A roasting method for reducing tsnas of different varieties of flue-cured tobacco by using strains
A curing method and strain technology, applied in the fields of tobacco, application, and treatment of tobacco, can solve the problems of reducing tobacco leaves, achieve the effects of reducing harm, increasing survival rate and activity, and expanding the scope of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
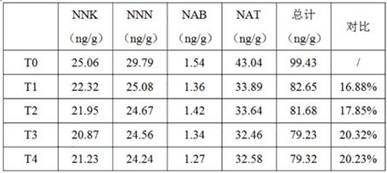
[0045] Example 1 Effect of the present invention on the content of TSNAs in Honghua Dajinyuan tobacco leaves
[0046] S100: Harvest the fresh flue-cured tobacco leaves of Honghua Dajinyuan with suitable maturity in Xiaguan Town, Dali Prefecture, Yunnan Province. The fresh tobacco leaves with suitable maturity have white and bright main veins, green and white branches, and green-yellow or light yellow leaves. And most of the fluff falls off, and it has the characteristics of rich e-liquid after touching it.
[0047] S200: classifying the harvested fresh tobacco leaves according to the amount of 90-110 pieces / stem to be compiled into stems.
[0048] S300: 3-5% of the weight of the tobacco leaves is evenly sprayed and inoculated on the surface of the woven tobacco leaves with a bacterial solution with an OD600 value of 1.
[0049] S400: Put the inoculated woven stem tobacco leaves into the air-flow descending intensive curing barn to more than 95% of the volume according to the ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2 Effect of conventional curing process on TSNAs content in Honghua Dajinyuan tobacco leaves
[0059] On the basis of Example 1, a control experiment was set up: in Example 1, the wet bulb temperature in the mid-yellowing period was adjusted to 36°C, and the baking time was adjusted to 22h; the wet bulb temperature in the late yellowing period was adjusted to 37°C, and the baking time Adjusted to 14h; other process parameters remain unchanged.
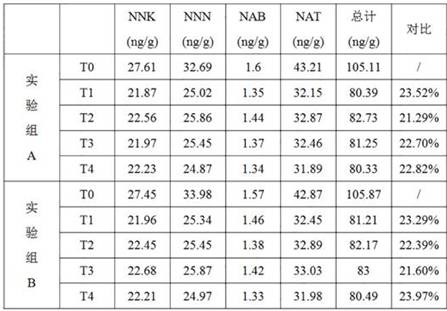
[0060] Table 2 Comparison of TSNAs content in flue-cured tobacco varieties of Honghua Dajinyuan after conventional roasting
[0061]
[0062] It can be seen from Table 1 that the TSNAs content of flue-cured tobacco in Honghua Dajinyuan reduced by 21.29-23.97% under the optimized process of the present invention; In the case of inoculated strains, the reduction was 17.41-20.43%, so the inoculated strains can significantly reduce the content of TSNAs in flue-cured tobacco, and the optimized process of the present inven...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Example 3 Effects of the present invention's baking process on the activity of Honghua Dajinyuan tobacco strains
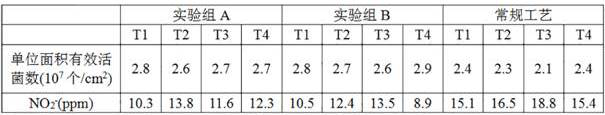
[0064] According to embodiments 1 and 2, when the initial stage of curing yellowing ends and enters the later stage of yellowing, the viable bacteria count and NO 2 - content.
[0065] Table 3 The number of effective viable bacteria and NO per unit area of tobacco leaves 2 - Content comparison
[0066]
[0067] It can be seen from Table 3 that compared with the conventional process, the number of effective viable bacteria per unit area of this method is obviously higher, and the precursor substance NO of its scavenging nitrosamine 2 - The ability is stronger, so it has been confirmed that this method technology can improve the survival rate of bacterial classification.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com