Phenotypic characterization of cells
A cellular, non-cellular technique for such phenotypic characterization of cells to address difficult cell capture or loading issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
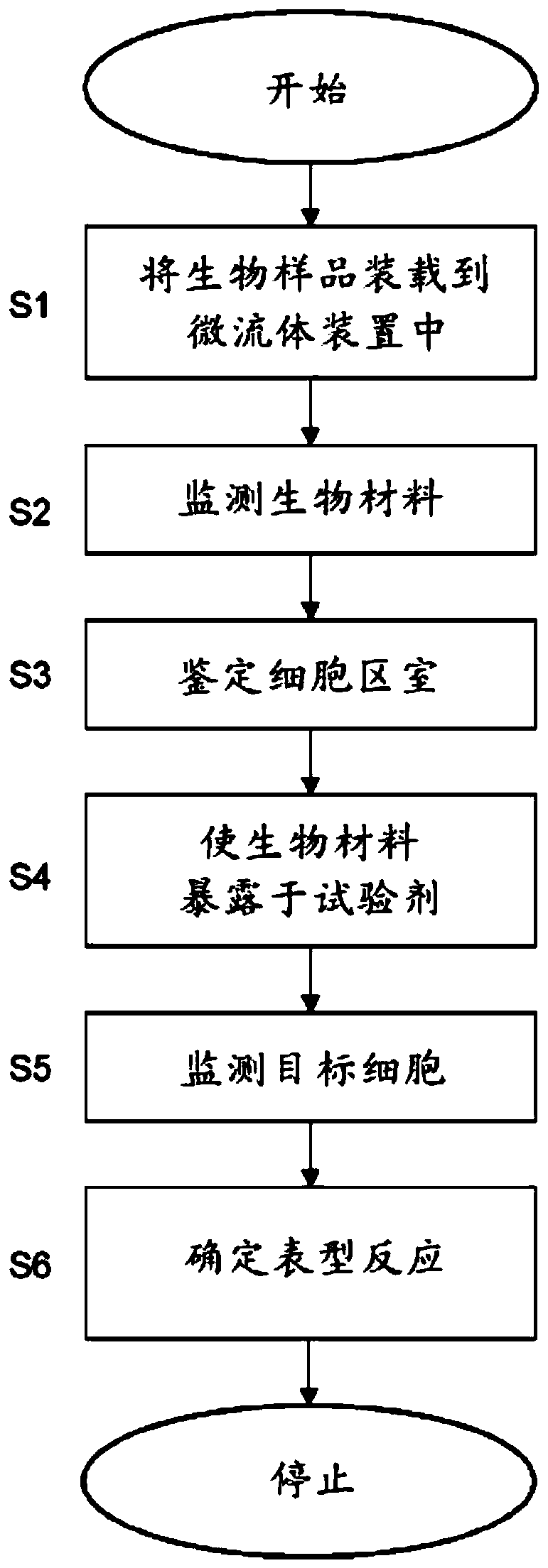
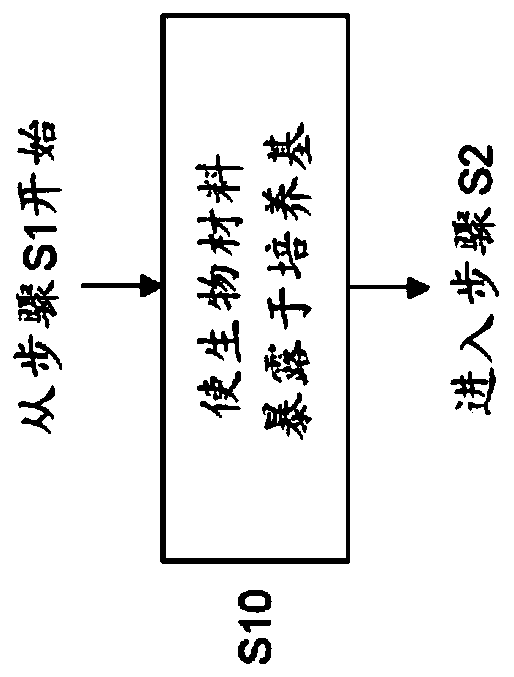
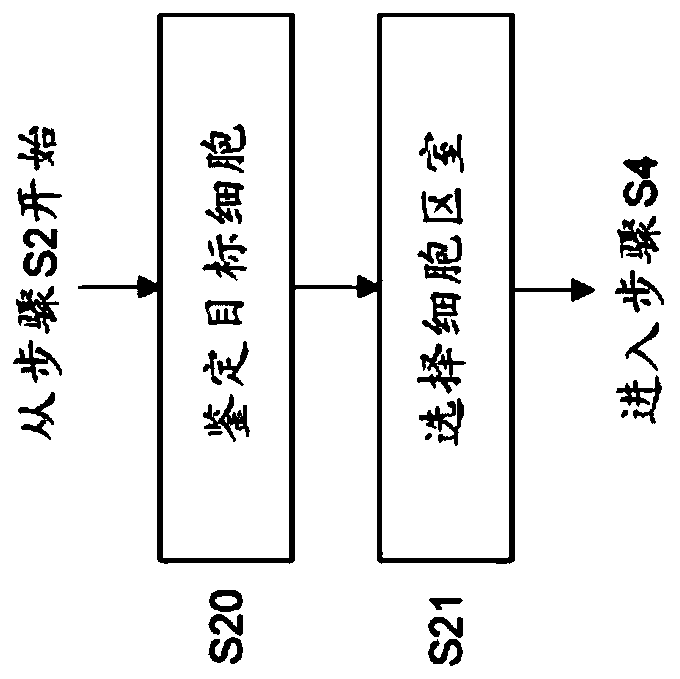
[0031] Embodiments of the present invention relate generally to phenotypic characterization of cells, and more particularly to such phenotypic characterization of cells in microfluidic devices.
[0032] Microfluidic devices, also known in the art as microfluidic chips, can be used for phenotypic analysis of cells, ie phenotypic characterization, in a time-sensitive manner. However, in real-world applications, the biological sample input into the microfluidic device may contain various biological materials (including target cells to be phenotyped, other cells, and cell debris) as well as non-biological materials (such as dirt, pollutants, etc.) complex heterogeneous samples. Thus, biological samples are often heterogeneous, and cells of interest may actually constitute a minority, or even a very small minority, of the material present in the biological sample.
[0033] Heterogeneity in biological samples can arise for various reasons. For example, the biological sample itself...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com