K-bit continuous collision bit detection split tree RFID tag anti-collision algorithm
An RFID tag and anti-collision algorithm technology, applied in the field of radio frequency identification, can solve the problems of long identification time period and large number of transmitted information bits.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0017] Firstly, the symbols, functions and commands used in the present invention are defined as shown in Table 1.
[0018] Table 1 Symbol Definition
[0019]
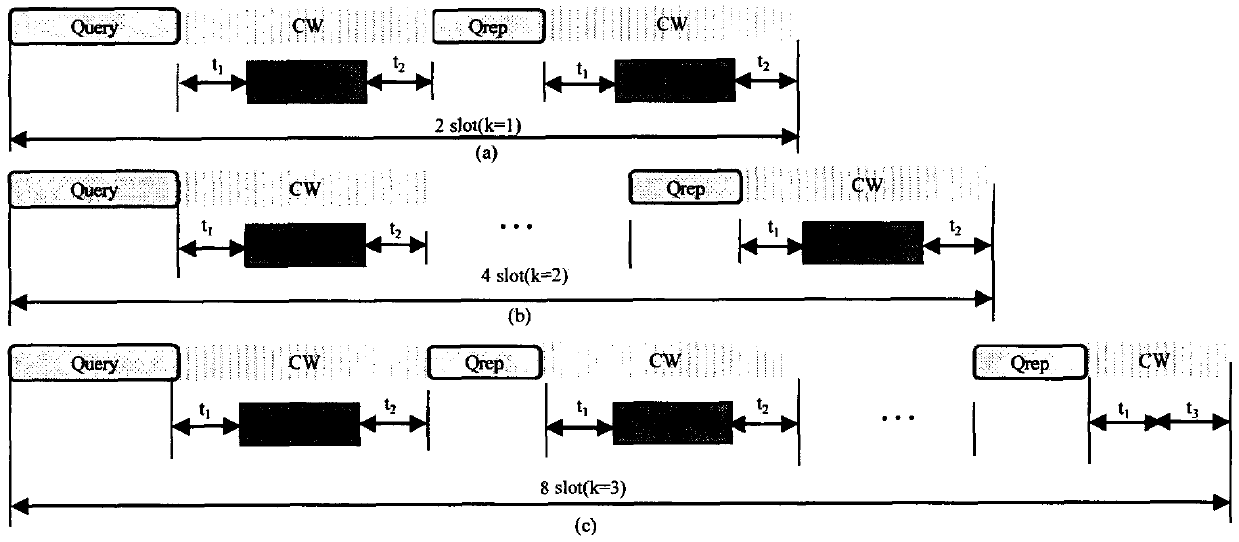
[0020] 1, based on the above-mentioned conditions, the specific implementation steps of the k bit continuous collision bit detection split tree RFID tag anti-collision algorithm proposed by the present invention are:
[0021] Step 1: At the beginning of the recognition process, the reader first initializes pre=□, k=0, and broadcasts the query command Query (pre, k) to start the first frame;
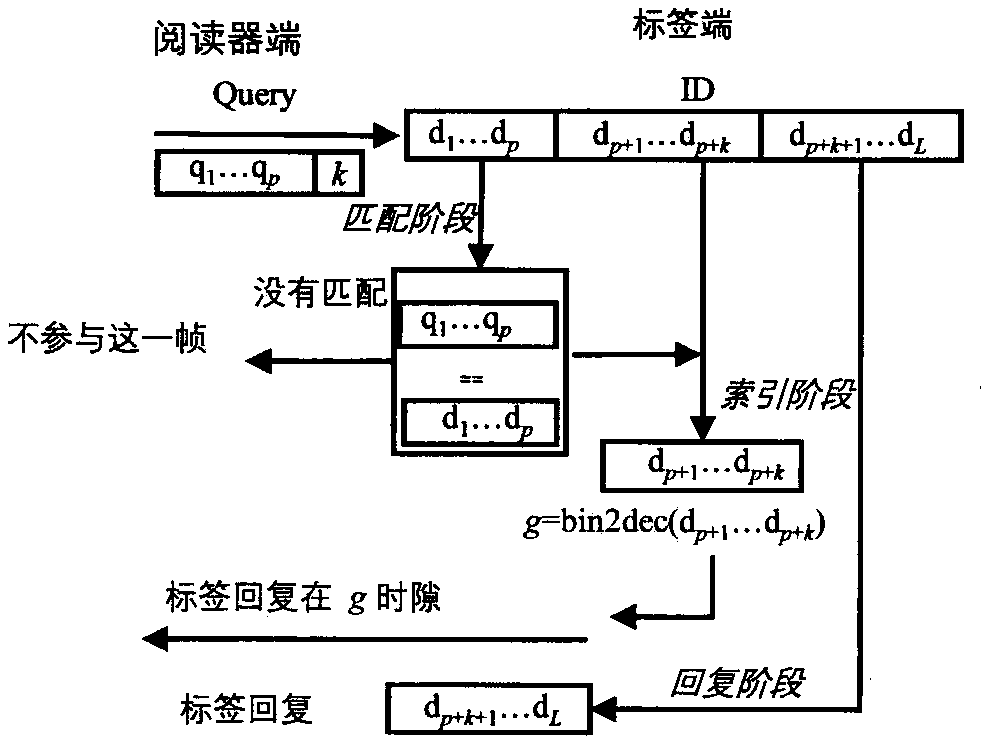
[0022] Step 2: After the tag receives the Query command, refer to the attached image 3 , the tag side will perform the following steps:
[0023] ①Matching stage: the tag first compares its previous L pre Bit-length IDs and matching prefixes pre. If the matching is successful, the tag ente...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com