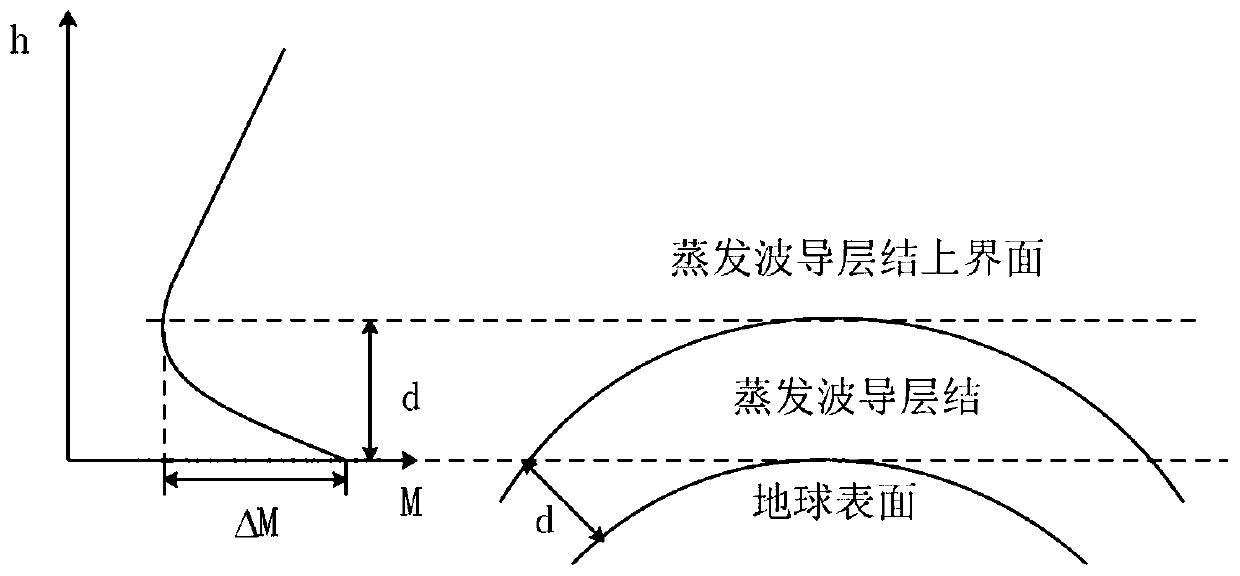
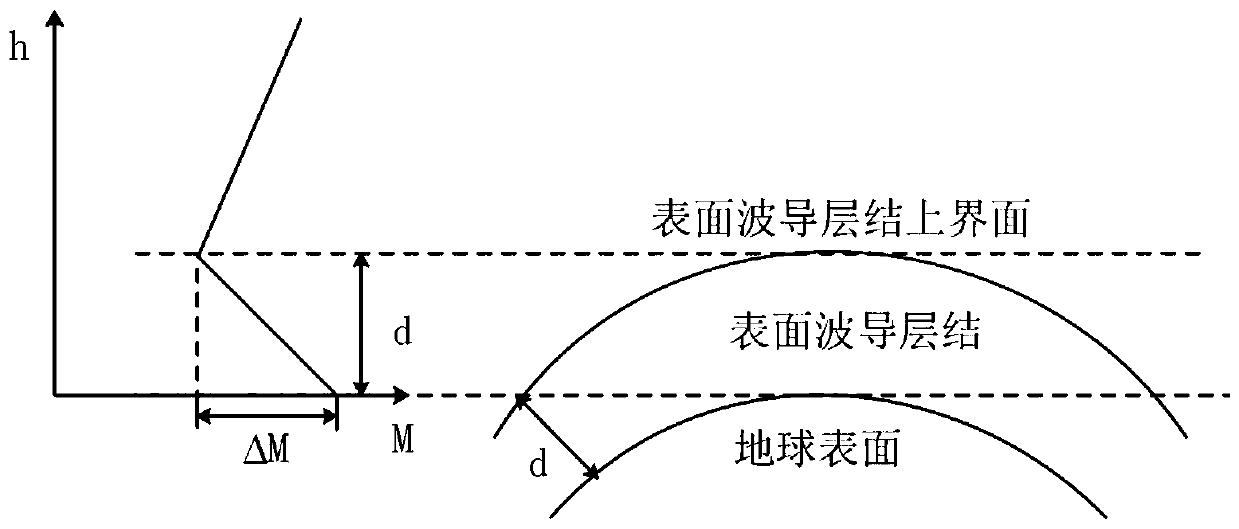
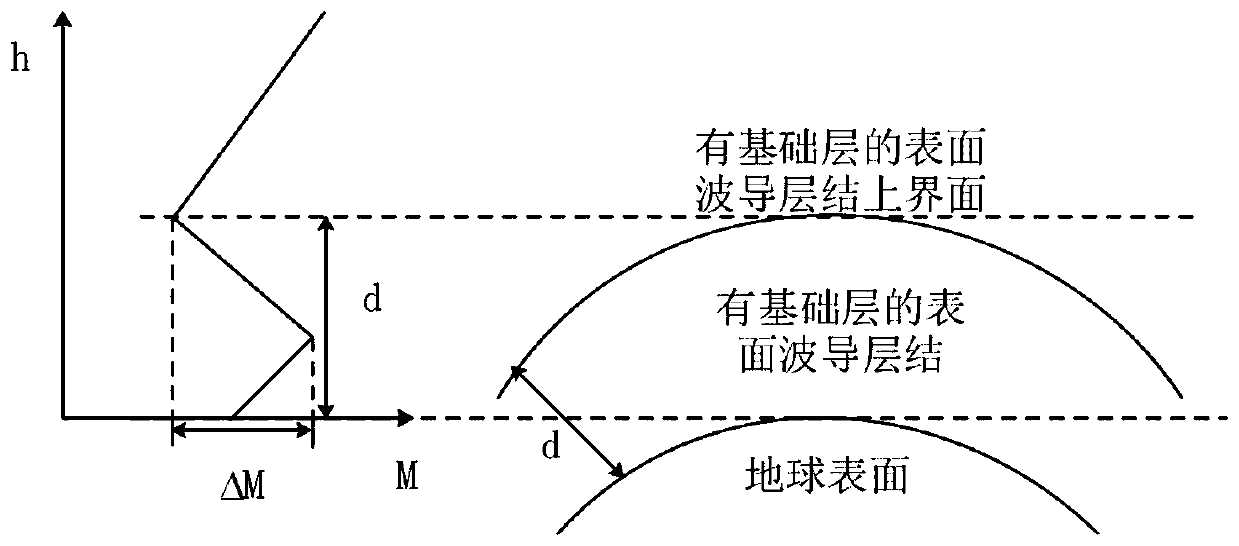
Wireless communication interference prediction method for atmospheric waveguide
A technology of wireless communication and prediction method, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, transmission monitoring and other directions, can solve problems such as communication failure, inaccurate description of waveguide height and strength, and inability to actively predict waveguide interference communication events, etc., to achieve improved quality. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] The following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some, not all, embodiments of the present invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
[0043]According to the theory of electromagnetic wave propagation, when the waveguide appears, if the emission elevation angle of the electromagnetic wave is less than the critical angle and the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave is less than the maximum trapping wavelength, the electromagnetic wave will be captured by the waveguide, and the propagation mode similar to that in the metal waveguide is realized to complete the beyond-horizon propagate and inte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com