Bottom boundary layer in-situ observation system suitable for shallow water viscous seabed and arrangement method thereof
An observation system and boundary layer technology, applied in the field of marine survey, can solve the problems of bottom boundary layer observation interference, influence observation effect, clumsy operation, etc., so as to reduce the cost of installation and observation, avoid the influence of turbulence, and ensure the effect of piling depth.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
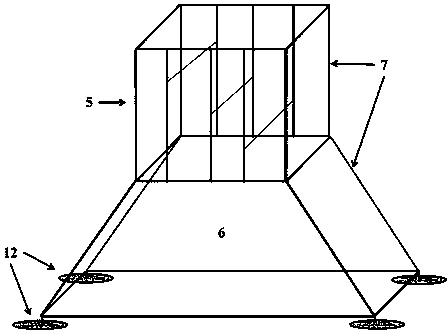
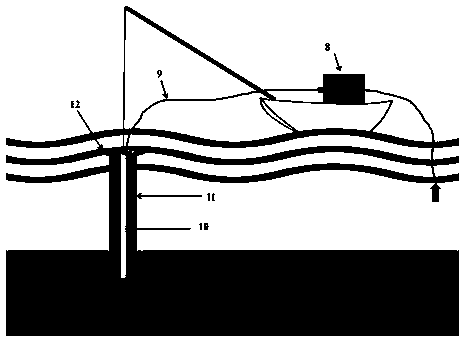
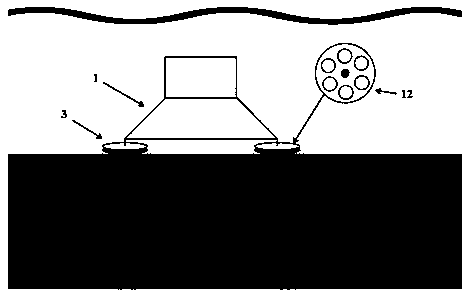
[0038]An in-situ observation system for the bottom boundary layer suitable for shallow water cohesive seabed, the system includes: an upper-layer assembled undisturbed observation unit 1, a lower-layer hydraulic pile foundation unit 2, and a connection unit 3 for connecting and fixing the two; and A positioning unit that helps the positioning of the hydraulic pile foundation unit 2 of the lower floor.
[0039] The upper assembled non-disturbance observation unit 1 is composed of stainless steel solid tubes 7 of different diameters and lengths, instrument buckles, and supporting screws and nuts. The upper instrument layout area can freely splice steel pipes and build fixed supports according to the number, size, orientation, and location of the instruments used, so as to achieve the purpose of multi-instrument, multi-parameter, and full-level observation. The trapezoidal design of the observation area in the lower part ensures that the turbulence of the diameter of the surround...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The in-situ observation system for water and sediment movement in the shallow-water viscous seabed bottom boundary layer (observation system provided in Example 1) has been deployed many times in coastal areas such as Bohai Bay, Laizhou Bay, and Jiaozhou Bay (see Example 1 for the deployment method). Long-term, continuous, and full-level observations of water and sediment processes have been obtained, and a large number of ideal observation data have been obtained under conditions including extreme weather, human activities, etc., and a number of research results have been obtained, which are based on actual observations and verified by observations Practical and universal invention. In the many observation cases that have been implemented, the deepest water depth in the observation area is 15 m, the shallowest point is 5 m, the shortest observation time is 3 days, the longest is 1 year, the maximum number of instruments used is 10 at a time, and the weight of the observ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com