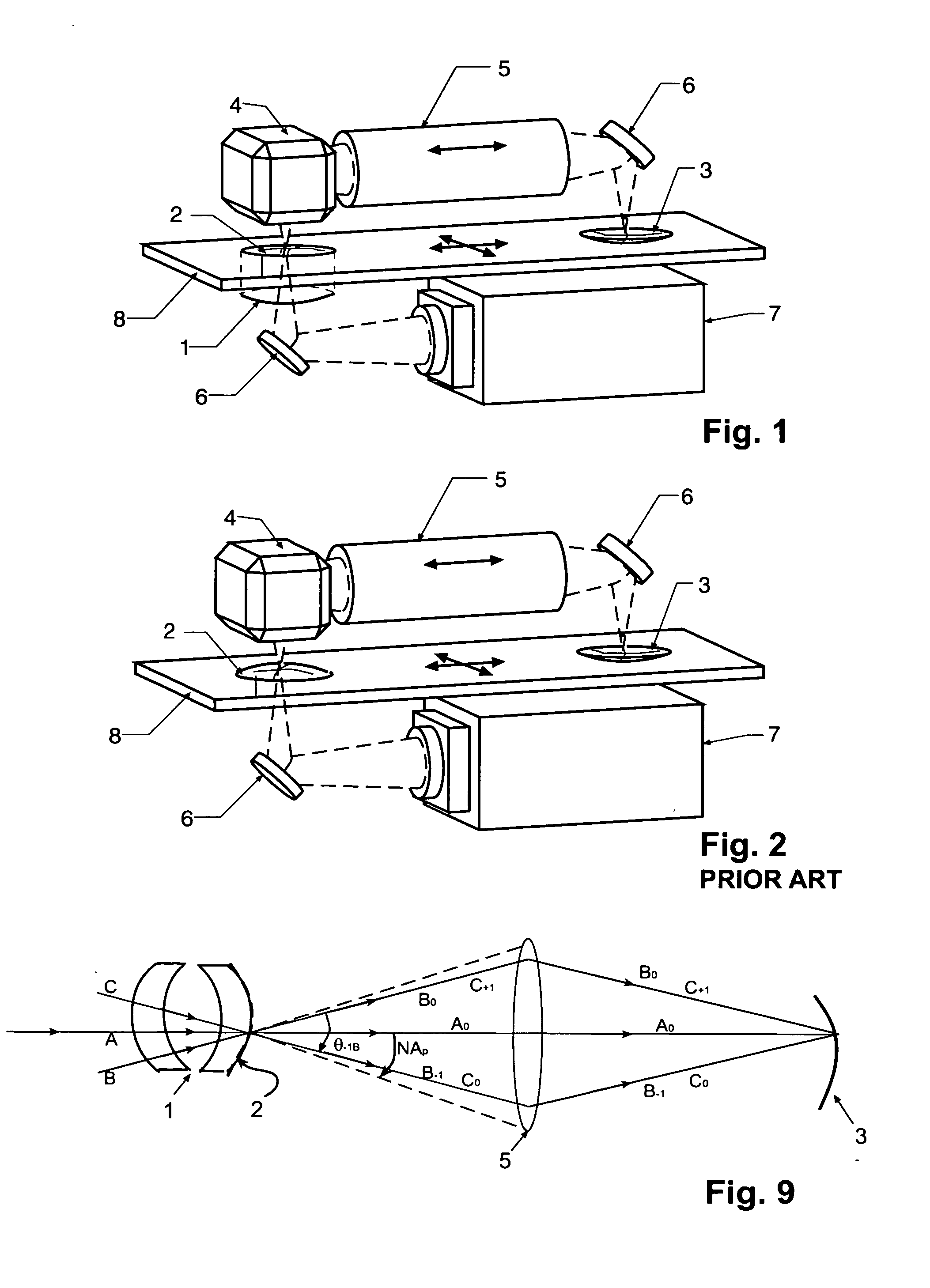
A partial coherence interferometer incorporates a focusing system for resolving measurement ambiguities. A focus-sensing beam is directed through a common objective with the measurement beam of the interferometer for conveying the beams to and from a test surface. An unambiguous measuring range is equated to a predetermined range of focusing errors.
Owner:QUALITY VISION INT
Method of identifying non-stationary abnormal noise source in automobile
ActiveCN106052849AEliminate interactionQuick identificationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSound sourcesPartial coherence
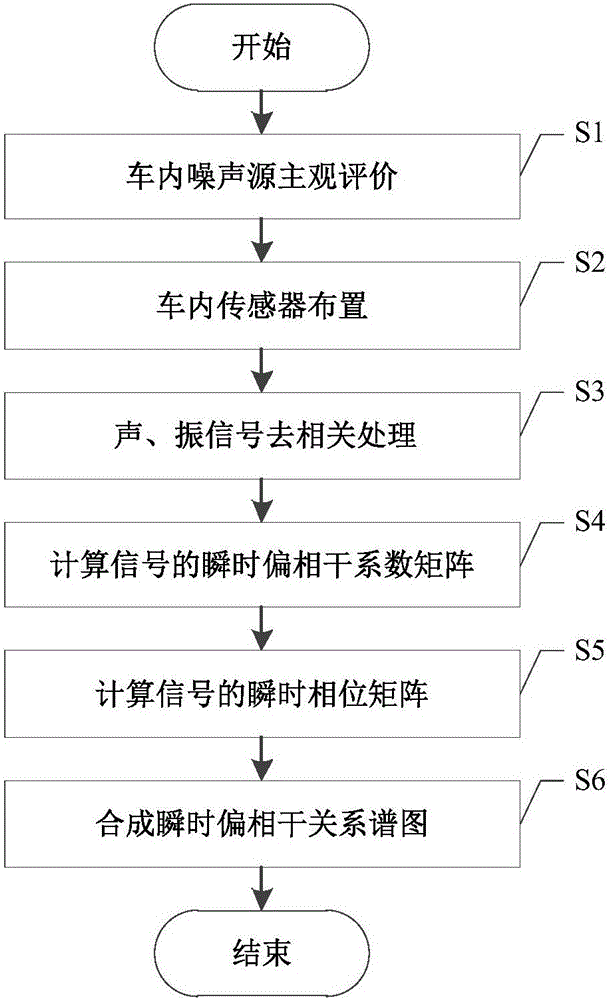
The invention discloses a method of identifying a non-stationary abnormal noise source in an automobile, which not only analyzes signal amplitude information, but also effectively utilizes phase information among signals. The method calculates an instantaneous partial coherence function among signals so as to eliminate mutual influence among automobile sound source signals; and based on this, the method combines the instantaneous partial coherence function with phase information to form an instantaneous partial coherence relation spectrum to rapidly and directly identify a noise source in an automobile. The method is suitable for stationary, non-stationary and instantaneous signal noise source identification analysis.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
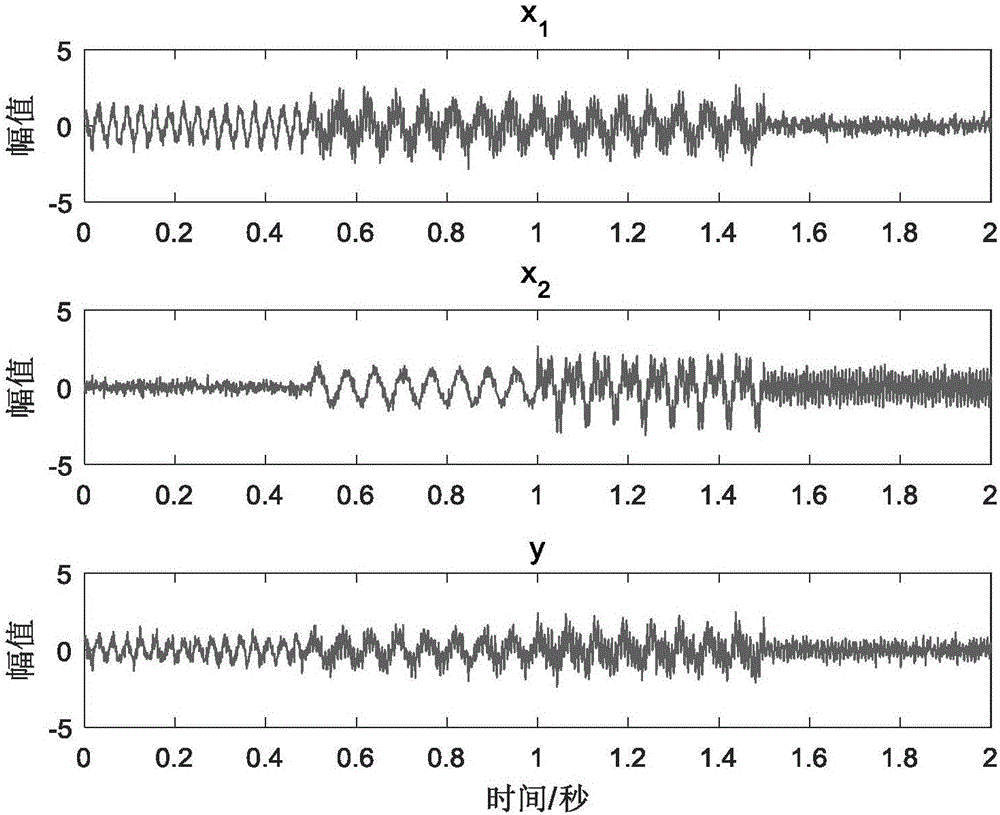
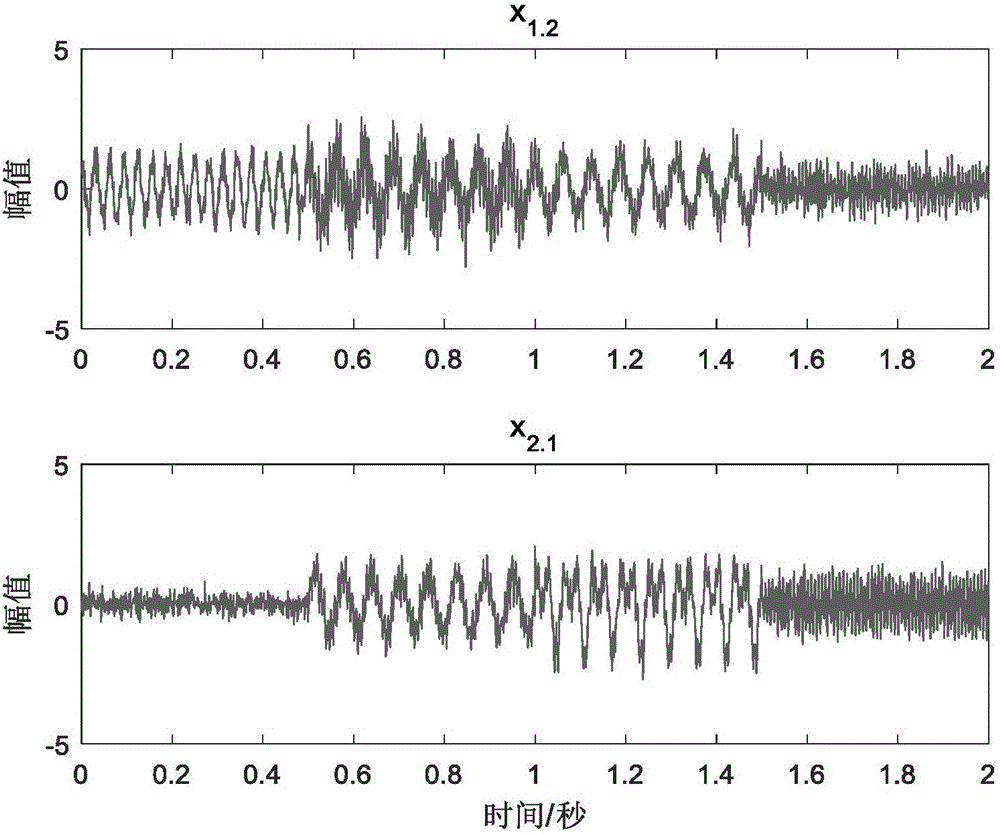
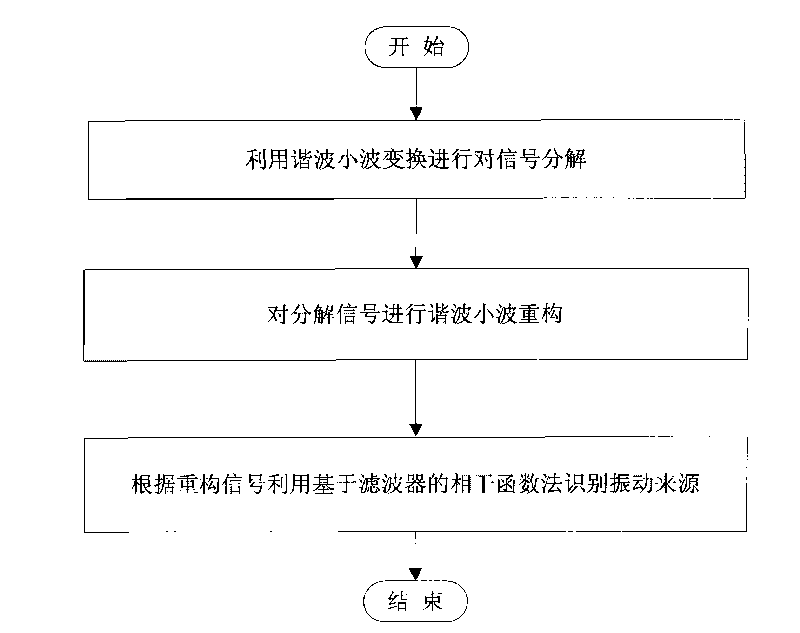
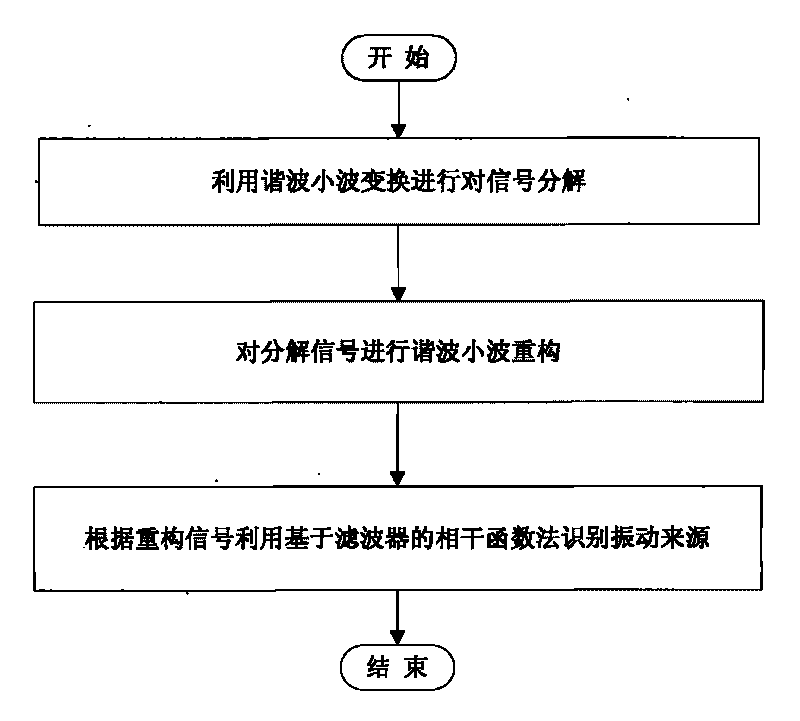
Harmonic wavelet frequency domain extraction and vibration source identification method for weak vibration signal
InactiveCN101726356AAccurate extractionAccurately and effectively extract the weak local signals in the vibration signalSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementTime domainHarmonic
The invention discloses a harmonic wavelet frequency domain extraction and vibration source identification method for a weak vibration signal. The method adopts harmonic wavelet transformation to realize frequency domain extraction and time domain reconstruction on the weak vibration signal, and realizes frequency domain extraction of a weak periodic vibration signal in the strong noise background. The invention also provides a vibration signal source identification method based on the coherence function analysis. The vibration signal source identification method comprises the following steps of: firstly judging the independent number of signal sources on the whole frequency band, then detecting whether important signals are missed or not, and finally respectively identifying the independent and non-independent conditions; for the non-independent signal sources, providing a filter method for carrying out priority ordering; and after carrying out priority ordering, detecting whether the important signal sources are missed or not by using a multiple coherence function, and then respectively identifying the independent signal sources and the non-independent signal sources by using a coherence function and a partial coherence function. By adopting the scheme, the weak vibration signal can be accurately detected, and the vibration sources can be effectively identified.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
DUV scanner linewidth control by mask error factor compensation
InactiveUS6922230B2Easy to modifyReduces linewidth varianceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUsing optical meansFeature DimensionLine width
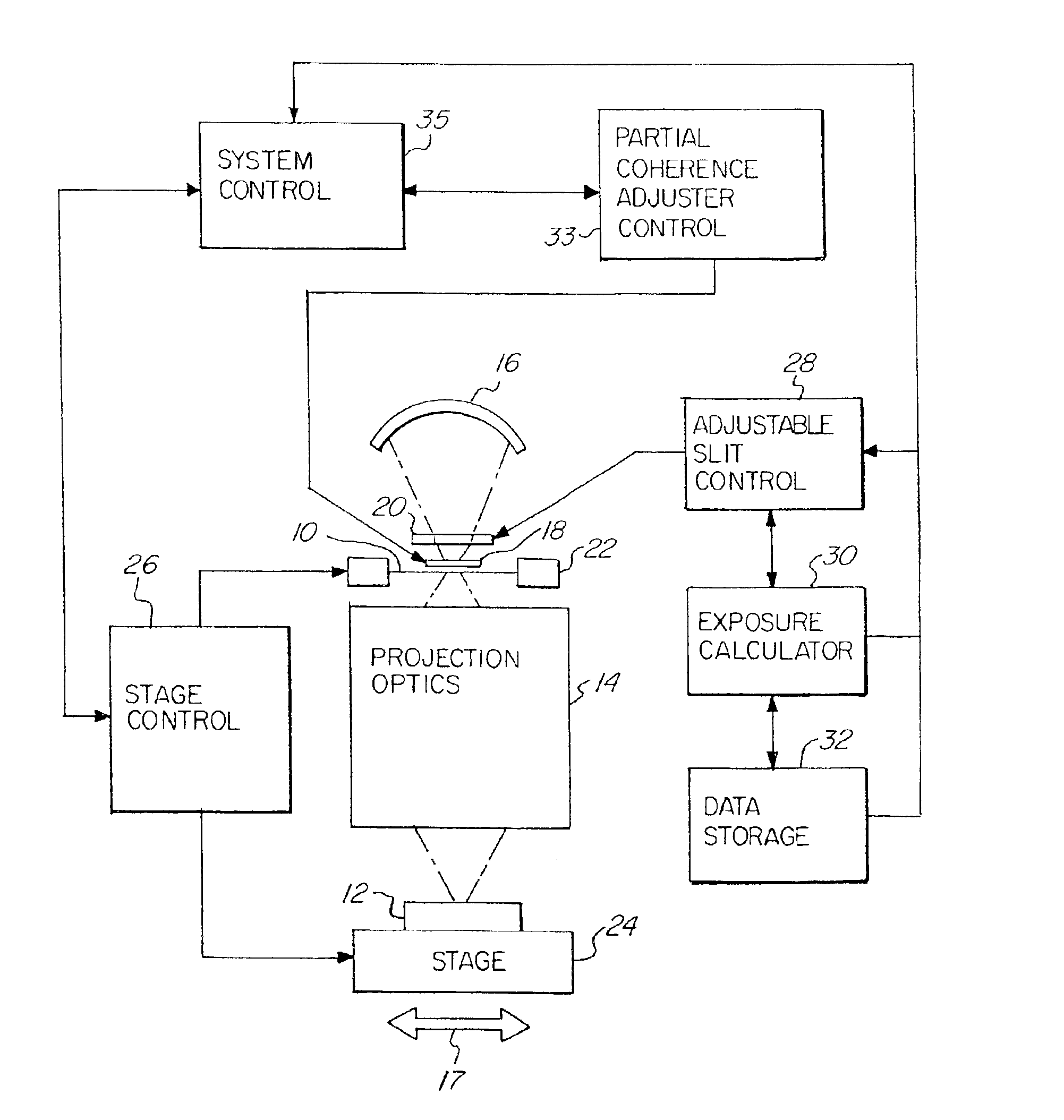
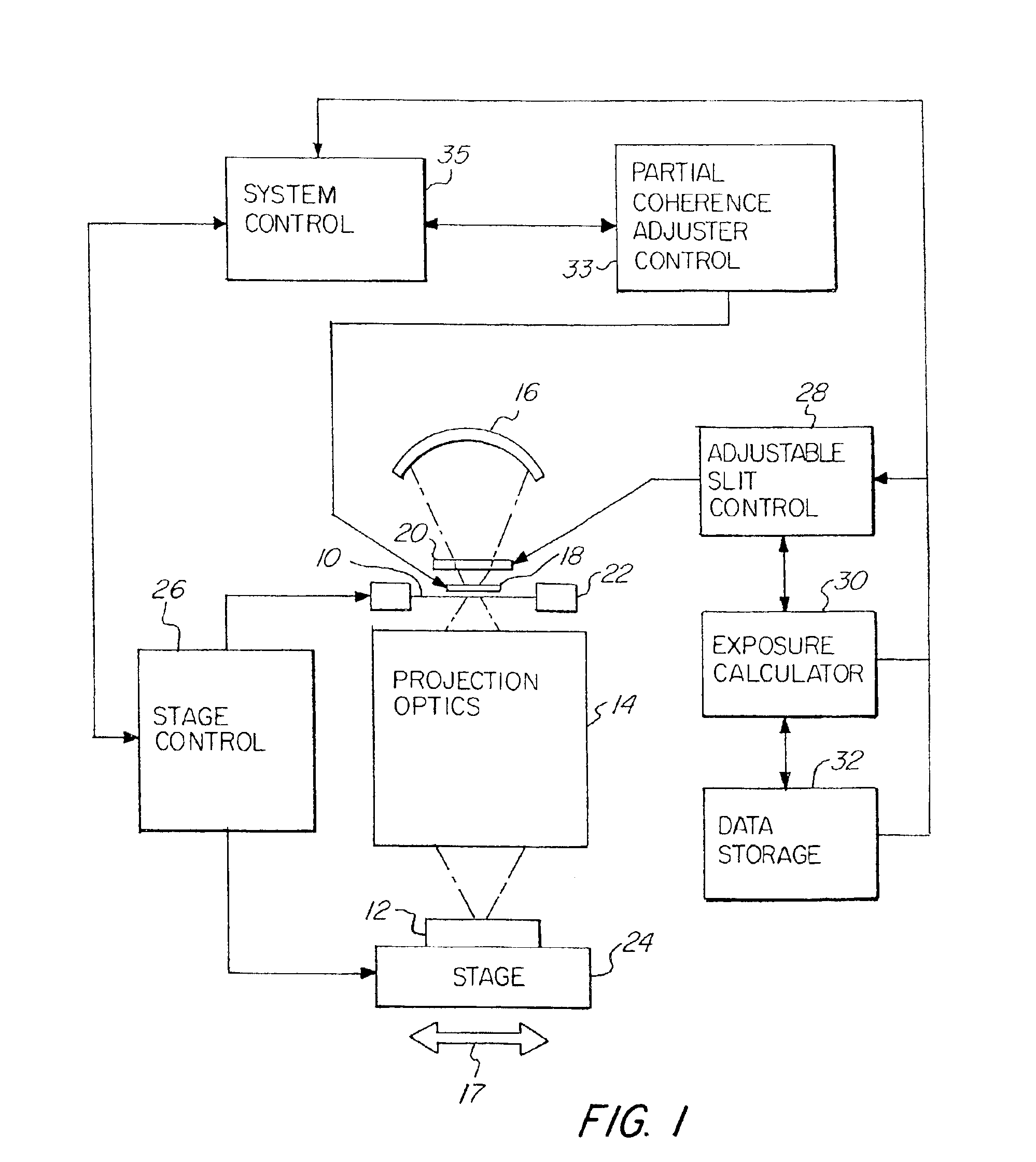
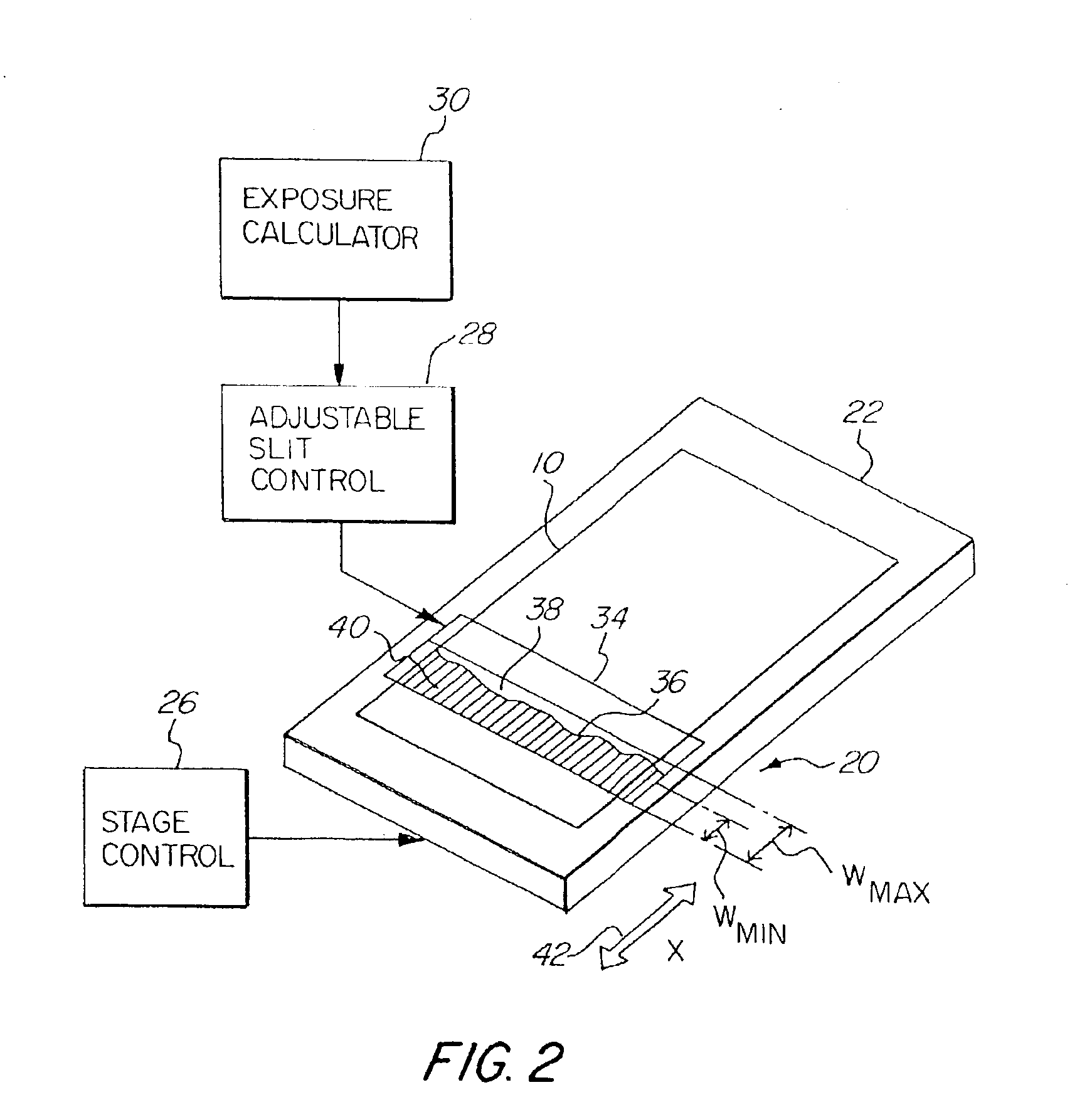
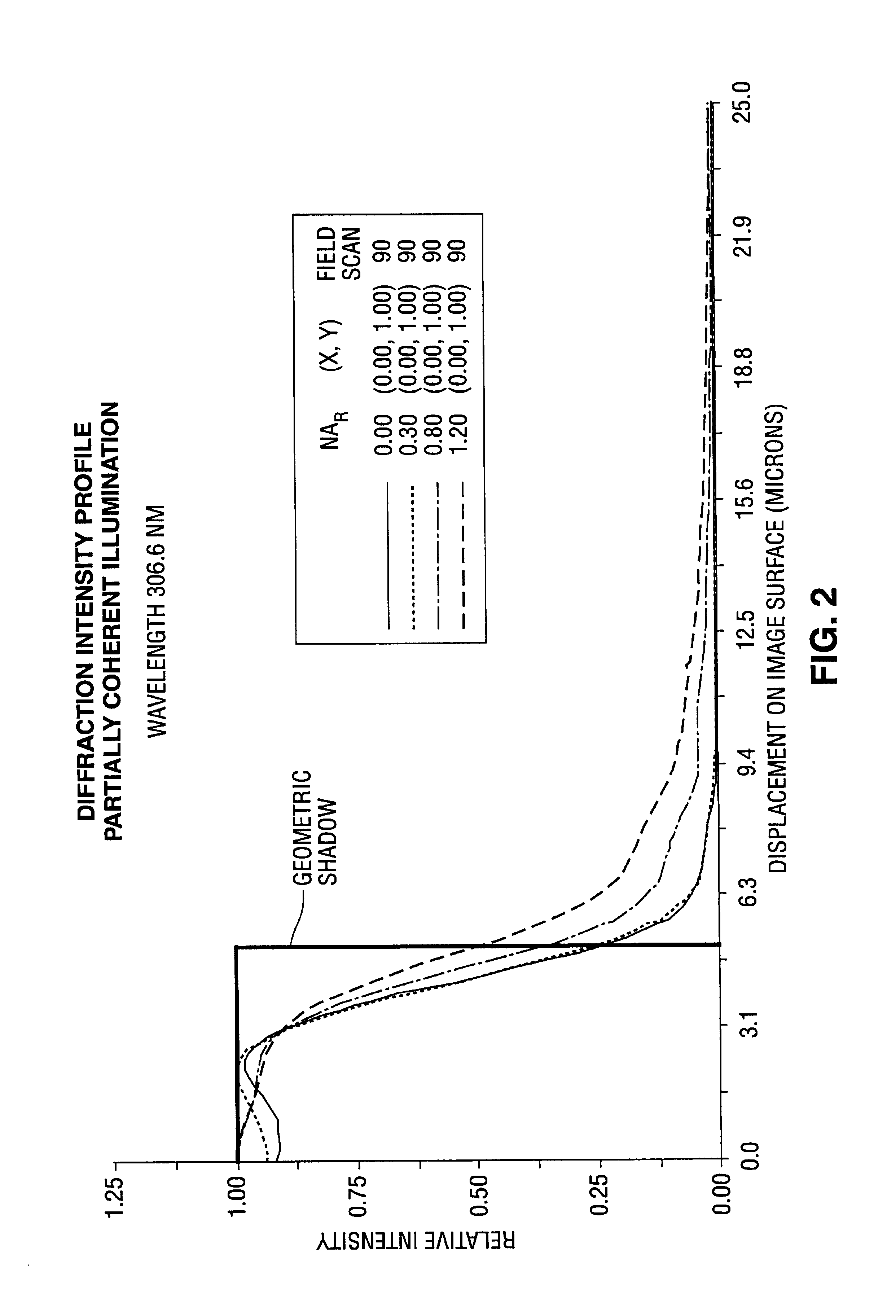
Linewidth variations and bias that result from MEF changes and reticle linewidth variations in a printed substrate are controlled by correcting exposure dose and partial coherence at different spatial locations. In a photolithographic device for projecting an image of a reticle onto a photosensitive substrate, an adjustable slit is used in combination with a partial coherence adjuster to vary at different spatial locations the exposure dose received by the photosensitive substrate and partial coherence of the system. The linewidth variance and horizontal and vertical or orientation bias are calculated or measured at different spatial locations with reference to a reticle, and a corrected exposure dose and partial coherence is determined at the required spatial locations to compensate for the variance in linewidth and bias on the printed substrate. Improved printing of an image is obtained, resulting in the manufacture of smaller feature size semiconductor devices and higher yields.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Photoetching machine projection objective lens wave aberration field measurement method
ActiveCN102129173AHigh measurement accuracyReduce occupancyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusPartial coherenceLight beam
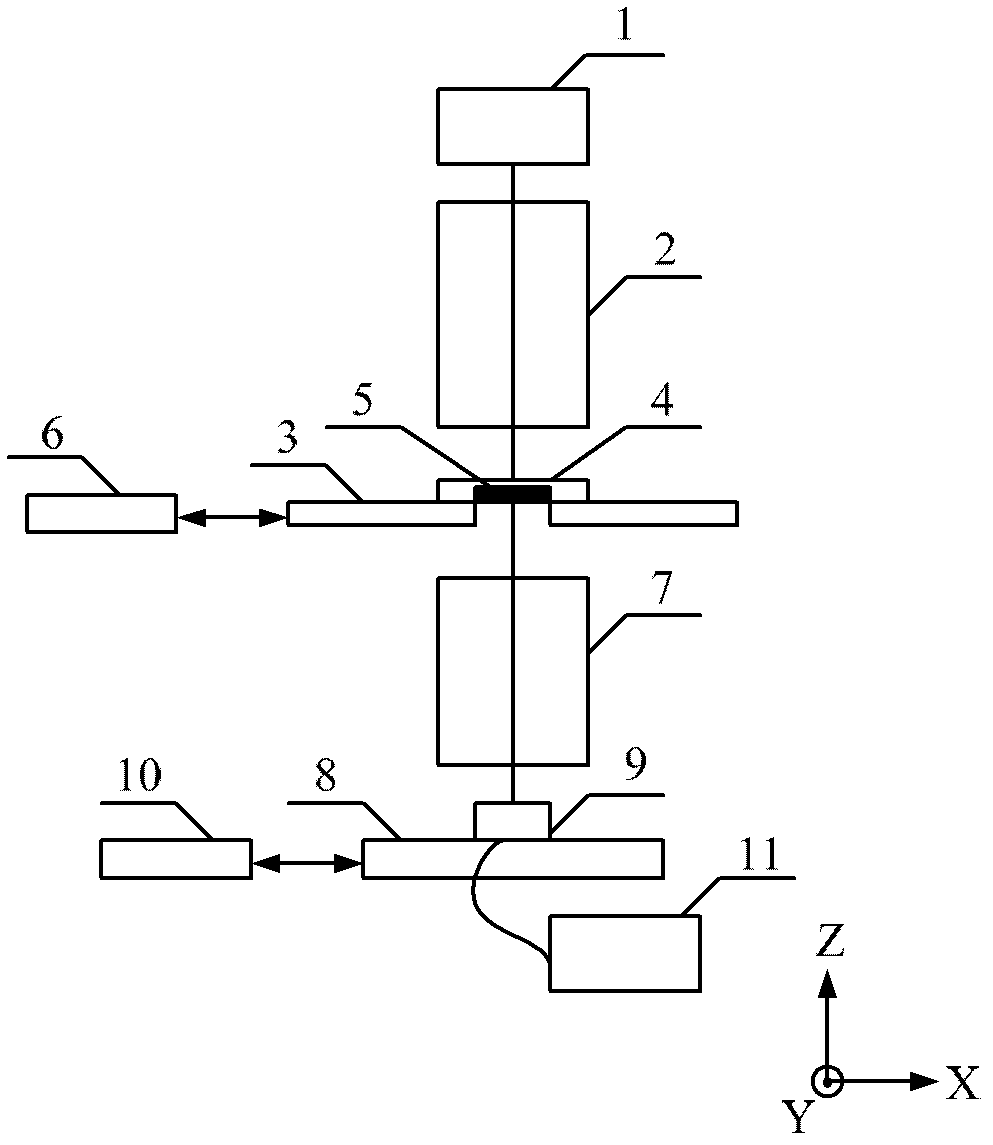
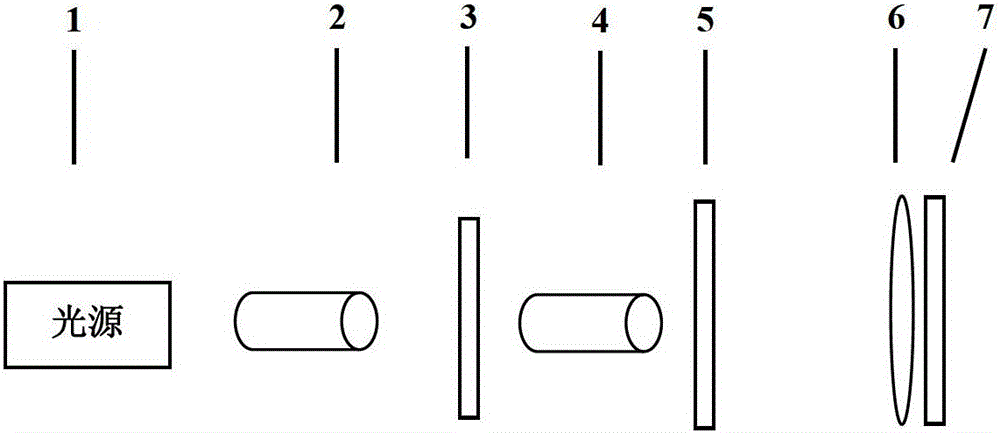
The invention discloses a photoetching machine projection objective lens wave aberration field measurement method, which utilizes a measurement system. The system comprises a light source, a lighting system, a mask table, a projection objective lens, a six-dimensional scanning worktable and an image sensor, wherein the light source is used for generating lighting light beams; the lighting system is used for adjusting the lighting light beams; the mask take can carry a test mask and position accurately; the projection objective lens can image a graph on the test mask and has an adjustable numerical aperture; the six-dimensional scanning worktable can position accurately; the image sensor is arranged on the six-dimensional scanning worktable and is used for measuring the image of the graph on the test mask; and the lighting system can adjust a beam waist size, light intensity distribution, a partial coherence factor and a lighting mode. When in measurement, the light intensity distribution of an aerial image is simulated and analyzed and a linear model of a Zernike coefficient is established based on the simulation and analysis first and then the Zernike coefficient is obtained by fitting by utilizing the linear model according to the aerial image measured by the image sensor.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Optical metrology tool having improved contrast
InactiveUS7050162B2Improve system performanceIncrease contrastSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCollection systemPartial coherence
The subject invention relates to broadband optical metrology tools for performing measurements of patterned thin films on semiconductor integrated circuits. Particularly a family of optical designs for broadband optical systems wherein the ratio of illumination system to collection system numerical apertures is less than 1. System performance is enhanced through selection and control of the optical system partial coherence; this is accomplished through installation of beam-control apertures within the illumination and collection optical systems. The invention is broadly applicable to a large class of broadband optical wafer metrology techniques including spectrophotometry, spectroscopic reflectometry, spectroscopic ellipsometry and spectroscopic scatterometry.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
Rapid calculation method for realizing tight focusing of partially coherent light
ActiveCN110531530AImprove computing efficiencyReduce computing timeOptical elementsFast Fourier transformFast algorithm
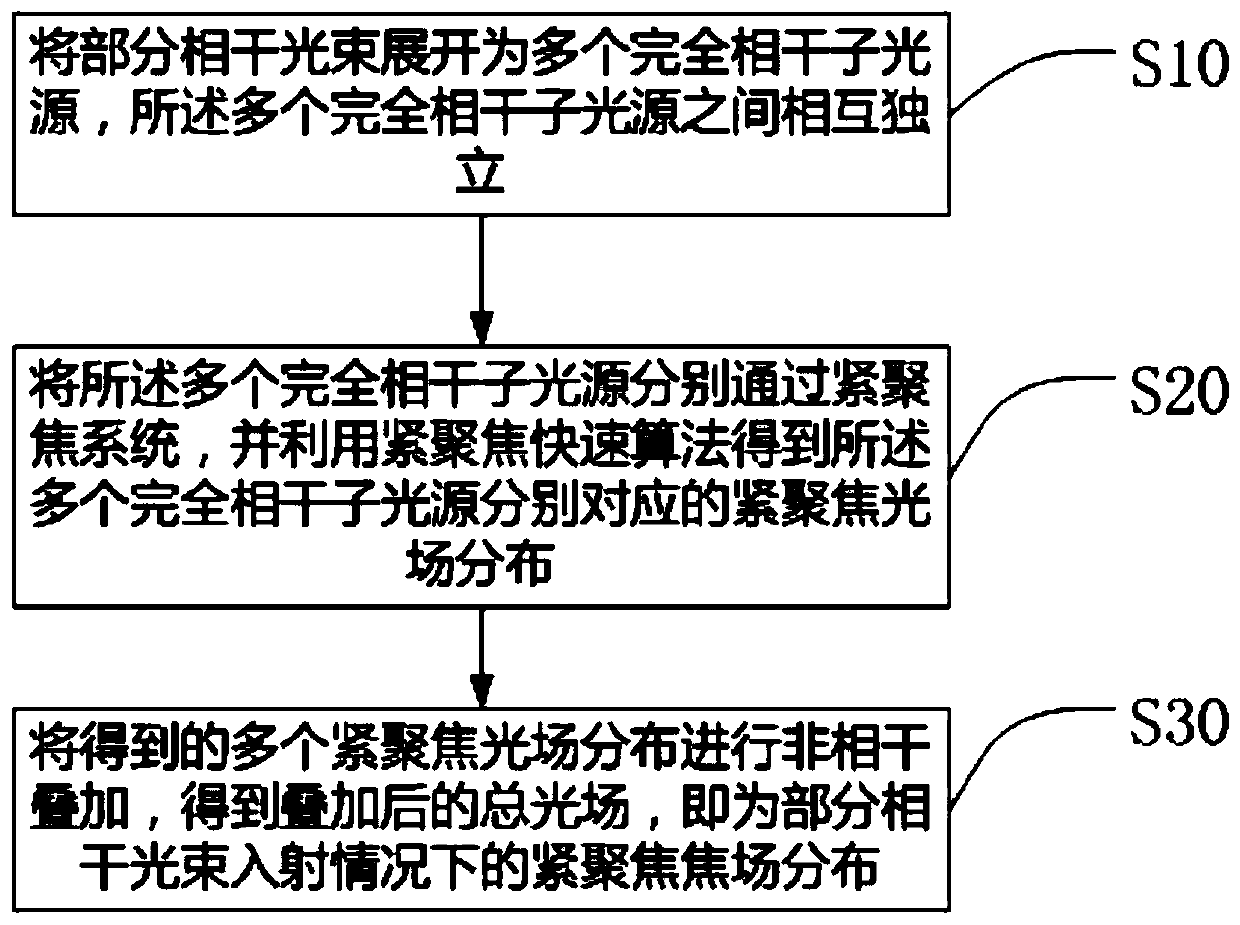
The invention discloses a rapid calculation method for realizing tight focusing of partially coherent light. The method comprises the following steps: S10, enabling one part of coherent light beam tobe expanded into a plurality of completely coherent sub light sources and enabling the plurality of completely coherent sub light sources to be independent from each other; S20, enabling the pluralityof completely coherent sub light sources to respectively pass through a tight focusing system and acquiring tight focusing light field distribution respectively corresponding to the plurality of completely coherent sub light sources by utilizing a tight focusing fast algorithm; S30, carrying out incoherent superposition on the obtained distribution of the plurality of tightly focused light fieldsto obtain a superposed total light field so as to obtain tightly focused focal field distribution under the partially coherent light beam incident condition. According to the disclosed method, the quadruple integral form of a vector diffraction integral formula under the condition of partial coherent light incidence is changed into a fast Fourier transform and summation form, so that the calculation time is shortened, the calculation efficiency is improved, and the tight focusing calculation precision under the condition of partial coherence is greatly improved; and the distortion in the calculation process is also reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for identifying non-stationary acoustic source characteristics by bias coherent technology
InactiveCN1472515ARealize visualizationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSound sourcesPartial coherence
The method is as the follows. First, quantity and position of reference source are confirmed, mike array of the reference source is arranged and signal of the reference source is picked up. Then, scan measurement for mike array to holographic face is designed and the holographic face data is collected. At least, sound field of each sound source is separated by utilizing analysis technique of circular sationary partial coherence.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Simplified controller with partial coherency
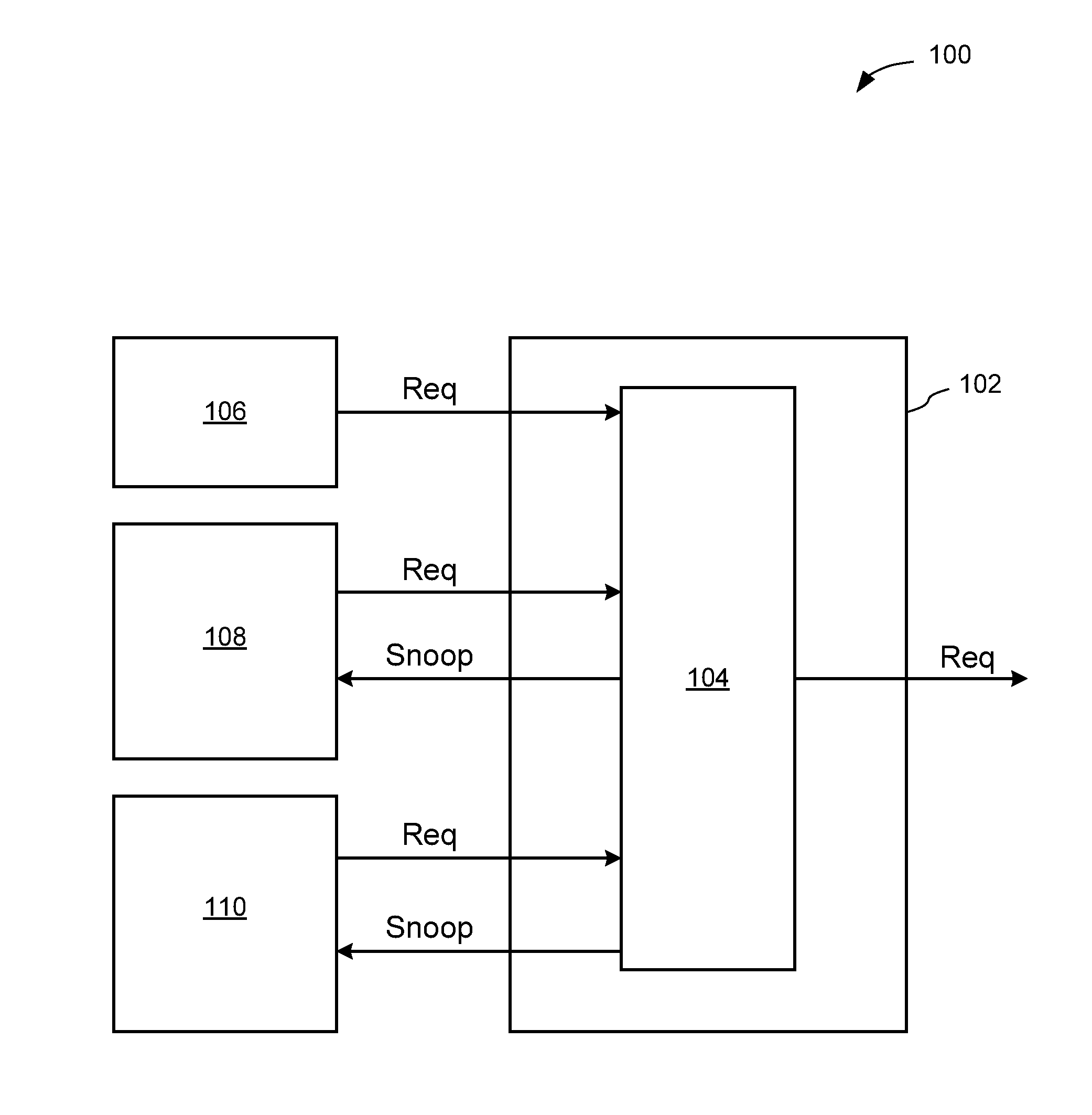
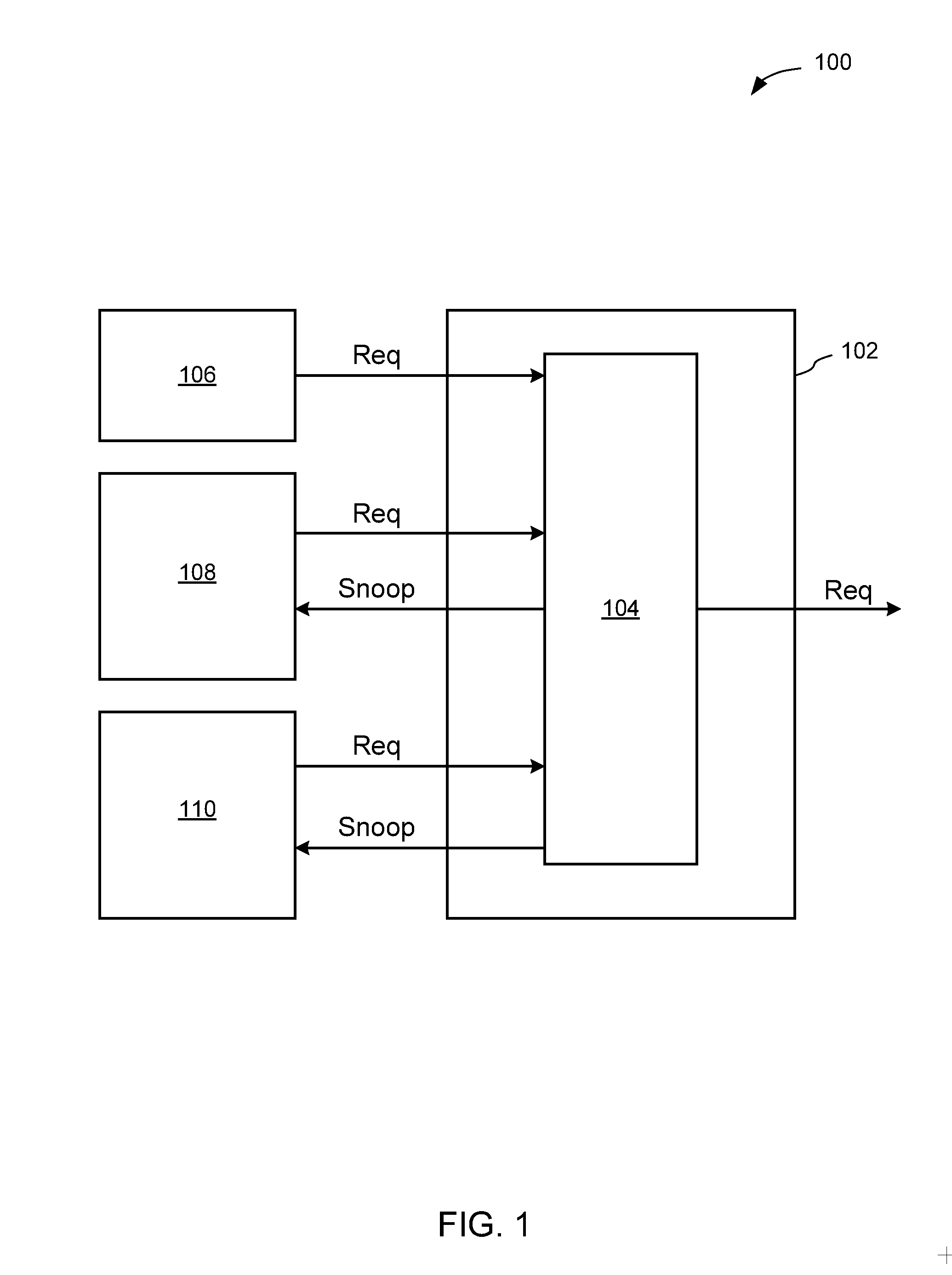
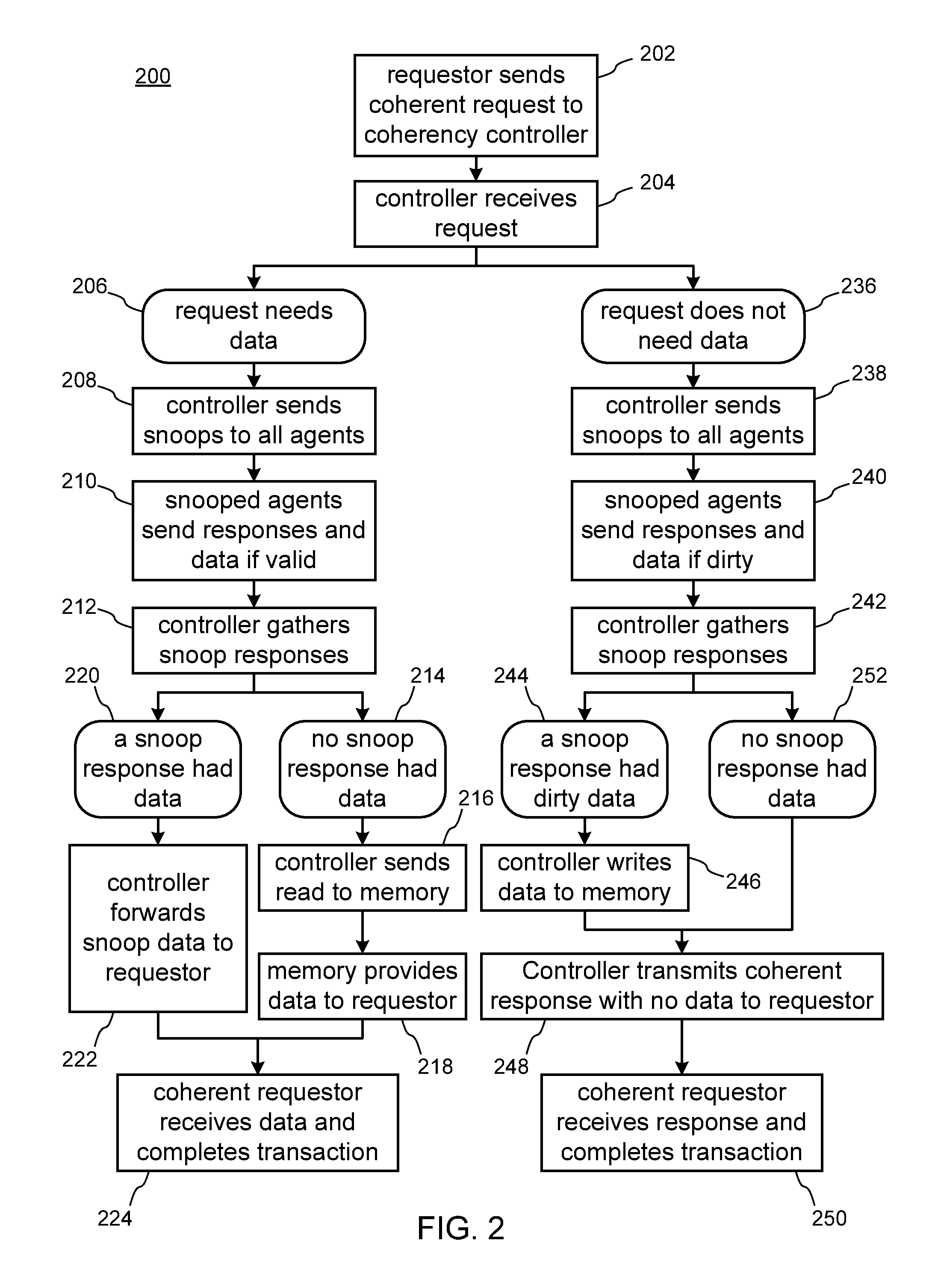
ActiveUS20140108744A1Reduce riskLess latencyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwarePartial coherence
A simplified coherency controller supports multiple exclusively active fully coherent agent interfaces and any number of active I / O (partially) coherent agent interfaces. A state controller determines which fully coherent agent is active. Multiple fully coherent agents can be simultaneously active during a short period of a transition of processing from one to another processor. Multiple fully coherent agents can be simultaneously active, though without a mutually consistent view of memory, which is practical in cases such as when running multiple operating systems on different processors.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECHNOLOGIES INC
Fast image simulation for photolithography
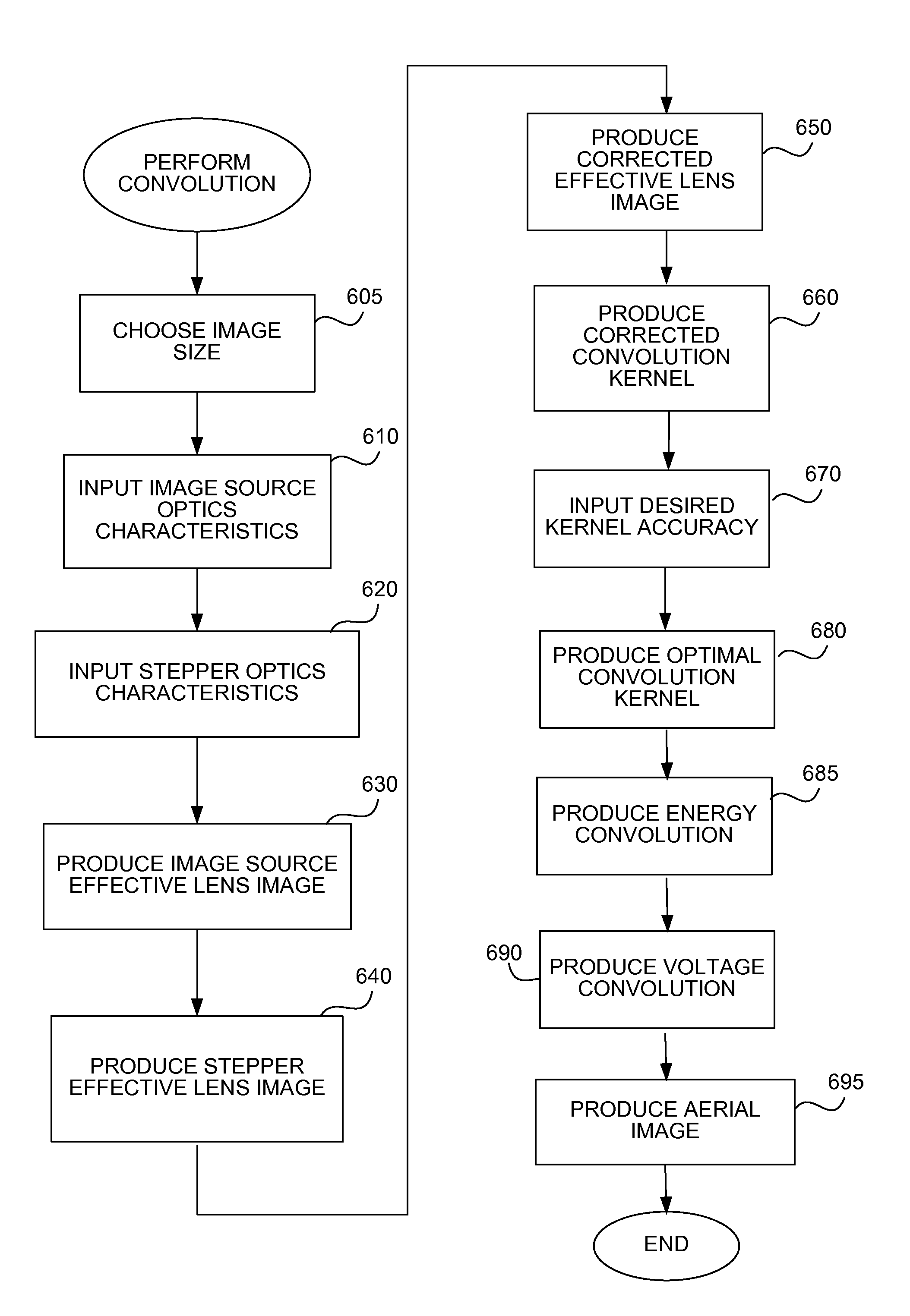
ActiveUS7472372B1Reduce the amount requiredDecrease false defect reportPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentCamera lensPartial coherence
A fast method simulates photolithography using conventional image processing techniques. Convolution simulates blurring due to optics; erosion and dilation correct for edge diffraction. To produce the convolution kernel, an effective projection lens image for the image source is produced by convolving the lens image with an image of the illuminator aperture shape. An effective projection lens image for the stepper is produced similarly. The stepper effective lens image is divided by the image source effective lens image to produce a corrected effective lens image. A corrected convolution kernel is produced by taking a Fourier transform of the corrected effective lens image. The kernel is used to convolve the image, once using energy and once using voltage, and then squaring the result. The aerial image is produced by blending the energy and voltage convolutions according to the computed partial coherence of the optics. Complex convolution is used to represent relative phases other than 180 degrees.
Owner:PETER J FIEKOWSKY
System and method used for producing Laguerre-Gaussian correlated partial coherence gauss beam
The invention discloses a system used for producing a Laguerre-Gaussian correlated partial coherence gauss beam. The system comprises a beam expander, a spatial light modulator, a beam shrinking mirror, a ground glass sheet, a lens and a Gaussian filter sheet along the direction of light in sequence. A computer-generated hologram forms a computer-generated holographic grating after being loaded on the spatial light modulator, and then a Laguerre-Gaussian beam with only an angular module is produced. The beam shrinking mirror is used for controlling the spot size of the Laguerre-Gaussian gauss beam on the rotary ground glass sheet to adjust coherence of an outgoing beam. The ground glass sheet is used for changing the Laguerre-Gaussian gauss beam to the Laguerre-Gaussian correlated partial coherence gauss beam. The lens is used for collimation of the partial coherence gauss beam. The Gaussian filter sheet is used for converting light distribution of the beam to Gaussian distribution. Due to flexibility of the computer-generated hologram, Laguerre-Gaussian beams with different orders and only angular modules can be produced by producing different holograms, and therefore Laguerre-Gaussian correlated partial coherence gauss beams with different orders are produced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Partial coherence interferometer with measurement ambiguity resolution
A partial coherence interferometer incorporates a focusing system for resolving measurement ambiguities. A focus-sensing beam is directed through a common objective with the measurement beam of the interferometer for conveying the beams to and from a test surface. An unambiguous measuring range is equated to a predetermined range of focusing errors.
Owner:QUALITY VISION INT
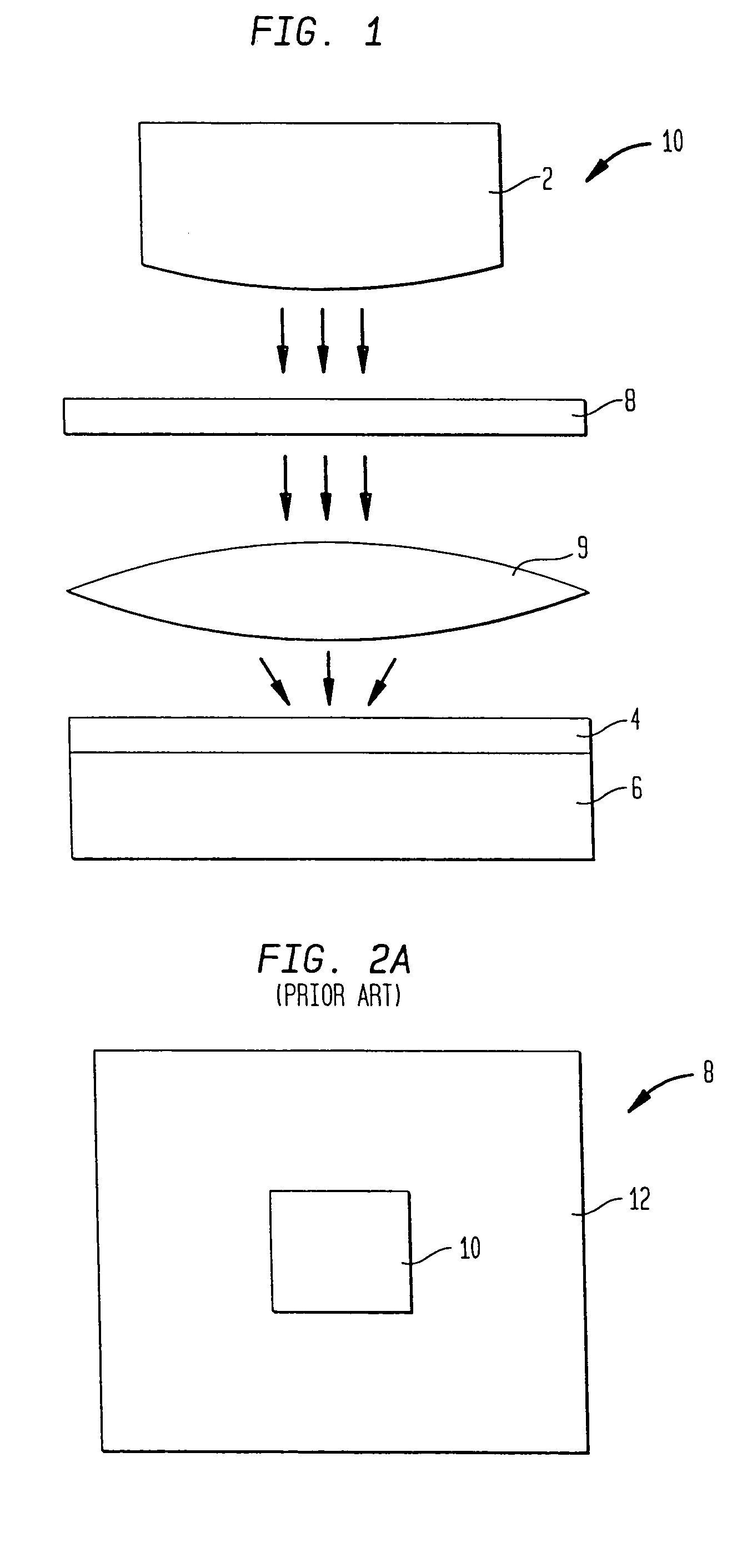
Illumination compensator for curved surface lithography
InactiveUS20050122494A1Efficient couplingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLithographic artistPartial coherence
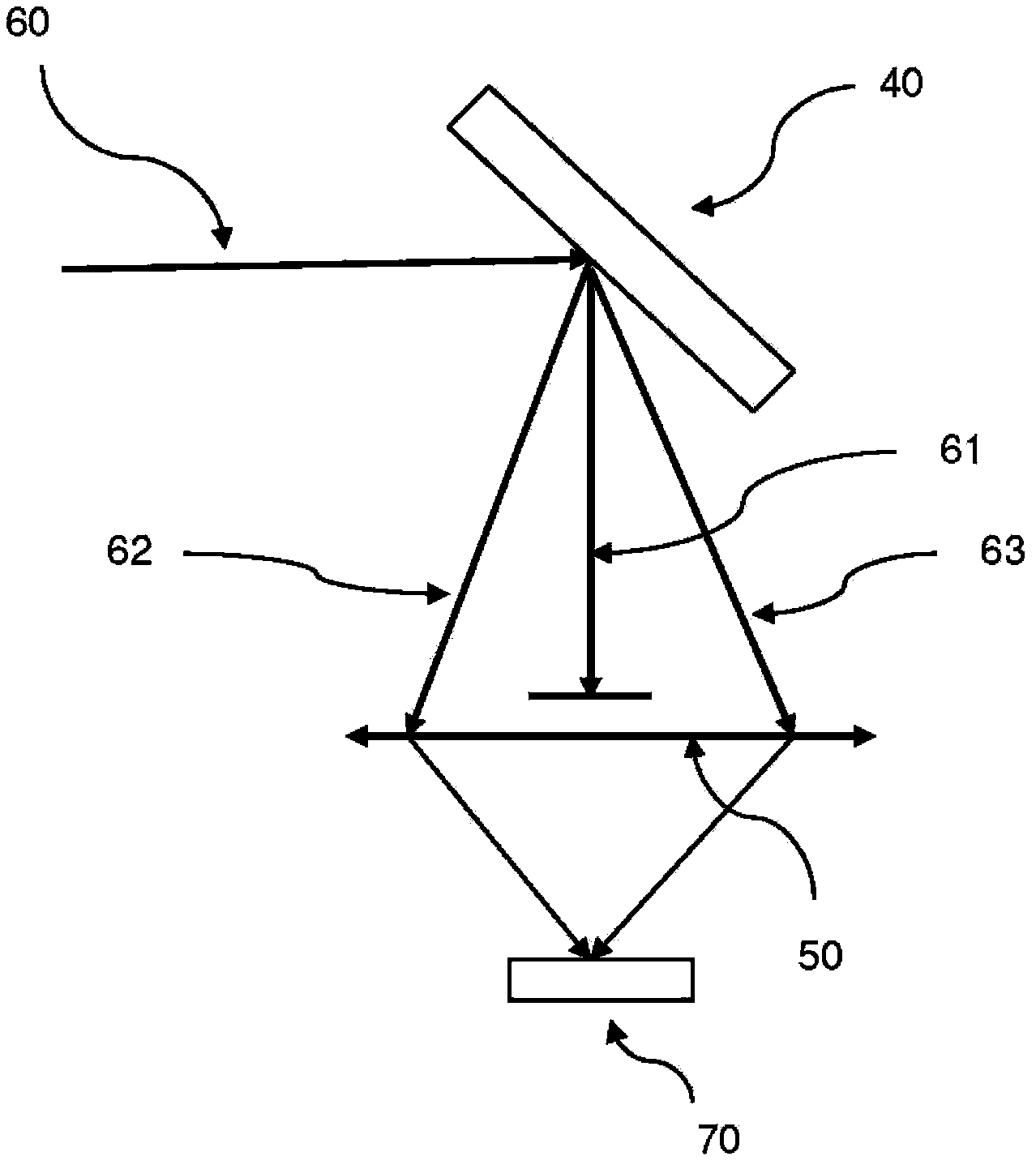
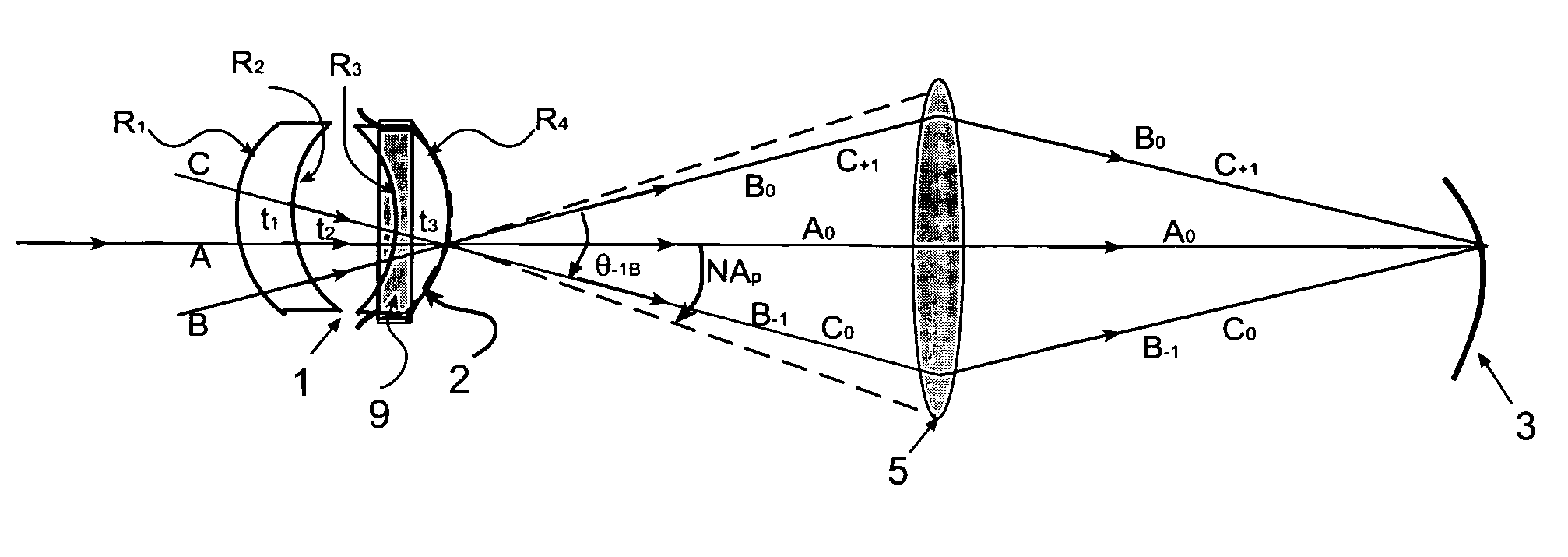
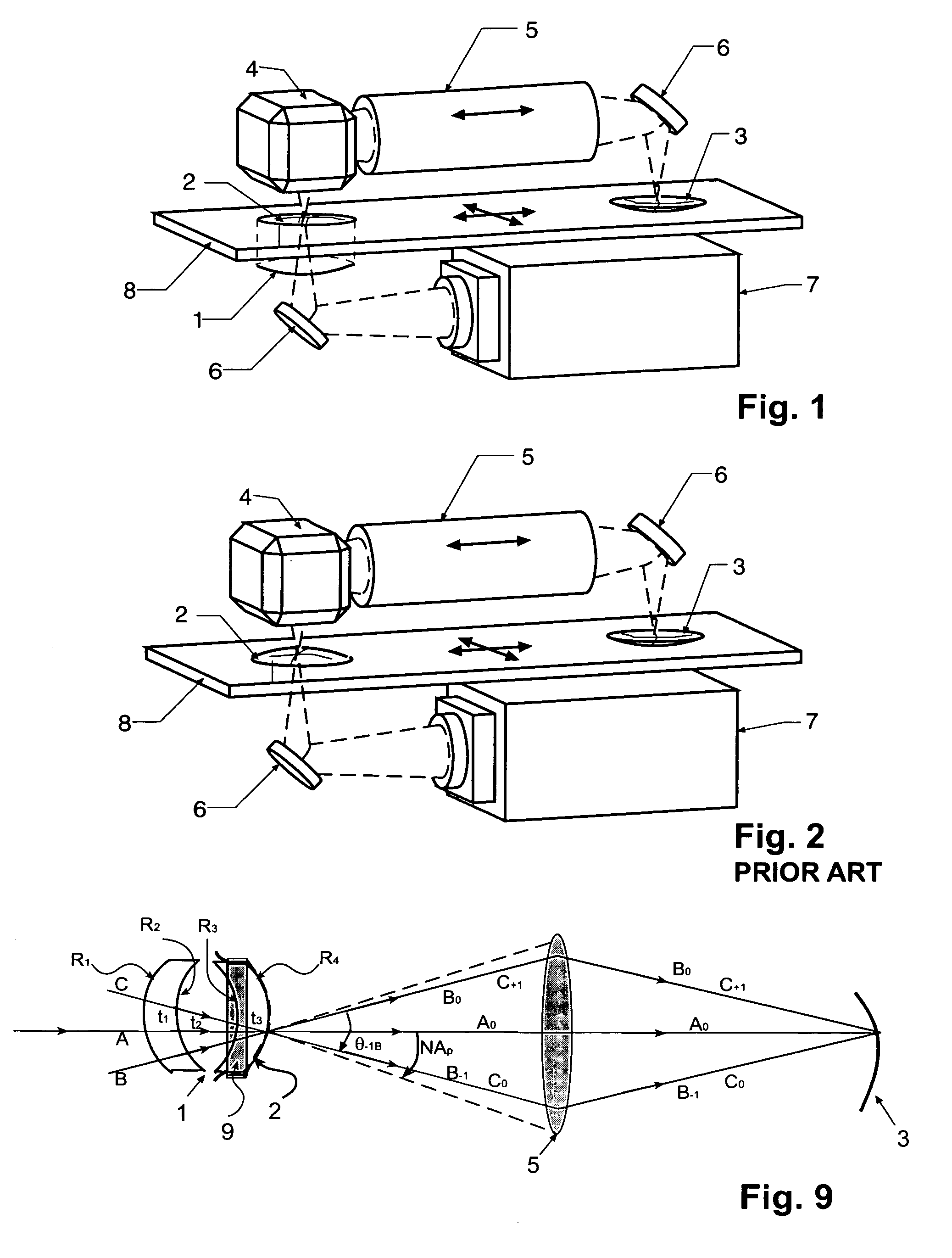
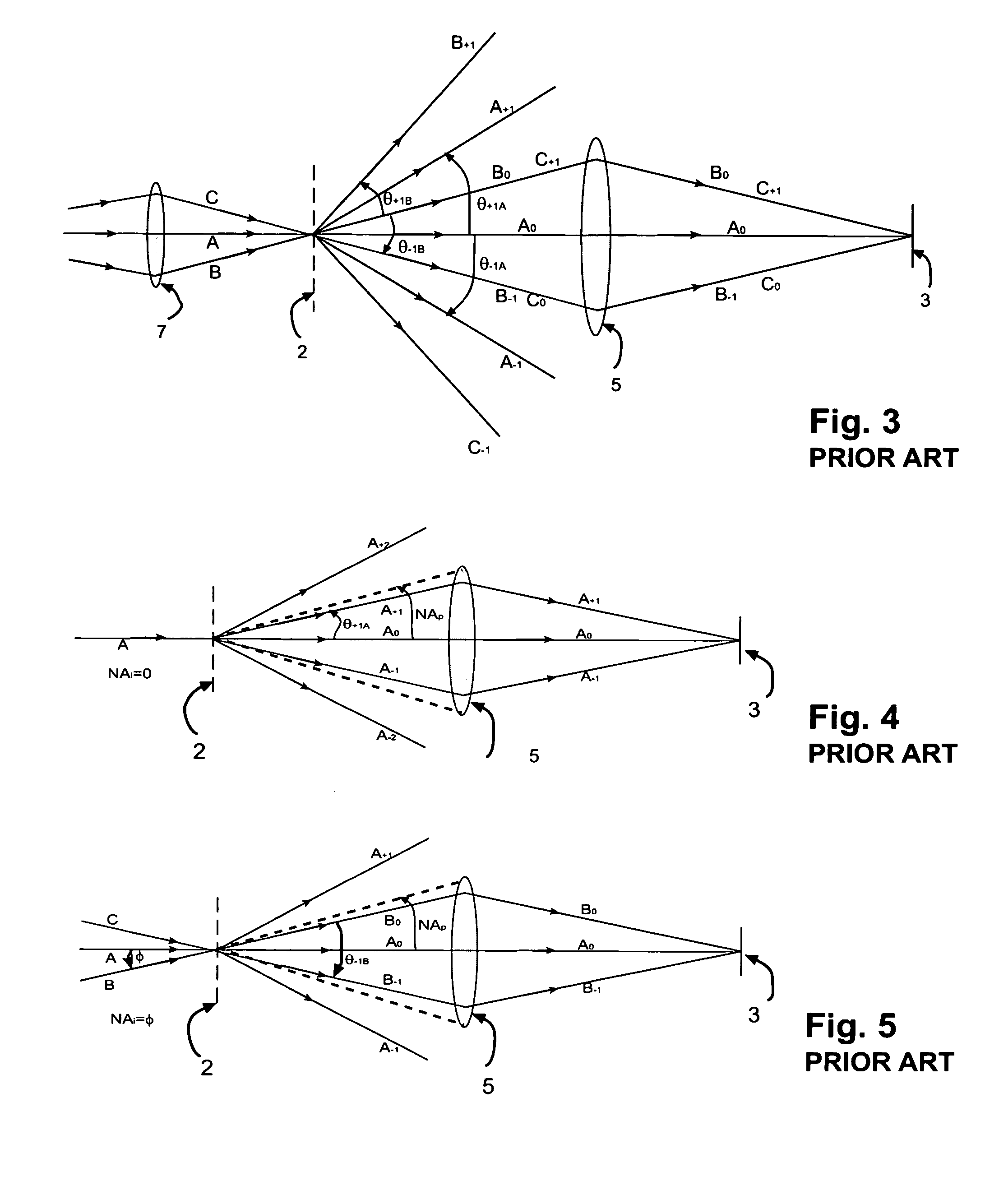
A Zerogon, a zero power identical pair of oppositely-oriented meniscus lens elements mounted in the illumination light path, serves as curved mask support while compensating for optical anomalies such as beam shift and beam deviations produced by other transparent supports for the curved mask. The Zerogon, without affecting the transmission beam characteristics, lets the beam diffract as efficiently as does a regular planar mask, thus preserving the partial coherence parameters and resolution capabilities of projection lithography. This novel optical device is not only expected to clear several barriers for curved mask projection lithography but also find place in other applications where collimated or converging light beams have to travel extra paths without significant aberration in any generic optical system.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
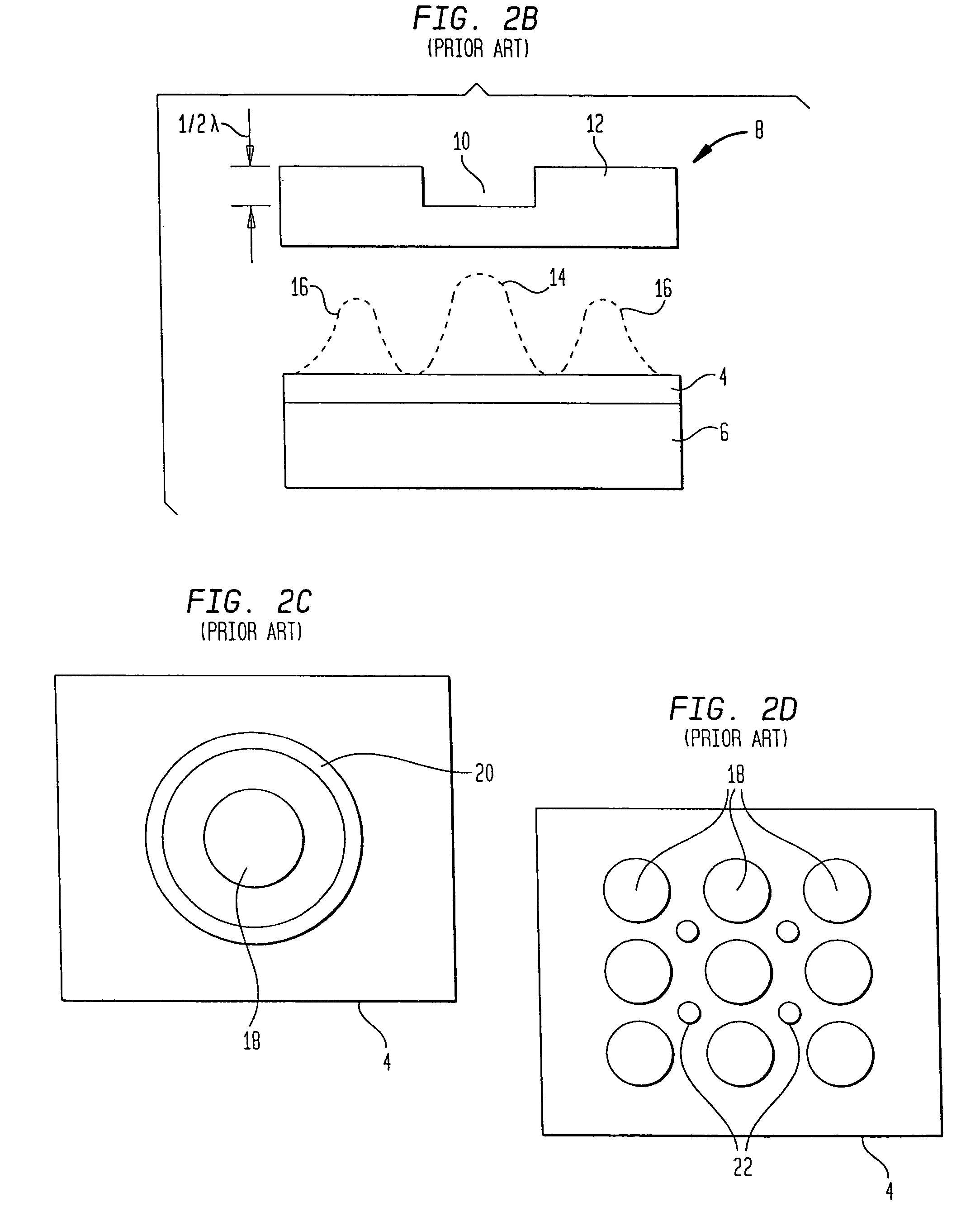
Method and apparatus for producing rectangular contact holes utilizing side lobe formation
An array of small square contact holes, on the order of magnitude of the exposing light wavelength, are formed by selecting the partial coherence and numerical aperture of the exposing light source and the pitch of the array of windows on an attenuating phase shifting mask so that side lobes formed by the exposing light being diffracted as it passes through the array of window constructively interfere with one another in the vicinity of a desired contact hole on the material surface. This constructive interference of side lobe patterns, in combination with the pattern formed by the light passing undiffracted through the array of windows, forms an array of square exposed regions on the material surface. When the material is a photoresist, the exposed regions can be selectively dissolved in order to form square patterns that can be used to etch square holes in the underlying substrate or layer. In subsequent steps, selected ones of the array of square holes can be filled in with a conductive material to form vias and selected others of the square holes can be filled in with an insulating material so as to avoid the formation of unintended vias or conducting paths.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Illumination system with spatially controllable partial coherence compensating for line width variances
InactiveUS7092070B2Easy to changeEnhance the imageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction gratingsProjection opticsLine width
An illumination system having an array optical element with different illumination regions corresponding or matched to different line width variations printed on a photosensitive material. The array optical element may be a filter, diffractive optical element, or micro lens array having illumination regions producing different types of illumination properties or characteristics. Each of the illumination regions are matched or correspond to a respective region on a patterning device to provide optimized exposure of a photosensitive material. The optical element may be used to tailor a conventional illumination system to the unique characteristics of the projection optics used in a system, thereby compensating for vertical and horizontal bias or variations in line width for features oriented in the vertical and horizontal direction.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
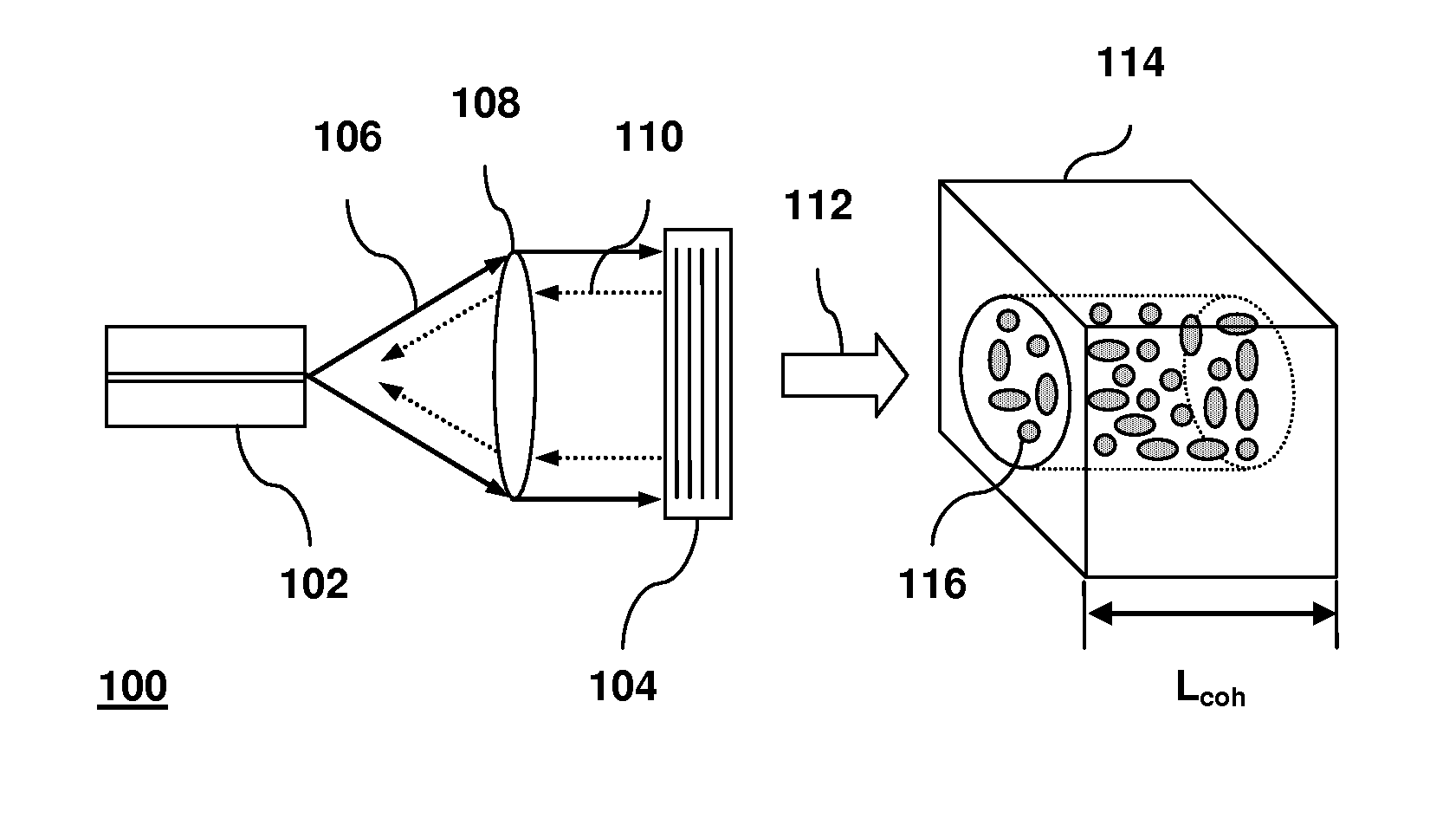
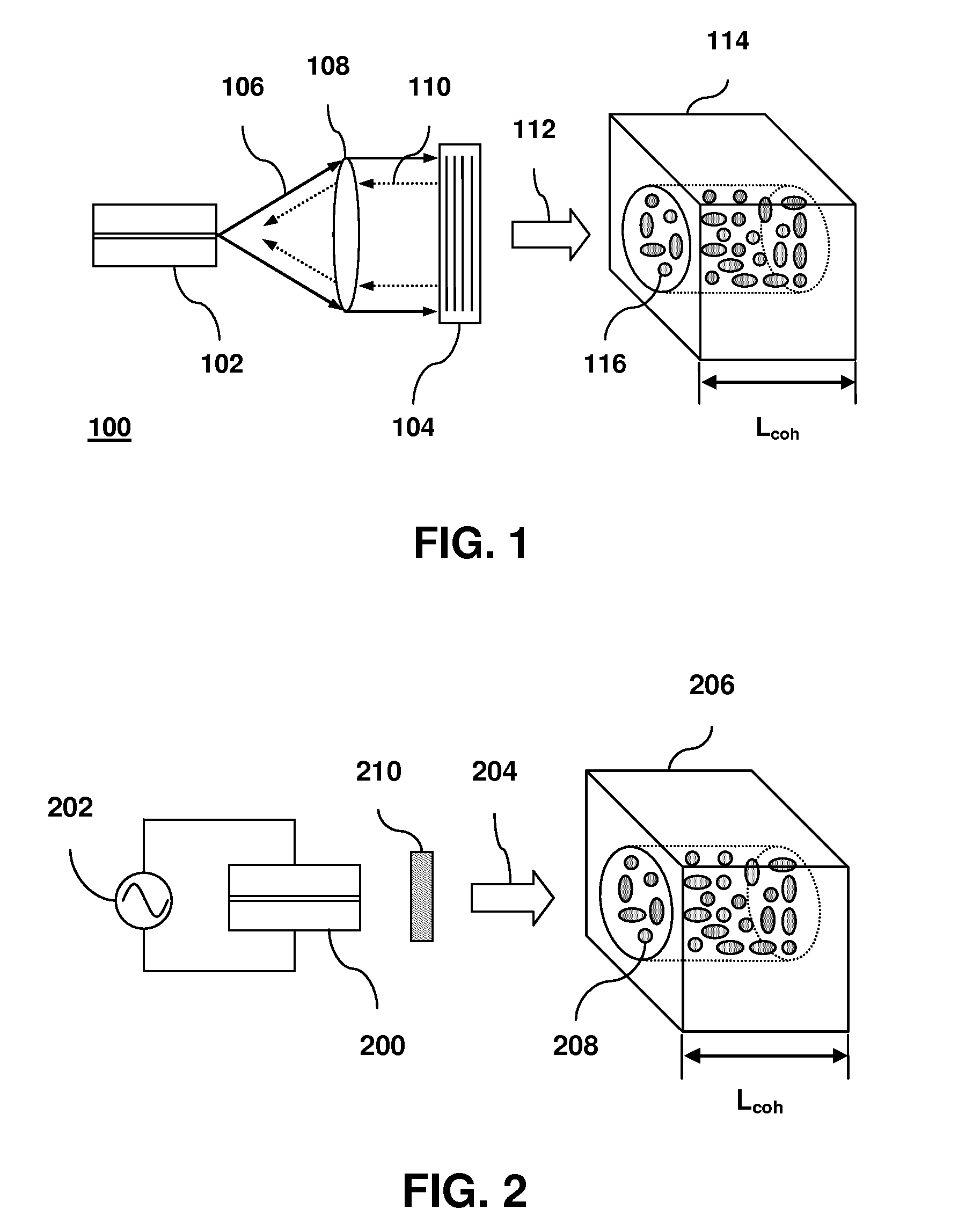
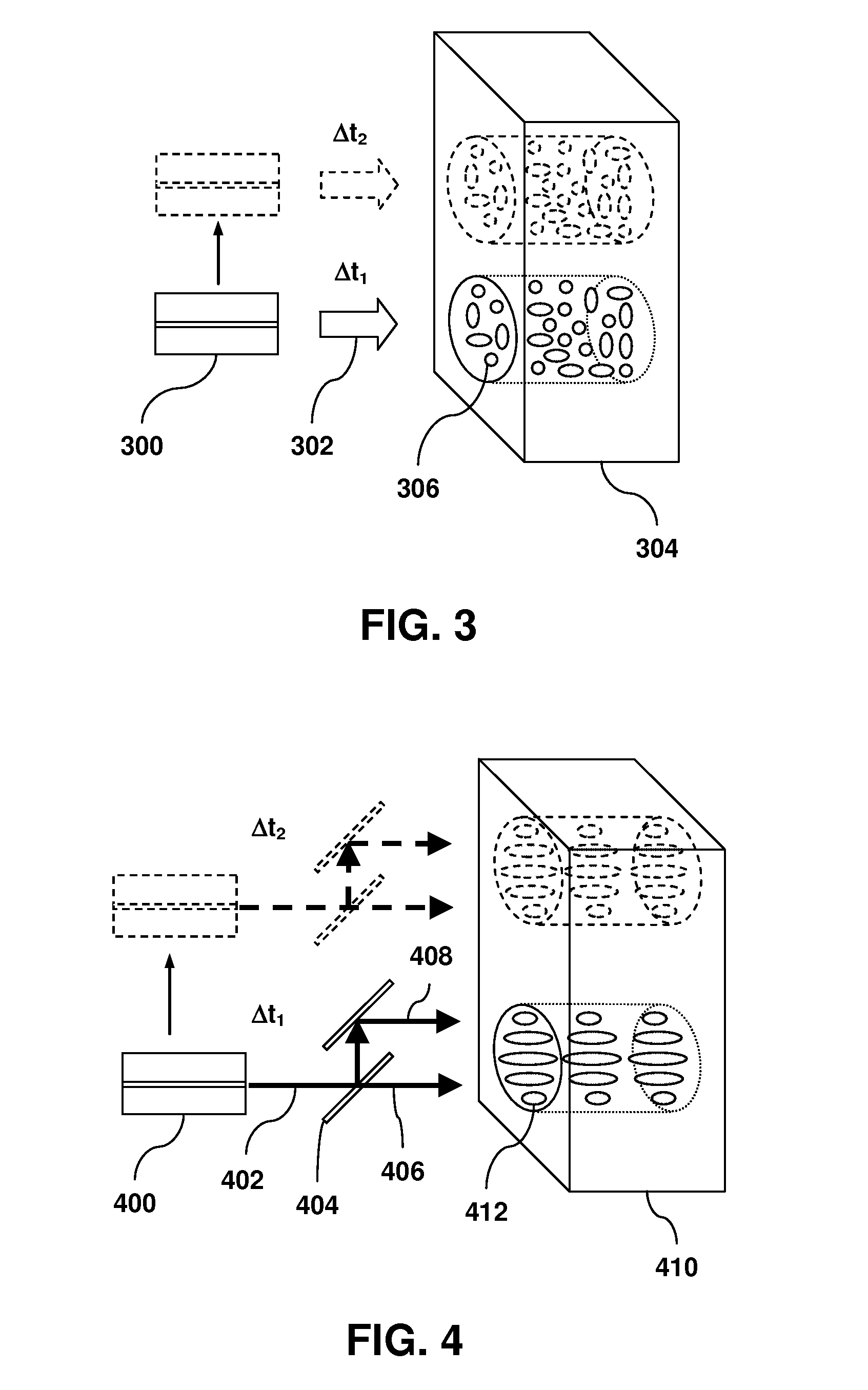
Adjustment of the partial coherence of the light energy in an imaging system
The present invention describes an apparatus comprising an optical array generating a distribution of partial coherence of light energy and an aperture to select a subset of said distribution of partial coherence.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Extreme ultraviolet lithography process and mask
ActiveCN103529641APhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusProjection opticsPartial coherence
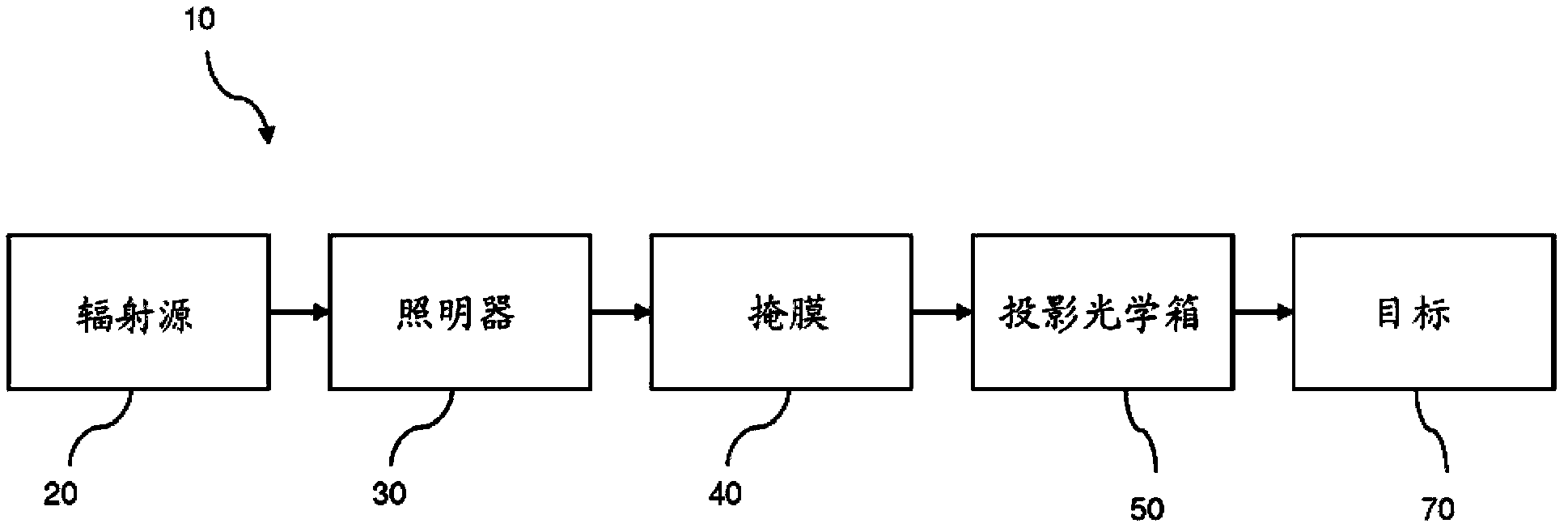
A process of an extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUVL) is disclosed. The process includes receiving an extreme ultraviolet (EUV) mask with multiple states. Different states of the EUV mask are assigned to adjacent polygons and adjacent sub-resolution polygons. The EUV mask is exposed by a nearly on-axis illumination (ONI) with partial coherence sigma less than 0.3 to produce diffracted lights and non-diffracted lights. Most of the non-diffracted lights are removed. The diffracted lights and the not removed non-diffracted lights are collected and directed to expose a target by a projection optics box.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Illumination system with spatially controllable partial coherence compensating for line width variances
InactiveUS20050041231A1Easy to changeEnhance the imageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction gratingsProjection opticsLine width
An illumination system having an array optical element with different illumination regions corresponding or matched to different line width variations printed on a photosensitive material. The array optical element may be a filter, diffractive optical element, or micro lens array having illumination regions producing different types of illumination properties or characteristics. Each of the illumination regions are matched or correspond to a respective region on a patterning device to provide optimized exposure of a photosensitive material. The optical element may be used to tailor a conventional illumination system to the unique characteristics of the projection optics used in a system, thereby compensating for vertical and horizontal bias or variations in line width for features oriented in the vertical and horizontal direction.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
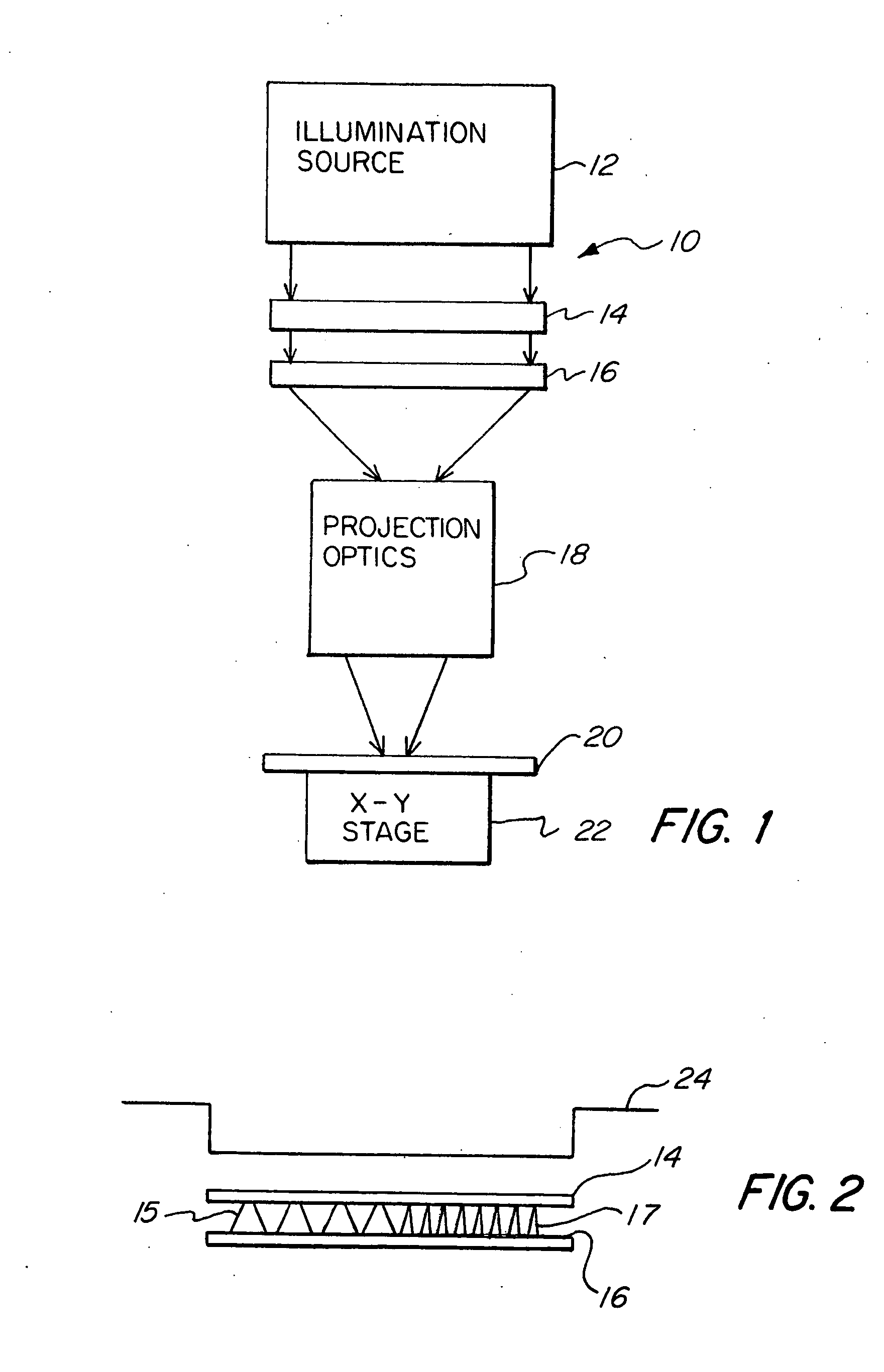
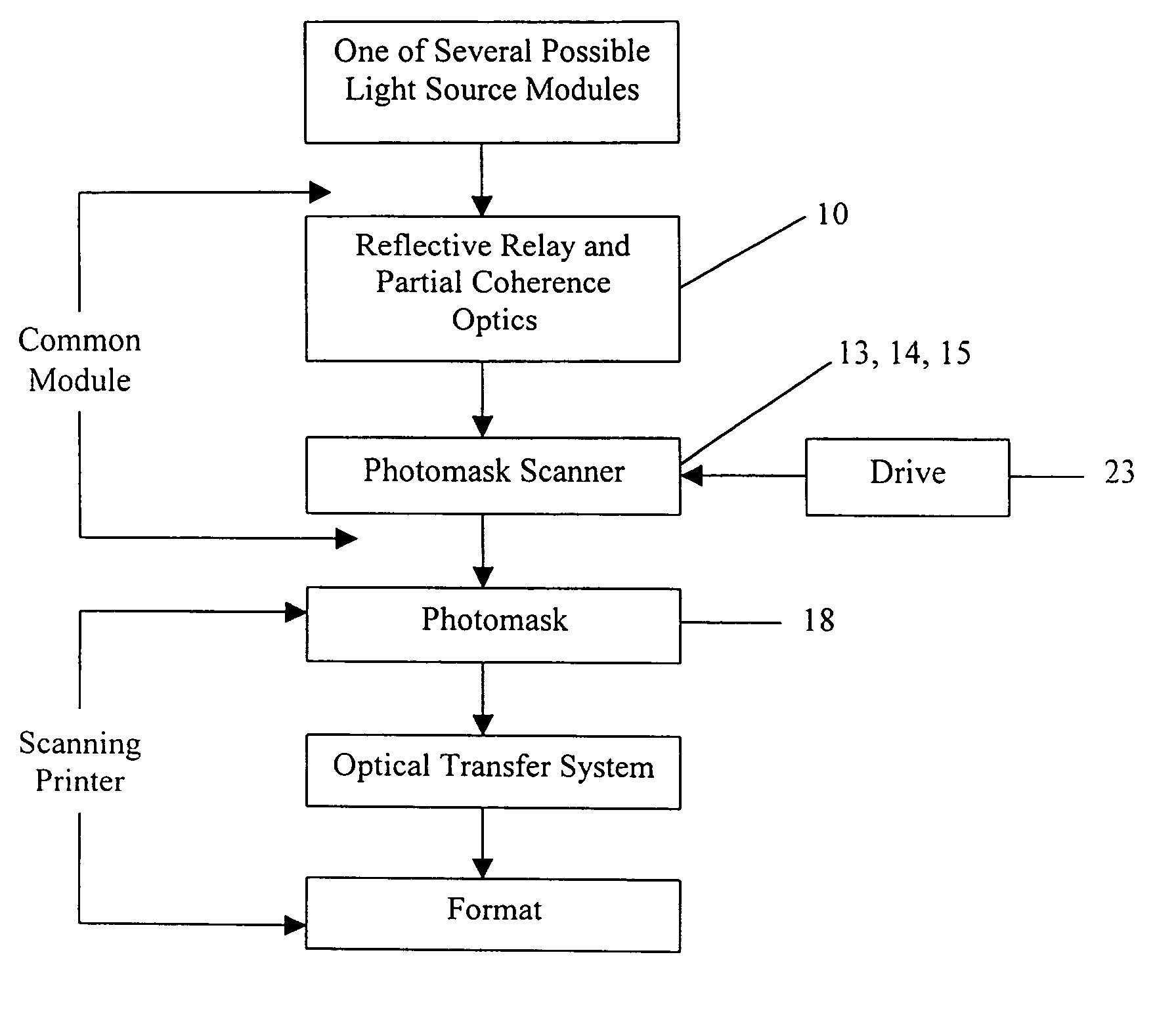
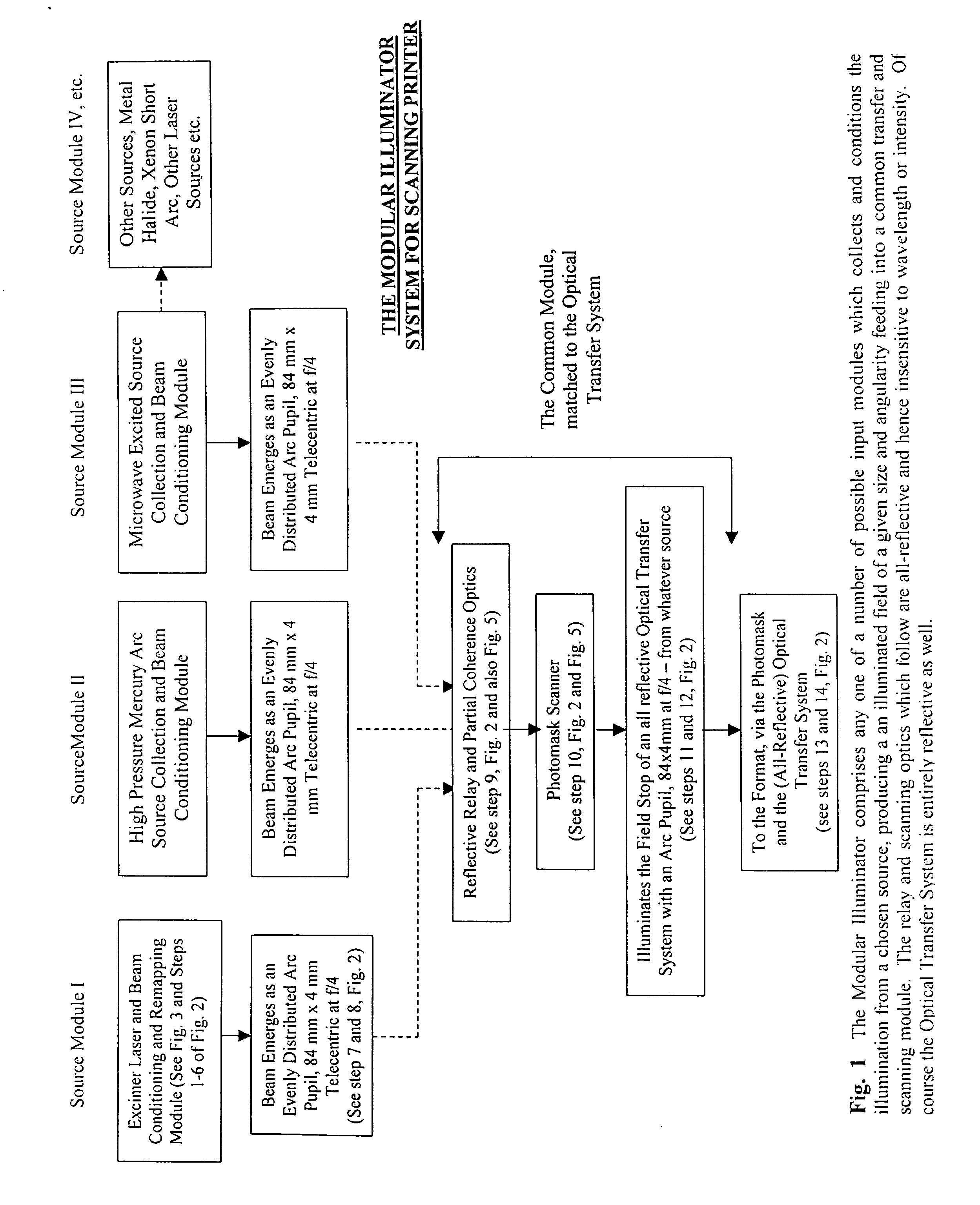
Modular illuminator for a scanning printer
InactiveUS20070109520A1High pulse rateApplicationProjectorsPhotomechanical apparatusPartial coherenceComputer printing
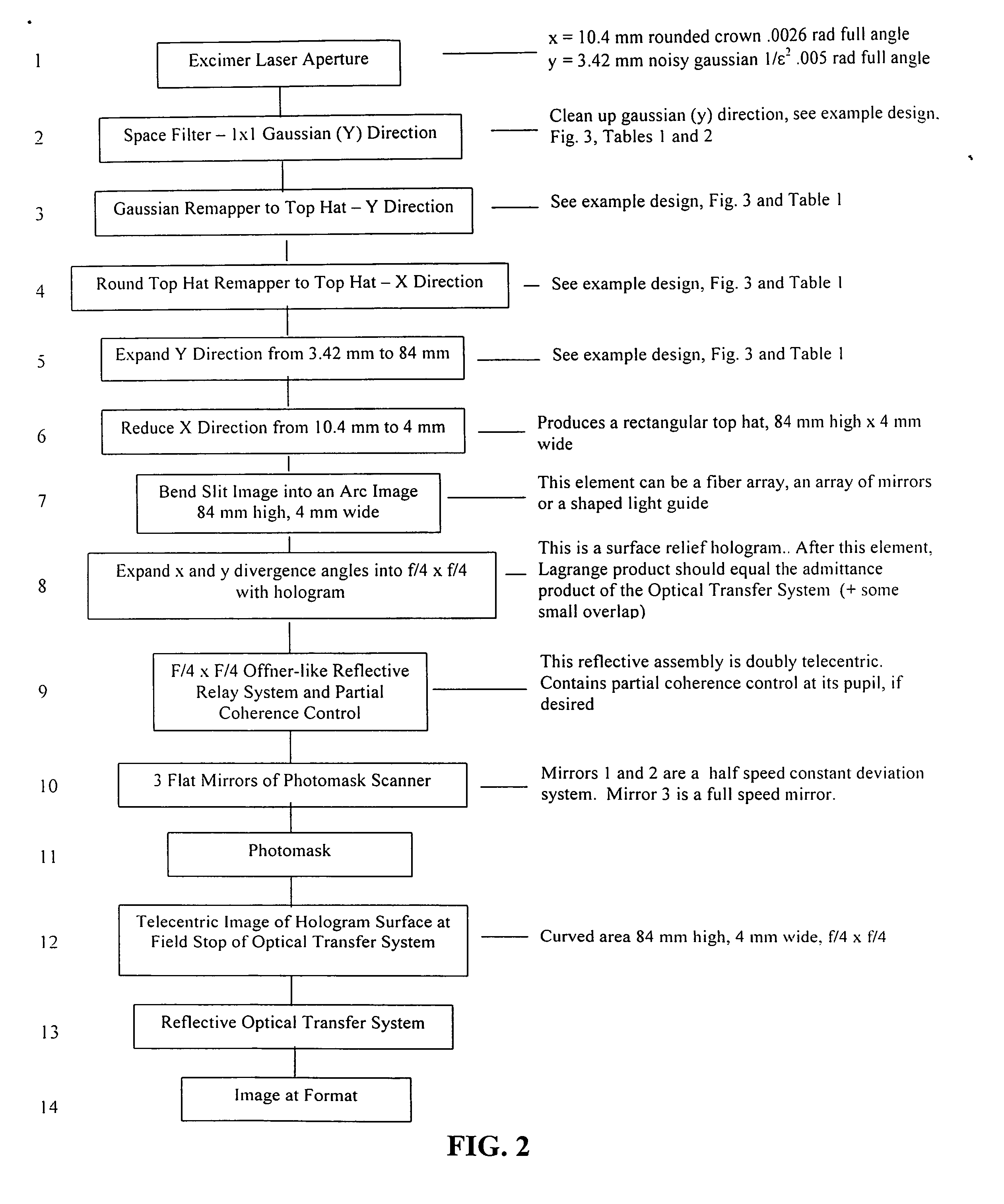
Disclosed herewith is a system and method for building an illuminator for a scanning printer. The design is modular enabling any of a number of different sources to be used with common partial coherence and scanning optics. The illuminated field, moves across the photomask in synchronism with the motion of the scanning printer, preserving telecentricity, entendue and optical distance invariance as it scans.
Owner:WHITNEY THEODORE ROBERT
Illumination compensator for curved surface lithography
InactiveUS7106415B2Efficient couplingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLithographic artistImage resolution
A zero power identical pair of oppositely-oriented meniscus lens elements mounted in the projection light path, serves as curved mask support while compensating for optical anomalies such as beam shift and beam deviations produced by other transparent supports for the curved mask. The zero-power meniscus lens pair, without affecting the transmission beam characteristics, lets the beam diffract as efficiently as does a regular planar mask, thus preserving the partial coherence effects and resolution concepts of projection lithography. This simple but novel optics device is not only expected to clear several barriers for curved mask projection lithography but also find place in other applications where collimated or converging light beams have to travel extra paths without significant aberration.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
Device for generating a light beam with atmospheric turbulence resistance
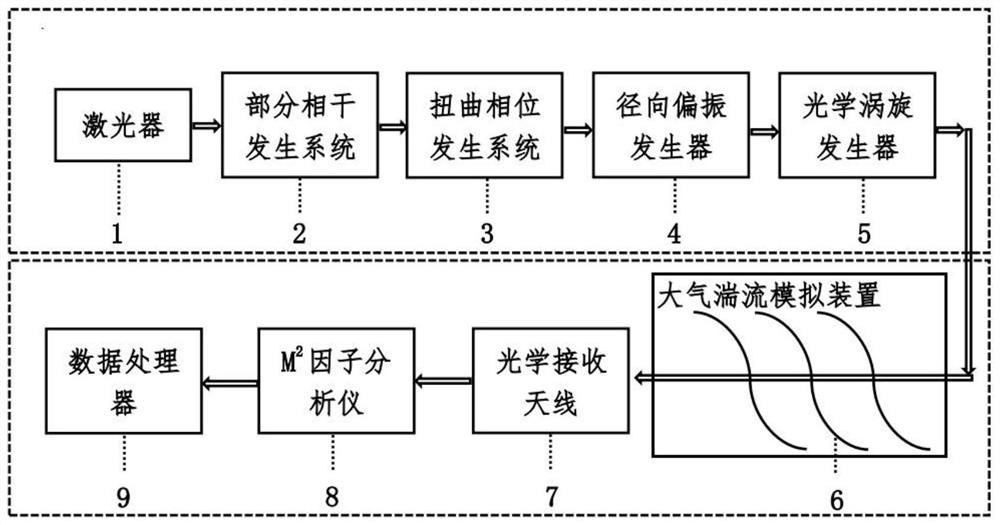
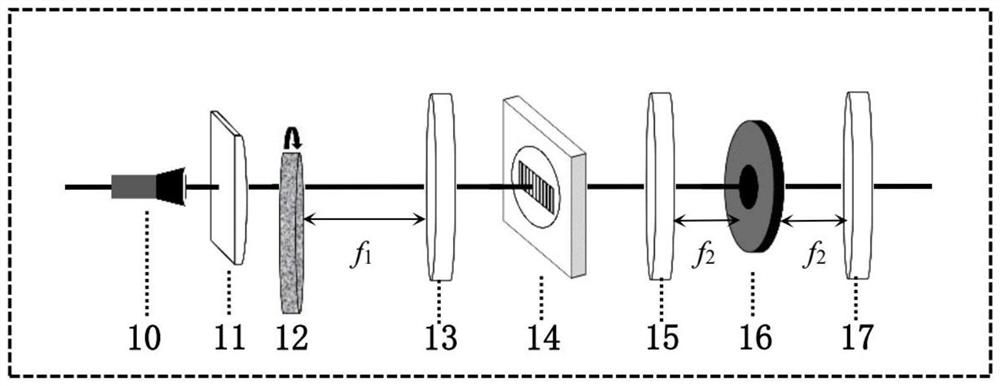
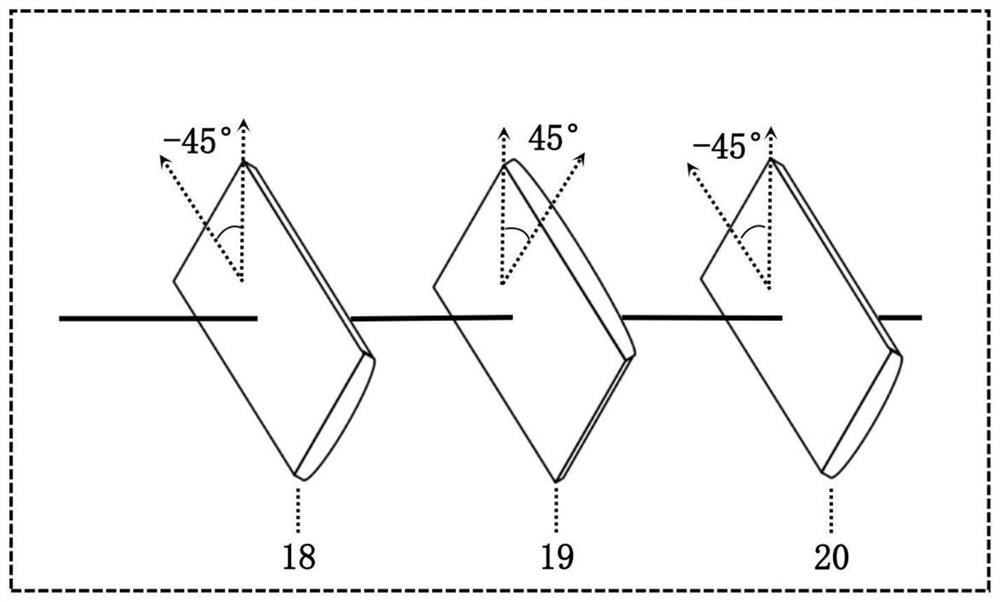
ActiveCN113655625ANo special needsSimple structureOptical elementsICT adaptationPartial coherenceLight beam
The invention relates to the field of laser free space communication, in particular to a device for generating a light beam with atmospheric turbulence resistance. According to the device, linearly polarized laser output by a laser sequentially passes through a partial coherence generation system, a distortion phase generation system, a radial polarization generator and an optical vortex generator to generate a partial coherence radial polarization distortion vortex beam. The light beam has four anti-atmospheric turbulence structures of partial coherence, twisted phase, vortex phase and non-uniform polarization, so that the influence of atmospheric turbulence on the phase structure of the light beam can be effectively inhibited, and the light beam has potential application value in the fields of free space optical communication, laser radar and the like.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
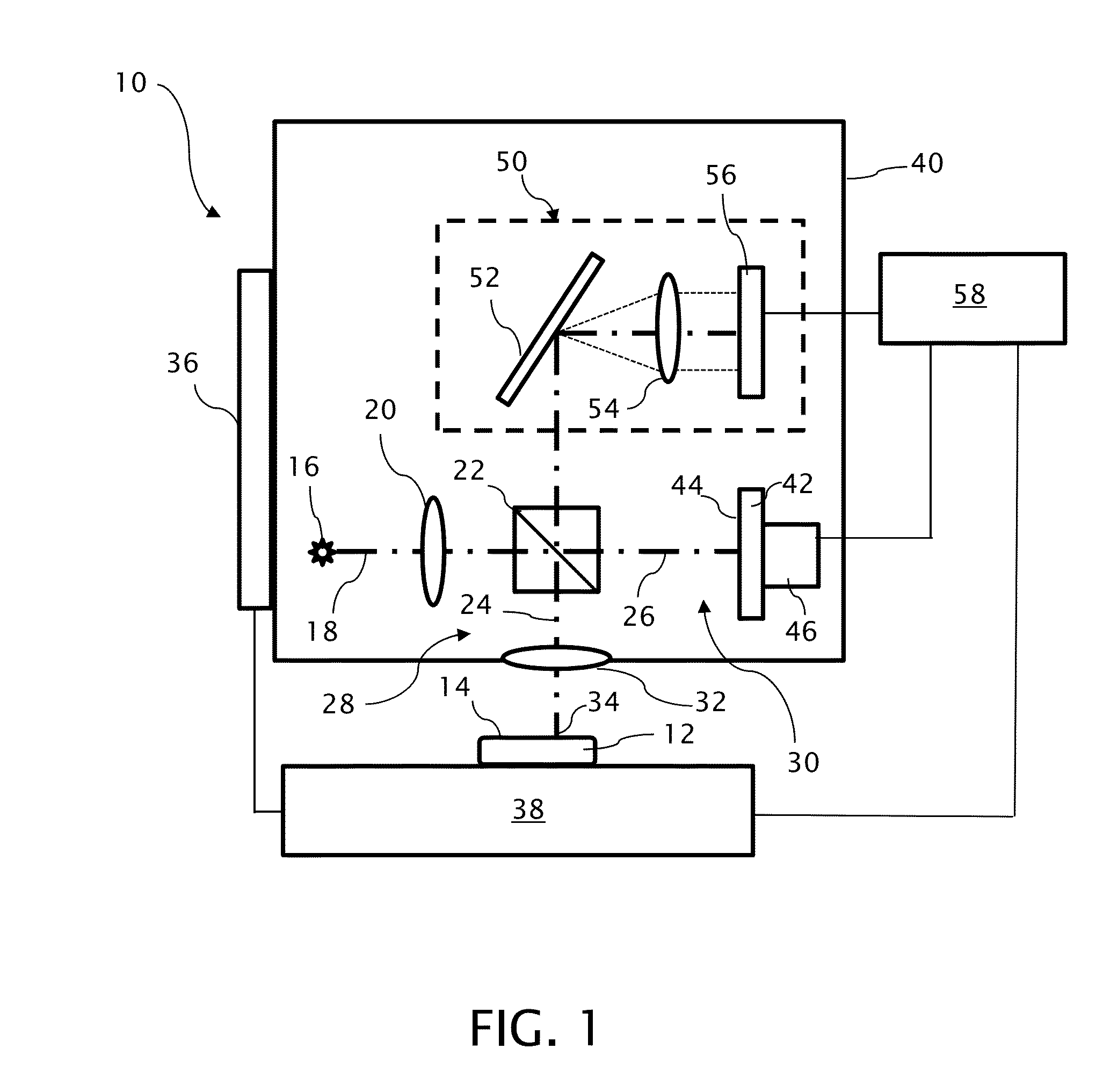
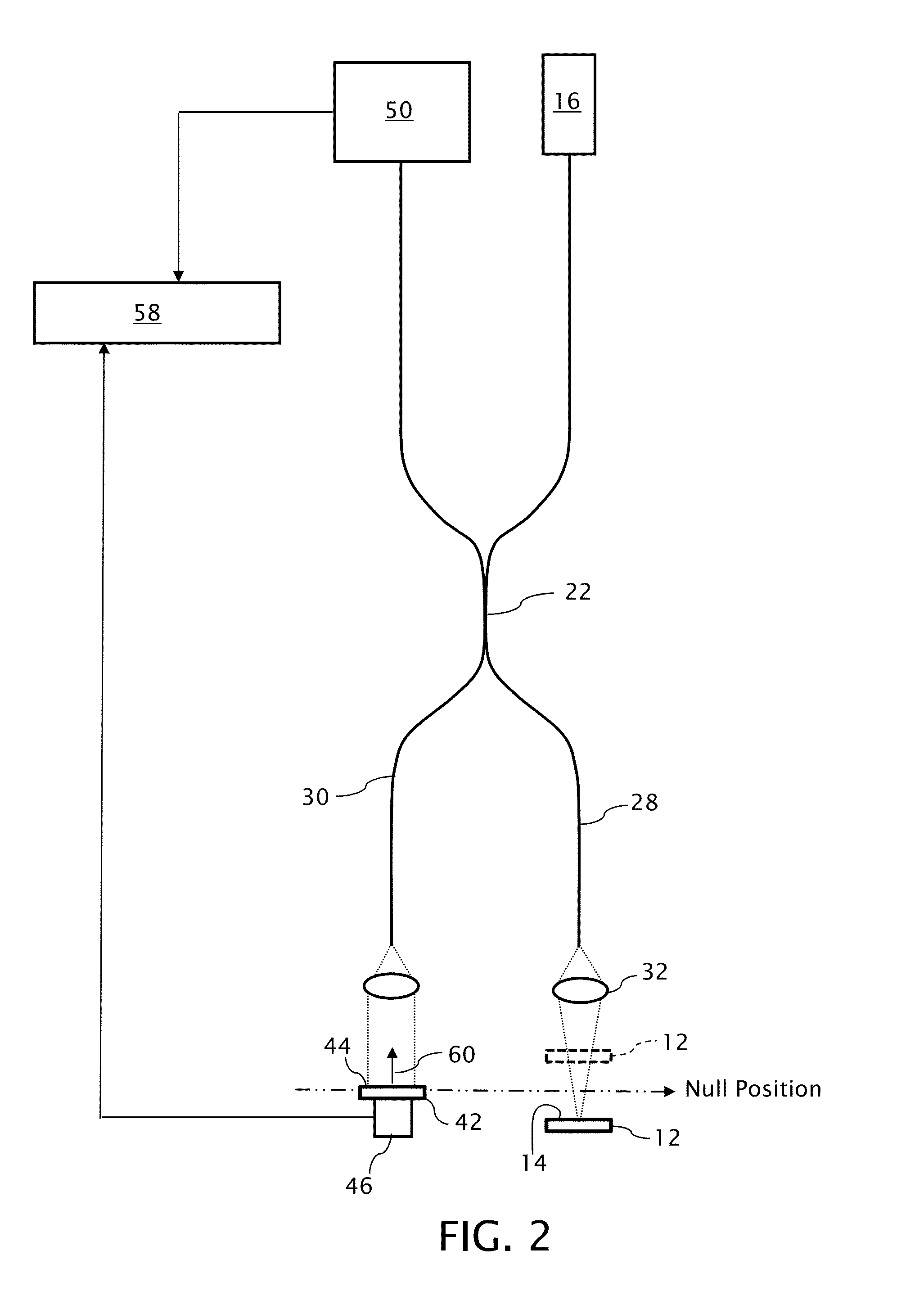
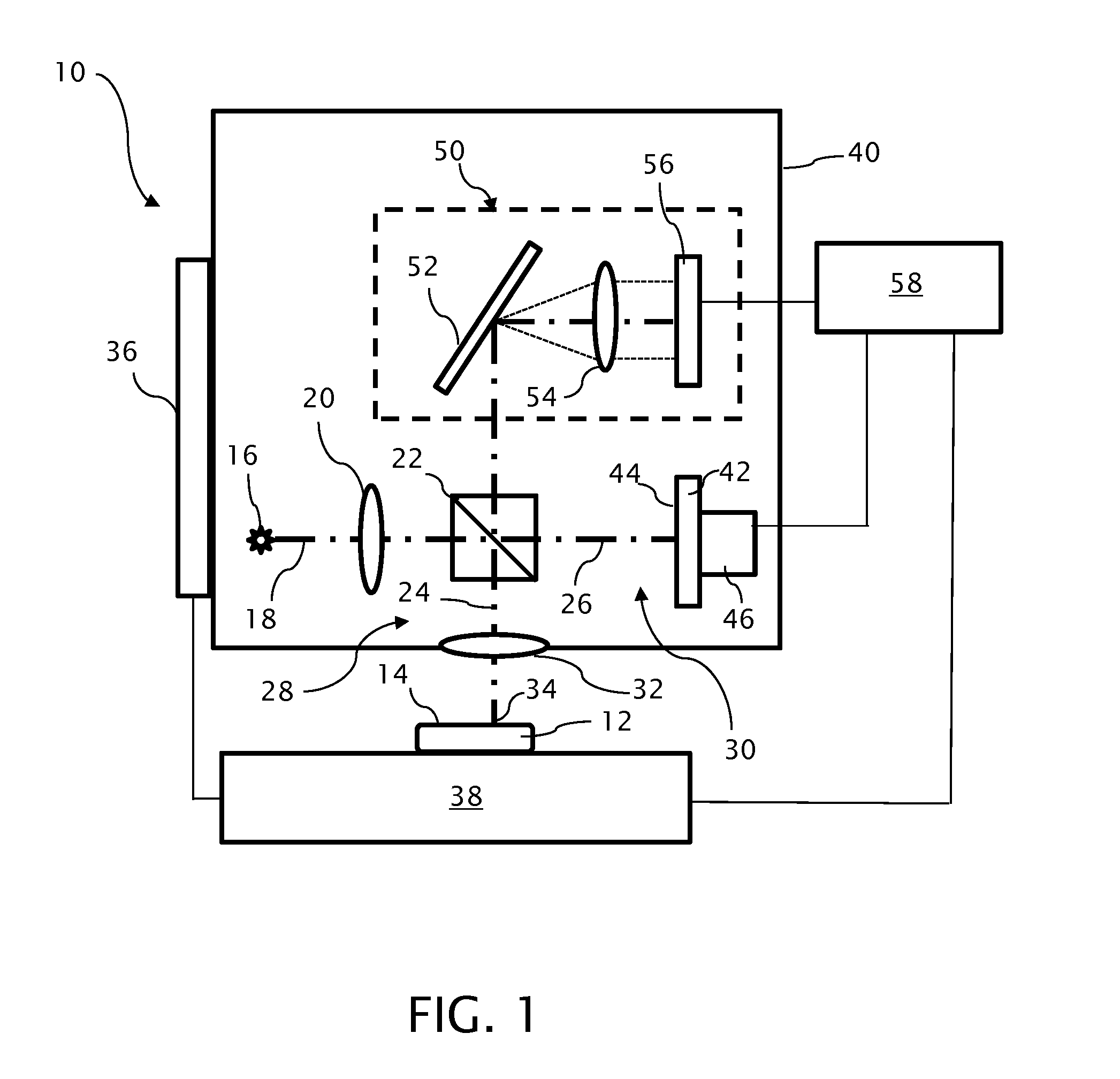
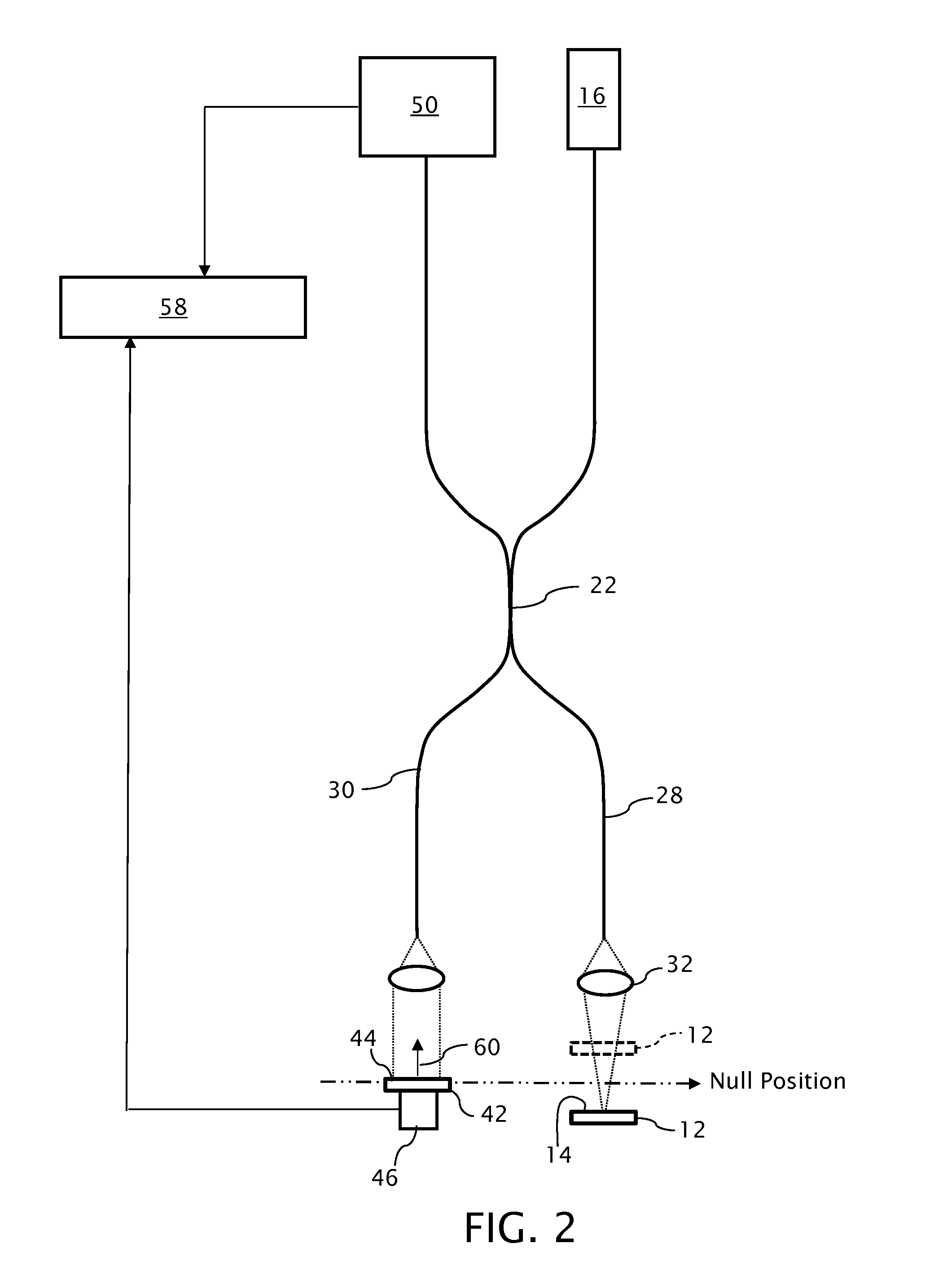
Profilometer with partial coherence interferometer adapted for avoiding measurements straddling a null position
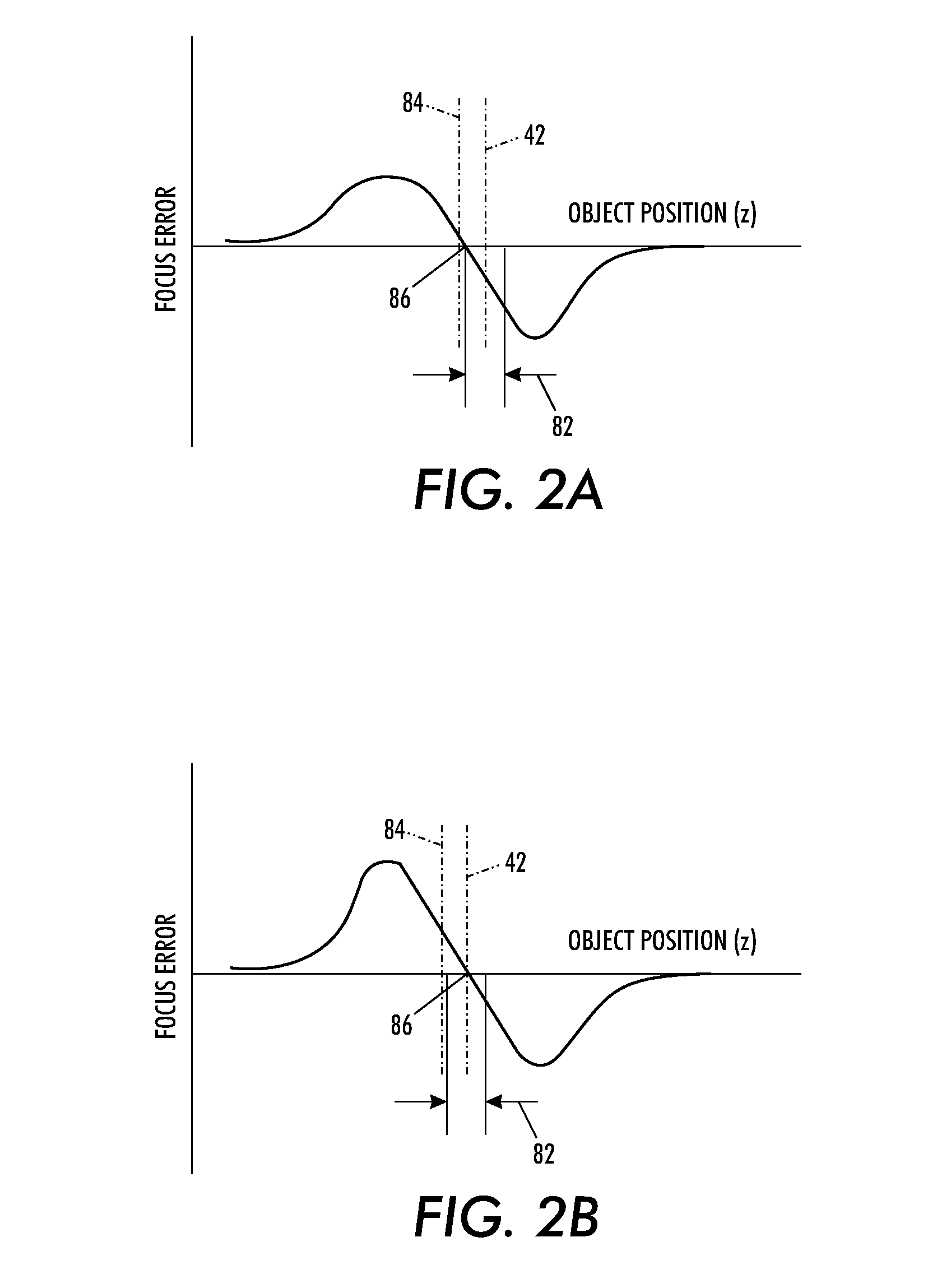
A profilometer incorporating a partial coherence interferometer directs a beam containing a band of wavelengths along object and reference arms of the interferometer into respective engagements with a test object surface and a reference object surface en route to a spectrometer for measuring a spectrum of the beam. Within the object arm, the test object surface is relatively moved through a range of positions offset from a null position at which optical path lengths of the object and reference arms are equal. Modulation frequencies of the beam spectrum are calculated at a succession of different focus spot positions across the test object surface. Changes in the modulation frequency are interpreted to distinguish between optical path length differences at which the optical path length of the object arm is longer or shorter than the optical path length of the reference arm.
Owner:QUALITY VISION INT
Method and system for determining network connections
ActiveUS20190021594A1Improve accuracyCancel noiseElectroencephalographyMedical data miningNODALEeg data
This invention relates to methods and systems for determining network connections. It is particularly, but not exclusively, related to methods and systems for determining network connections in sparse networks, and has particular application to EEG data. An aspect of the invention provides a method for identifying, in a network of interacting nodes simultaneously producing signals, connections between said nodes and of estimating connection coefficients between nodes identified as connected which includes the steps of setting to zero connection coefficients where the calculated coherence or partial coherence is below a first predetermined threshold and subsequently setting to zero connection coefficients where the estimated connection coefficients are below a second predetermined threshold, and then re-estimating the connection coefficients for the combinations of nodes for which the connection coefficients have not already been set to zero.
Owner:GENTING TAURX DIAGNOSTIC CENT SDN BHD
Laser therapy apparatus with controlled optical coherence
ActiveUS9283036B2Maximize the effectControlling energy of instrumentLight therapyMedicinePartial coherence
A laser therapy method and apparatus is disclosed. The optical coherence property of the therapy laser is actively controlled to provide optimum therapy results for difference types of biological tissue and body parts.
Owner:LITECURE
Method and apparatus for measurement of exit pupil telecentricity and source boresighting
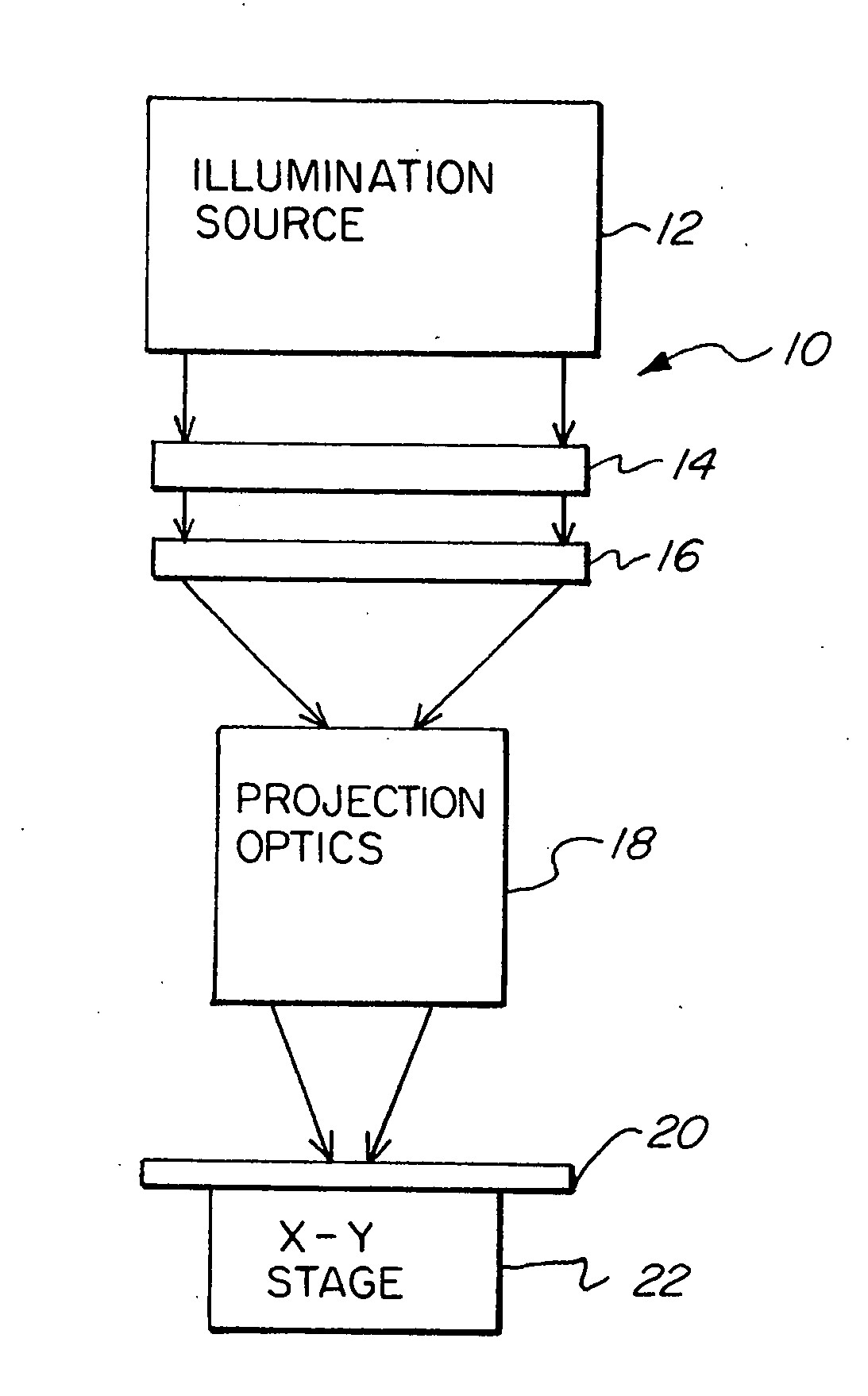
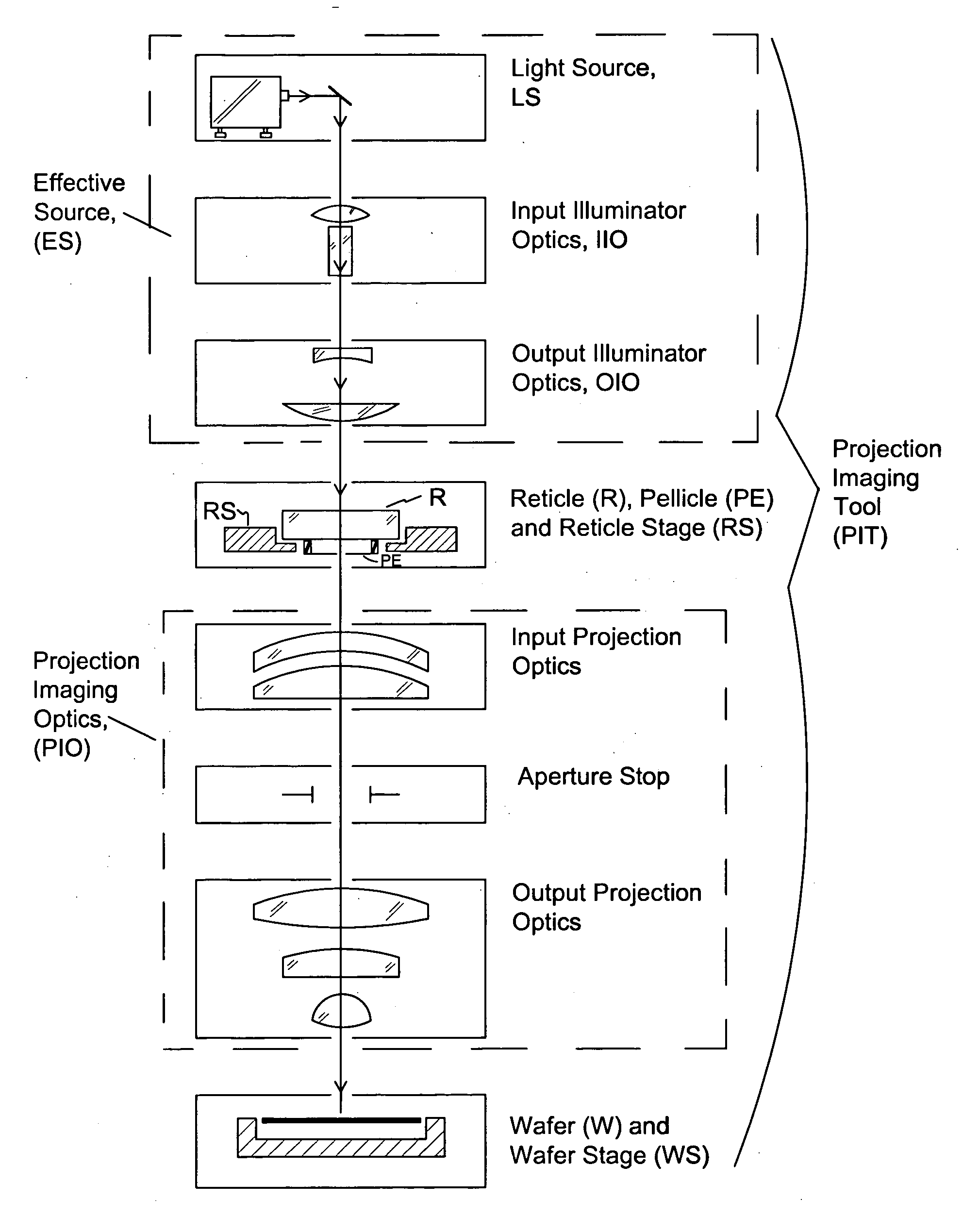
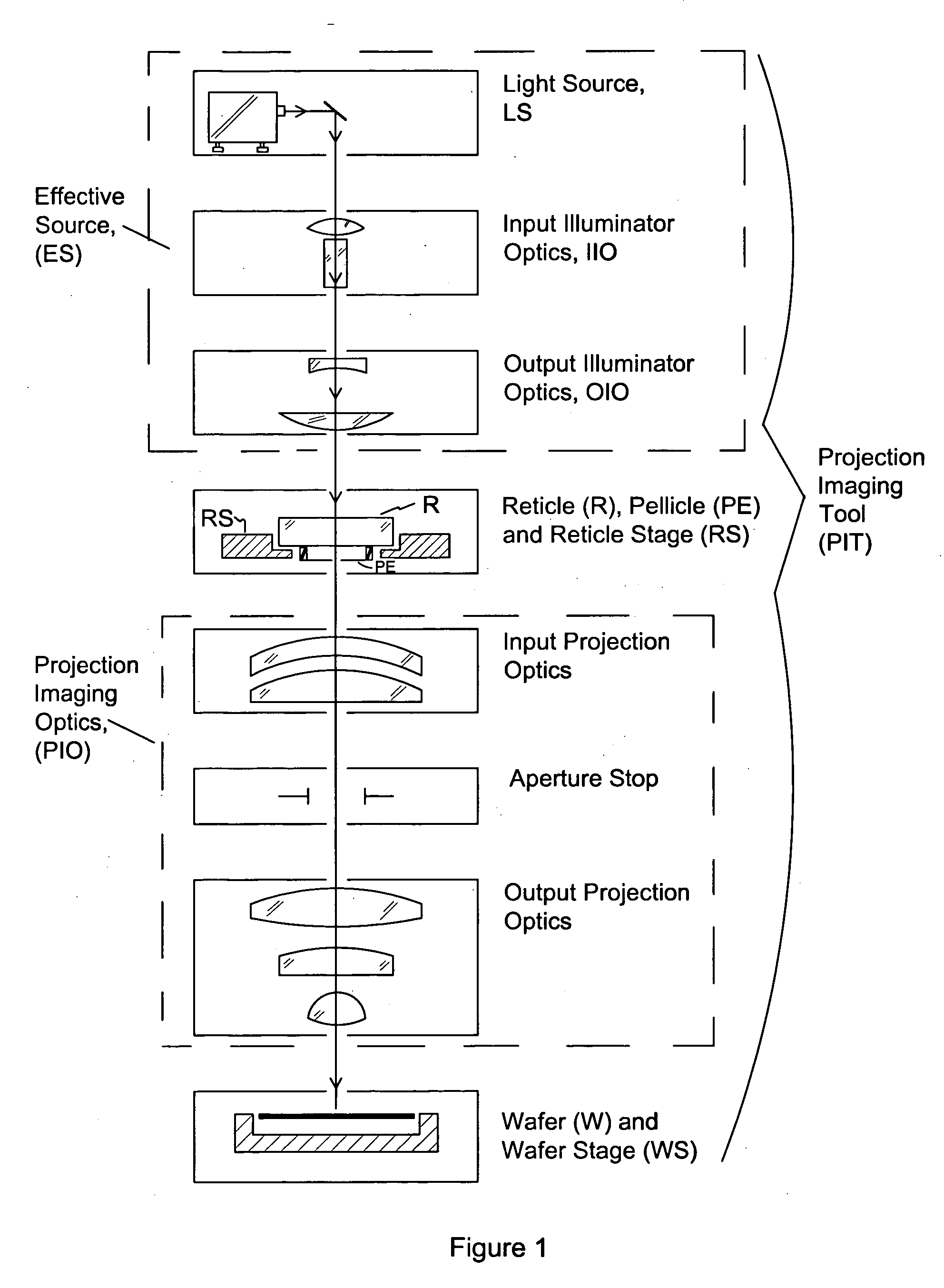
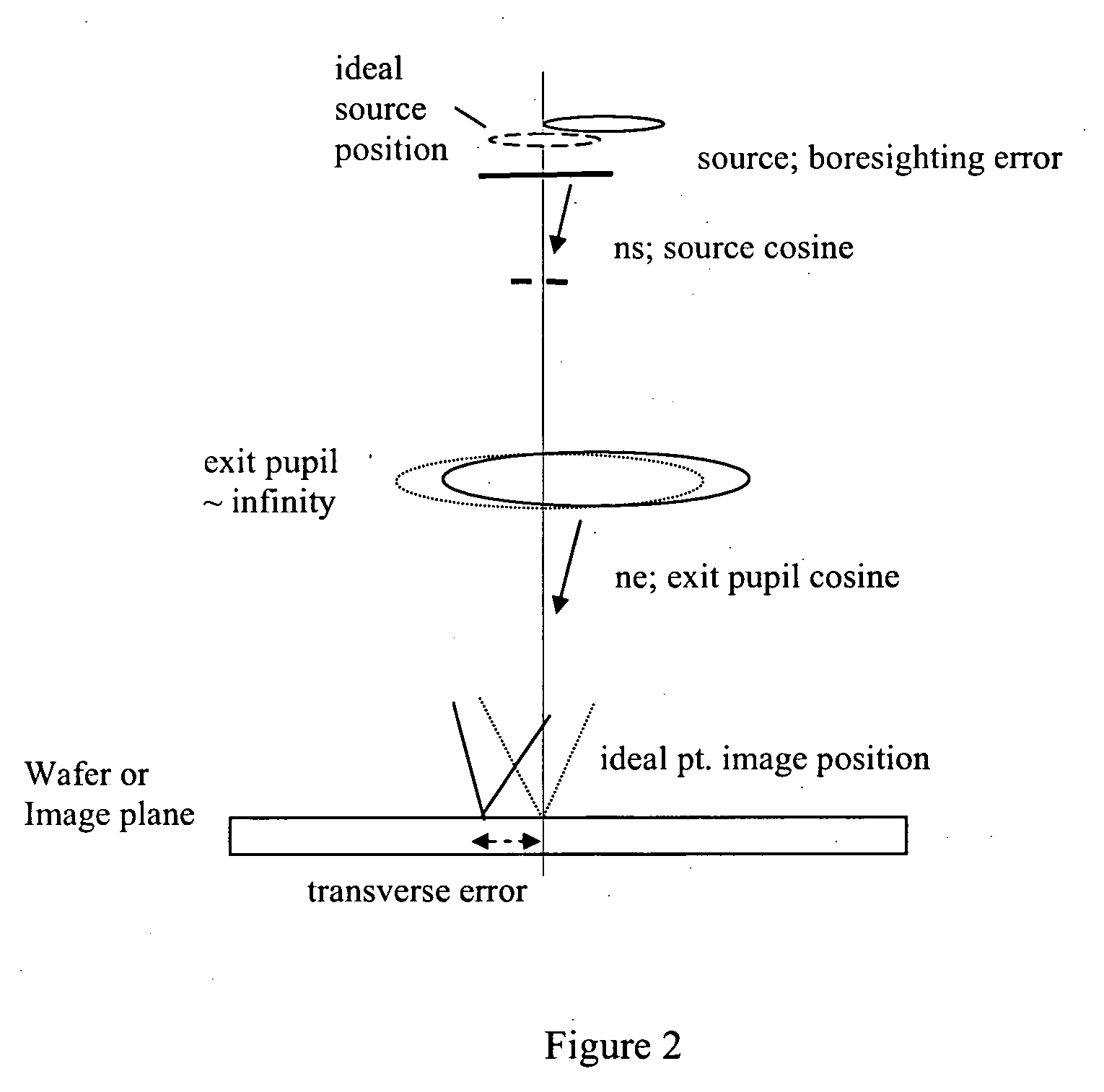
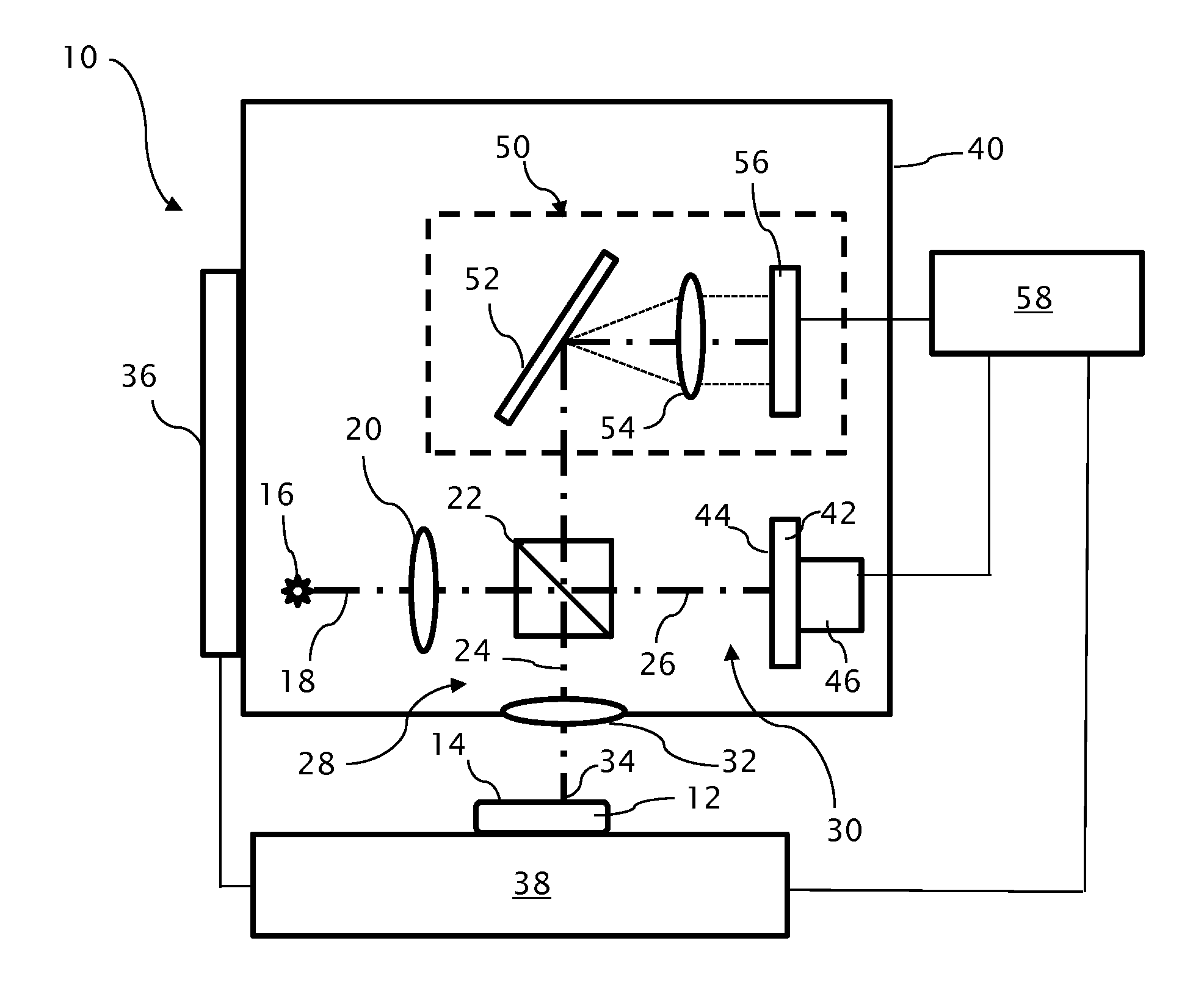
InactiveUS20060164618A1Simplify spacePhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingExit pupilProjection image
Exit pupil and source telecentricity of a projection imaging tool system is determined. The system contains a light source, an optical imager, a reticle, a substrate, and a positioner. The light source is optically coupled to the optical imager, the optical imager having an exit pupil. The combination of the light source and the optical imager define a projection imaging tool, are characterized by a partial coherence. The reticle has an array of patterns, each pattern having at least a first feature and a second feature. A substrate may be used to record at least a first image and a second image of the features. The positioner is used to dispose the first image and the second image such that the first image has a first defocus and the second image has a second defocus different from the first defocus. A processor is used to calculate the telecentricity based on an exit pupil and light source differential shift coefficient and positional offsets between features contained in the first image and features contained in the second image.
Owner:LITEL INSTR
Profilometer with partial coherence interferometer adapted for avoiding...
ActiveUS20150022817A1Resolve ambiguityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryPartial coherenceLight beam
A profilometer incorporating a partial coherence interferometer directs a beam containing a band of wavelengths along object and reference arms of the interferometer into respective engagements with a test object surface and a reference object surface en route to a spectrometer for measuring a spectrum of the beam. Within the object arm, the test object surface is relatively moved through a range of positions offset from a null position at which optical path lengths of the object and reference arms are equal. Modulation frequencies of the beam spectrum are calculated at a succession of different focus spot positions across the test object surface. Changes in the modulation frequency are interpreted to distinguish between optical path length differences at which the optical path length of the object arm is longer or shorter than the optical path length of the reference arm.6
Owner:QUALITY VISION INT
Adjustment of the partial coherence of the light energy in an imaging system
InactiveUS20040008424A1NanoinformaticsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPartial coherenceLight energy
The present invention describes an apparatus comprising an optical array generating a distribution of partial coherence of light energy and an aperture to select a subset of said distribution of partial coherence.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method for identifying non-stable acoustic source characteristics by bias coherent technology
InactiveCN1202407CRealize visualizationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSound sourcesPartial coherence
A method for identifying non-stationary sound source characteristics using partial coherence technology belongs to the field of noise in physics. In the case where multiple sound sources generate complex cyclostationary sound fields, the present invention adopts cyclostationary theory instead of Fourier transform, proposes a partial coherence analysis technology suitable for cyclostationary sound fields, and uses it in the partial sound field separation of cyclostationary sound fields, the method As follows: first determine the number and location of the reference source, arrange the reference source microphone array, extract the reference source signal, then design the microphone array to scan and measure the holographic surface, collect the holographic surface data, and then use the cyclostationary partial coherence analysis technology to separate Part of the sound field for each sound source. The present invention can analyze the complex cyclostationary sound field formed by multiple cyclostationary sound sources, obtain the partial sound field formed by each sound source, and also calculate the three-dimensional sound field formed by a single sound source from the sound pressure signal measured on the holographic plane. The sound field distribution realizes the visualization of the propagation path of each sound source.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
System and method for carrying out in-situ detection on odd aberration of projection objective for photoetching machines
ActiveCN102253606BEasy to measureImprove detection accuracyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusPartial coherencePeak value
The invention discloses a system and method for carrying out in-situ detection on the odd aberration of a projection objective for photoetching machines. The system comprises a light source, a lighting system, a masking platform, a mask, a projection objective, an operating platform, an image sensing device, an interferometer and a data processing device, wherein the mask contains a detection mark, and the interferometer is used for position control. The method comprises the following steps: calibrating corresponding odd-aberration sensitivity coefficients of the projection objective through setting different partial coherence factors and numerical apertures; then, measuring the value of difference between the peak value and light intensity of a space image of the detection mark by using the image sensing device; and finally calculating the odd aberration of the projection objective by using the calibrated odd-aberration sensitivity coefficients. The system and method disclosed by theinvention have the advantage of improving the accuracy of detection on the odd aberration of the projection objective for photoetching machines.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Systems and methods for generating Laguerre-Gaussian correlated partially coherent Gaussian beams
The invention discloses a system used for producing a Laguerre-Gaussian correlated partial coherence gauss beam. The system comprises a beam expander, a spatial light modulator, a beam shrinking mirror, a ground glass sheet, a lens and a Gaussian filter sheet along the direction of light in sequence. A computer-generated hologram forms a computer-generated holographic grating after being loaded on the spatial light modulator, and then a Laguerre-Gaussian beam with only an angular module is produced. The beam shrinking mirror is used for controlling the spot size of the Laguerre-Gaussian gauss beam on the rotary ground glass sheet to adjust coherence of an outgoing beam. The ground glass sheet is used for changing the Laguerre-Gaussian gauss beam to the Laguerre-Gaussian correlated partial coherence gauss beam. The lens is used for collimation of the partial coherence gauss beam. The Gaussian filter sheet is used for converting light distribution of the beam to Gaussian distribution. Due to flexibility of the computer-generated hologram, Laguerre-Gaussian beams with different orders and only angular modules can be produced by producing different holograms, and therefore Laguerre-Gaussian correlated partial coherence gauss beams with different orders are produced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com