Optimization device and control method of optimization device
A technology for optimizing devices and control methods, applied in adaptive control, general control systems, control/regulation systems, etc., can solve problems such as time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
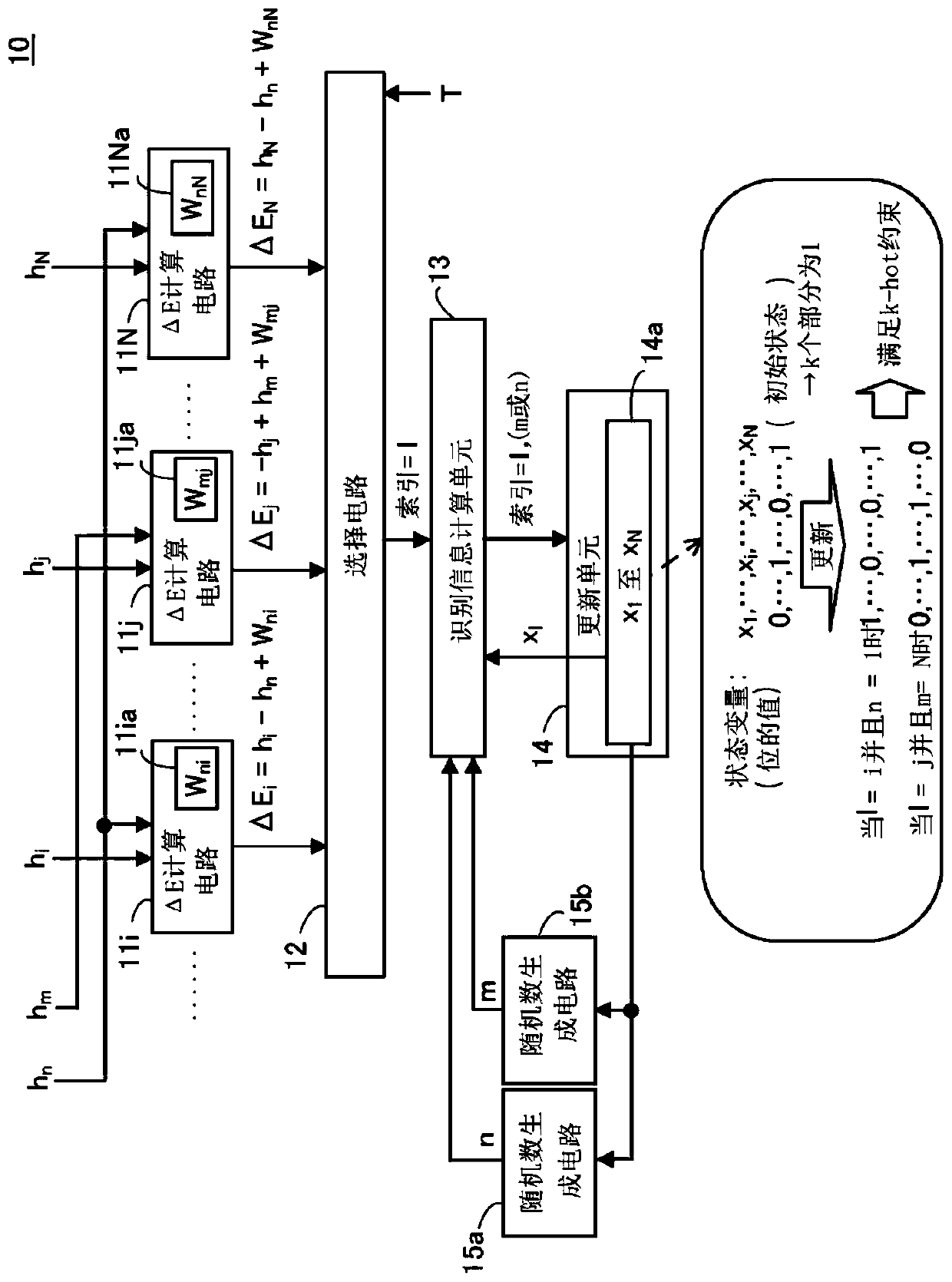
[0047] figure 1 is a diagram showing an example of the optimization device according to the first embodiment.
[0048] The optimization device 10 includes N ΔE calculation circuits (for example, including figure 1 ΔE calculation circuits 11i, 11j, and 11N), selection circuit 12, identification information calculation unit 13, update unit 14, and random number generation circuits 15a and 15b.
[0049] Among the N ΔE calculation circuits, k (k>1) ΔE calculation circuits ( figure 1 The ΔE calculation circuits 11i and 11N in the example in , etc.) execute the following processing.
[0050] Among the N bits, the local field value (for example, h i and h N ) is supplied to each of the k ΔE calculation circuits. Local field value (h n ) is supplied to each of the k ΔE calculation circuits. exist figure 1 In , the circuit for calculating the local field value, the circuit for controlling the propagation of the local field value to the ΔE calculation circuit, etc. are not shown...
no. 2 approach
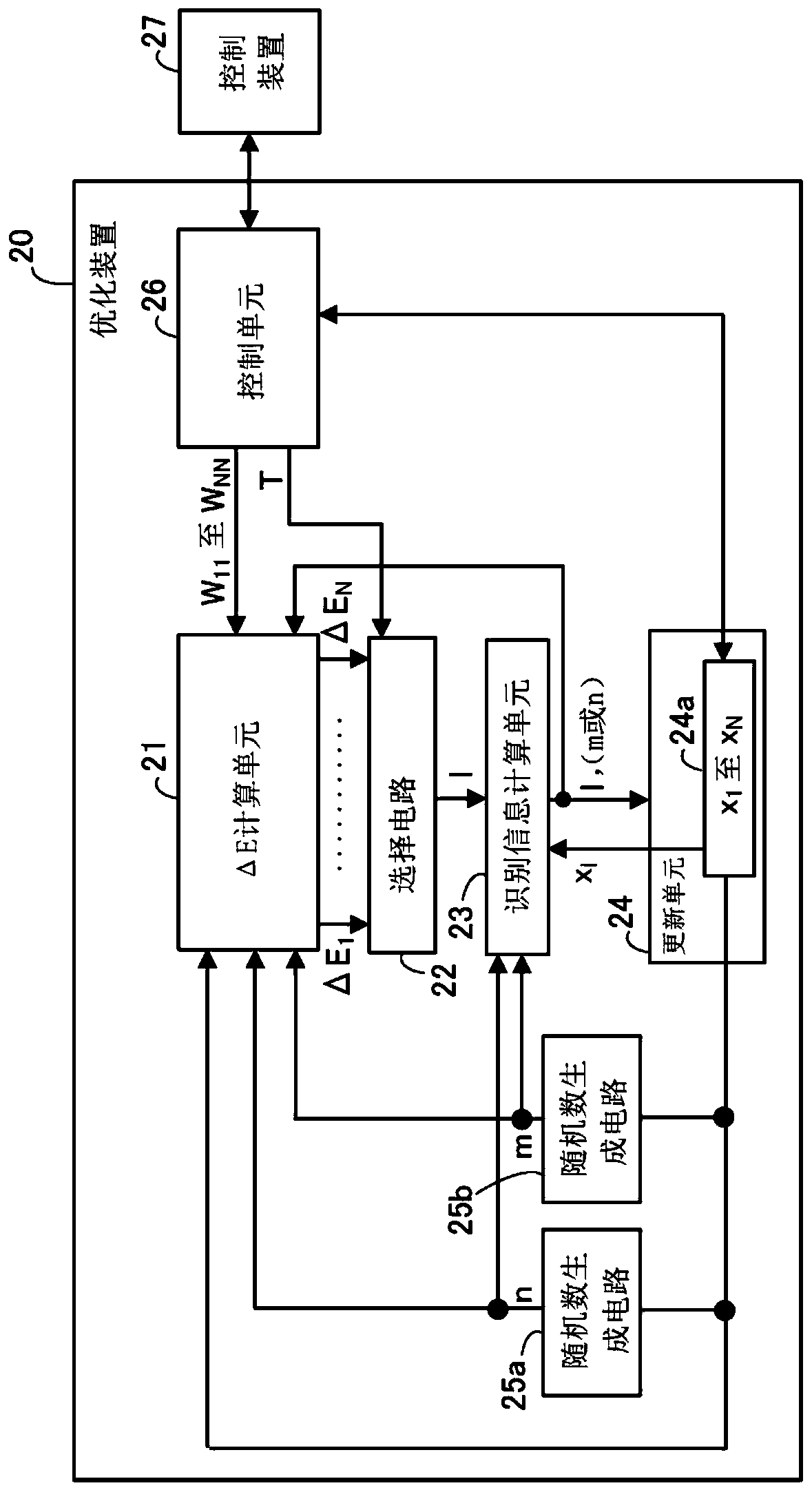
[0086] figure 2 is a diagram showing an example of an optimization device according to the second embodiment.
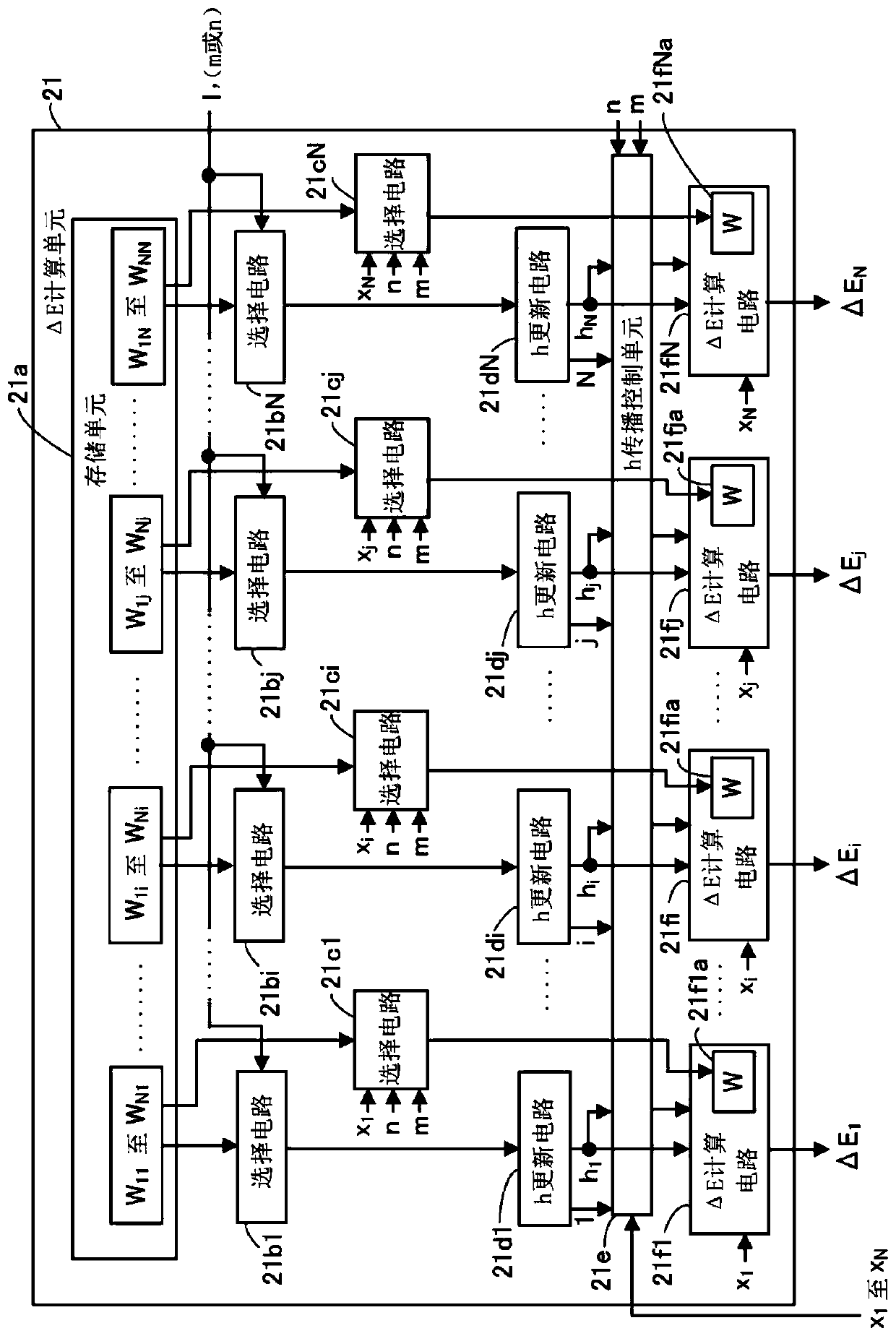
[0087] The optimization device 20 includes a ΔE calculation unit 21 , a selection circuit 22 , an identification information calculation unit 23 , an update unit 24 , random number generation circuits 25 a and 25 b , and a control unit 26 .
[0088] The ΔE calculation unit 21 calculates the energy change (ΔE 1 to ΔE N ).
[0089] Based on thermal excitation energy and ΔE 1 to ΔE N The selection circuit 22 outputs an index=1 identifying a bit having a value that is allowed to be updated among the N bits. The thermal excitation energy is determined based on the random number and T input from the control unit 26 . In some cases, according to the thermal excitation energy and ΔE 1 to ΔE NThe size relationship between even for one of the N bits does not allow updates. Assume that the selection circuit 22 outputs a flag indicating whether updating is permitted. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com