Positioning device for guiding bonding of labial brackets and manufacturing method of positioning device
A technology for positioning devices and manufacturing methods, which is applied in the fields of brackets, medical science, and dentistry, and can solve the problems of affecting the bonding accuracy, cumbersome procedures, and increasing costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
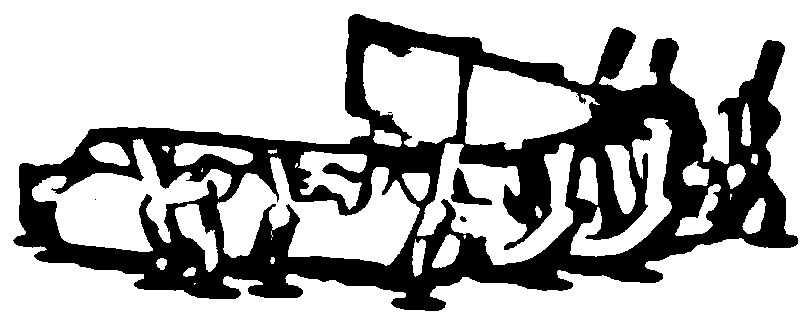
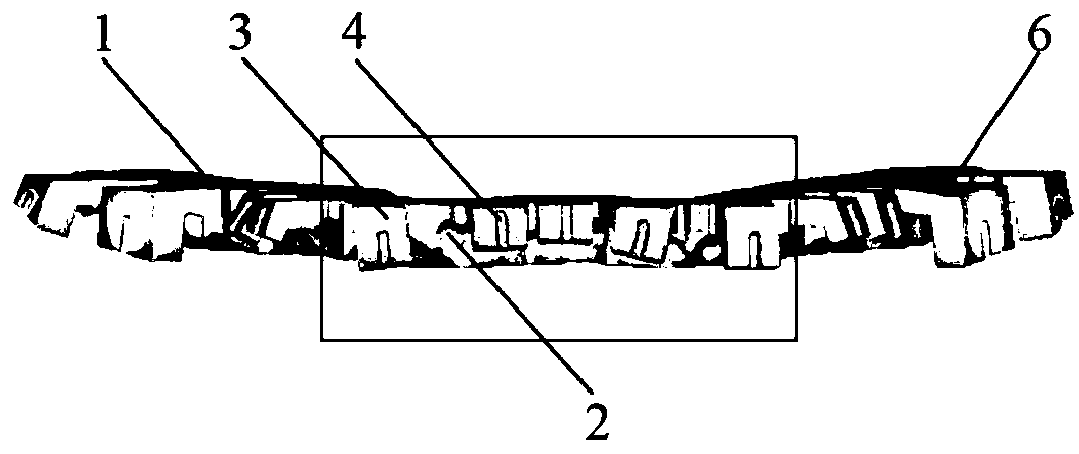
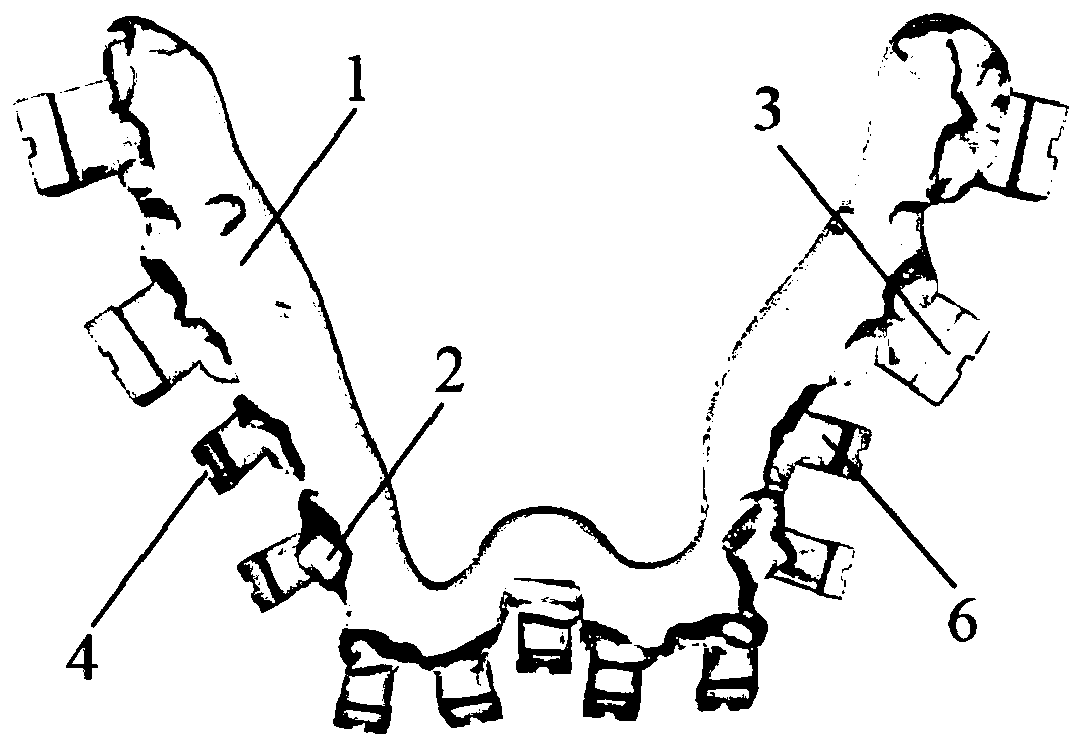
[0065] What this embodiment provides is the positioning device for guiding the bonding of the labial brackets of the mandibular 37-32, 41-47 tooth segments (31 missing teeth), its structure is as follows Figure 2-6 As shown, it is specifically composed of a plywood 1, a marking block 3 and a connecting block 6 that are fixedly connected as one.
[0066] The splint 1 of this embodiment is horseshoe-shaped, matches the shape of the orthodontic patient's gums, and has a thickness of 4 mm. There are occlusal teeth marks 2 matching the teeth of the patient's lower jaw 37-32, 41-47 on the functional surface covering the dentition. The depth is 3mm at the cusp of the 33rd tooth, 2mm at the distal buccal cusp of the 37th tooth, and 2-3mm at the anatomical parts of the rest of the teeth. The non-functional surface is a horizontal smooth surface whose outer edges on both sides match the labio-buccal surfaces of the mandibular teeth and whose inner edges match the palatolingual surfaces...
Embodiment 2
[0071] This example presents a positioning device for guiding the bonding of a single labial bracket of 12 maxillary teeth. Its structure is as follows: Figure 7-9 As shown, it is specifically composed of a plywood 1, a marking block 3 and a connecting block 6 that are fixedly connected as one.
[0072] The difference from Example 1 is: 1) The plywood 1 is oval in shape, with a thickness of 1.5mm, and the depth of the bite marks 2 is 0.5mm. The outer edges on either side of the non-functional surface match the labial and buccal surfaces of the maxillary teeth, and the inner edges match the palatoglossal surfaces of the corresponding maxillary teeth. The splint covers the incisal margin of the 12 maxillary teeth and part of the palatolingual side. 2) There is one marking block 3, which is an inverted trapezoid turned 90°, with a thickness of 1 mm, a length of 2.5 mm, and a width of 2 mm; in this embodiment, there is a guide concave in the middle of the lip and buccal side of ...
Embodiment 3
[0075] This embodiment provides a positioning device for guiding the bonding of the labial brackets of the 16-26 tooth segments of the upper jaw, and its structure is as follows Figure 10-11 As shown, it is specifically composed of a plywood 1, a marking block 3 and a connecting block 6 that are fixedly connected as one.
[0076] The difference from Example 1 is: 1) The functional surface of the splint 1 covering the dentition has an occlusal tooth mark 2 matching the patient's maxillary 16-26 teeth, see Figure 11 , the thickness of the splint 1 is 4mm, the depth of the occlusal tooth impression 2 is 0.8mm at the palatal tip of the 24th tooth, 2.5mm at the incisal edge of the 22nd tooth, and 0.8-2.5mm at the rest of the teeth. The outer edges on either side of the non-functional surface match the labial and buccal surfaces of the maxillary teeth, and the inner edges match the palatoglossal surfaces of the corresponding maxillary teeth. The splint covers the incisal edge of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com