Adversarial sample defense method based on spoofing attacker
A technology against samples and attackers, applied in the fields of instrument, calculation, character and pattern recognition, etc., can solve the problems of inappropriate defense methods and can not significantly improve defense performance, and achieve the effect of improving security performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
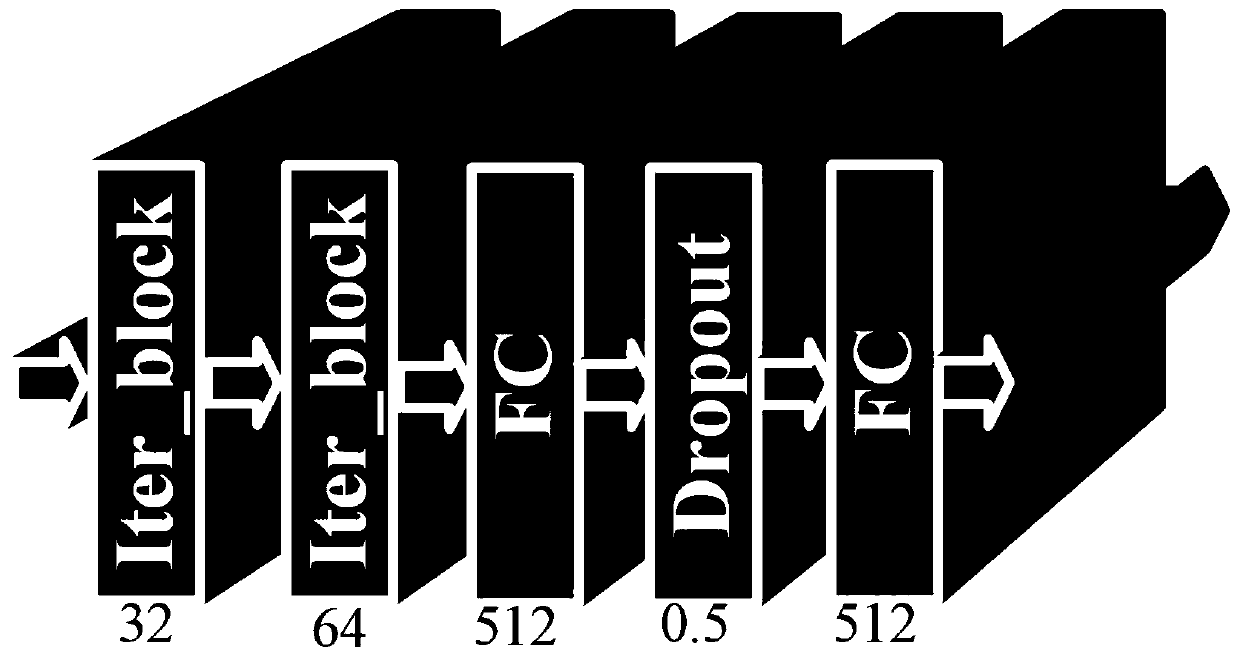
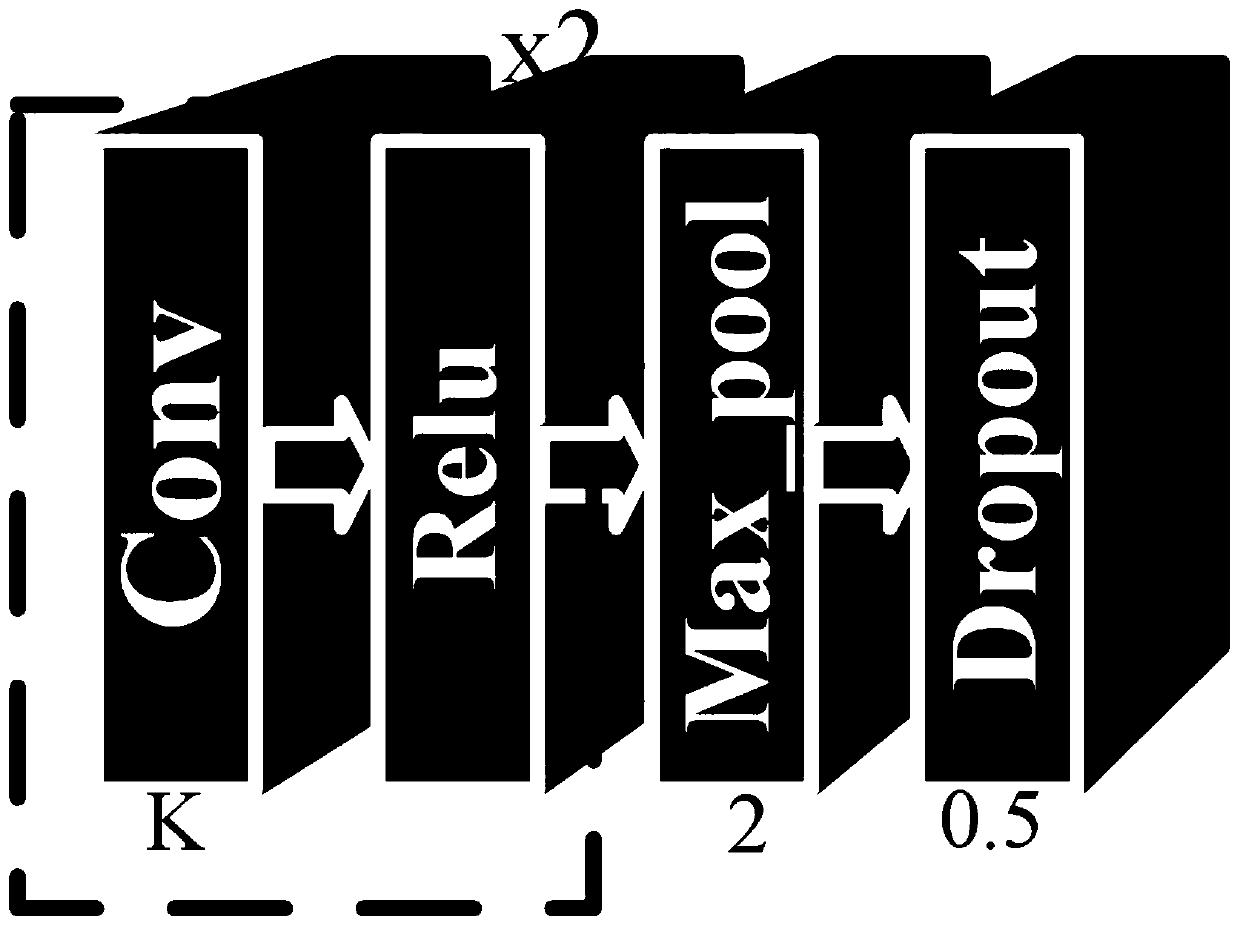
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Defense performance against non-target generated adversarial examples:
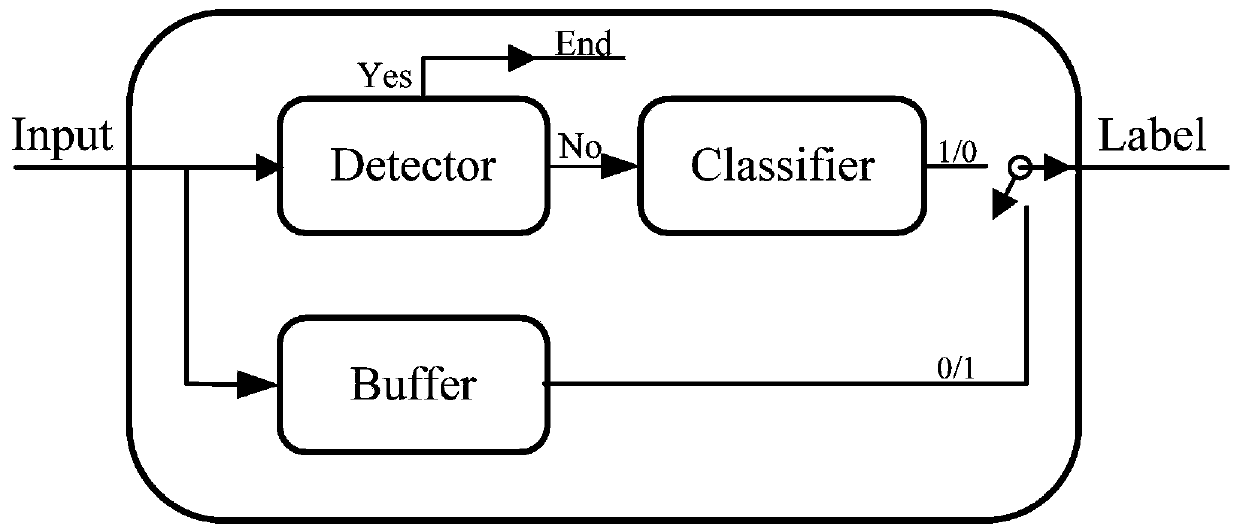
[0051] Assumption 1: We assume that the attacker uses an iterative method to generate adversarial examples. The iterative goal of generating adversarial examples is misclassification. When the attacker achieves the goal, it turns to generate an adversarial example for the next image.
[0052] We first consider the case of processing a single image. The initial value of the buffer is set to a matrix of 0 with a size of image length × image width × 3. When the attacker adopts TRCS as the original classifier, the input will be stored in m1. Next, the images saved in m1 will be transferred to m2, and the newly generated images will be stored in m1 again. When the attacker performs t+1 iterations, the buffer will overflow. We denote the overflow value as P. If P is not a 0 matrix, we calculate the difference D between the current m1 and P. The L1 norm or MSE value is used to calculate the differe...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Defensive Performance Against Targeted Generative Adversarial Sample Attacks
[0082] The training process is not interrupted until the classifier achieves the target attack or the number of iterations reaches the upper limit. While the buffer controls the generation process, classifier 2 will output its classification results. At this point, the result needs to meet the requirements for determining the target classification. However, untrained networks cannot achieve this goal. So, we can use other trained networks. We adopt a network that generalizes poorly to the original classifier as classifier 2. When we feed the same images into the classifier, both the original classifier and classifier 2 can classify them correctly, but the output labels are different.
[0083] As mentioned above, detectors cannot classify adversarial examples well. The low detection performance of the front detector will greatly affect the normal classification of the system. At the same...
Embodiment 3
[0089] A defense method for adversarial samples based on deceiving attackers, the steps are as follows:
[0090] S1. Train the classifier 2 so that the generalization performance of the classifier 2 and the original classifier is poor. Specifically, the adversarial samples generated by the attack classifier 2 can be accurately identified by the original classifier;
[0091] S2. A buffer is constructed, and the buffer and the classifier are connected in parallel.
[0092] S3. Constructing a detector for detecting adversarial samples generated by a single-step or less-step attack. The detector is preceded by the original classifier.
[0093] S4. Construct a standard library and a comparator, which can replace the detector. The comparator is a non-gradient defense method, which can effectively defend against gradient attacks. after the original classifier.
[0094] Further, the specific steps of steps S1-S3 are as follows:
[0095] T1. Train the classifier 2 so that both the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com