Method for efficiently extracting public edges of large-data-volume topology-vector-free polygon
A technology with large data volume and polygons, applied in structured data retrieval, geographic information database, still image data retrieval, etc. The effect of reducing the number of cycles and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
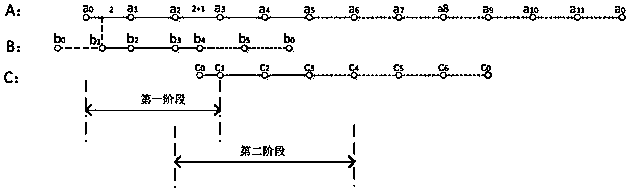
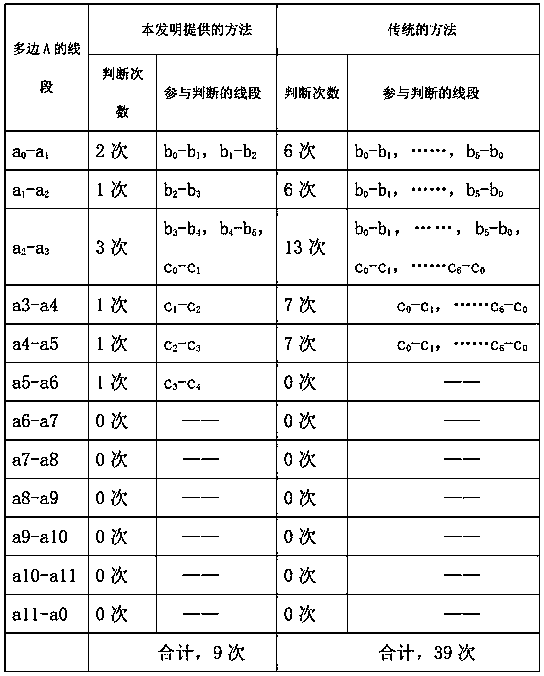
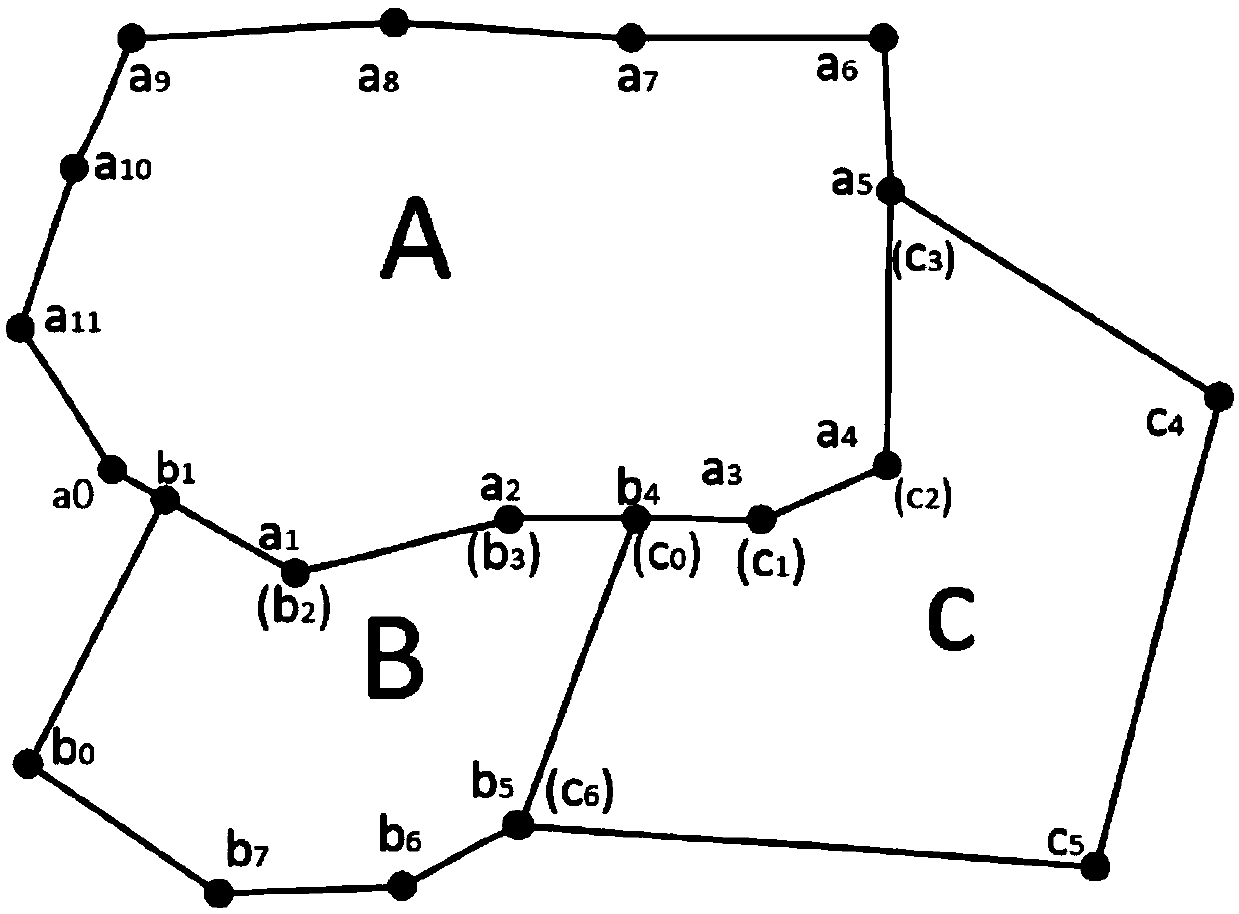
[0045] Only adopt the synchronously increasing node method proposed in the method provided by the present invention, instead of sorting the polygons according to the order of the number of nodes contained, such as randomly extracting the common edges between adjacent polygons in the order of polygons B, C, and A:
[0046] The first step is to extract the common edges between polygon B and its adjacent polygons. The theoretical maximum number of cycles for this step is N c +N a +G bc +G ba =1007+G bc +G ba The second step is to extract the common side of polygon C and its adjacent polygons. Similarly, polygon B has been processed, and this step is no longer compared with it. Therefore, the theoretical maximum number of cycles in this step is N a +G ca =1000+G ca The third step is to extract the common side of polygon A and its adjacent polygons. Similarly, the common side of polygon B and C has been extracted, and polygon A is the last polygon. Therefore, the common side ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The three polygons are sorted into A, B, and C according to the number of nodes contained in descending order, and then the method of synchronously adding nodes is used to extract the common edges of polygons A, B, C and their adjacent polygons: the first step is to extract The common side of polygon A and its adjacent polygons, the theoretical maximum number of cycles of this step is N b +N c +G ab +G ac =307+G ab +G ac times; the second step is to extract the common edge between polygon B and its adjacent polygons, the theoretical maximum number of cycles of this step is N c +G bc =7+G bc Second-rate;
[0050] The third step is to extract the common edge between polygon C and its adjacent polygons, which needs to be looped 0 times.
[0051] Thus, the method provided by the present invention can be used to extract all common edges between polygons A, B, and C, and the total theoretical maximum cycle is 307+G ab +G ac +7+G bc =314+G ab +G ac +G bc Second-r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com