Information transmission method and device
A technology of information transmission and message, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as the lack of IAB control plane information transmission scheme
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] An embodiment of the present application provides a mobile communication network (including but not limited to a 5G mobile communication network), and the network architecture of the network may include network-side devices (such as base stations) and terminals. This embodiment provides an information transmission method that can run on the above-mentioned network architecture. It should be noted that the operating environment of the above-mentioned information transmission method provided in the embodiment of the present application is not limited to the above-mentioned network architecture.
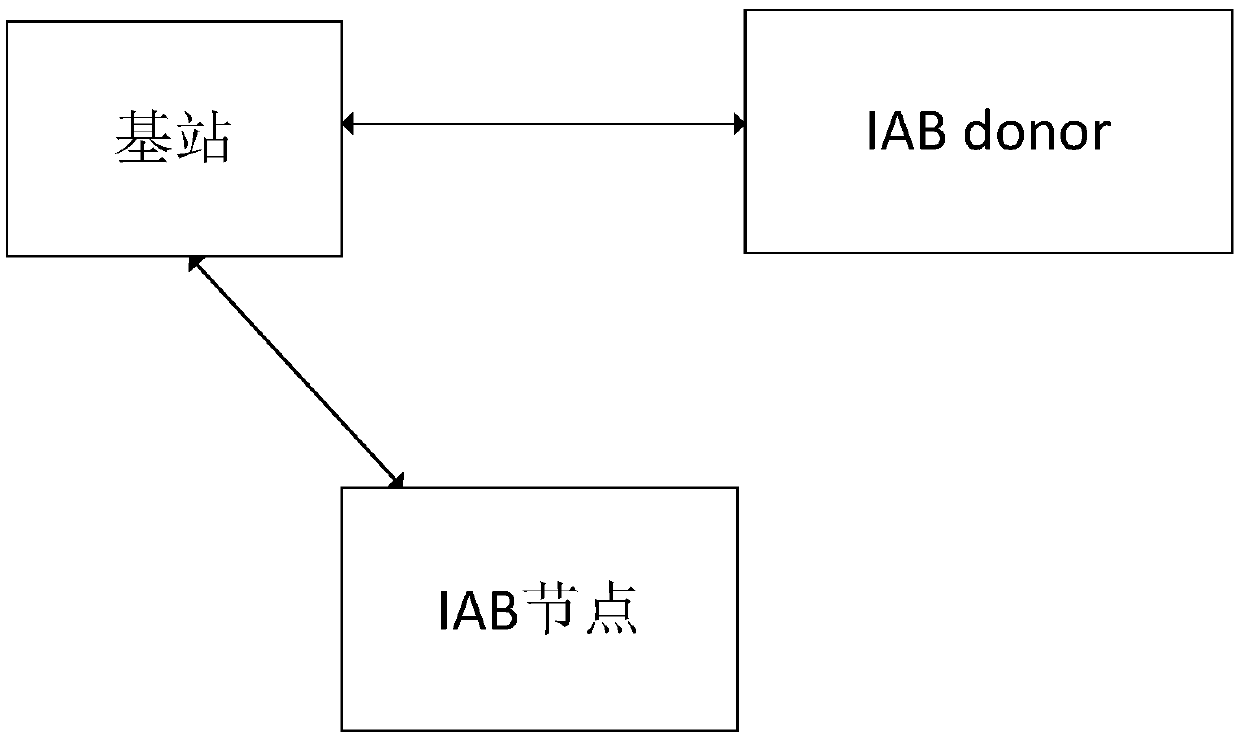
[0036] The embodiment of this application can run on figure 2 On the network architecture shown, figure 2 is a schematic diagram of the network architecture according to this application document, such as figure 2 As shown, the network architecture includes: A, an IAB node; B, a base station; C, an IAB donor.
[0037] In this embodiment, an information transmission method runn...
specific Embodiment 1
[0091] The method in this embodiment is a method in which the RRC message of the IAB node is forwarded by the base station, Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of the protocol stack according to the specific implementation 1 of the application document.
[0092] like Figure 5 As shown, for uplink, IAB node1 generates RRC message 1, encapsulates RRC message 1 into RRC message 2 (for example, ULInformationTransferMRDC message) and sends it to MeNB. After receiving it, the MeNB parses out the RRC message 1 generated by the IAB node1, encapsulates the RRC message 1 into an X2 message (for example, RRC transfer message) and sends it to the IABdonor.
[0093] Optionally, the RRC message 1 or RRC message 2 or X2 message includes source and / or target node identification information. Among them, the node identification information is used to identify the DU part or CU part or the base station of the IAB node or IAB donor, including but not limited to: gNB-DU ID, base station ID, DU ...
specific Embodiment 2
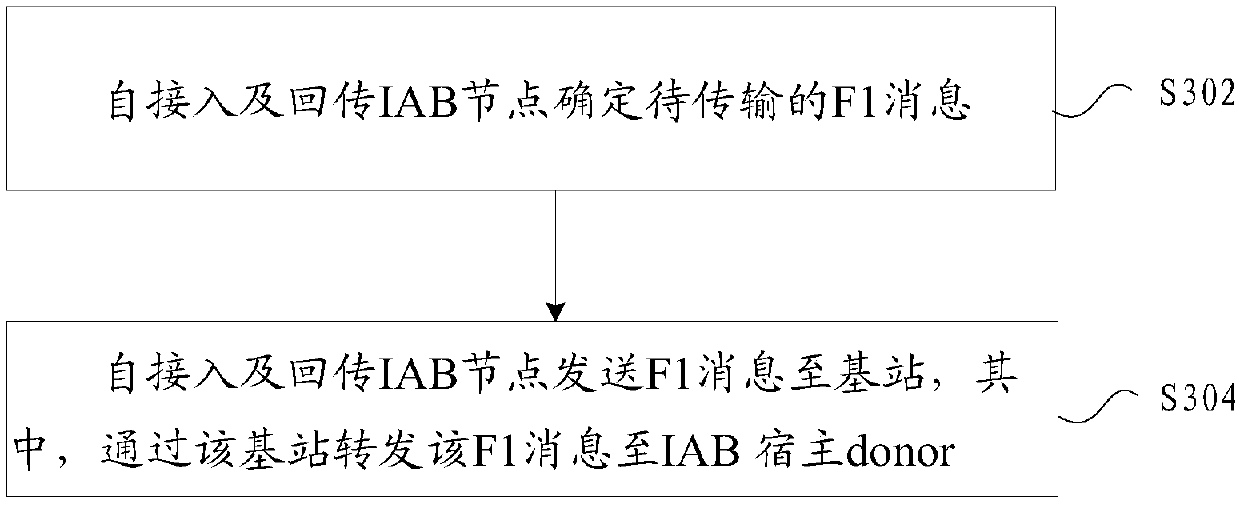
[0097] The method in this embodiment is the first method in which the F1 message of the IAB node is forwarded by the base station. Image 6 It is a schematic diagram of a protocol stack according to Embodiment 2 of the present application. Note that, Image 6 There may or may not be an RRC protocol layer between the IAB node 1 and the MeNB.
[0098] like Image 6 As shown, for the uplink, after IAB node1 generates the F1 message, it is encapsulated into RRC message 1 (for example, ULinformation transfer message, newly defined RRC message); or, IAB node 1 directly delivers the F1 message to the PDCP layer for processing without After RRC layer processing. Optionally, IAB node 1 sends it to MeNB through the SRB dedicated to forwarding F1 messages; optional, IAB node 1 obtains bearer configuration information from the donor CU through RRC messages or F1 messages, and the bearer configuration information is used to configure the information dedicated to forwarding F1 messages ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com