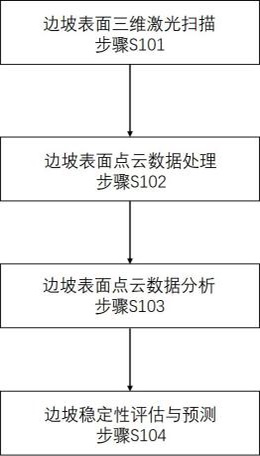
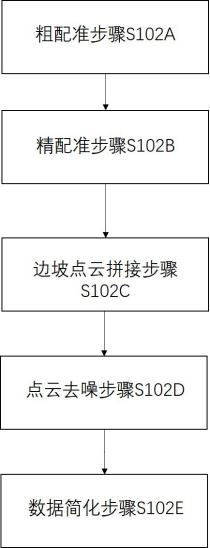
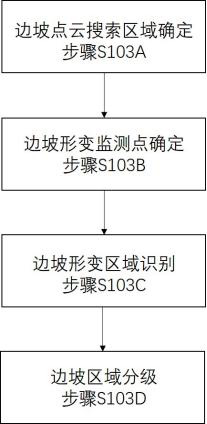
Slope deformation three-dimensional monitoring system and method based on multiple sensors
A multi-sensor, slope technology, applied in instruments, measuring devices, image data processing and other directions, can solve the problems of difficulty in extracting local error areas, low automation, large extraction errors, etc., and achieve accurate analysis and prediction of stability status. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be described in more detail below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention.
[0033] It should be noted that: in the drawings, the same or similar symbols represent the same or similar elements or elements with the same or similar functions. The described embodiments are part of the embodiments of the present invention, but not all of the embodiments. In the case of no conflict, the embodiments in the present application and the features in the embodiments can be combined with each other. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
[0034] In this document, "first", "second" and so on are only used to d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com