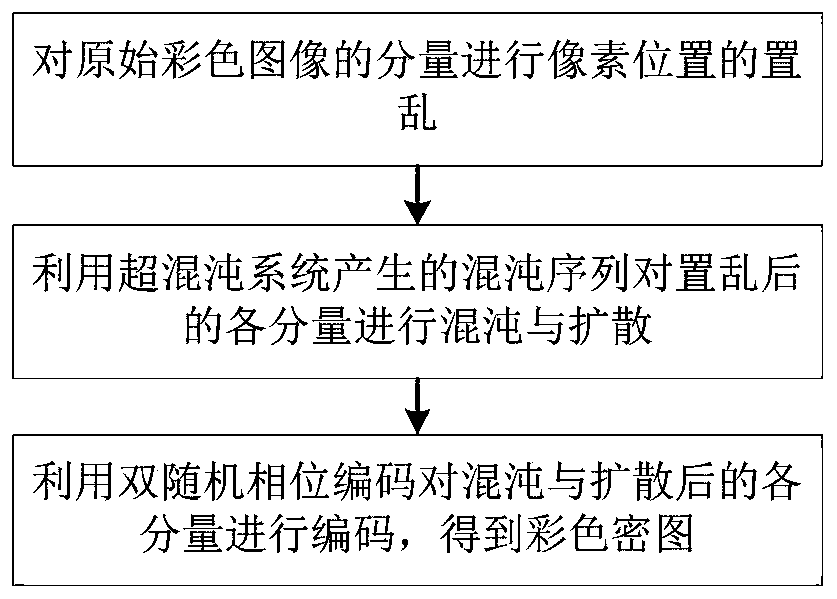
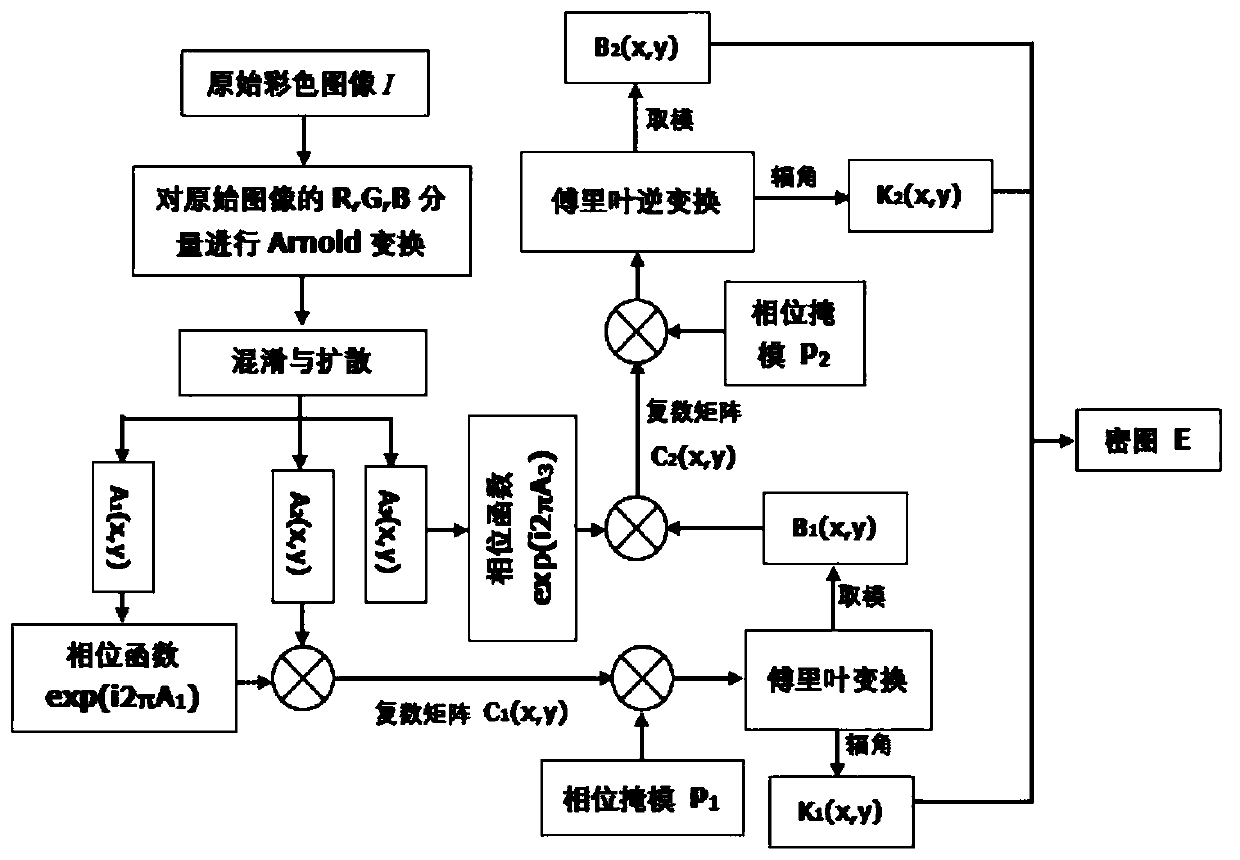
Color image encryption method and system based on hyperchaos and double random phase encoding
A double random phase, color image technology, applied in image watermarking, image data processing, image data processing and other directions, can solve the problems of key cracking, affecting the efficiency of image encryption and decryption, and taking a long time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0122] Example 1: Key Sensitivity Experiment
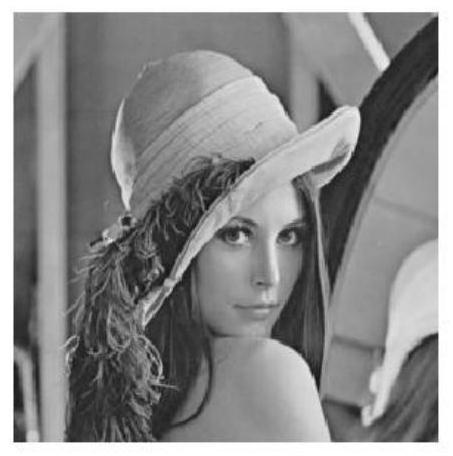
[0123] Such as Figure 3-8 As shown, this example sets the key to x 0 =1,y 0 =0.1,z 0 =1.3, h 0 =4, for the plaintext image Lena( image 3 ) to encrypt and get the secret map ( Figure 4 ), the decrypted graph obtained by decrypting the secret graph with the correct key ( Figure 5 ). Then, the ciphertext image is decrypted with three groups of small perturbation keys respectively. Among them, the first group is x in the original key 0 perform a 10 -14 A small disturbance of the level, that is, x 0 =1+10 -14 ; The second group is the y in the original key 0 perform a 10 -14 A small disturbance of the level, ie y 0 =1+10 -14 ; The third group is z in the original key 0 perform a 10 -14 A small disturbance of the level, that is, z 0 =1+10 -14 . Figure 6-Figure 8 It shows the images after the secret image is decrypted with the first, second and third groups of keys respectively. Visible, even though the keys d...
Embodiment 2
[0124] Example 2: Key Sensitivity Experiment
[0125] In this example, 8000 pairs of adjacent pixels are randomly selected from the plaintext image and the ciphertext image, and then the correlation coefficient of adjacent pixels is calculated. Table 1 shows the correlation coefficients of the R, G and B components of plaintext and ciphertext images in three directions (horizontal, vertical and diagonal).
[0126] Table 1 Correlation coefficients of plaintext and ciphertext images in three directions
[0127]
[0128] It can be seen that in the plaintext image, the correlation between adjacent pixels is close to 1 in all directions, while in the ciphertext image, the correlation between adjacent pixels is close to 0 in all directions. This shows that the present invention can effectively eliminate the correlation between adjacent pixels. Figure 9 and Figure 10 Shown is the adjacent pixel distribution diagram of the plaintext image and the ciphertext image in the vert...
Embodiment 3
[0129] Example 3: Differential analysis experiment
[0130] As we all know, in cryptography or cryptanalysis, there are four classic attack methods: known plaintext attack, known ciphertext attack, chosen plaintext attack and chosen ciphertext attack. Among these attack methods, chosen-plaintext attack poses the greatest threat to cryptosystems. In the attack mode of chosen-plaintext attack, the attacker can pre-select a certain amount of plaintext to encrypt the encryption algorithm under attack to obtain the corresponding ciphertext. The attacker's goal through this process is to obtain some information about the encryption algorithm so that later the attacker can more efficiently crack information encrypted by the same encryption algorithm (and associated keys). If a small change (even 1 bit) of the plaintext image can change more than half of the pixels of the encrypted ciphertext image, then the differential attack will fail. Therefore, resisting differential attacks ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com