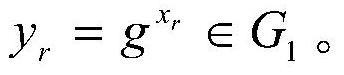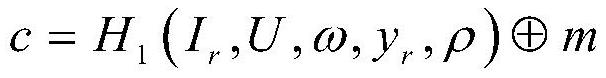Certificateless Ring Signcryption Method Based on Multiplicative Group
A certificateless, ring signcryption technology, applied in the field of network information security
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
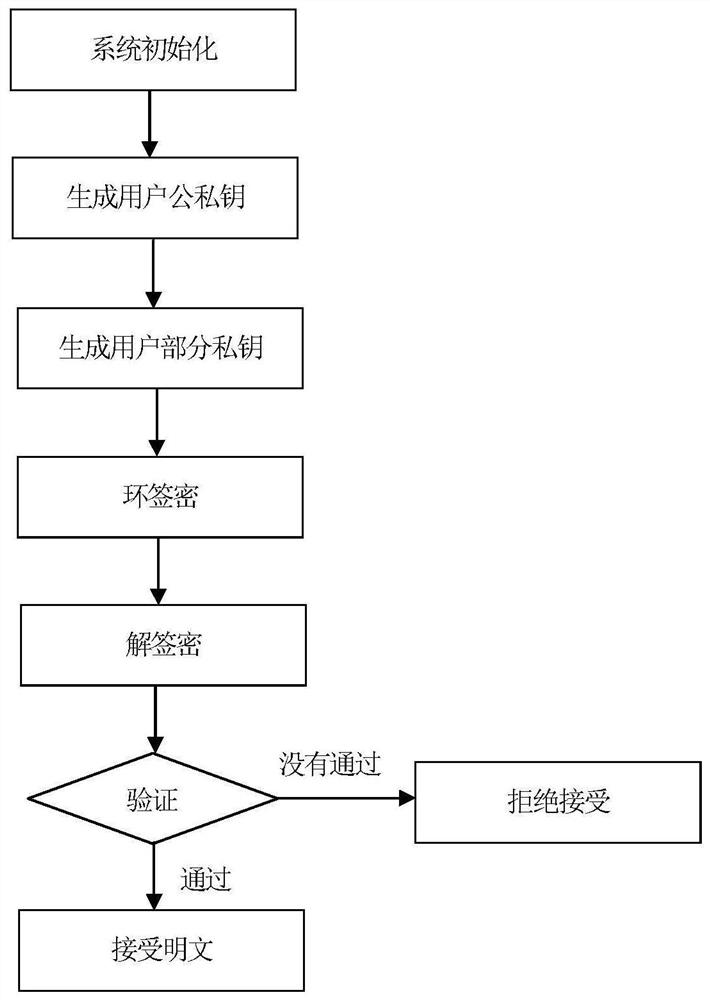
[0053] A large prime number q selected by the key generation center, q is 2 192 -2 64 -1 as an example, such as figure 1 As shown, the steps of the multiplicative group-based certificateless ring signcryption method in this embodiment are as follows:
[0054] A. System initialization
[0055] (A1) The key generation center selects a large prime number q of k bits, and this embodiment adopts q as 2 192 -2 64 -1, k is a security parameter, a finite positive integer, set G 1 ,G 2 ,G 3 are three q factorial cyclic groups, g is the group G 1 A generator of , e is G 1 ×G 2 →G 3 is a bilinear map.
[0056] (A2) The key generation center selects three cryptographically secure hash functions H 0 、H 1 、H 2 :H 0 : h 1 : h 2 : Where l1 is the length of the message, l2 is the length of any identity, n is the number of ring members, which is a finite positive integer, Z q * is {1,2,...,2 192 -2 64 -2}, is a message of length l1 consisting of 0s and 1s, is an i...
Embodiment 2
[0098] A large prime number q selected by the key generation center, q is 2 224 -2 96 +1 as an example, the steps of the certificateless ring signcryption method based on the multiplicative group are as follows:
[0099] A. System initialization
[0100] (A1) The key generation center selects a large prime number q of k bits, and this embodiment adopts q as 2 224 -2 96 +1, k is a security parameter, a finite positive integer, set G 1 ,G 2 ,G 3 are three q factorial cyclic groups, g is the group G 1 A generator of , e is G 1 ×G 2 →G 3 is a bilinear map.
[0101] (A2) The key generation center selects three cryptographically secure hash functions H 0 、H 1 、H 2 :H 0 : h 1 : h 2 : where l 1 is the message length, l 2 is the length of any identity, n is the number of ring members, which is a finite positive integer, Z q * is {1,2,...,2 224 -2 96}, is a length l composed of 0 and 1 1 news, is a length l composed of 0 and 1 2 identity of, It is n+1...
Embodiment 3
[0108] A large prime number q selected by the key generation center, q is 2 256 -2 224 +2 192 +2 96 +1 as an example, the steps of the certificateless ring signcryption method based on the multiplicative group are as follows:
[0109] A. System initialization
[0110] (A1) The key generation center selects a large prime number q of k bits, and this embodiment adopts q as 2 256 -2 224 +2 192 +2 96 +1, k is a security parameter, a finite positive integer, set G 1 ,G 2 ,G 3 are three q factorial cyclic groups, g is the group G 1 A generator of , e is G 1 ×G 2 →G 3 is a bilinear map.
[0111] (A2) The key generation center selects three cryptographically secure hash functions H 0 、H 1 、H 2 :H 0 : h 1 : h 2 : where l 1 is the message length, l 2 is the length of any identity, n is the number of ring members, which is a finite positive integer, Z q * is {1,2,...,2 256 -2 224 +2 192 +2 96}, is a length l composed of 0 and 1 1 news, is a length l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com