Low-speed unmanned vehicle obstacle avoidance method and device, equipment and medium
An unmanned vehicle and obstacle avoidance technology, applied in vehicle position/route/altitude control, two-dimensional position/channel control, non-electric variable control and other directions, can solve the problem of uneven obstacle avoidance route and lack of vehicle body size steering angle Changes, difficult obstacles and other problems to achieve the effect of avoiding obstacles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
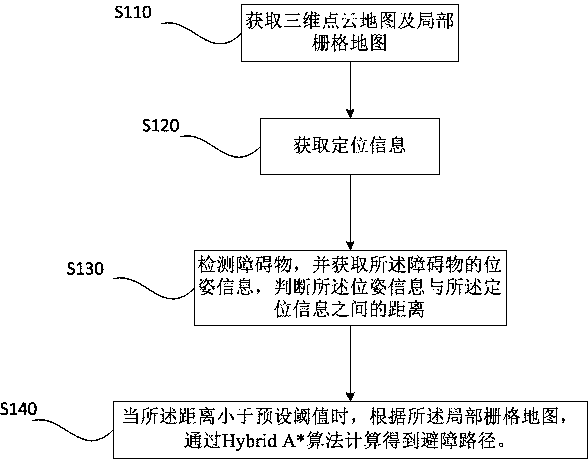
[0058] Embodiment 1 provides a low-speed unmanned vehicle obstacle avoidance method, which aims to achieve global positioning by obtaining a three-dimensional point cloud map of the low-speed unmanned vehicle driving area, and complete the real-time obstacle avoidance path based on the local grid map and the Hybrid A* algorithm. Construct.
[0059] Please refer to figure 1 As shown, a low-speed unmanned vehicle obstacle avoidance method includes the following steps:
[0060] S110. Obtain a three-dimensional point cloud map and a local grid map;
[0061] The specific method for generating the 3D point cloud map in S110 is not specifically limited in this embodiment, and any method that can generate a 3D point cloud map can be used in step S110.
[0062] The local grid map is a map constructed in real time. The local grid map is a low-speed unmanned vehicle as the coordinate system, and the local grid map is constructed. The local grid map is mainly used for the local cost map...
Embodiment 2
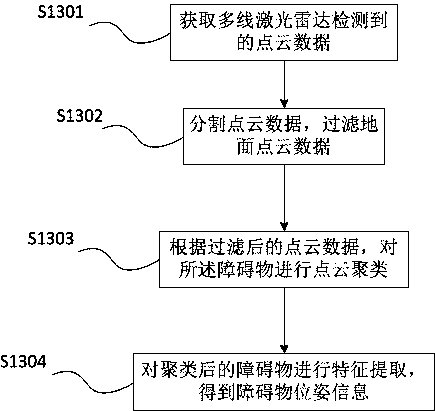
[0085] The second embodiment is carried out on the basis of the first embodiment, mainly explaining and illustrating the status polling mechanism of the low-speed unmanned vehicle.
[0086] Specifically, when detecting obstacles, the following steps are included:
[0087] Polling the vehicle status through the finite state machine mechanism, the vehicle status includes tracking status, stop status and obstacle avoidance status;
[0088] When the state of the vehicle is in the tracking state, control the low-speed unmanned vehicle to drive along the global path point; detect obstacles in real time and obtain the obstacle pose information, and judge the pose information and the positioning information the distance between;
[0089] When the distance between the pose information and the positioning information is less than a preset threshold, switch the tracking state to the stop state;
[0090] After obtaining the obstacle avoidance path calculated by the Hybrid A* algorithm, ...
Embodiment 3
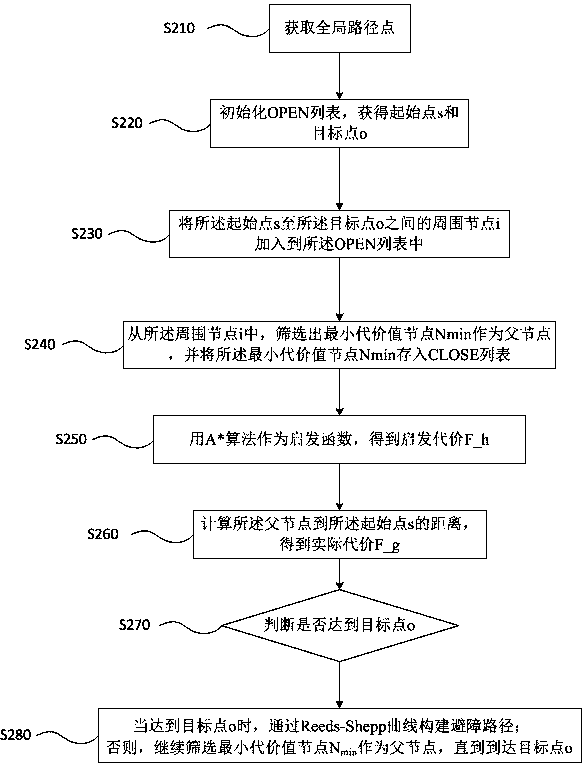
[0103] Embodiment 3 mainly explains and illustrates the specific process of calculating the obstacle avoidance path by the Hybrid A* algorithm.
[0104] Please refer to image 3 As shown, when the distance is less than the preset threshold, according to the local grid map, the obstacle avoidance path is calculated by the Hybrid A* algorithm, including the following steps:
[0105] S210. Obtain a global path point;
[0106] The above-mentioned global waypoint refers to a fixed driving route of a low-speed unmanned vehicle in a specified area, such as a park. The global waypoint can be a path obtained through recording, or a manually set path reference line.
[0107] S220. Initialize the OPEN list, and obtain a starting point s and a target point o from the global path point, and the starting point s and the target point o are in the local grid map;
[0108] The OPEN list in S220 is a list of stored parameters in the Hybrid A* algorithm. The starting point s is the current po...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com