Plateau wet area railway embankment structure and construction method thereof
A technology in areas and plateaus, applied in infrastructure engineering, roads, excavation, etc., can solve problems such as destructive impact, large temperature difference between day and night, and roadbed deformation, so as to save investment, simplify construction procedures, and reduce roadbed deformation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
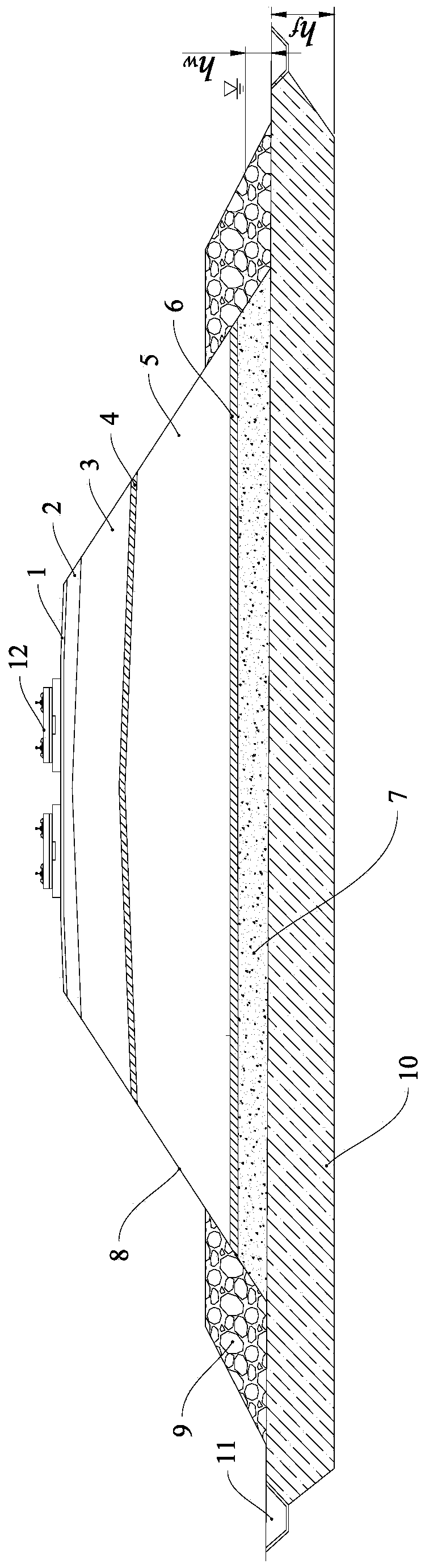
[0032] like figure 1 As shown, a railway embankment structure in a plateau wet area, including a waterproof subgrade surface layer 1, an anti-frost heave subsurface layer 2, a slight frost heave subgrade bottom layer 3, a subgrade bed water-resistant layer 4, a weak frost heave body layer 5, and a base The water-proof layer 6, the water-passing layer 7 and the base replacement layer 10, the surface layer 1 of the waterproof foundation bed is arranged below the subgrade surface, and the lower surface layer 2 of the anti-frost foundation bed is arranged successively below the surface layer 1 of the waterproof foundation bed. The bottom layer 3 of the slight frost heave foundation bed, the water-proof layer 4 of the foundation bed, the weak frost-heave body layer 5, the base water-proof layer 6, the water-passing layer 7 and the base replacement layer 10 .
[0033] The surface layer 1 on the waterproof foundation bed is filled with high-performance asphalt concrete, and its thic...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A construction method for a railway embankment structure in a plateau wet area, constructing the plateau wet area railway embankment structure as described in embodiment 1, comprising the following steps:
[0040] Step 1: Excavate the frost heaving soil within a certain depth range of the base, and the excavation depth is greater than or equal to the maximum freezing depth h in the area f , constructing the base replacement layer 10 in the excavated area;
[0041] Step 2: fill the water-passing layer 7 in layers, and the filling height of the water-passing layer 7 is greater than or equal to the maximum surface water depth h in the area w ;
[0042] Step 3: constructing the base water-resisting layer 6 on the top surface of the water-passing layer 7, and the thickness of the base water-resisting layer 6 is greater than or equal to 10 cm;
[0043] Step 4: Filling the weak frost-heave body layer 5, after the weak frost-heave body layer 5 passes the test, construct the f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com