Three-dimensional model two-dimensional nested placement method based on three-dimensional printing
A 3D model and 3D printing technology, applied in genetic models, genetic rules, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency, low time efficiency, and a large amount of remaining space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
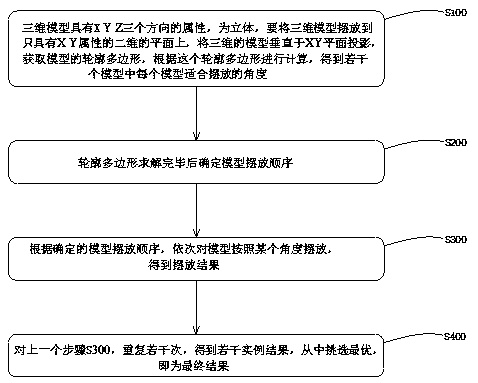
[0044] Such as figure 1 , A method for two-dimensional nesting of three-dimensional models based on three-dimensional printing, including the following steps:
[0045] S100: 3D models, such as .stl format files, have properties in three directions, XYZ, and are three-dimensional. To place the three-dimensional model on a two-dimensional plane with only XY properties is to place the three-dimensional model perpendicular to the XY plane Projection, obtain the contour polygon of the model, calculate according to this contour polygon, and get the angle that each model is suitable for placement (there may be infinitely many, at this time, select several discretely). On how to solve contour polygons, including but not limited to the following:
[0046] (1) According to the information of the points on the 3D model, project all the points of the 3D model to the XY plane, that is, convert the 3D points with XYZ attributes to zero Z value, which is equivalent to plane points with only XY at...
Embodiment 2
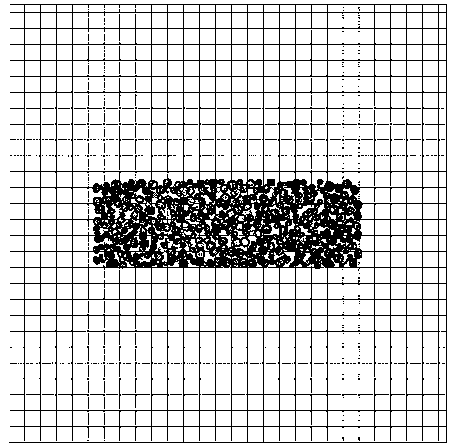
[0072] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the scheme used in step S300 is the minimum X-direction length. The platform size is 550mm*550mm. The result is image 3 display.
Embodiment 3
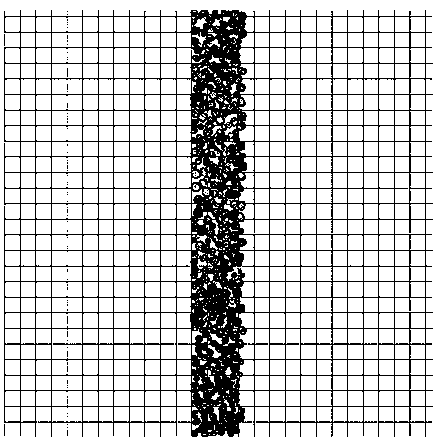
[0074] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the scheme used in step S300 is the minimum length in the Y direction. The platform size is 550mm*550mm. The result is Figure 4 display.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com