Track fastener looseness detection method based on angle comparison
A track fastener and detection method technology is applied in the field of track fastener looseness detection based on angle comparison, which can solve the problems of limited application range, low efficiency, poor accuracy, etc., and achieve the effect of eliminating potential safety hazards in train operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
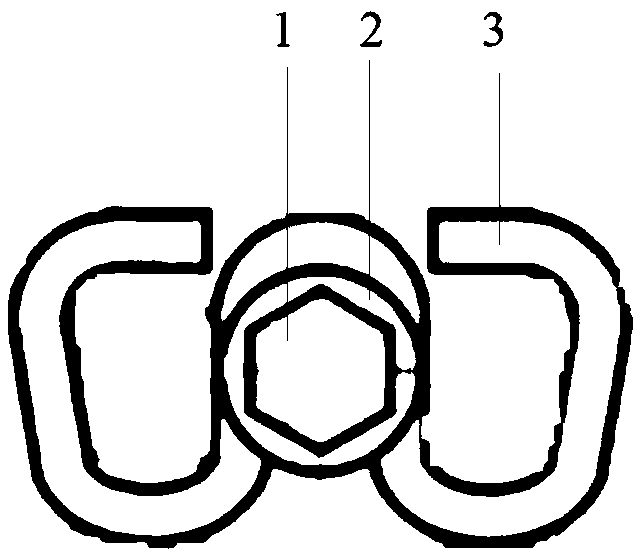
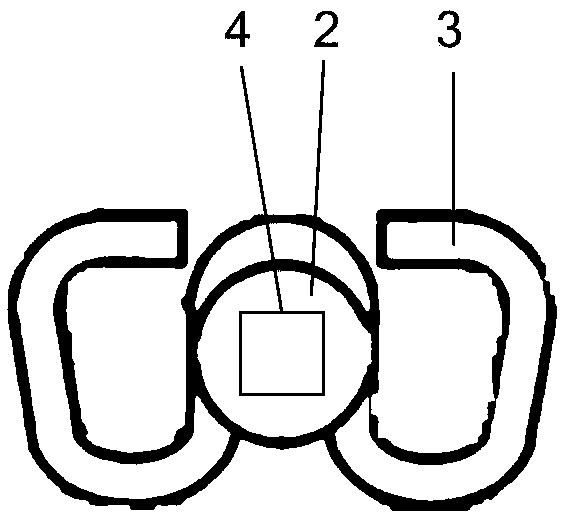
[0043] Embodiment 1 Determines whether the fastener is loose by measuring the angle value of the hexagonal bolt of the W-shaped fastener. In this embodiment, the W-shaped fastener using the hexagonal bolt is as follows: figure 2 As shown, the fastener includes a hexagonal bolt 1 , a bolt washer 2 and an elastic strip 3 .
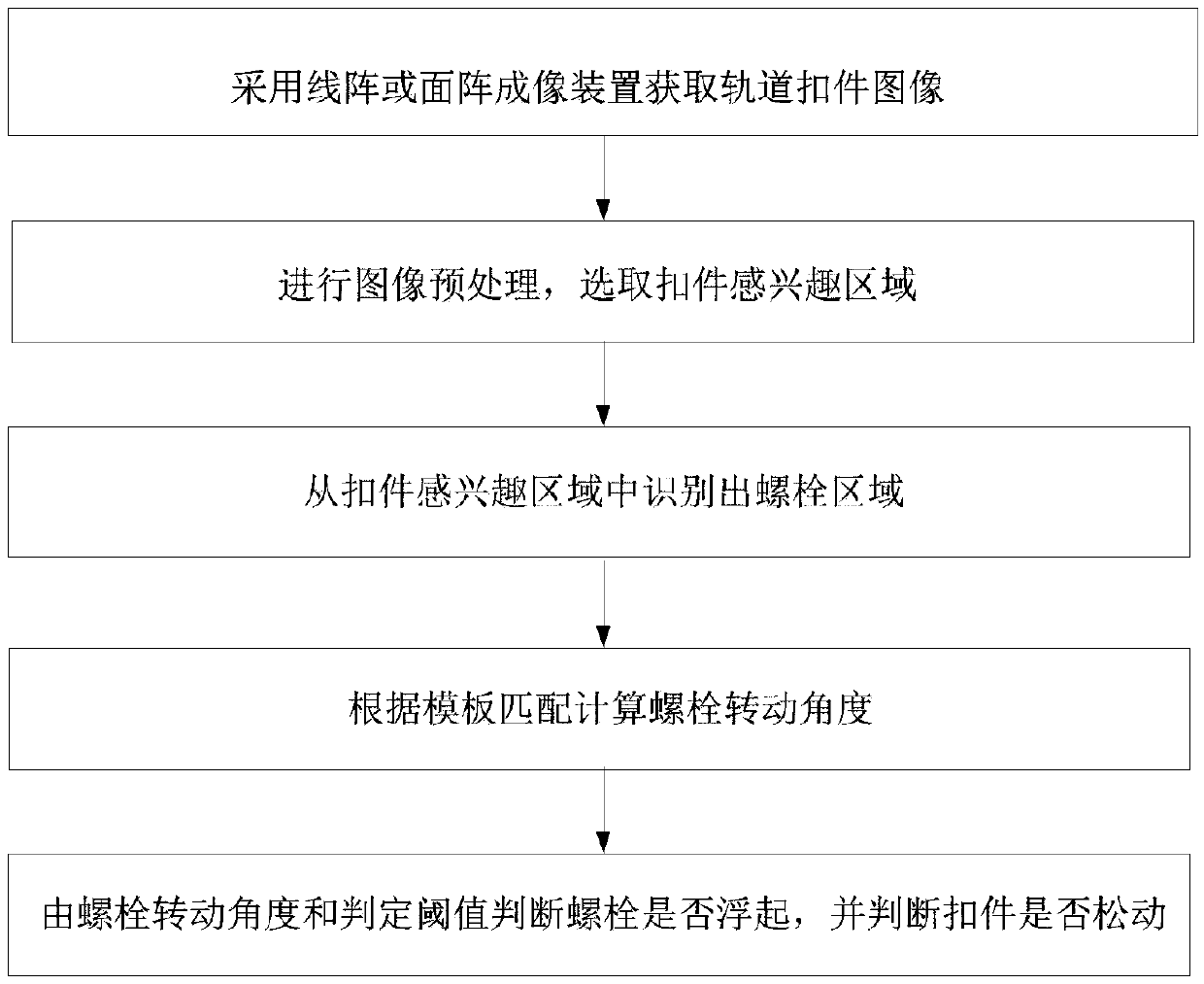
[0044]Step 1: Use a line array or area array imaging device to obtain the image of the rail fastener, and the optical axis of the line array or area array imaging device is perpendicular to the track road surface for imaging.
[0045] Step 2: Perform fastener image preprocessing, select the region of interest of the fastener, image preprocessing includes: image denoising, lens distortion correction of the imaging device, and transform the acquired fastener image into a bird's-eye view image according to the external parameters of the imaging device , to perform subsequent processing on the bird's-eye view image; when using a line scan imaging device to obta...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Different from Embodiment 1, the image matching method based on image edge similarity is adopted in step 4.2:
[0057] D=∑|S E (i,j)-T E (i,j)| (2)
[0058] Among them, S E (i,j) and T E (i, j) represent the edge at position (i, j) in the current detection image S and the template image T respectively, (i, j) represent the pixel coordinates of the overlapping area, ∑ represents the summation operation, D represents the matching degree, for Each angular rotation step extracts the overlapping area between the template image T and the current detection image S, and calculates the matching degree D according to formula (2). The smaller the D value, the greater the matching degree.
Embodiment 3
[0060] Steps 1 to 4 in Examples 1 and 2 are replaced by: using a 3D imaging system to obtain a 2D depth image of the fastener, performing bolt region segmentation on the 2D depth image, and performing bolt shape matching based on the 2D depth image, Calculate the bolt rotation angle, and the subsequent steps are the same as in Embodiments 1 and 2.
[0061] The area of interest of the fastener selected in step 2 in Embodiments 1 and 2 can also be automatically detected in the preprocessed image by using methods such as SVM, deep learning, or neural network classification.
[0062] The bolts in Embodiments 1, 2 and 3 can also be replaced by nuts in the rail fastener.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com