Unbalance parameter identification method suitable for polyhedral rotor
A technology of balance parameters and identification methods, applied in the field of unbalance parameter identification of multi-faceted rotors, can solve problems such as difficulty in practical application of the method, increase computational complexity, unbalance solution accuracy, etc., so as to increase the unbalance identification accuracy, solve the Pathological problems, easy-to-use effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
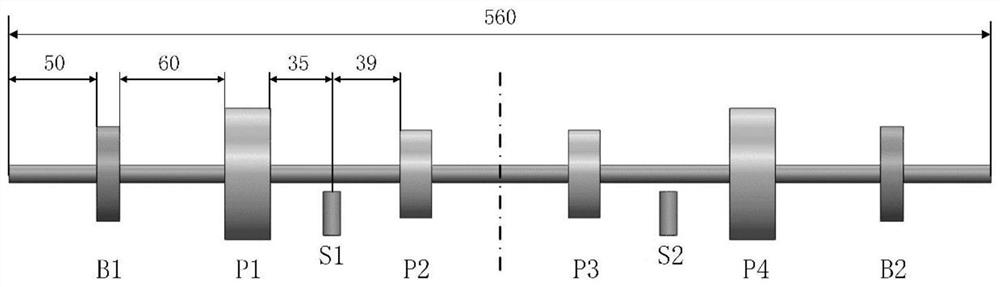
[0036] Such as figure 1 As shown, the rotor model used in the dynamic balance experimental system of the embodiment is a single-span four-balance surface double-measuring-point rotor model. The total length of the rotor is 560mm, and each 8mm shaft segment is divided into a unit, which is divided into 70 units from left to right; B1 and B2 are rolling bearings located at nodes 8 and 65, P1, P2, P3 and P4 are weighted balance surfaces located at nodes 18, 30, 42 and 56, S1 and S2 are vibration sensors, and the measurement system Unbalanced response, located at node 24, node 48.
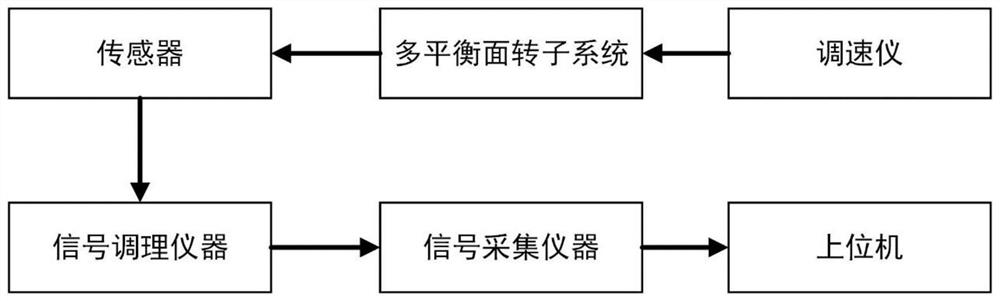
[0037] Such as figure 2 As shown, the rotor system experiment platform of the embodiment is composed of motor speed controller, multi-balance rotor system, sensors, signal pre-processor, signal acquisition instrument, host computer, etc.; in the experiment, the multi-balanc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com