High cohesion double crosslinking artificial glass body and preparation method thereof
A double cross-linking and vitreous technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems of not paying attention to the cohesion of hydrogels, achieve good cohesion and adhesion, good biocompatibility, and reduce the pain of patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1, high cohesion double cross-linked artificial vitreous body complete set of raw materials
[0056] The complete set of high cohesion double cross-linked artificial vitreous body raw materials in this embodiment is composed of a first component and a second component, the first component is aldylated hyaluronic acid, and the second component is aminated hyaluronic acid; The ring-opening rate of the formylated hyaluronic acid is 10-20%, and the grafting rate of the aminated hyaluronic acid is 40-80%. Note: In the preparation method of each component, the ring-opening rate of aldylated hyaluronic acid can be controlled to 10-20%, and the grafting rate of aminated hyaluronic acid can be controlled by controlling the ratio of materials and reaction time. 40-80%.
[0057] The first component of this embodiment is made by following method:
[0058] F1. Dissolve hyaluronic acid in purified water to form a 5-100 mg / mL hyaluronic acid solution (in this embodiment: ...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Embodiment 2, high cohesion double cross-linked artificial vitreous body
[0076] The high cohesive double crosslinked artificial vitreous body of this embodiment is prepared from the complete set of raw materials for the high cohesive double crosslinked artificial vitreous body in Example 1 through the following steps:
[0077] H1. Dissolve the first component in physiological saline containing phosphorus hydrochloric acid to form the first solution of 5-20 mg / mL, and dissolve the second component in physiological saline containing phosphorus hydrochloric acid to form a solution of 5-20 mg / mL Second solution; the concentration of the first component in the first solution is the same as the concentration of the second component in the second solution. In the physiological saline containing phosphorous hydrochloric acid, the concentration range of phosphate is 0.01-0.1M (0.05M is used in this embodiment).
[0078] Note: In actual use, after step H1, pass each solution t...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Embodiment 3, swelling degree measurement experiment
[0087] This embodiment is used to detect the swelling degree of the artificial vitreous body obtained in Example 3 of Example 2.
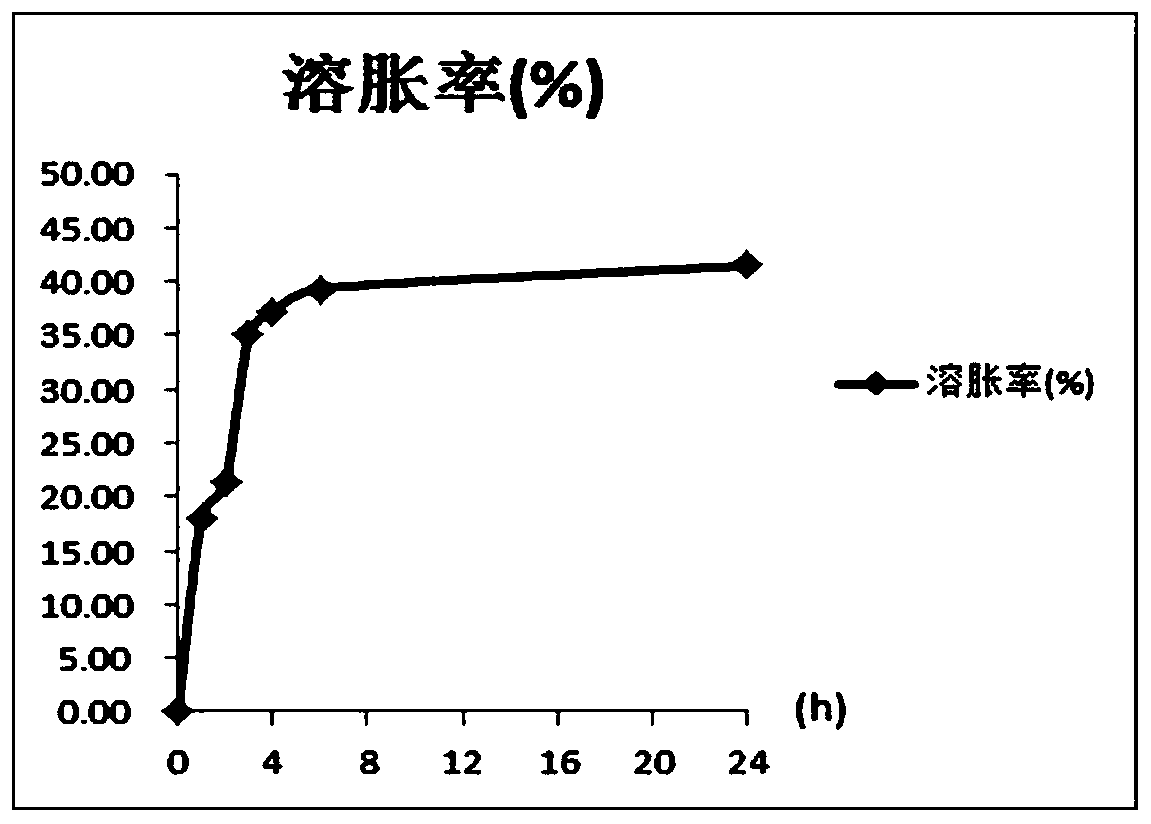
[0088]The sample of Example 3 of Example 2 was placed in PBS solution after in-situ cross-linking to measure the swelling degree, the weight of the gel was 0.10 g, and the PBS was 10 mL. Take out the sample when it is immersed in PBS for 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 24 hours, absorb excess water with filter paper, weigh it, and calculate the swelling rate. Swelling rate=(sample weight at a specific time-sample original weight) / sample original weight×100%, the result is as attached figure 1 shown. It can be seen from the figure that the product swells completely within 6 hours, and does not change after that, and the swelling degree is only 40%, which is far lower than the swelling degree of ordinary gels by hundreds or even thousands.
[0089] It should be noted that the degree of swelling o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of grafting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com