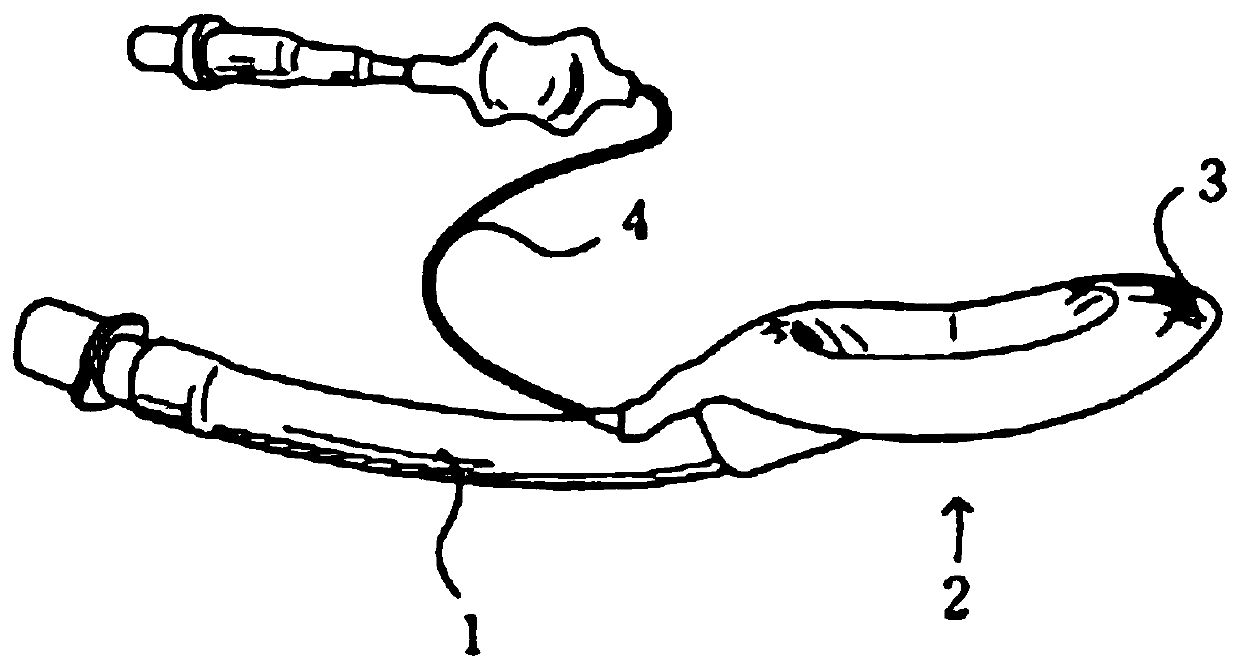
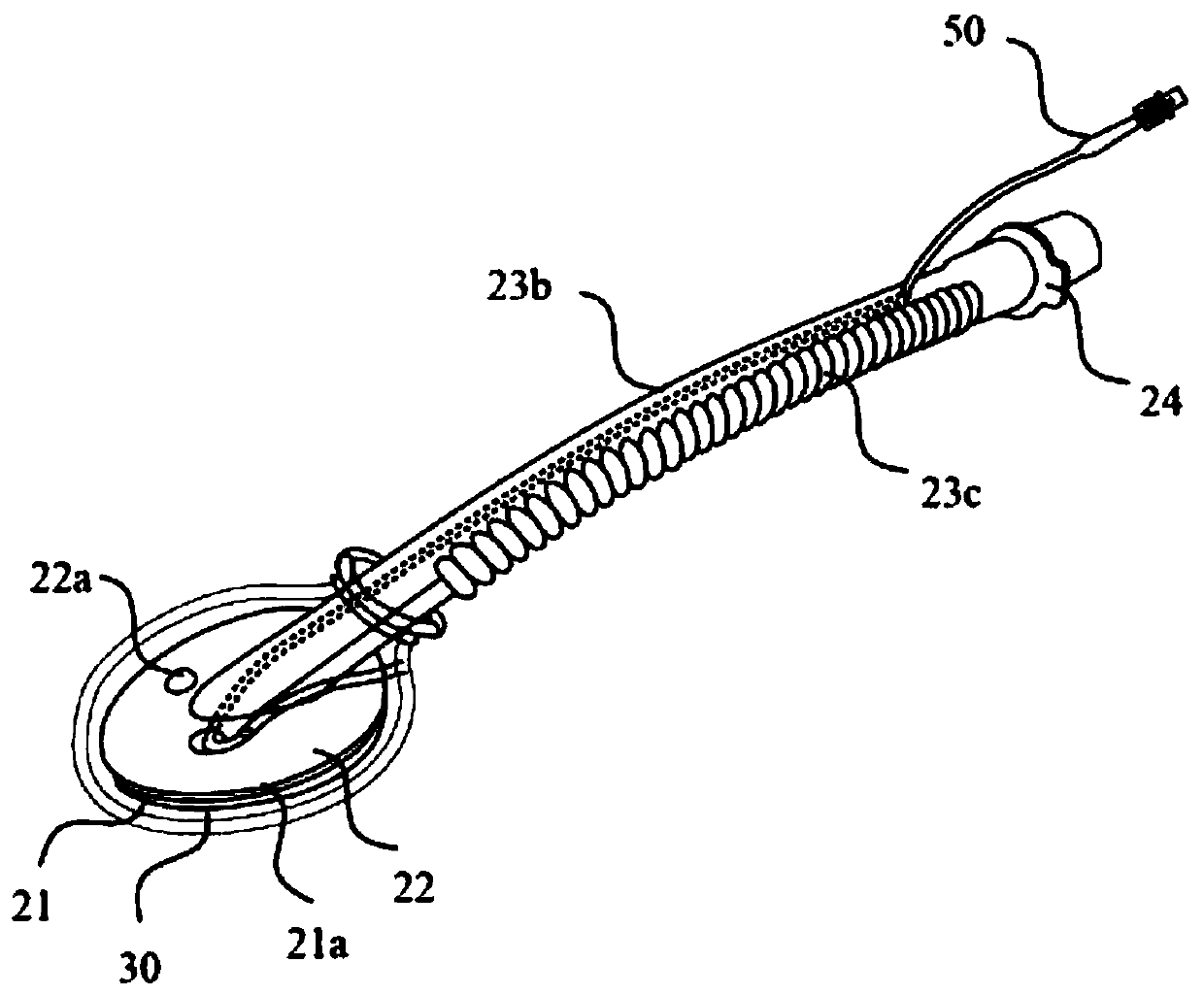
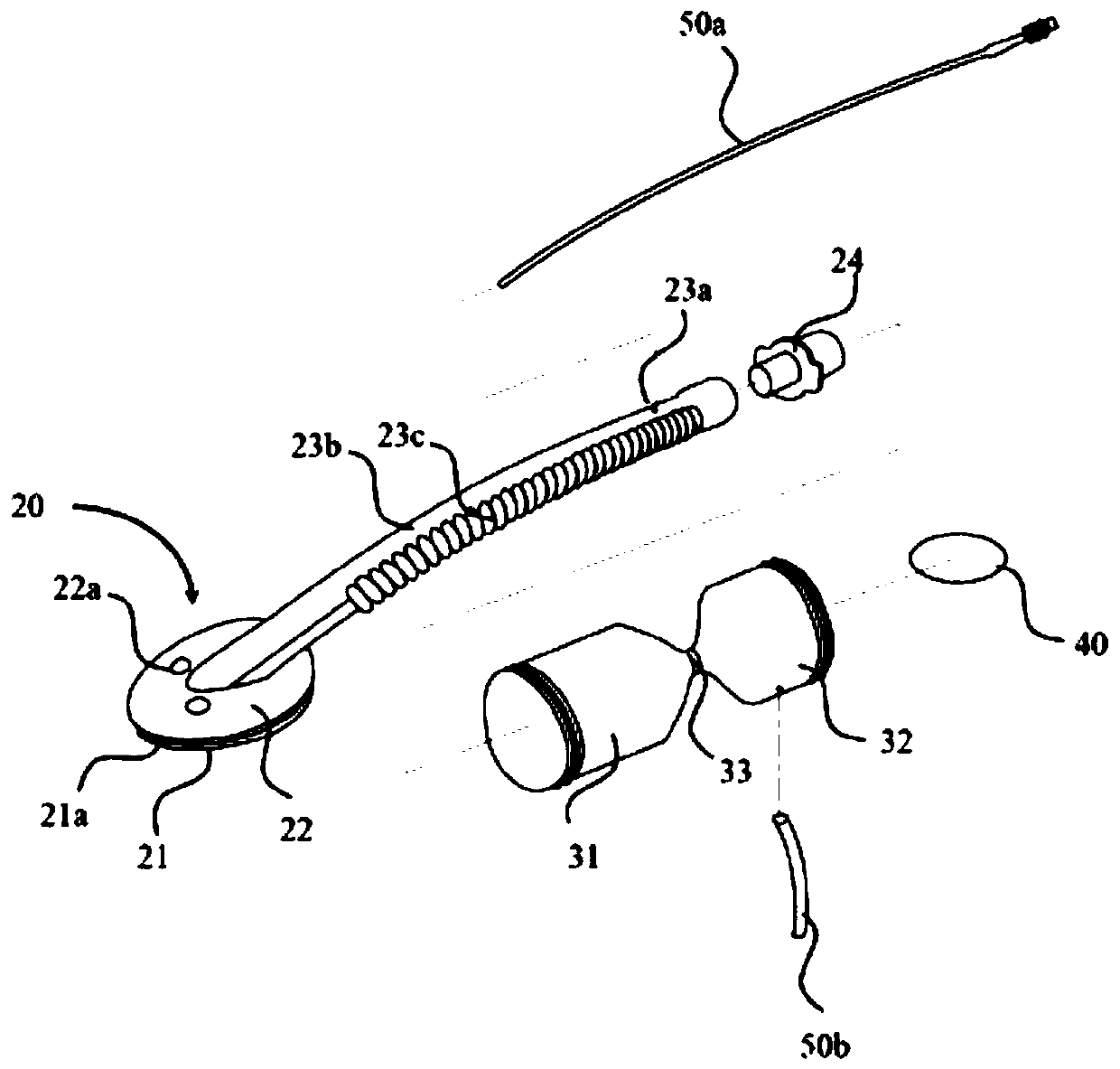
[0007] First, the teaching of the general use of the
inflatable laryngeal mask currently on the market is to place it in the patient's
throat so that the inflation pressure should be maintained at 60cm-H2O. Use inflation pressure to prop up the side walls of the collapsed
cuff 3 to have the function of sealing the
airway and avoiding air leakage. However, in order to avoid air leakage during the operation, it is often necessary to pressurize and expand the side walls. When the inflation pressure is as high as When the pressure is 60~120cm- H2O, the laryngeal
mucous membrane is compressed by the over-inflated pressure. Over time, the
mucous membrane of the
larynx will fester, and even cause ischemic damage to the
mucous membrane. Once the pressure on the side wall of the
larynx exceeds 25 cm- H2O will affect the submucosal
blood flow, which will easily cause
throat pain after the patient wakes up. Therefore, it is known that the laryngeal mask cannot be placed for a long time, and it must be taken care of during the return of the pressure. Whether there is air leakage, not ideal
[0008] For the other two, the size of the laryngeal mask for conventional use must be selected according to the patient's weight, mainly because the
material design of the mask bag 3 cannot provide a large space for expansion and contraction, and the expansion range is small, so a single-sized laryngeal mask cannot satisfy most patients. If the size of the laryngeal mask is used on an unsuitable patient, it will affect the success rate of
insertion, and forced
insertion will be accompanied by the risk of air leakage. Therefore, it is necessary to prepare various sizes to prevent various emergencies
[0009] For the third, due to the poor elastic coefficient of the mask body of the conventional laryngeal mask, even if a higher air pressure is introduced, it cannot produce a large amount of deformation. Therefore, it is necessary to choose a laryngeal mask that matches the patient's throat size. The space at the laryngeal mask is larger than the throat opening. During the placement process, the operator must pass the front end of the laryngeal mask through the throat opening, and must first overcome the psychological pressure to avoid harming the patient. Generally, medical institutions operate the laryngeal mask as a way to unblock the airway, and usually require
anesthesia In addition, it will also reduce the contact area between the
cuff and the inner wall of the patient's throat, and it is also prone to displacement during the setting process, thereby increasing the risk of air leakage. In addition, the poor elastic coefficient is also accompanied by The softness is not good, and more skills need to be trained during the setting process, which prolongs the familiarization time of trainers
[0010] Fourth, because the overall shape of the general laryngeal mask is relatively fixed, the
catheter cannot be turned moderately. When installing, it must be turned skillfully to avoid the
epiglottis. The artificial skill method naturally comes with the risk of installation proficiency, and it is easy to insert it forcibly. Injury to the patient's throat will affect the subsequent
recovery. Therefore, the operator must be given sufficient
training time in advance to avoid improper installation during the operation. This is also an important key to the patient's subsequent
recovery.
[0011] Fifth, it is known that a
mouthpiece is often added to the laryngeal mask during use to prevent the patient from
biting the
inflatable tube 4 due to physiological reactions and affecting the intake flow of
oxygen. The known
mouthpiece is mainly divided into two types, one It is an external
mouthpiece, which is generally installed close to at least one of the left and right sides of the
inflatable tube 4, and the side corners of the patient's mouth will be bitten first without pressing the mouthpiece. to the inflatable tube 4, but the mouthpiece is placed on the side corner of the mouth for a long time in this way, because it is placed on one side, it is easy to rub against the side corner of the mouth of the patient with fragile
skin, causing discomfort such as
broken skin and bleeding; The other is a fixed mouthpiece, which is generally directly fixed on the outside of one end of the air tube 4. Although the mouthpiece can improve the bite from the upper and lower rows of teeth in the middle, it can avoid damaging the more fragile side corners of the epidermis. However, in the process of setting the laryngeal mask, it is often necessary to rotate skillfully to avoid the position of the
epiglottis. At this time, the fixed mouthpiece will also rotate together and easily get stuck in the patient's mouth due to insufficient space. The
operability still needs to be improved. , and even affect the success rate of laryngeal mask placement
[0012] Based on the above-mentioned deficiencies, its functions have not yet been perfected, and there is still room for improvement in the prior art
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More