IPv6 wireless sensor node load balancing implementation method based on 6LoWPAN
A wireless sensor and implementation method technology, applied in wireless communication, advanced technology, network traffic/resource management, etc., can solve problems such as load imbalance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] 6LoWPAN is a low-speed wireless personal area network standard based on IPv6. 6LoWPAN is called a WPAN network with an IPV6-based protocol.
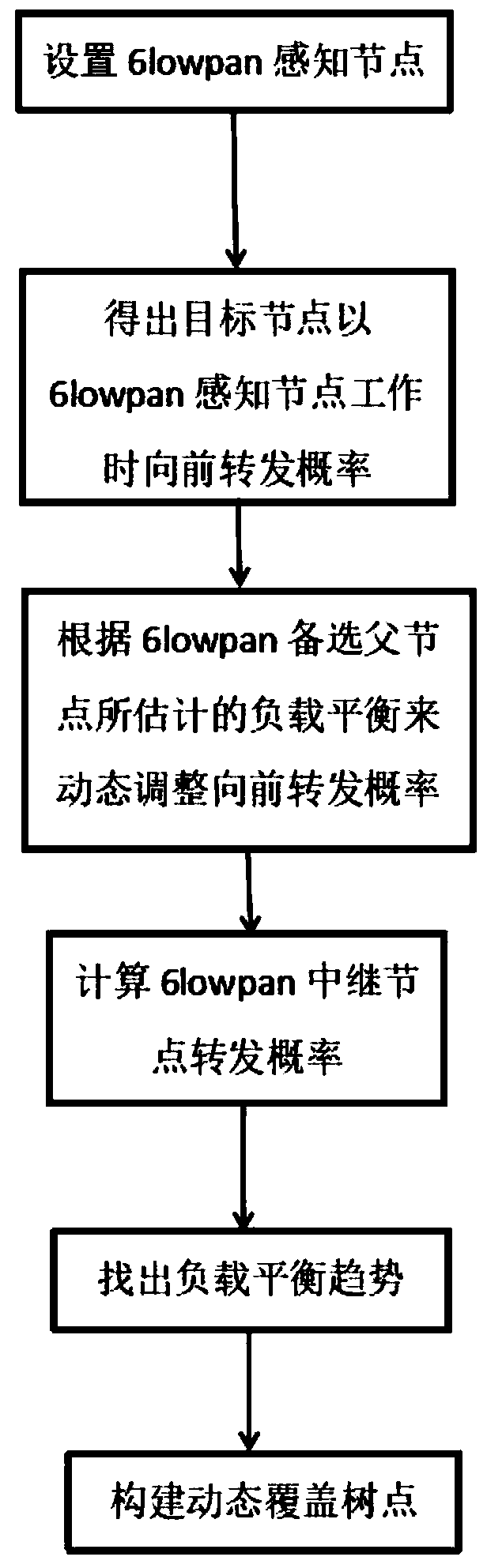
[0052] Such as figure 1 As shown, based on the dynamic construction of the load balancing routing coverage tree to achieve the maximum coverage of the 6LoWPAN wireless sensor node load balancing implementation method:
[0053] Step 1 Set up a 6LoWPAN sensing node.
[0054] Step 1.1 Use the square of the ratio of the remaining energy of a 6LoWPAN node to the forwarding distance to represent the weight of a one-hop forwarding path between an IPv6 parent node and a child node.
[0055] Step 1.2 Define when S i When working as a 6LoWPAN sensing node, the candidate IPv6 parent node S rj ∈ Q rt (S i )’s forward forward probability is defined as:
[0056]
[0057] where e rj (τ') means node S at time τ' rj the remaining energy; e k (τ') means to divide node S at τ' time rj The remaining energy of a certain node outside; α re...
Embodiment
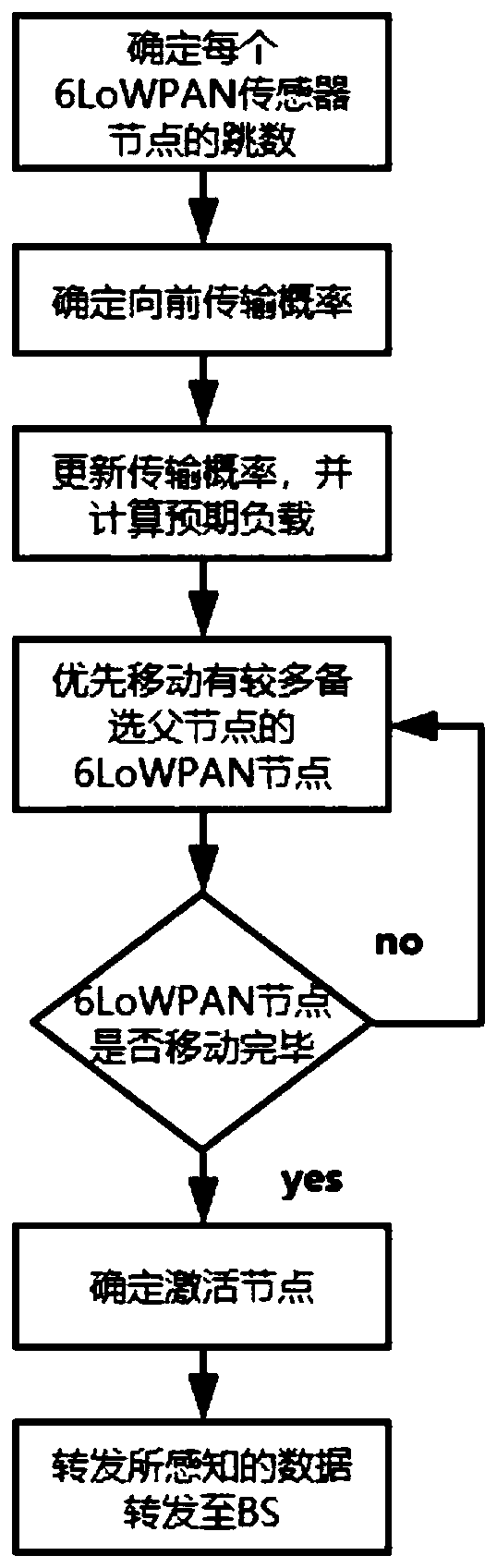
[0080] 1. Experimental system and process
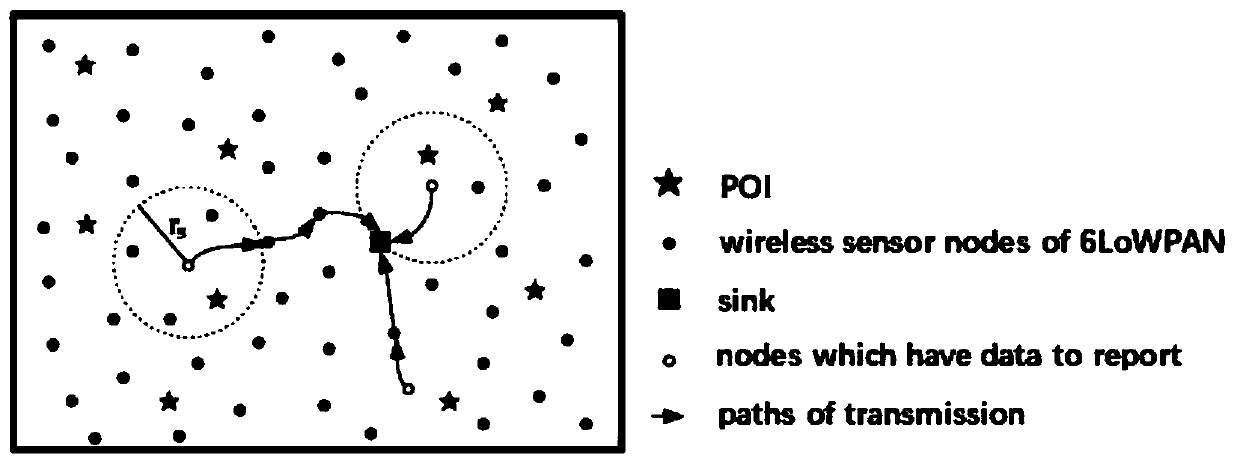
[0081] In a 100m×100m wireless sensor network monitoring area, 64 information points are randomly deployed, and 50-500 sensor nodes are arranged. The perception range of each node is 17.675m. All sensor nodes are arranged randomly. Each experimental situation was simulated 30 times. The problem of wireless sensor network sensor node coverage: the cost of deploying nodes (minimum number of activated nodes) is the lowest so that all information points are covered. If there are redundant sensor nodes in the coverage area, turn it off and let it go to sleep; if there is an information point that is not covered due to the energy depletion of a certain sensor node, you can wake up some dormant nodes to cover this information point.
[0082] The purpose of the probabilistic load balancing (PLB) scheme is to achieve load balancing by adjusting the forwarding probability. Consider any node S in the K layer (that is, the number of hops = K...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com