Small current ground fault location method and system, monitoring device, equipment, medium
A small current grounding and fault location technology, applied in the field of distribution network, can solve problems such as high requirements for wave recording data, weak fault signals, and difficult detection, so as to improve application reliability, improve accuracy, and expand the opposite difference of mutation direction The effect of the coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
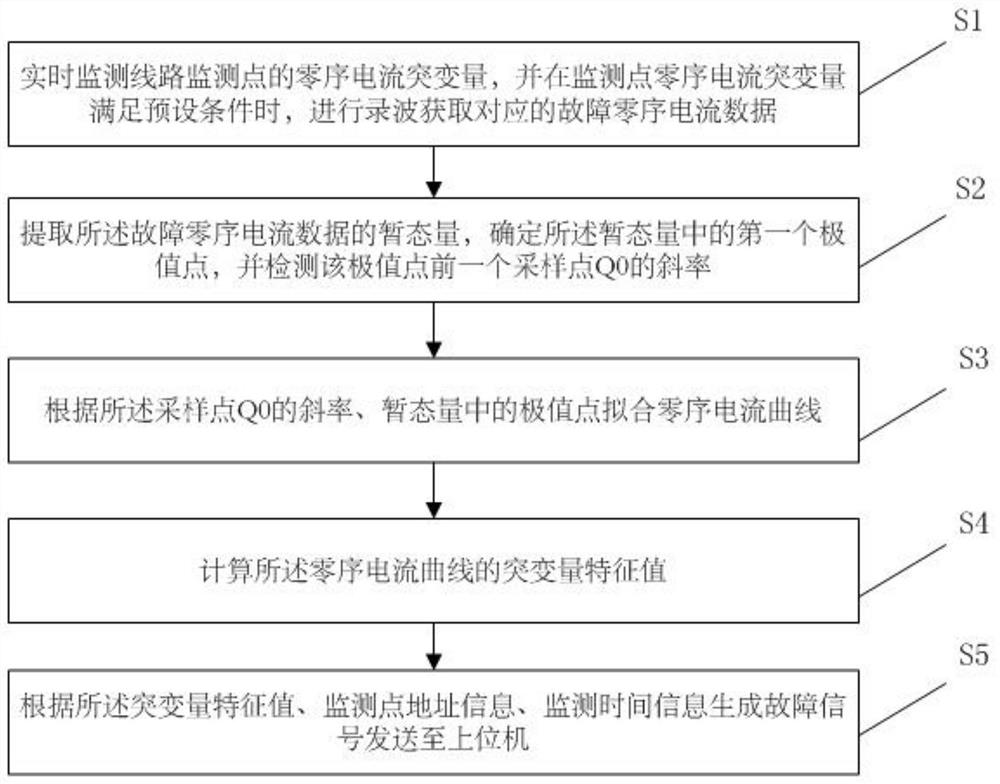
[0050] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a method for locating a small current ground fault, figure 1 For the flowchart of the method described in Embodiment 1, refer to figure 1 , the method described in the first embodiment includes the following steps:
[0051] Step S1, monitoring the zero-sequence current mutation of the line monitoring point in real time, and when the zero-sequence current mutation of the monitoring point meets a preset condition, perform wave recording to obtain corresponding fault zero-sequence current data;
[0052] Among them, the preset conditions are:
[0053] The zero-sequence current of the monitoring point line is sampled according to the preset sampling frequency. If the amplitude of n-1 or more sampling points in the n continuous sampling points satisfies the following formula (2), the recording is started to obtain the corresponding The fault zero-sequence current data is obtained and enter step S2, otherwise the wave recording ...
Embodiment 2
[0075] The second embodiment of the present invention provides a low-current grounding fault monitoring device, which is used to implement the steps of the low-current grounding fault monitoring method described in the first embodiment of the present invention, Figure 4 For a schematic diagram of the frame of the device described in the second embodiment, refer to Figure 4 , the device includes:
[0076] The monitoring and recording unit 1 is used for real-time monitoring of the zero-sequence current mutation of the line monitoring node, and when the zero-sequence current mutation of the monitoring point meets the preset condition, the recording is performed to obtain the corresponding fault zero-sequence current data;
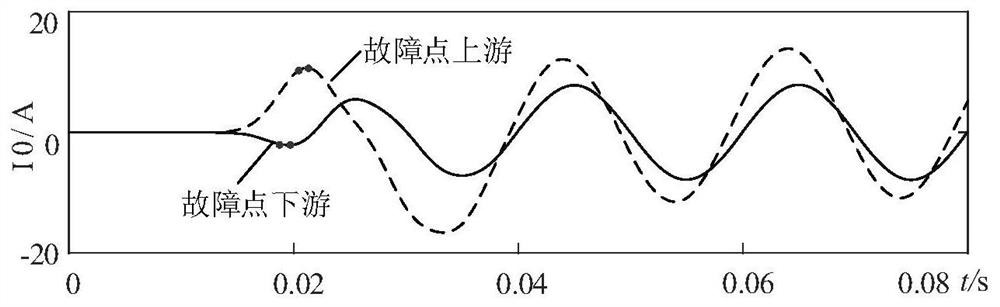
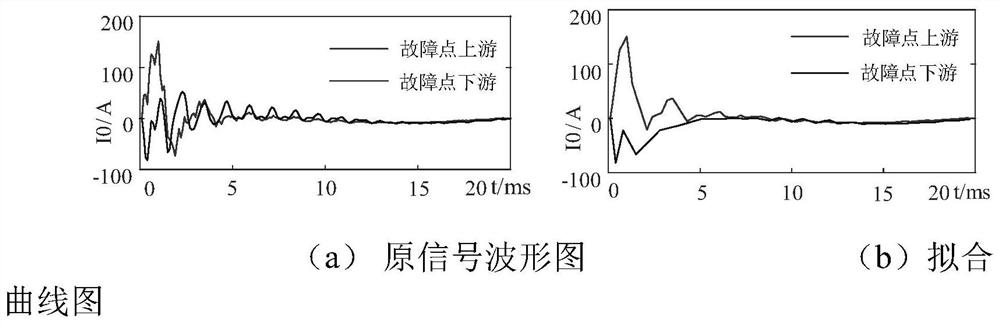
[0077] The node monitoring unit 2 is used to extract the transient value of the fault zero-sequence current data, determine the first extreme point in the transient value, and detect the sampling point Q before the extreme point 0 The slope of;
[0078] Th...
Embodiment 3
[0087] The third embodiment of the present invention proposes a low-current grounding fault location system, Figure 5 For the frame diagram of the system described in Embodiment 3, refer to Figure 5 , the system includes: a plurality of the small-current grounding fault monitoring devices 100, and a host computer 6; the plurality of monitoring devices are respectively arranged at a plurality of monitoring nodes of the line; the host computer 6 is used to detect the fault according to the fault The signal identifies the fault location. Specifically, the upper computer 6 is a master station or a distributed proxy terminal, and one upper computer 6 correspondingly receives fault signals of multiple monitoring devices 100 .
[0088] in, Image 6 This is a working flow chart of the low-current grounding fault location system described in this embodiment.
[0089] Wherein, the upper computer is specifically used for: when a positive angle fault occurs, if the S i (n)>0, it is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com