A Probabilistic Determination Method for Nondeterministic Problems
A non-deterministic and deterministic technology, applied in neural learning methods, biological neural network models, neural architectures, etc., and can solve problems such as limited application of neuron circuits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
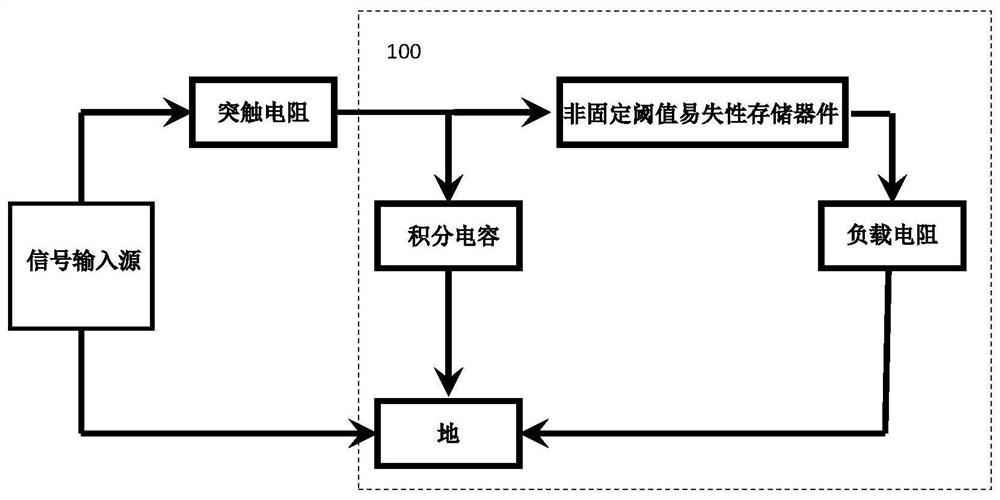
[0044] A probabilistic neuron circuit 100, such as figure 1 As shown, including: integrating capacitor, non-fixed threshold volatile device and load resistance; one end of the integrating capacitor is grounded, the other end is connected to a synaptic resistor to connect an external signal input source and one end of the non-fixed threshold volatile device, non-fixed The other end of the threshold volatile device is connected to one end of the load resistor, and the other end of the load resistor is grounded.
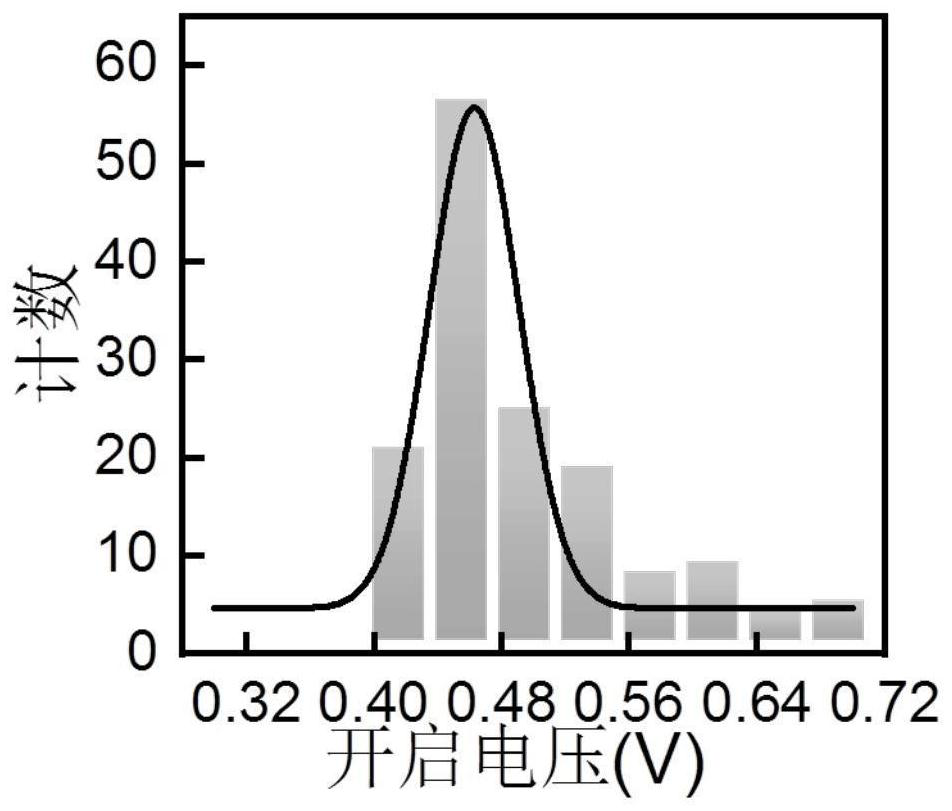
[0045] Due to the characteristics of the non-fixed threshold volatile device, its excitation (turn-on) voltage threshold is not fixed and is a randomly changing value. The probability corresponding to each excitation voltage is generally different, and the variation law roughly satisfies the Gaussian distribution. figure 2 As shown, the voltage required for a volatile memory device to change from a high-resistance state to a low-resistance state becomes the turn-on vol...
Embodiment 2
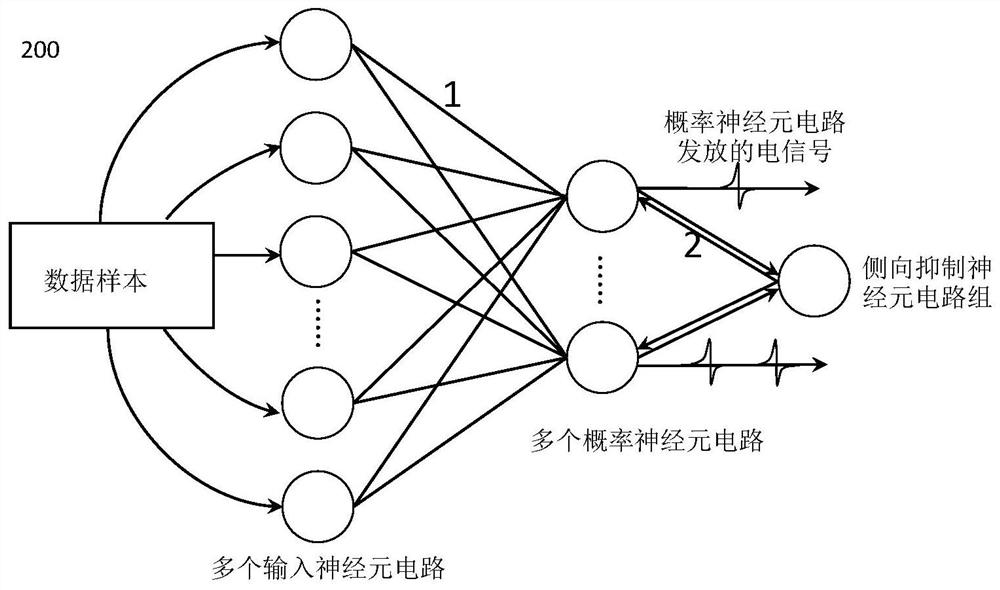
[0049] A probabilistic neural network topology 200, such as image 3 As shown, it includes: a plurality of input neuron circuits, a plurality of output neuron circuits, a lateral inhibitory neuron circuit, and a signal processor; wherein, the output neuron circuits are the probabilistic neuron circuits described above;
[0050] Each input neuron circuit is used to send a discharge signal to each probability neuron circuit; each probability neuron circuit is used for random excitation based on its non-fixed excitation threshold and the electrical signal emitted by each input neuron circuit; lateral inhibition The neuron circuit is used to inhibit the subsequent excitation of other probability neuron circuits when receiving the signals excited by the first n probability neuron circuits, where n≥1; the signal processor is used to collect whether the excitation of each probability neuron circuit is not signal and perform signal processing.
[0051] A plurality of input neuron cir...
Embodiment 3
[0060] An application of any of the probabilistic neural network topology structures described in the second embodiment above is applied to probability determination of non-deterministic problems.
[0061] It should be noted that the non-deterministic problem is called Uncertainty Quantification.
[0062] Based on the foregoing, the excitation threshold of the non-fixed threshold volatile device is not fixed and the excitation is random, so the excitation has uncertainty, not the higher the membrane voltage (turn-on voltage) of the non-fixed threshold volatile device. Exciting first, this is a probabilistic event. Therefore, using non-fixed threshold volatile devices for probability determination of non-deterministic problems, using hardware on natural properties, the probability generated is with real probability properties, and at this stage, computer In , the method of generating probability is to generate a random number, and then realize it by mathematical algorithm, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com