Methods for multiplex detection of alleles associated with corneal dystrophy
A technology for dystrophy and cornea, which is applied to the probe for detecting or diagnosing corneal dystrophy, in the field of detecting or diagnosing corneal dystrophy, and can solve problems such as corneal dystrophy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0093] Example 1: Global Literature Search
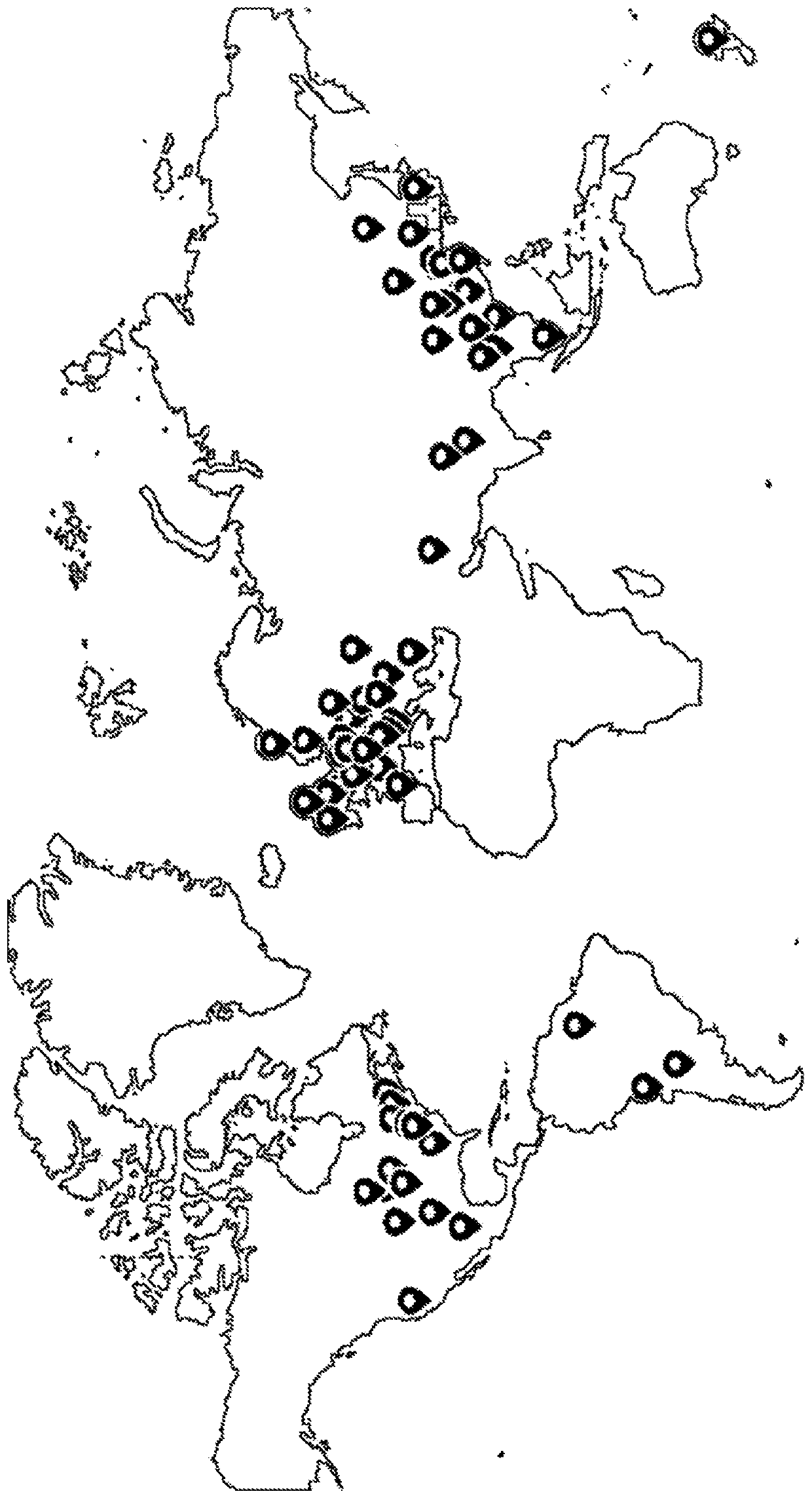
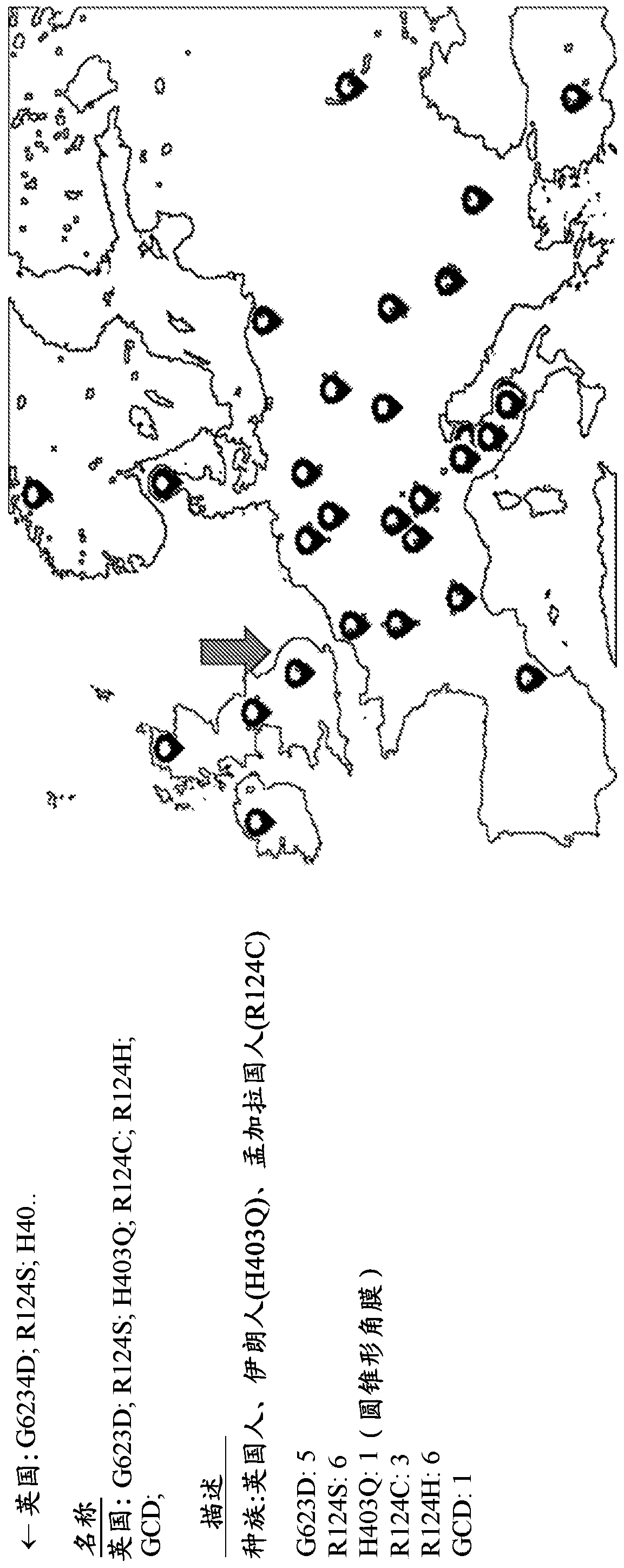
[0094] Interrogation of the HGMD database revealed 62 different TGFBI mutations. The HGMD database was used to identify papers in which these mutations were described in order to construct a global distribution map ( Figure 1A with Figure 1B ). Each flag in the world map contains an overview of mutations reported in a particular region or country. Overview includes race, mutation, and total number of cases reported for each mutation ( Figure 1A ). There were no clear differences in the distribution of mutations among specific populations or geographic regions. Few cases have been reported from South America, and none have been reported from Africa or Russia. The map can be used to extract country-specific information, such as Figure 1B London indicated by the red arrow in .
[0095] Globally, 75% of TGFBI mutations reported in more than 1,600 cases consist of one of five mutations currently detected by available genetic te...
Embodiment 2
[0098] Example 2: Analysis of Globally Available Genetic Test Data
[0099] Since 2008, more than 600,000 samples have been tested worldwide with available genetic tests; the majority of samples are from Korea and Japan, where the test is used for pre-refractive surgery screening. An analysis of global testing data showed South Korea had a detection rate of about 15 in 10,000, compared with a reported prevalence of 1 in 870 10 very close. Japan's TGFBI mutation detection rate (3 per 10,000) was lower than that of South Korea. In Korea, the test is used as a routine screening for all candidates for refractive surgery, whereas in Japan, patients are first subjected to a rigorous clinical examination, and only those patients with no detected corneal abnormalities are submitted for genetic testing.
[0100] Clinics / hospitals in Korea and Japan use genetic testing for screening purposes as it forms part of the practice guidelines for refractive surgery. In the United States, som...
Embodiment 3
[0101] Example 3: Evaluation of an expansion panel with six additional mutations
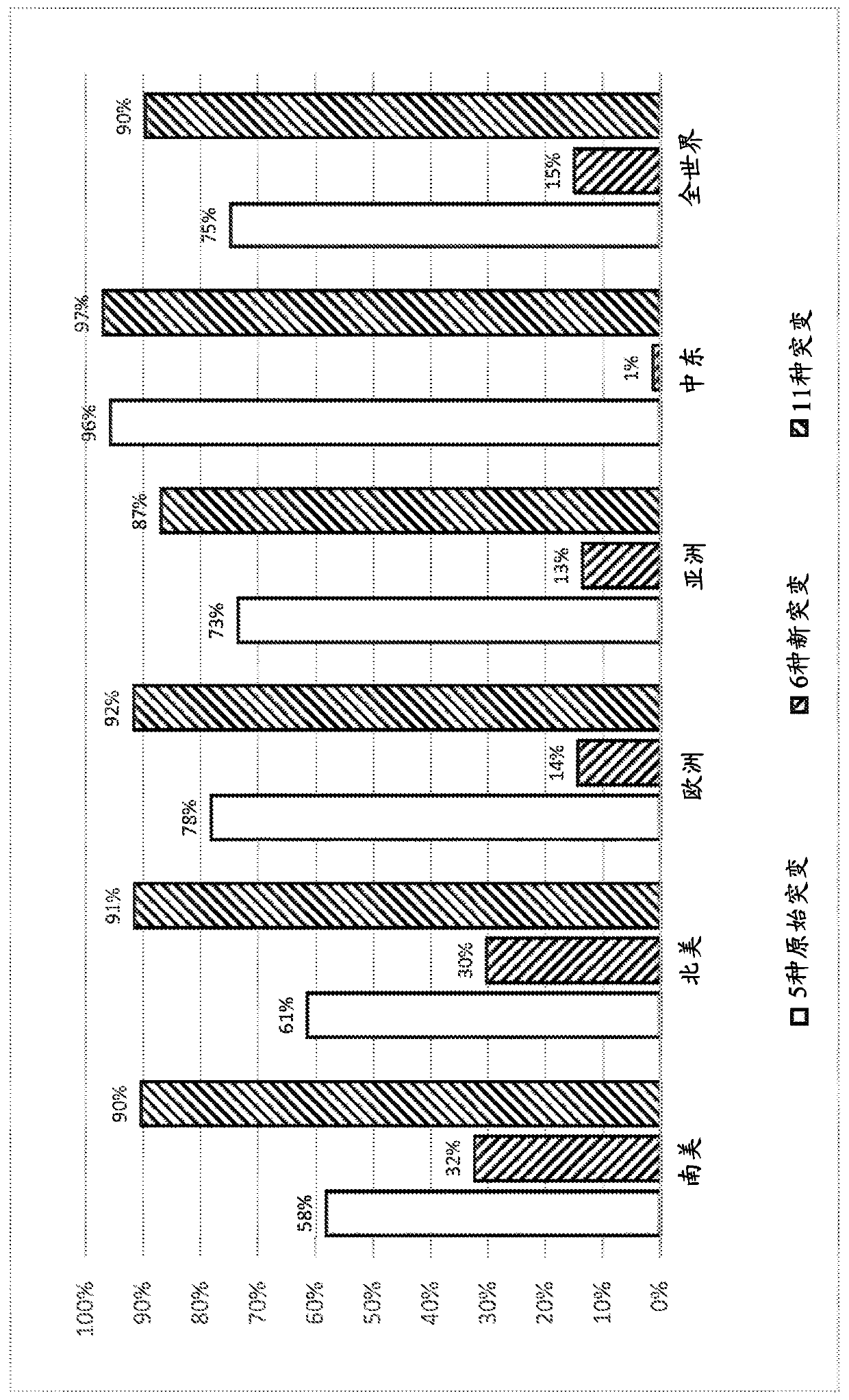
[0102] Few studies such as the 2016 UCL Moorfield corneal dystrophy population study performed Sanger sequencing on the entire TGFBI gene. This study provides us with a set of data on which to evaluate the addition of six new mutation sites to increase the call rate for a given population. Briefly, the study consisted of 91 unrelated cases of TGFBI corneal dystrophy, of which 68 were diagnosed as epithelial-mesenchymal TGFBI-related dystrophies (RBCD, TBCD, LCD, and GCD) and 23 were diagnosed as bilateral epithelial-basal Membrane Dystrophy (EBMD) 4 . For the UK population, a panel of six TGFBI mutations was assessed to determine the appropriateness of these mutations in combination with the five mutated gene tests. The data showed that the detection rate in the UK population increased from 90% to 97% ( Figure 4 table in ). Other candidate mutations may be considered, such as Figure 4 V6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com