Safety protection method and device for train data
A safety protection device and safety protection technology, applied in the field of train data safety protection methods and devices, can solve problems such as accidents and affecting the safe operation of high-speed trains, and achieve the goals of preventing attacks, protecting integrity and confidentiality, and preventing equipment masquerading Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
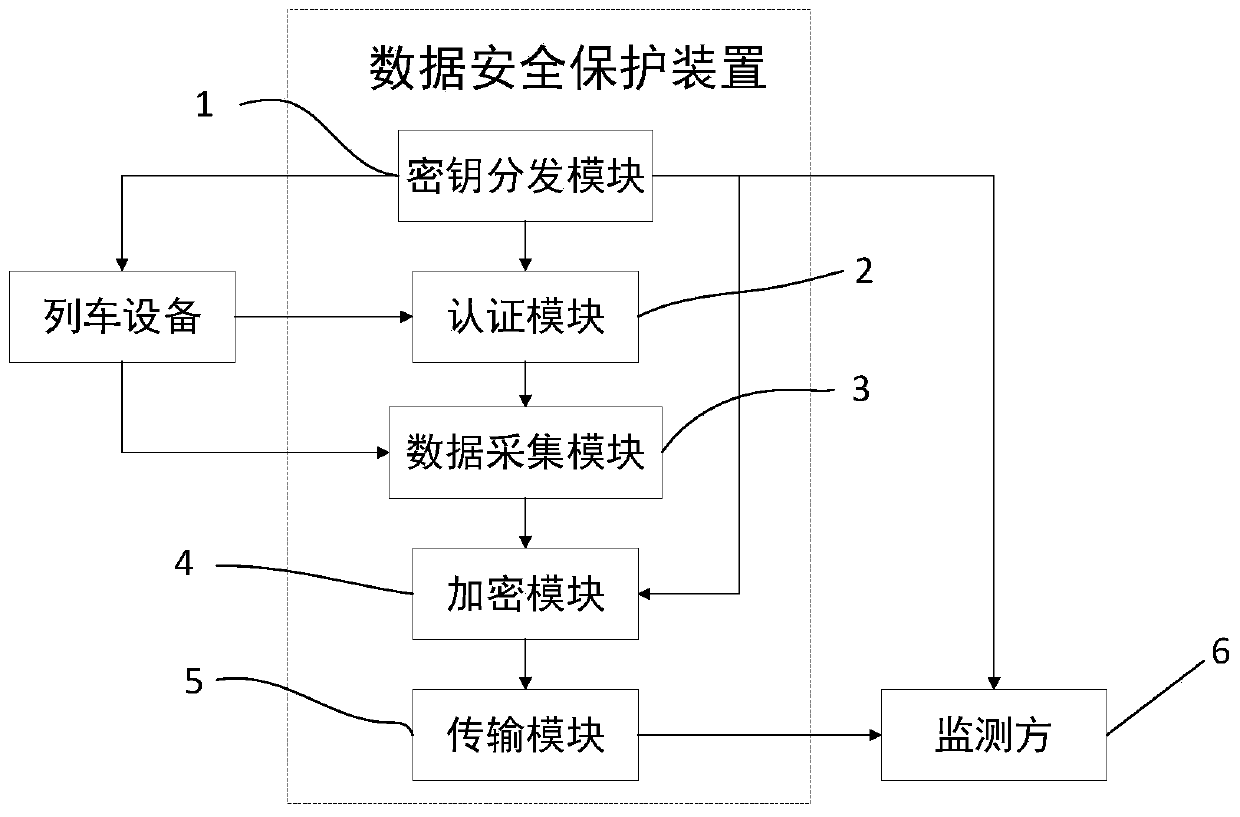
[0045] This embodiment provides a security protection method for train data, including a key distribution step, an encryption step and a transmission step;
[0046]The key distribution step distributes the unique identification number ID and the corresponding key PW to each train that needs to be monitored, and sends the unique identification number ID and the corresponding key PW of each train to the monitoring party;
[0047] In the encryption step, identify its identity according to the unique identification number ID carried by the train, and utilize the key PW corresponding to the train to symmetrically encrypt the train data of the train collected;
[0048] The transmission step is to transmit the encrypted train data to the monitoring party;
[0049] The monitoring party uses the key PW corresponding to the train to decrypt its data and then monitor and view it.
[0050] The above data security protection method protects the train data when it is transmitted to the mon...
Embodiment 2
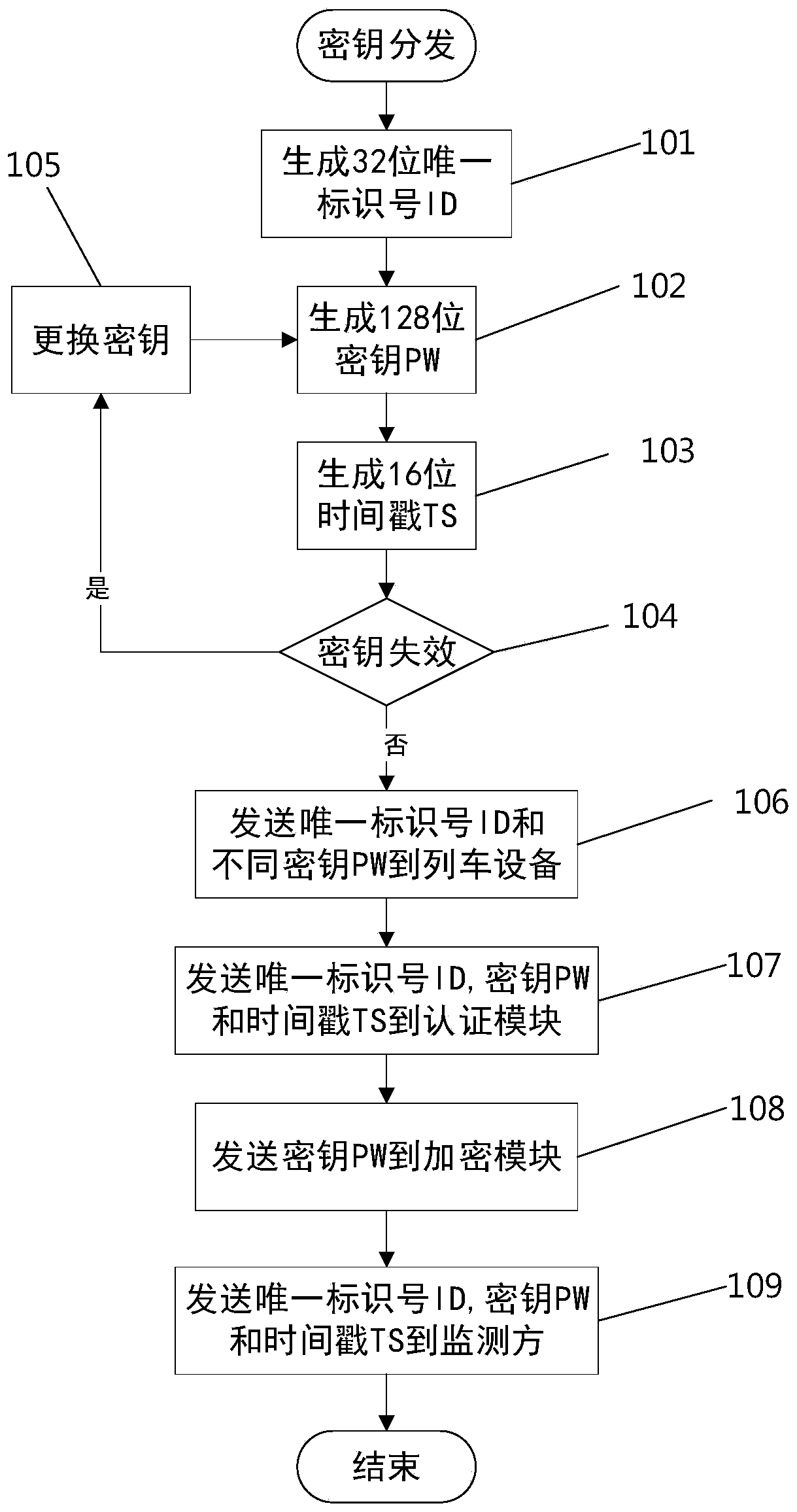
[0052] This embodiment is based on Embodiment 1. In the key distribution step, the key PW distributed to each train is regularly changed, and the unique identification number ID of each train, the corresponding changed key PW and its The time stamp TS is sent to the monitoring party so that the monitoring party can judge whether the key PW is valid.
[0053] Key distribution consists of the following steps:
[0054] Generate a different 32-bit unique identification number ID for each device that needs to be monitored, where the first bit is always 0, the second to eleventh bits are the device type code, and the twelfth to thirty-second bits are the serial number;
[0055] For each unique identification number ID, a pseudo-random sequence is generated through a symmetric encryption algorithm (AES128 encryption algorithm), and a 128-bit key PW is generated. At the same time, the key survival time is set to 30s, and then the key is regenerated;
[0056] Generate a 16-bit time st...
Embodiment 3
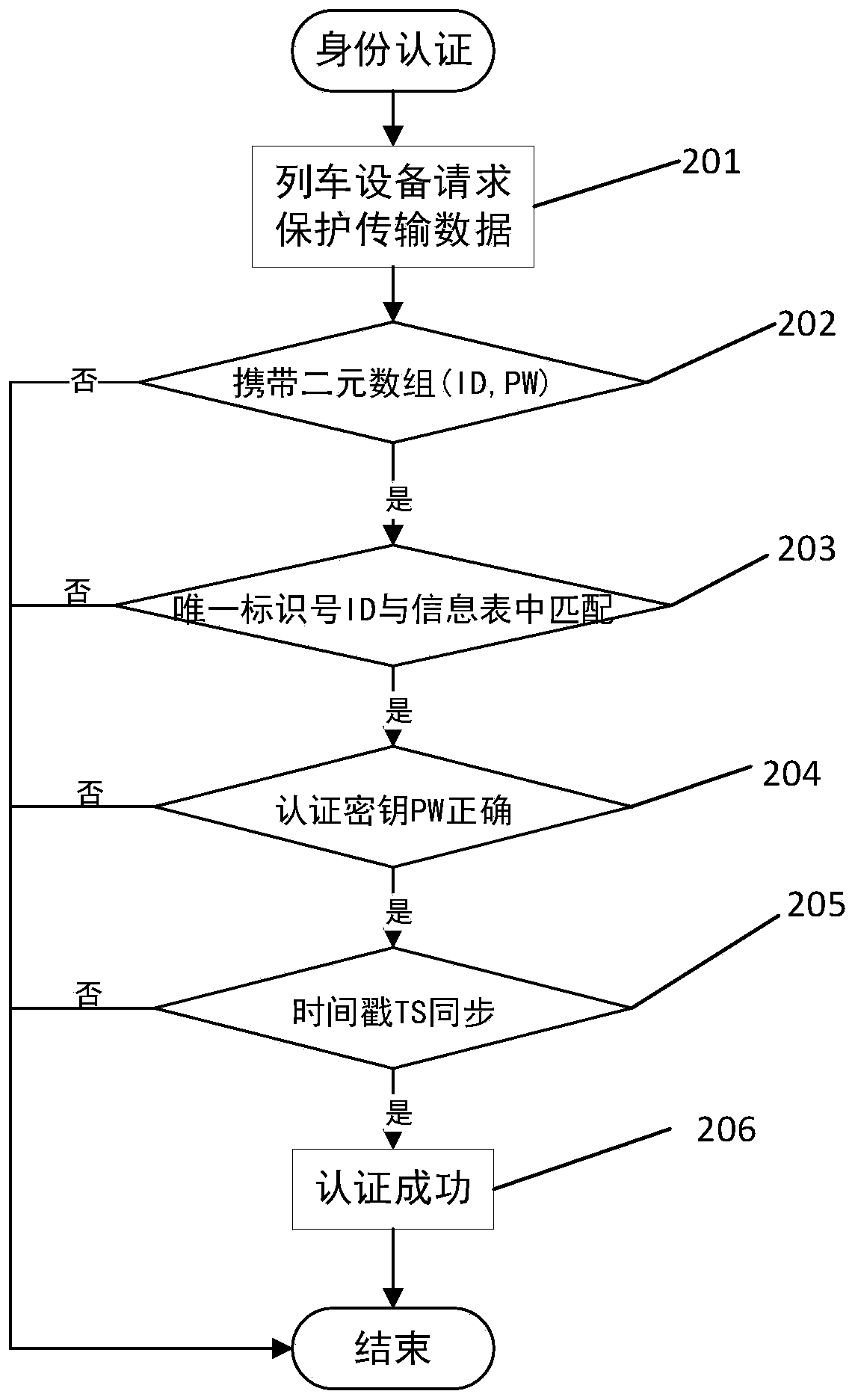
[0059] Present embodiment is on the basis of embodiment 2, and the safety protection method of described train data is characterized in that it also includes an authentication step, which distributes an information table according to the key distribution step, i.e. the ternary array (ID, PW, TS), that is, the unique identification number ID, the corresponding key PW, and the time stamp TS of the key PW, perform security authentication on all nodes that request access to the train network; perform security authentication on any node that requests access to the train network Authentication (identity authentication) includes the following steps:
[0060] Step 1. Determine whether the node carries a binary array (ID, PW). If it does, perform the matching judgment in step 2. If it does not carry it, the node has not passed the authentication;
[0061] Step 2. Determine whether the unique identification number ID carried by the node matches the information table distributed in the k...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com