Lossless compression method and device for video data
A lossless compression technology for video data, applied in the field of compression, can solve problems such as poor prediction effect, large redundancy, and inability to improve coding efficiency, and achieve the effect of reducing theoretical limit entropy and improving image coding compression rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
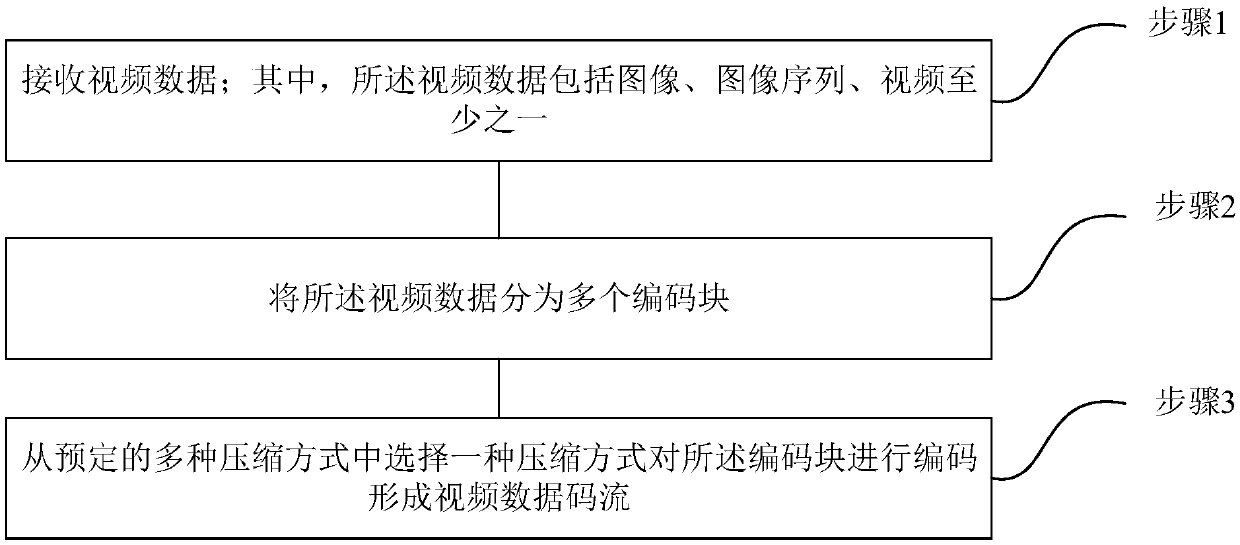
[0024] See figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic flowchart of a lossless compression method for video data provided by an embodiment of the present invention; this embodiment describes in detail a lossless compression method for video data provided by the present invention, and the method includes the following steps:
[0025] Step 1. Receive video data; wherein, the video data includes at least one of images, image sequences, and videos;
[0026] Step 2, dividing the video data into a plurality of encoding blocks;
[0027] Further, the coding block may be a 64×64 image macroblock (Macro block, MB for short), or may be a sub-image macroblock of a 64×64 image macroblock, or may have a smaller size The sub-picture macroblocks of the standard picture macroblocks, for example, 1 / 4, 1 / 8, 1 / 16 or 1 / 32 sub-samples.
[0028] Step 3: Select a compression method from a plurality of predetermined compression methods to encode the coding block to form a video data stream.
[0029] Whe...
Embodiment 2
[0044] On the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments, this embodiment describes in detail the steps of using an adaptive texture compression method to encode the coding block to obtain the first compressed data, including:
[0045] Step 1. Define the size of the encoding block
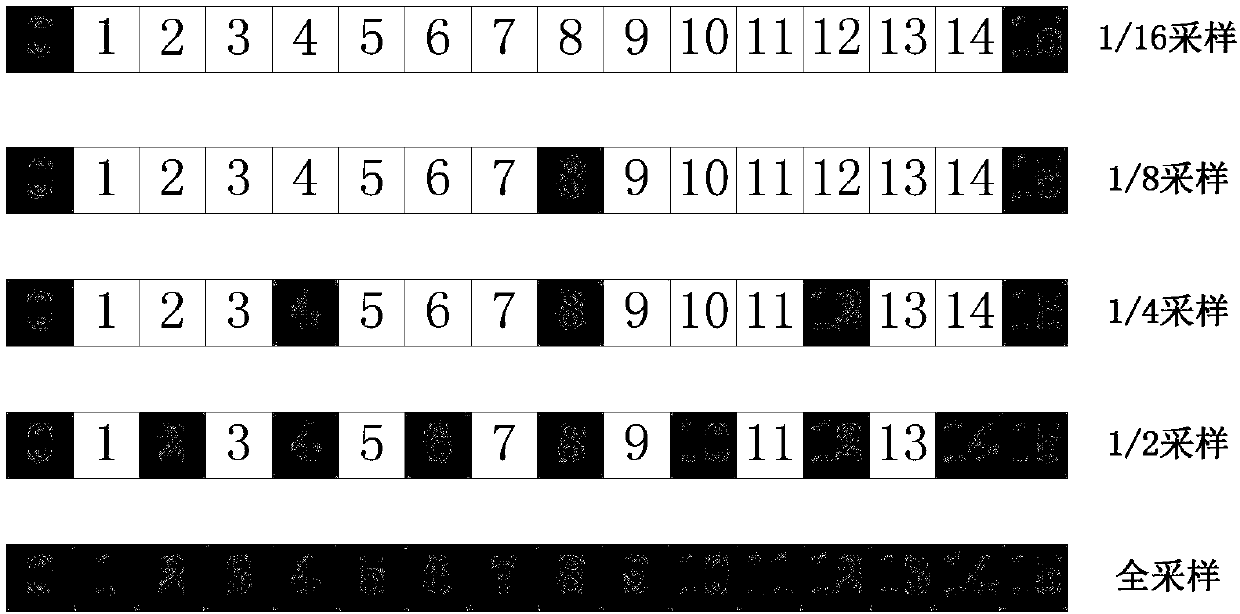
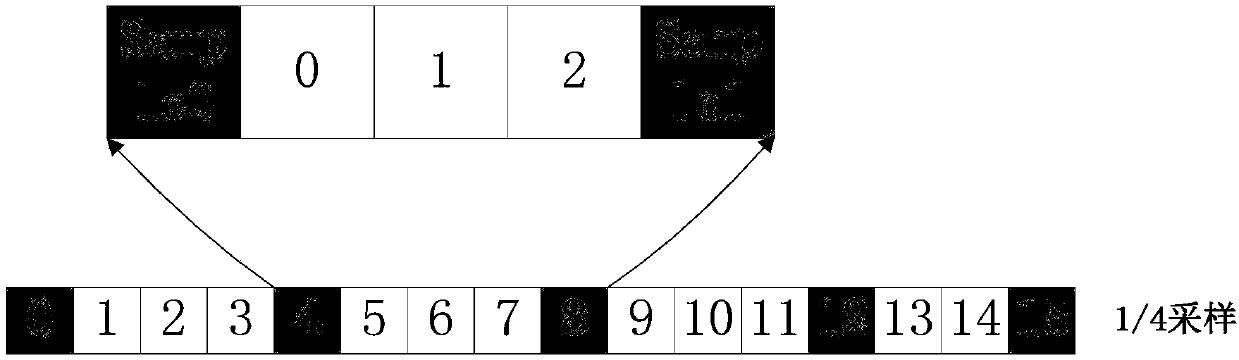
[0046] Suppose the size of the coding block is m*n, that is, the coding block has m*n pixels, where m≥1, n≥1;
[0047] Preferably, the size of the coding block can be defined as 8*1 pixels, 16*1 pixels, 32*1 pixels, and 64*1 pixels; in this embodiment, the size of the coding block is 16*1 pixels as an example Note that the same applies to other coding blocks of different sizes. The pixels in the coding block are arranged in order from left to right according to the serial number from 0 to 15, and each serial number position corresponds to a pixel.
[0048] Step 2. Define the sampling method of the coding block
[0049] According to the texture correlation existing in the coding block, the closer t...
Embodiment 3
[0069] On the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments, this embodiment describes in detail the steps of encoding and obtaining the second compressed data by using the encoding block in the block-skipping and scanning compression mode, including:
[0070] Step 1. Divide the image into several coding blocks. In this embodiment, the coding block size is 8*4, and the image size is 128*64 as an example for description.
[0071] Step 2. Mark each coding block in the image, and select P marking symbols. In the horizontal direction, a plurality of marking symbols are used to complete the marking of the coding blocks in the horizontal direction in sequence; in the vertical direction, a plurality of marking symbols are used to complete the marking of the coding blocks in the vertical direction in sequence. The segmentation and labeling of the image in this embodiment are as follows: Figure 4 as shown, Figure 4 A schematic diagram of coded block division marking provided for the em...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com