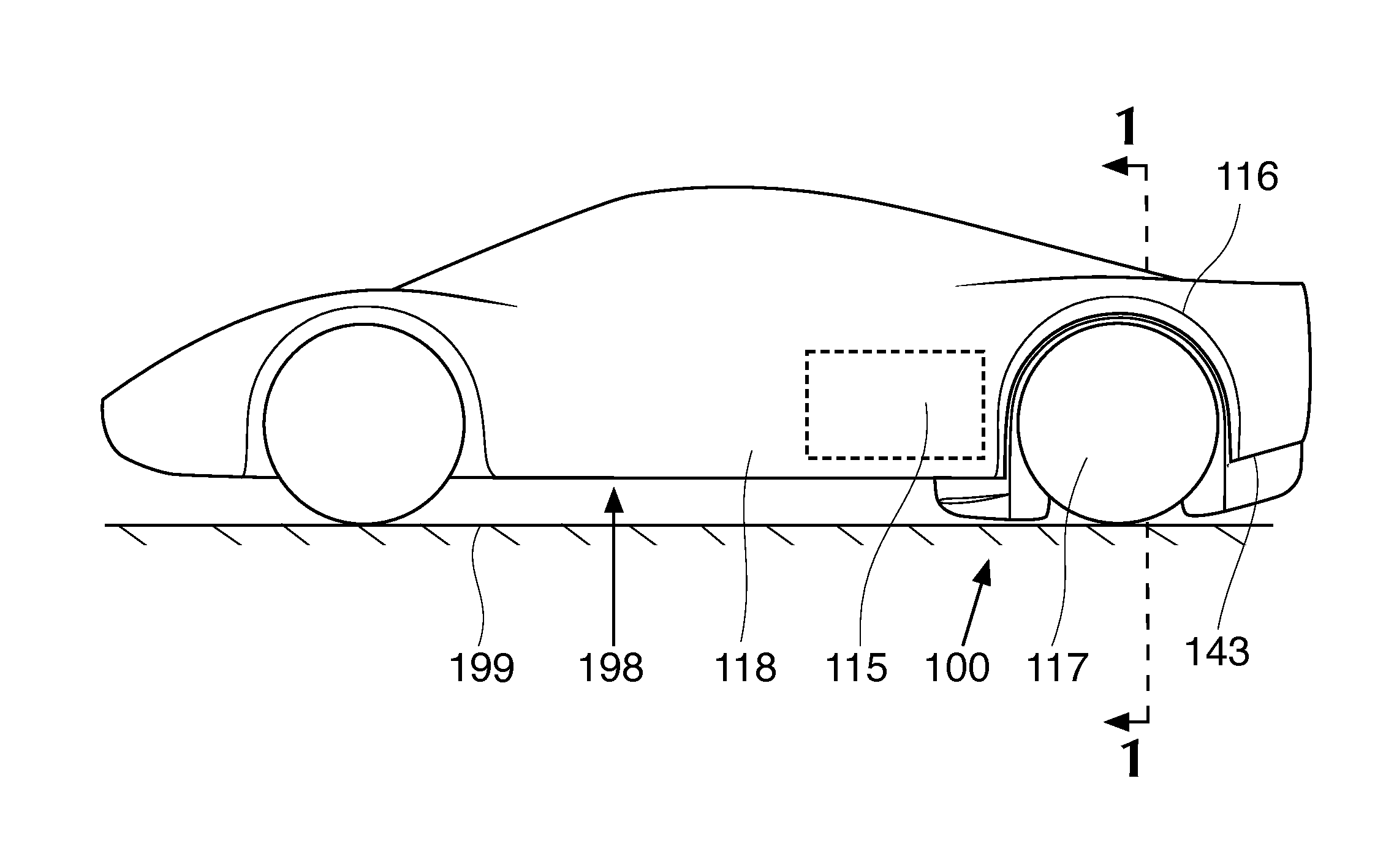
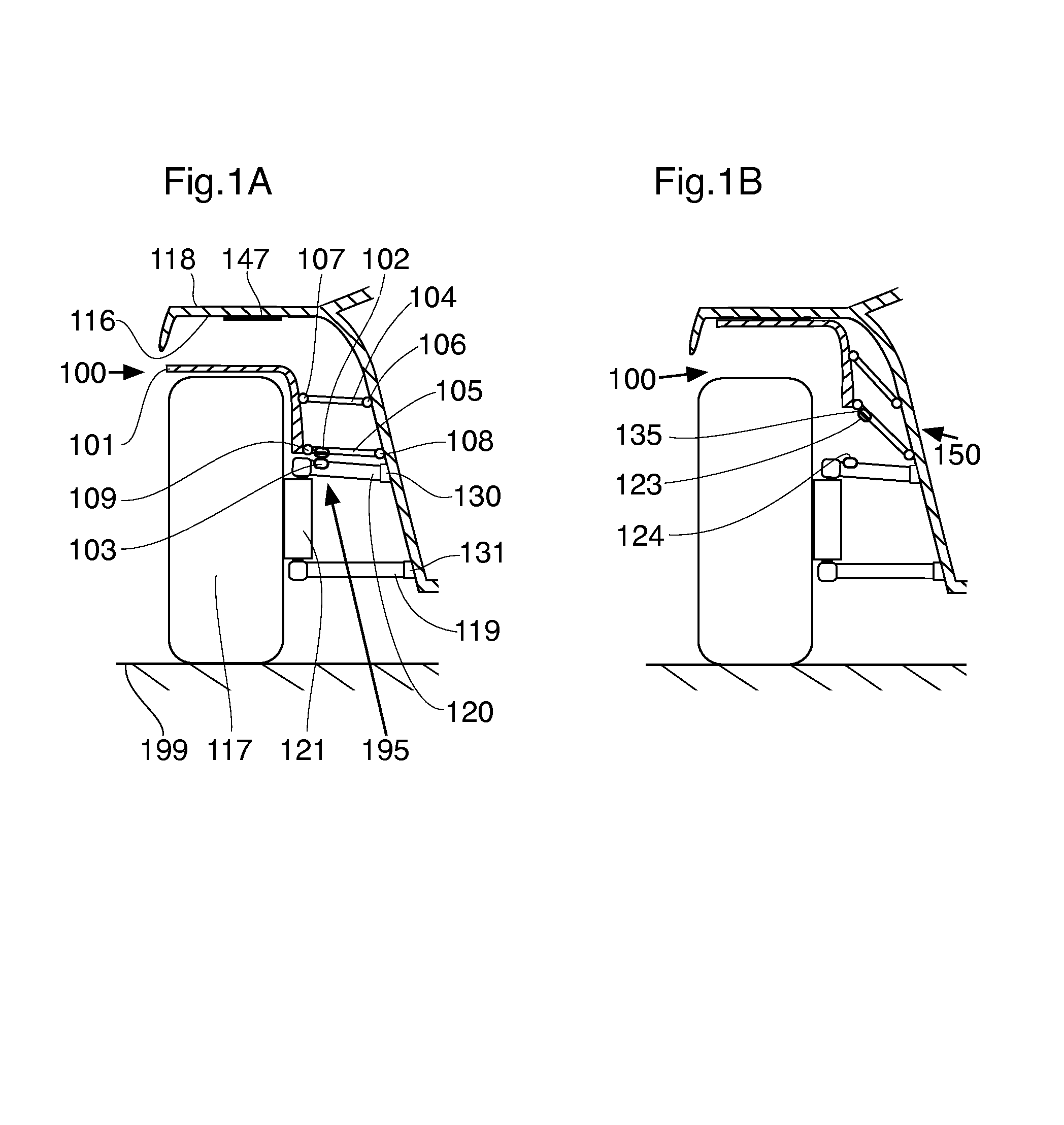
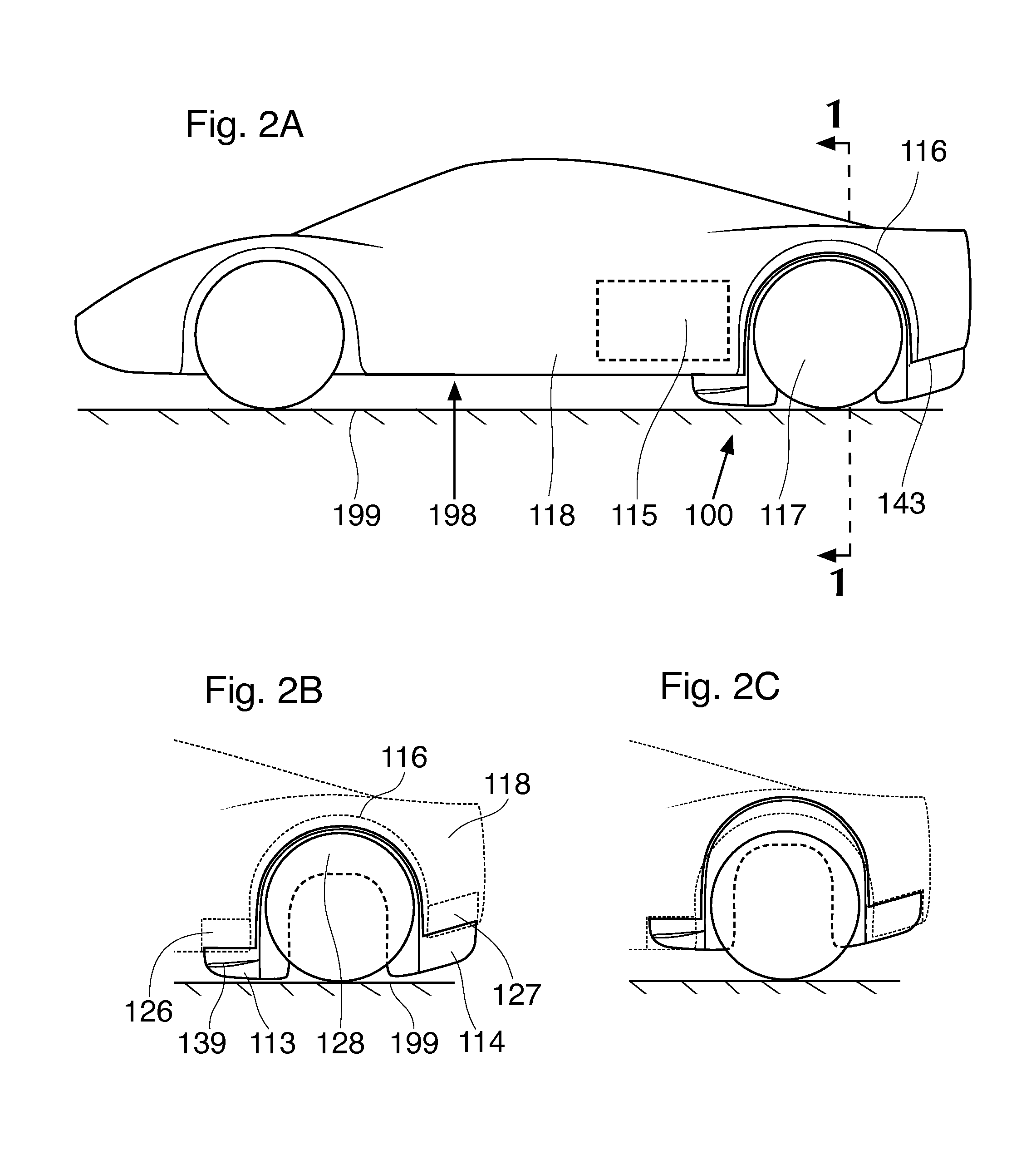
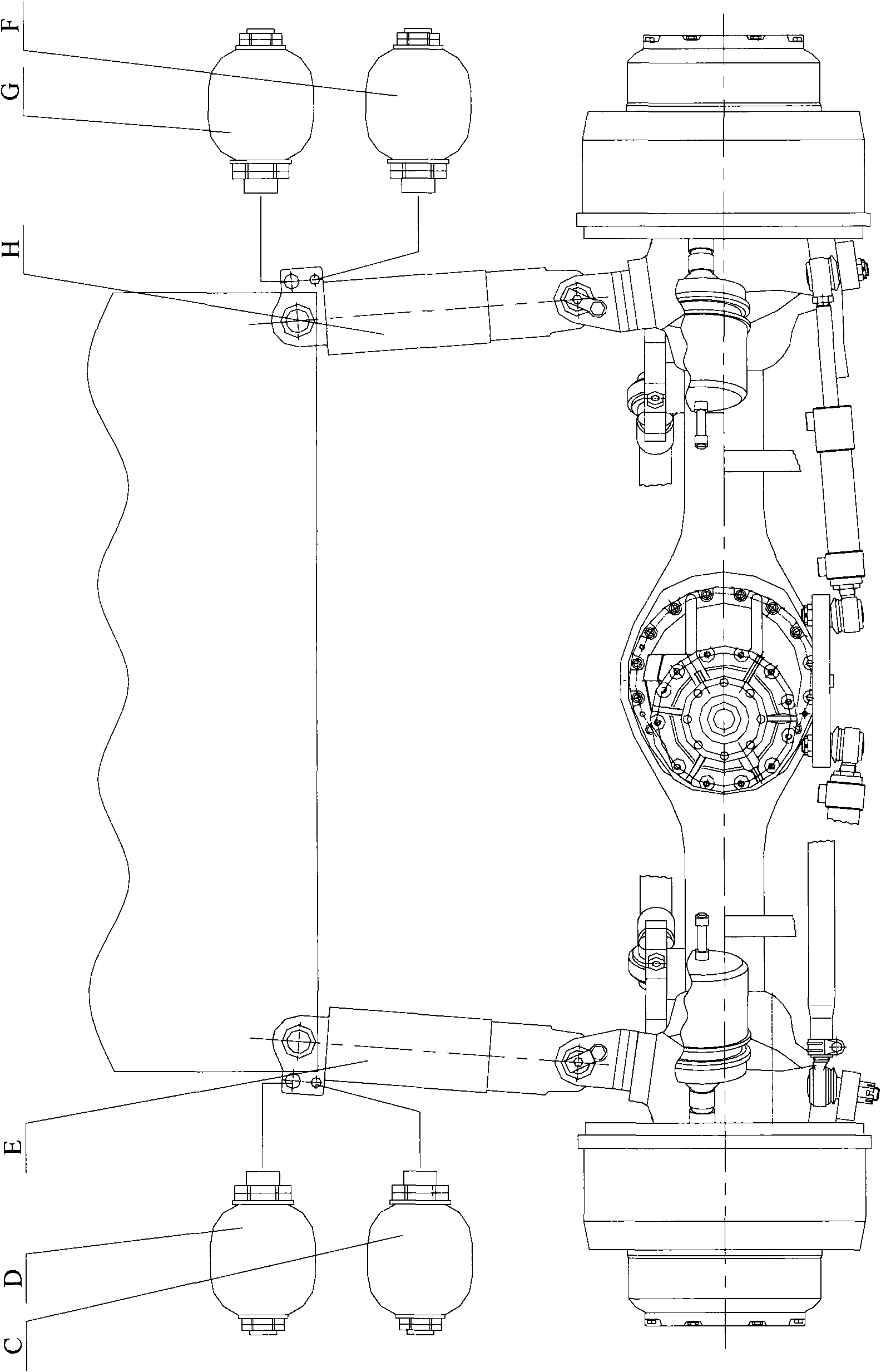
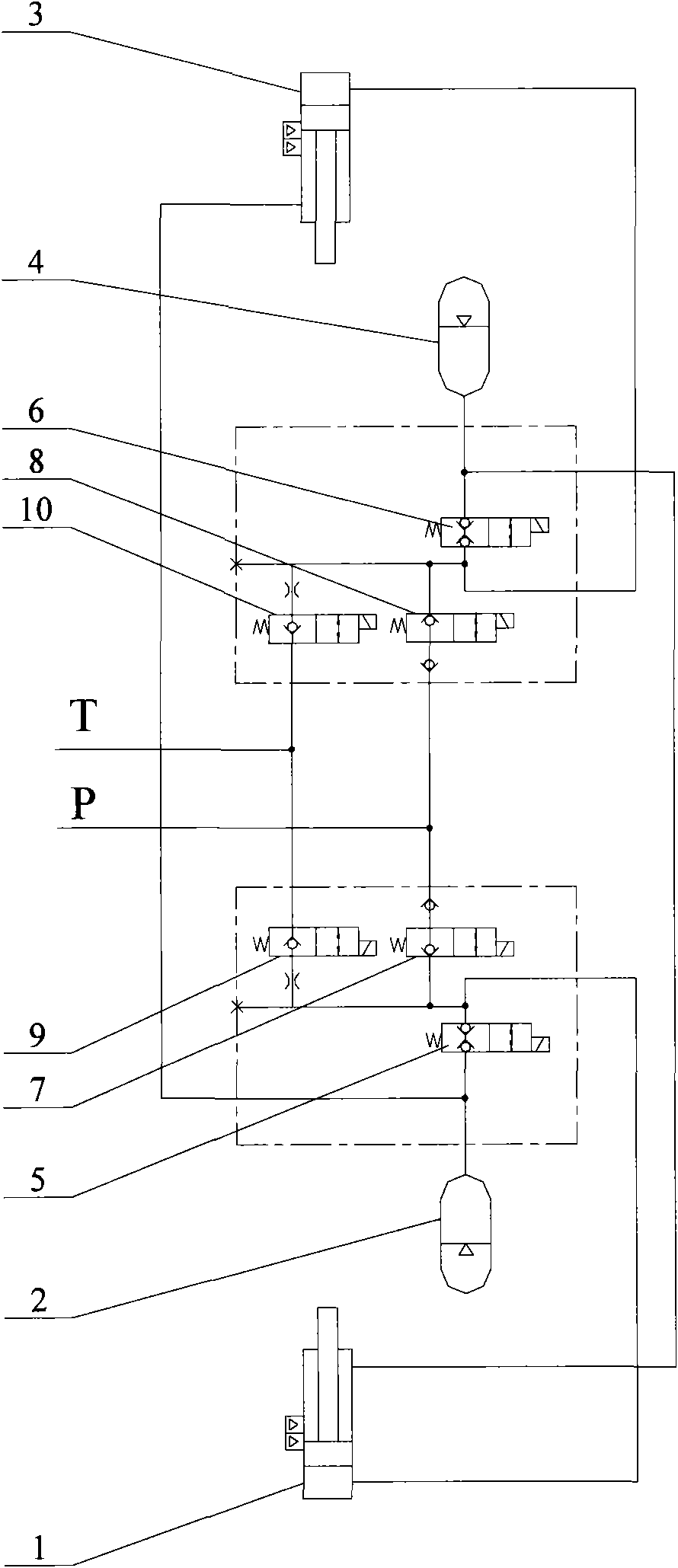
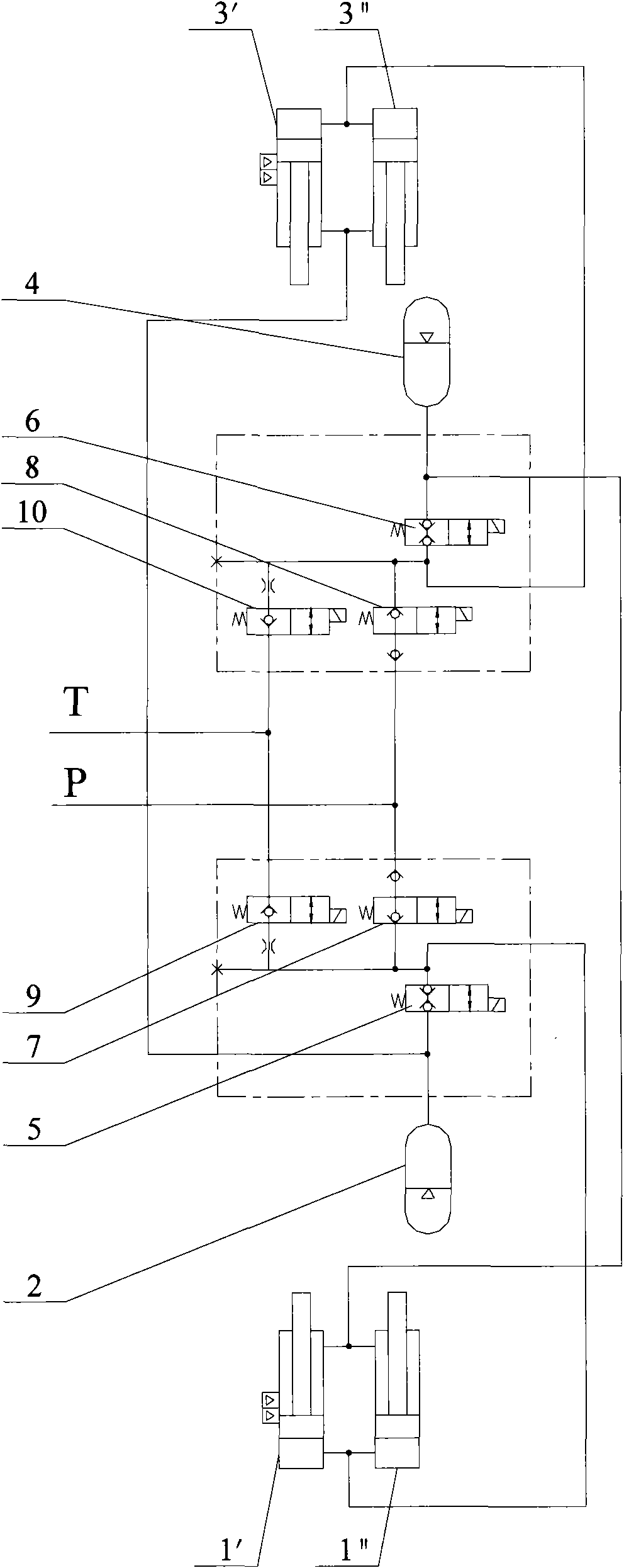
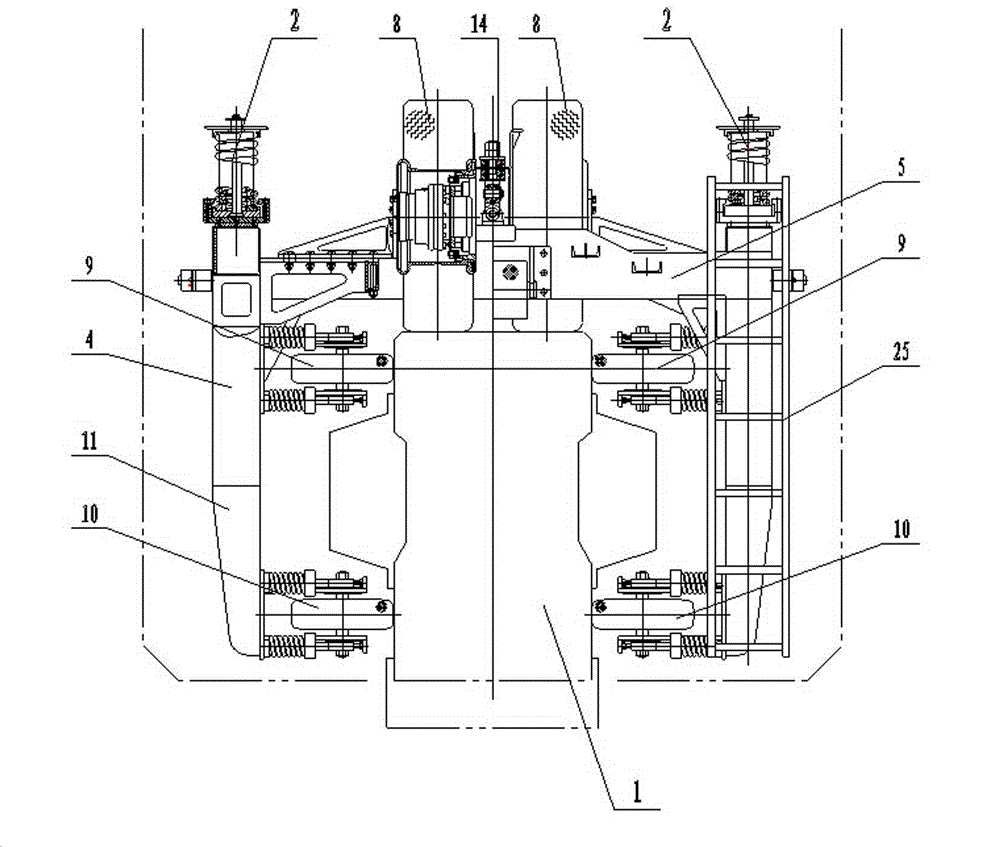
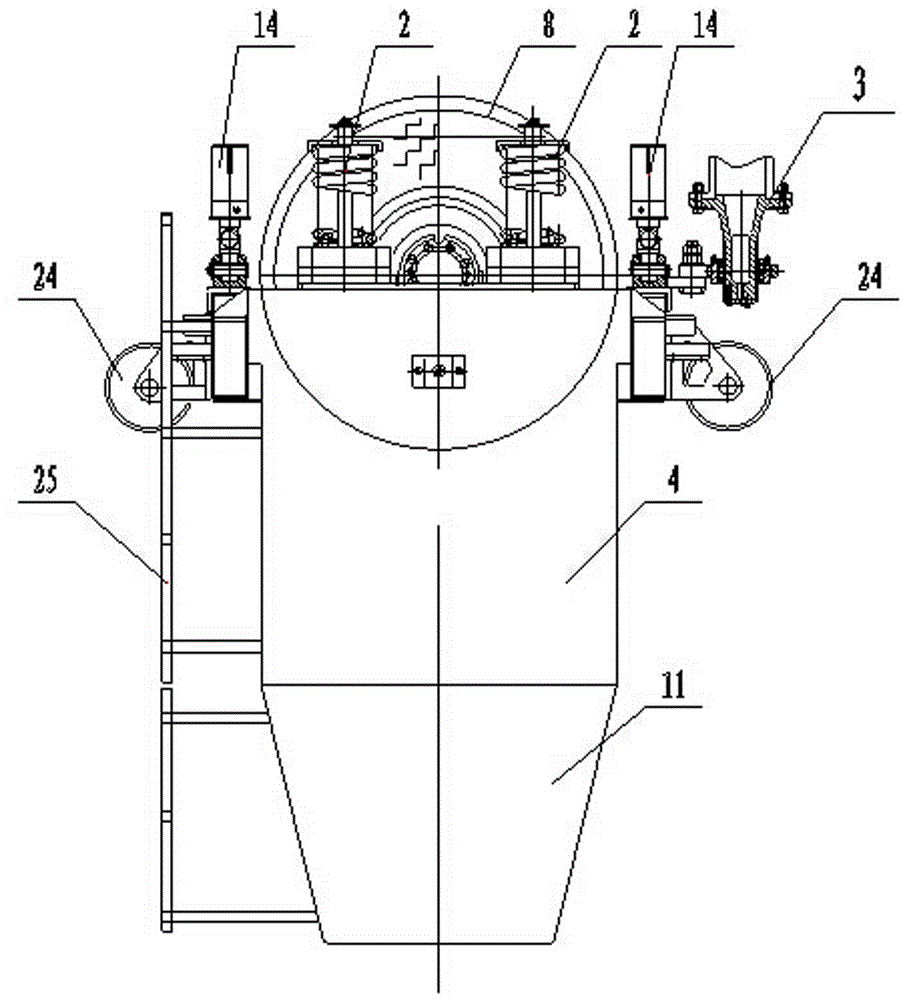
Patents
Literature
4194 results about "Suspension (vehicle)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
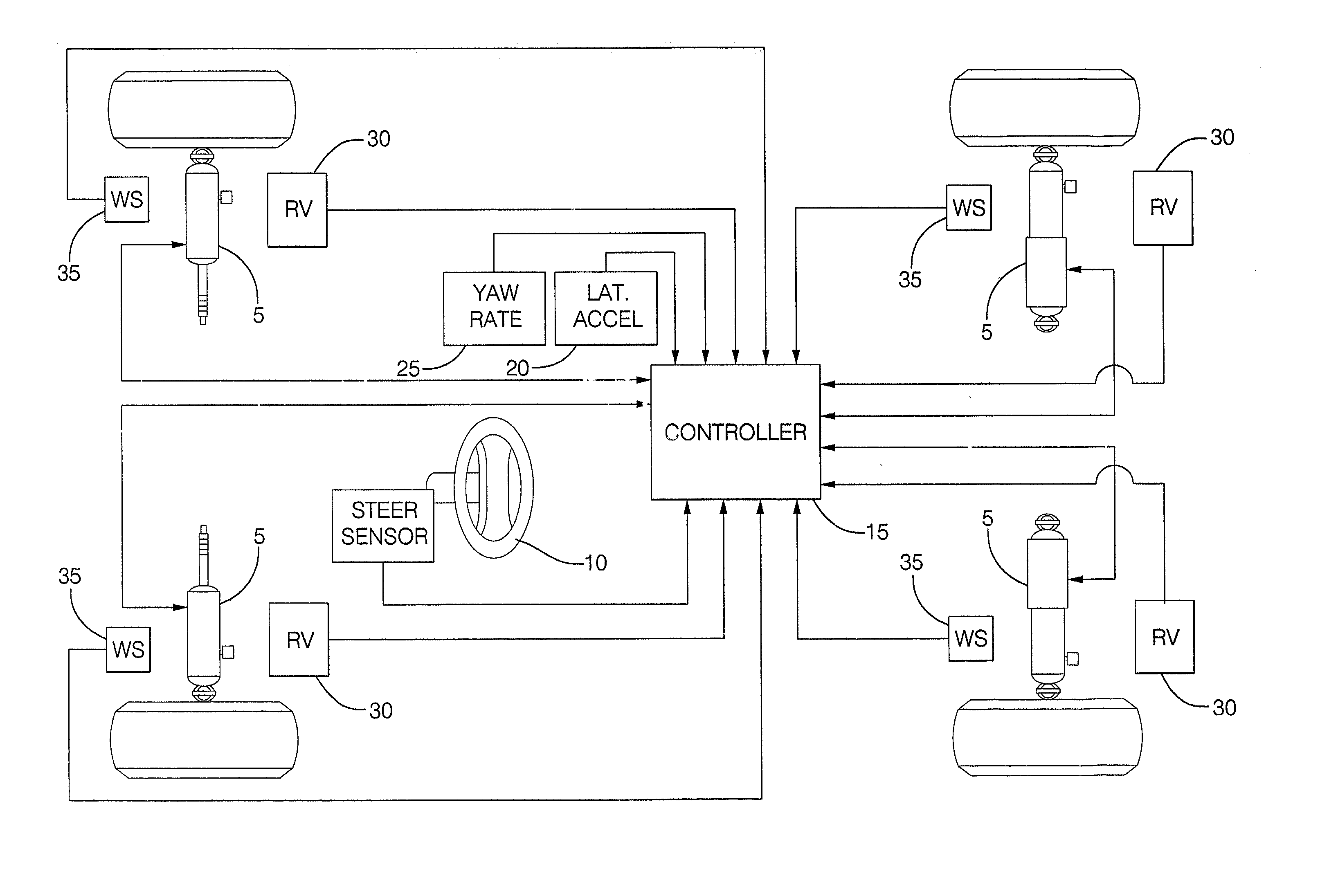
Suspension is the system of tires, tire air, springs, shock absorbers and linkages that connects a vehicle to its wheels and allows relative motion between the two. Suspension systems must support both road holding/handling and ride quality, which are at odds with each other. The tuning of suspensions involves finding the right compromise. It is important for the suspension to keep the road wheel in contact with the road surface as much as possible, because all the road or ground forces acting on the vehicle do so through the contact patches of the tires. The suspension also protects the vehicle itself and any cargo or luggage from damage and wear. The design of front and rear suspension of a car may be different.
Vehicle control
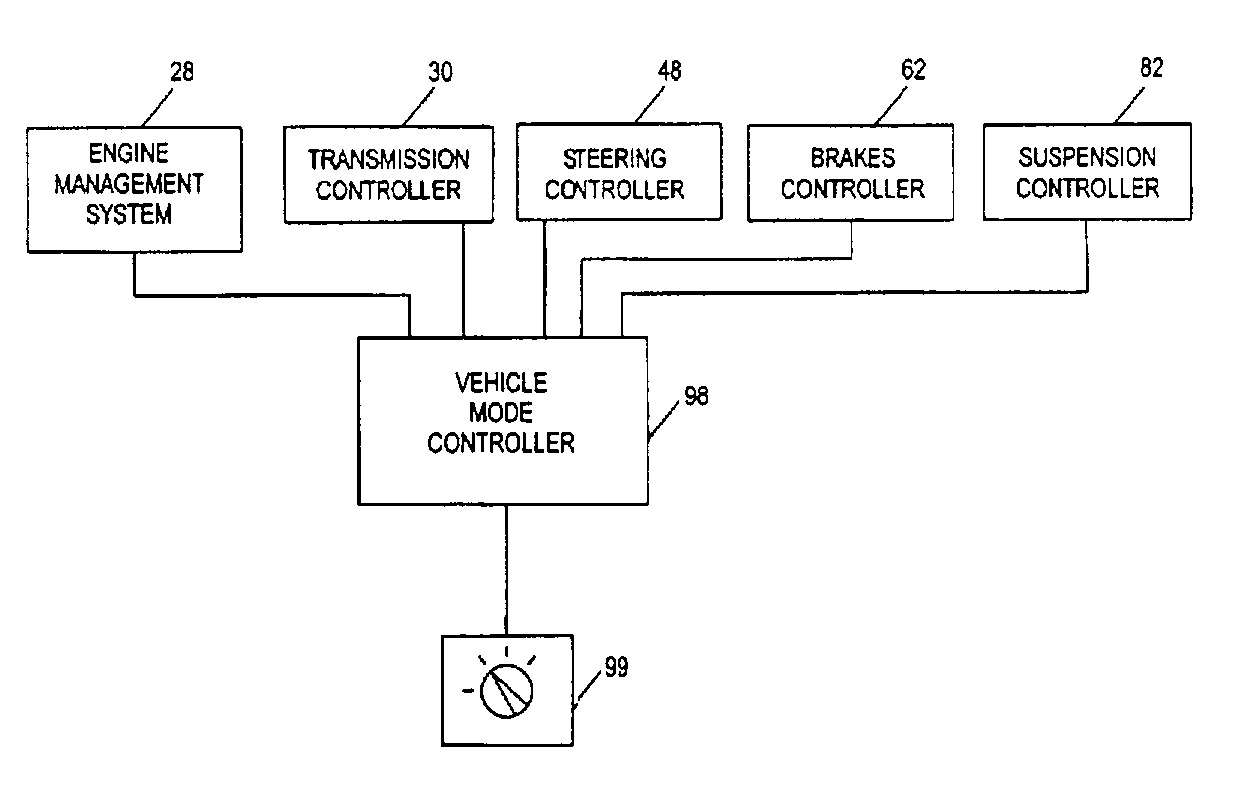
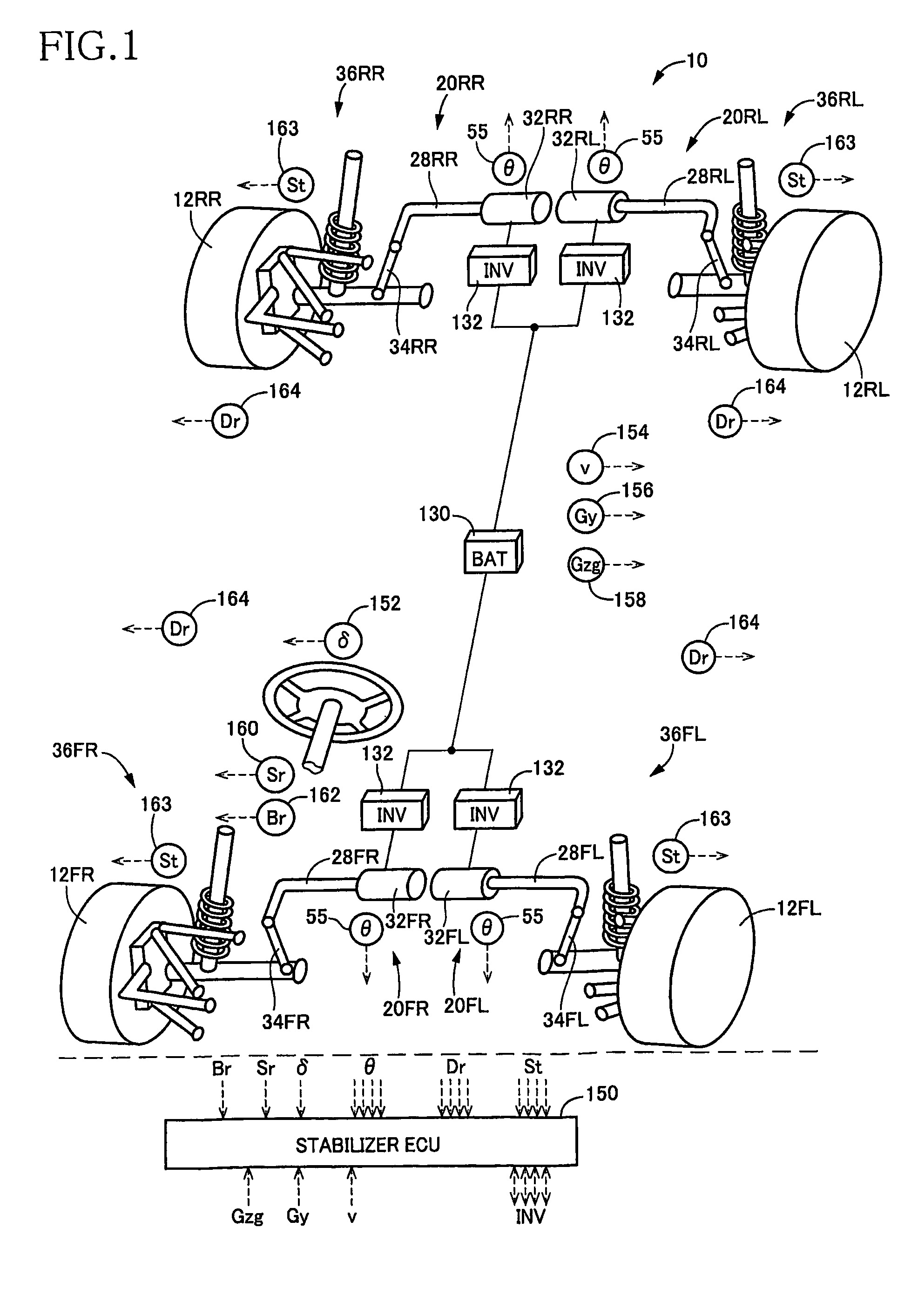
ActiveUS7349776B2Improved vehicle controlEasy to controlBrake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsControl systemMode control
A vehicle control system has a plurality of subsystem controllers including an engine management system 28, a transmission controller 30, a steering controller 48, a brakes controller 62 and a suspension controller 82. These subsystem controllers are each operable in a plurality of subsystem modes, and are all connected to a vehicle mode controller 98 which controls the modes of operation of each of the subsystem controllers so as to provide a number of driving modes for the vehicle. Each of the modes corresponds to a particular driving condition or set of driving conditions, and in each mode each of the functions is set to the function in mode most appropriate to those conditions.
Owner:JAGUAR LAND ROVER LTD
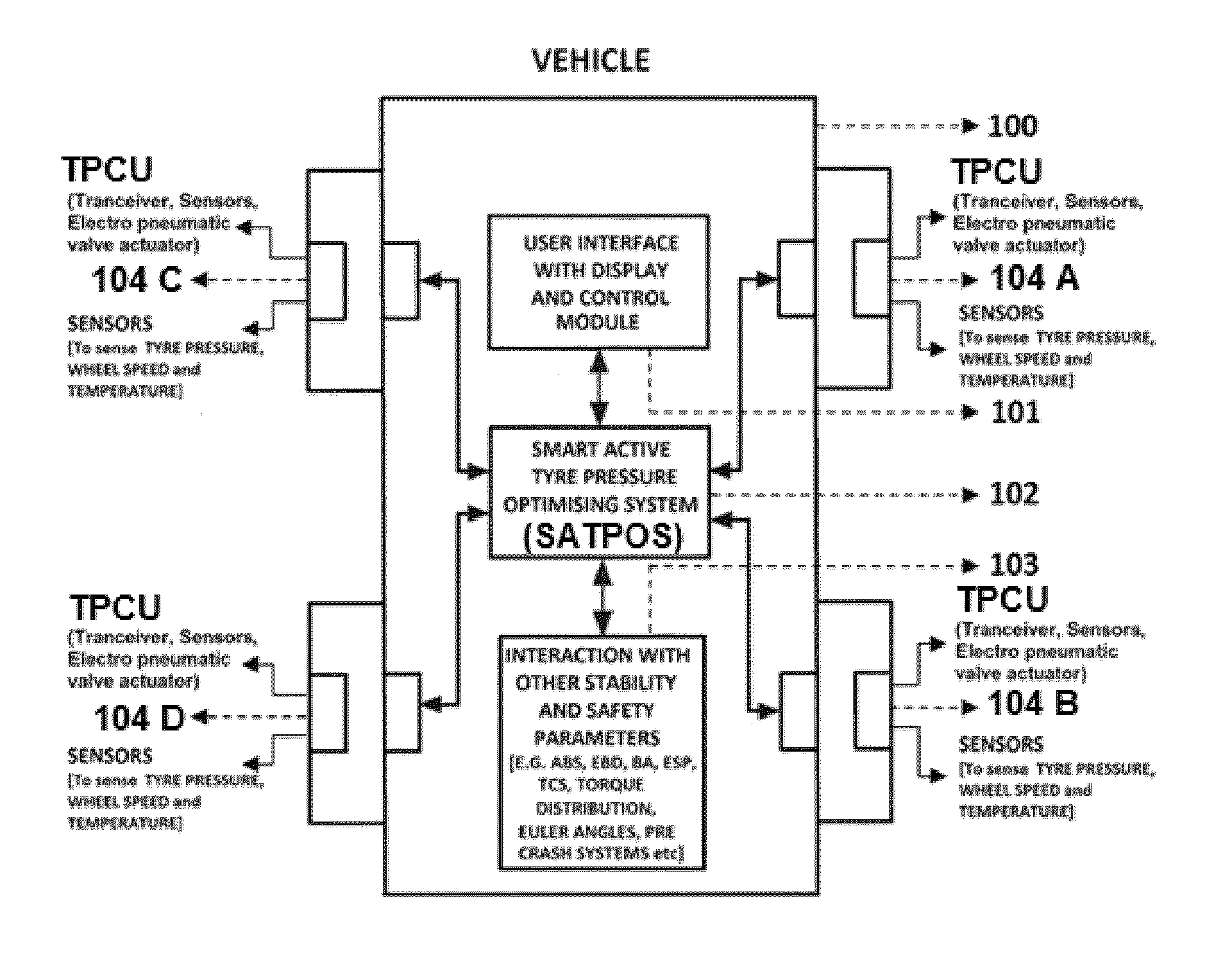
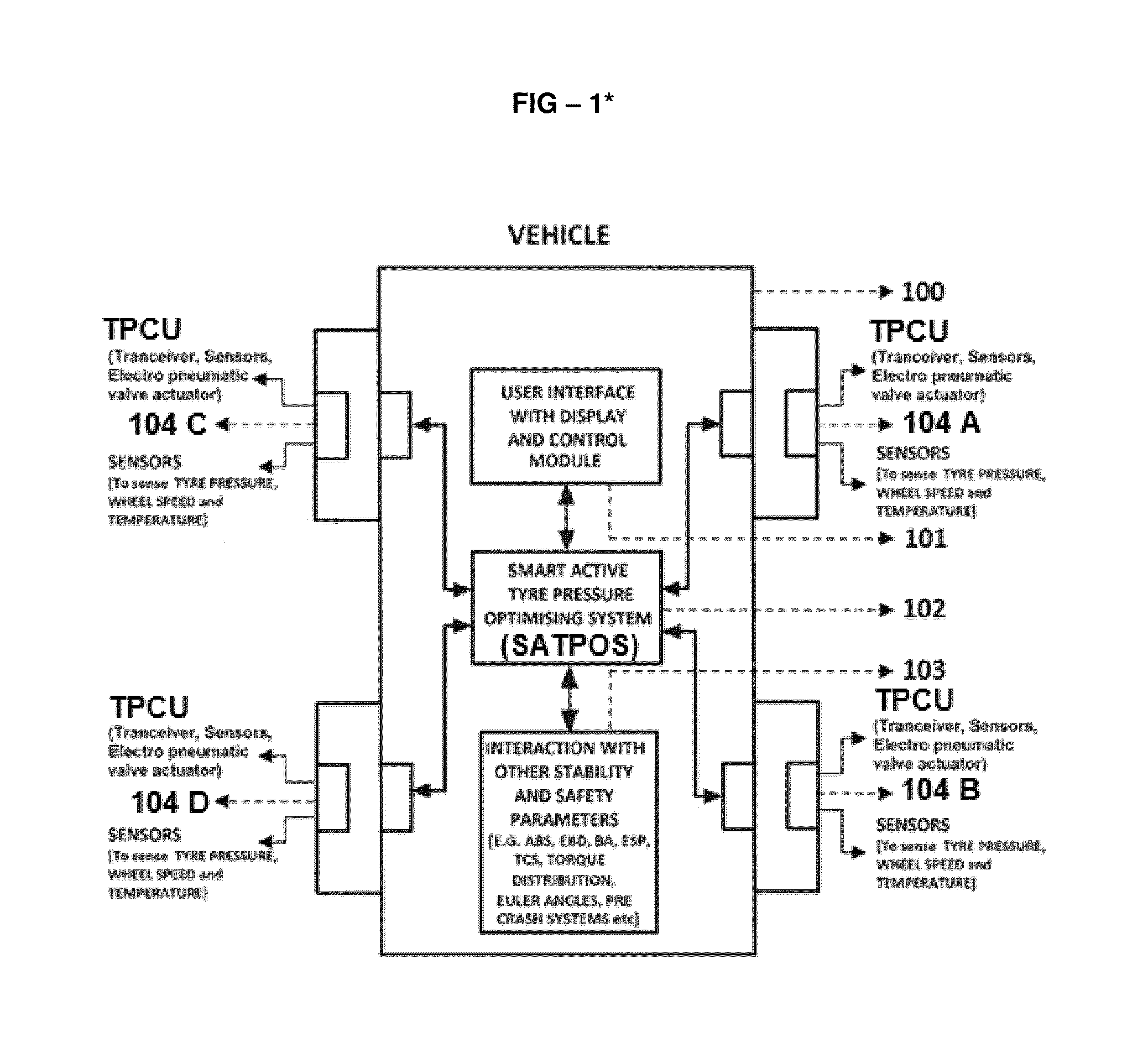
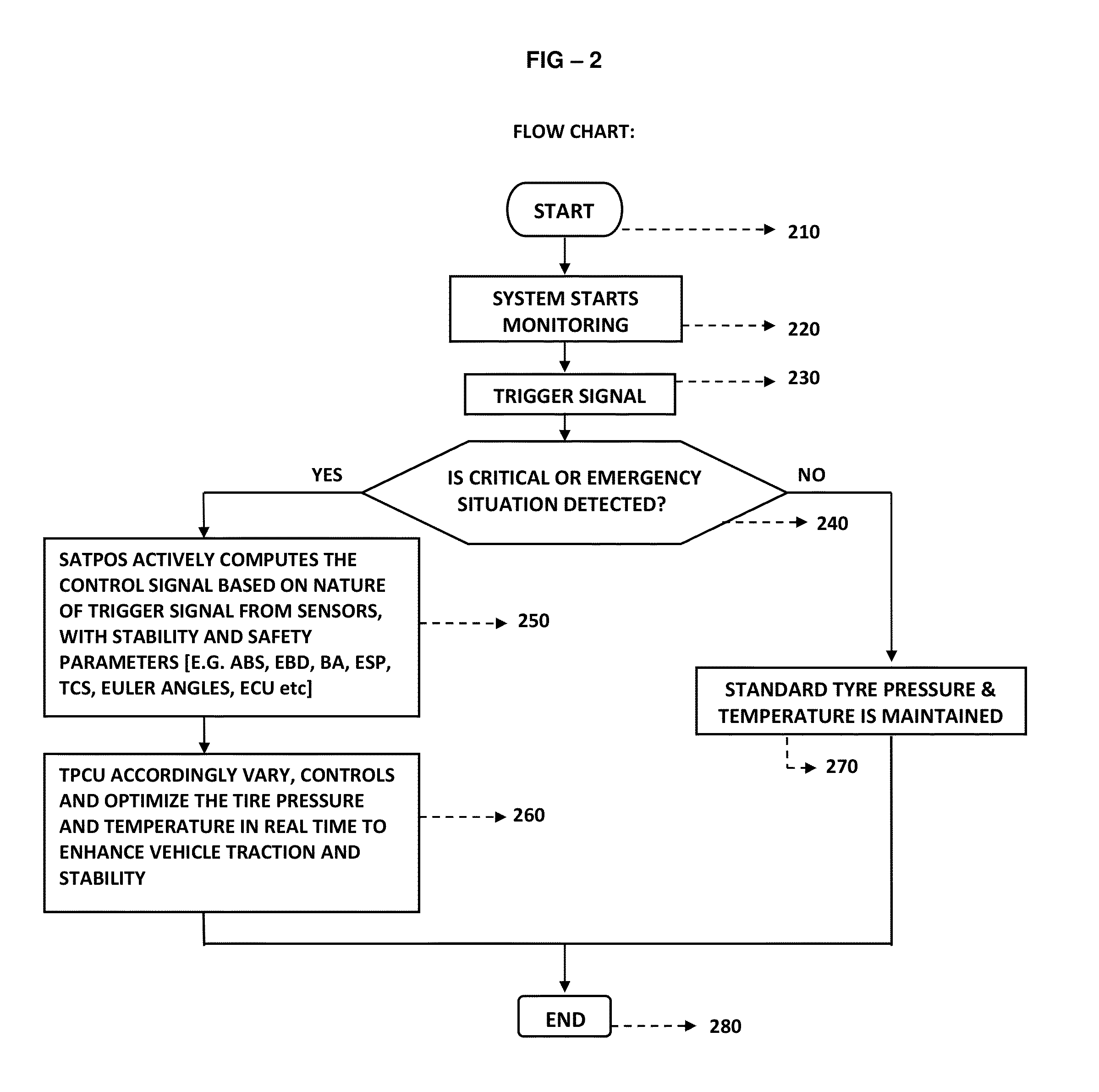
Smart active tyre pressure optimising system
ActiveUS20150005982A1Improve stabilityGreat tractionBraking element arrangementsInflated body pressure measurementSafe drivingMoisture
Smart Active Tyre Pressure Optimising System [TPOS]102 is a highly time sensitive design and technique that acts instantaneously in sensing and controlling the tire pressure particularly in imminent and inevitable critical driving situations to reduce emergency & high speed breaking distance, mitigate—loss of traction, hydroplaning, roll over, loss of stability, over & under steering, break failure, loss of control due to puncture by smartly sensing, perform context aware computing and directing the Tyre Pressure Control Units [TPCU]104 to instantaneously control the tyre pressure in right time with right pressure on right tyres thereby actively controlling the footprint and sidewall deformation rate to enhance traction & stability simultaneously sustaining drivability or steerability ultimately to avoid or reduce the impact of collusion and overcome or mitigate critical situations for protecting the vehicles, occupants, pedestrians and other objects around or on the way; also according to design, configurations and scenarios the system instantaneously optimises the tyre pressure on all tyres for further safe driving till next restoration else restores the pressure to optimum preset value utilising inbuilt reservoir or other external restoration systems immediately after the vehicle overcomes the critical situation to continue with safe and comfortable driving. In critical situations TPOS performs sensing, pre computing, current computing for controlling the tire pressure during critical situation, post computing to optimise tire pressure after overcoming accordingly. TPOS 102 utilise smart and adaptive closed loop processing algorithm with predetermined and tested lookup table to instantaneously check and compare the effects between predetermined and tested real world scenarios to the actual real world scenarios for actively sensing, computing and controlling the tire pressure accordingly to mitigate the critical situations. The controlling of tyre pressure is computed mainly based on parameters comprising of sensor system, vehicle safety and stability systems, nature of breaking & break force distribution, tires upper & lower cut-off pressure values, sensing reservoirs and tires internal & external pressure, temperature, moisture, humidity, wheel & tire specifications, vehicle & wheel speed, acceleration & deceleration, vehicle orientation & axial rotation, transverse motion & lateral acceleration, tires position or angle of attack, load & torque distribution, tire traction, steering position, cornering effects, change in Centre of gravity, over & under steering, hydroplaning, sensing road conditions, etc and to further enhance the efficiency, the system interoperates with vehicles existing safety and stability systems like ABS, EBD, ESC, TCS, Rollover mitigation systems, ECU, BA, Precrash systems, suspension & vertical dynamics, radar assisted auto breaking, cruise control system, aerodynamics & airbrakes etc. Other aspects of present invention are controlling the tire temperature according to environmental temperature, moisture and humidity thereby to enhance traction and vary tire pressure according to change in centre of gravity & load, driving modes—comfort, standard and sports modes.
Owner:MUTHUKUMAR PRASAD
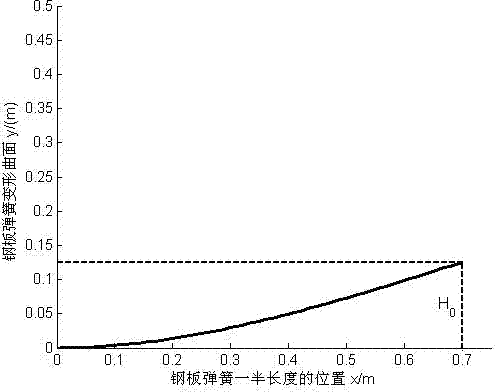
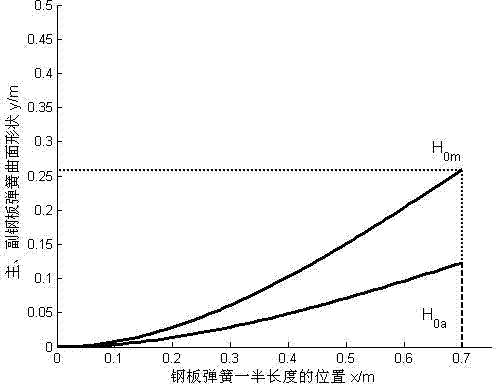
Analytical design method of camber and surface shape of automobile plate spring
InactiveCN102734364AAccurate and reliable designAvoid trial and error and modificationLeaf springsAutomotive engineeringSurface shape
The invention relates to an analytical design method of a camber and a surface shape of an automobile plate spring, belonging to the field of automobile springs. According to the invention, the performances of a suspension are influenced by the camber and the surface shape of the plate spring, but an accurate design method for the camber and the surface shape is not provided. According to the performance requirements of the automobile suspension on the plate spring, the analytical design method of the camber and the surface shape of the automobile plate spring can be established by using elastic mechanical theory. The analytical design method of the camber and the surface shape of the automobile plate spring, provided by the invention, is simple and reliable, and requirements of precise design of the thickness of the automobile plate spring can be satisfied by utilizing the analytical design method. The analytical design method can be used for design of the vehicle suspension plate spring.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
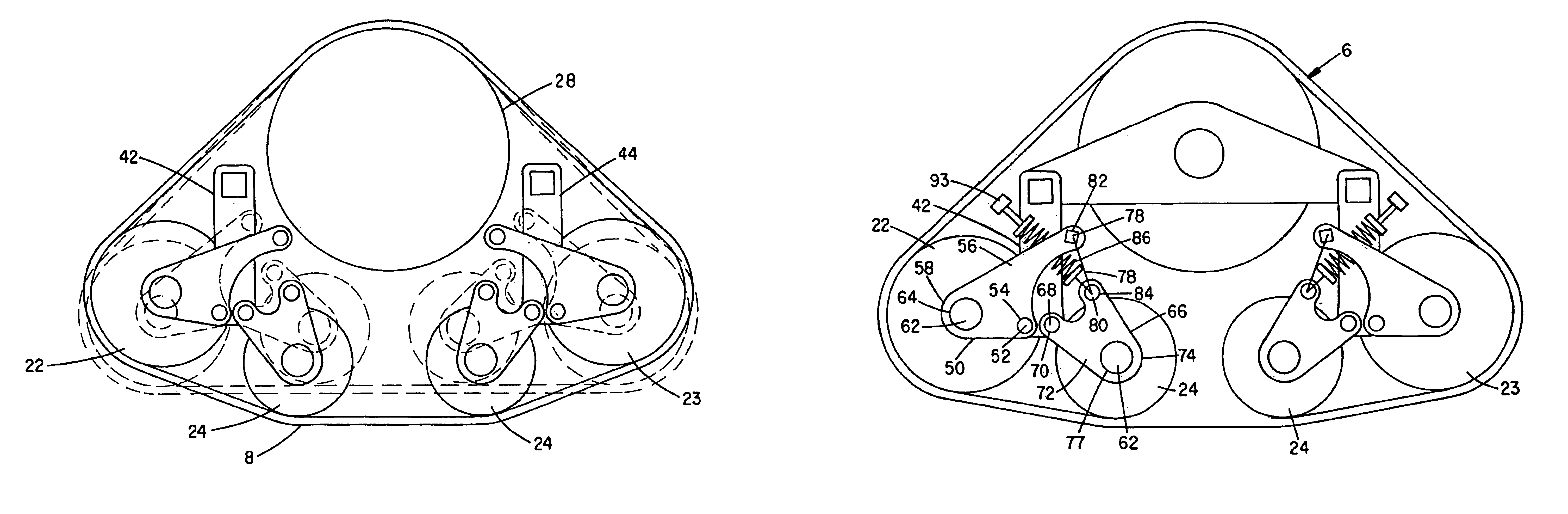
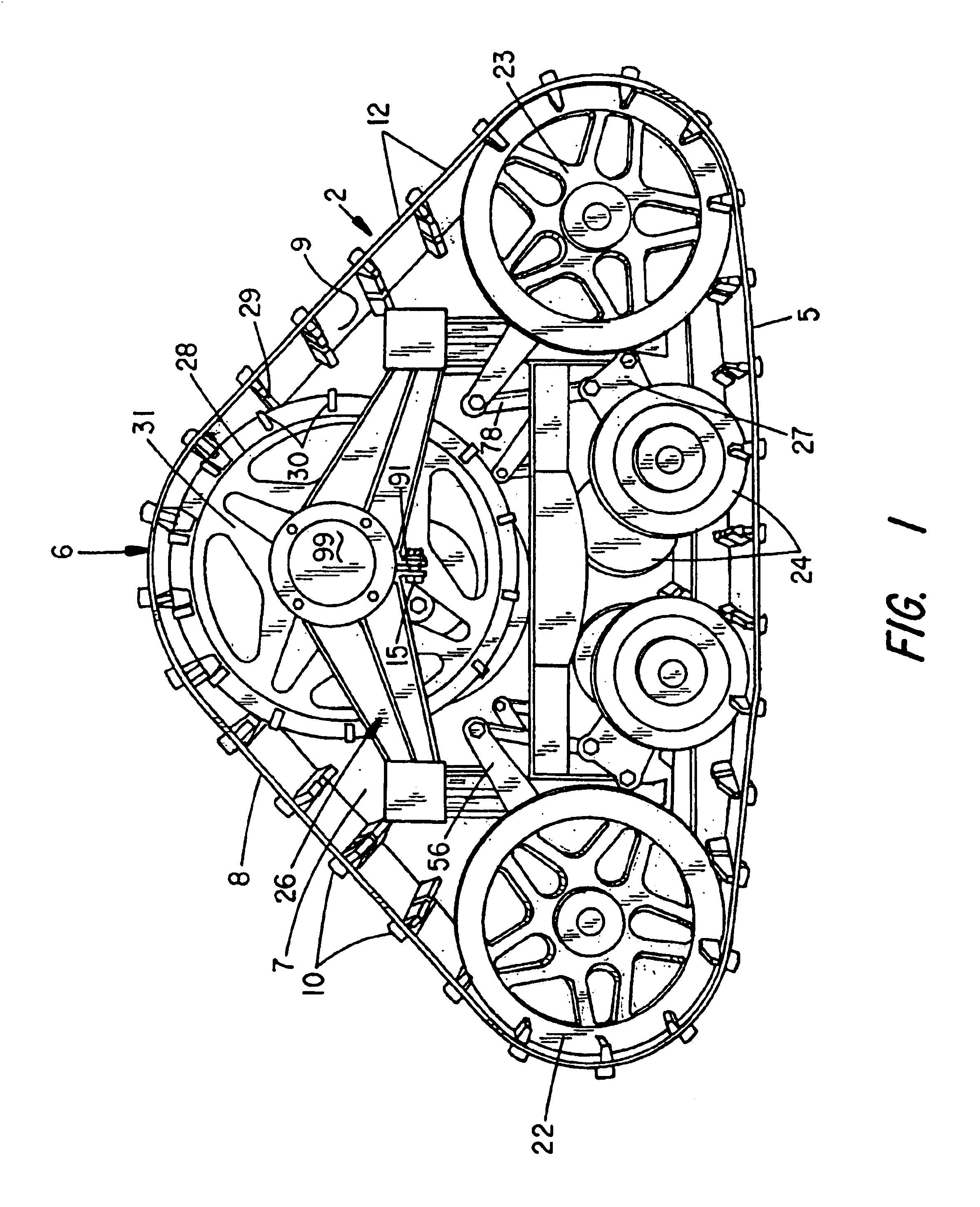
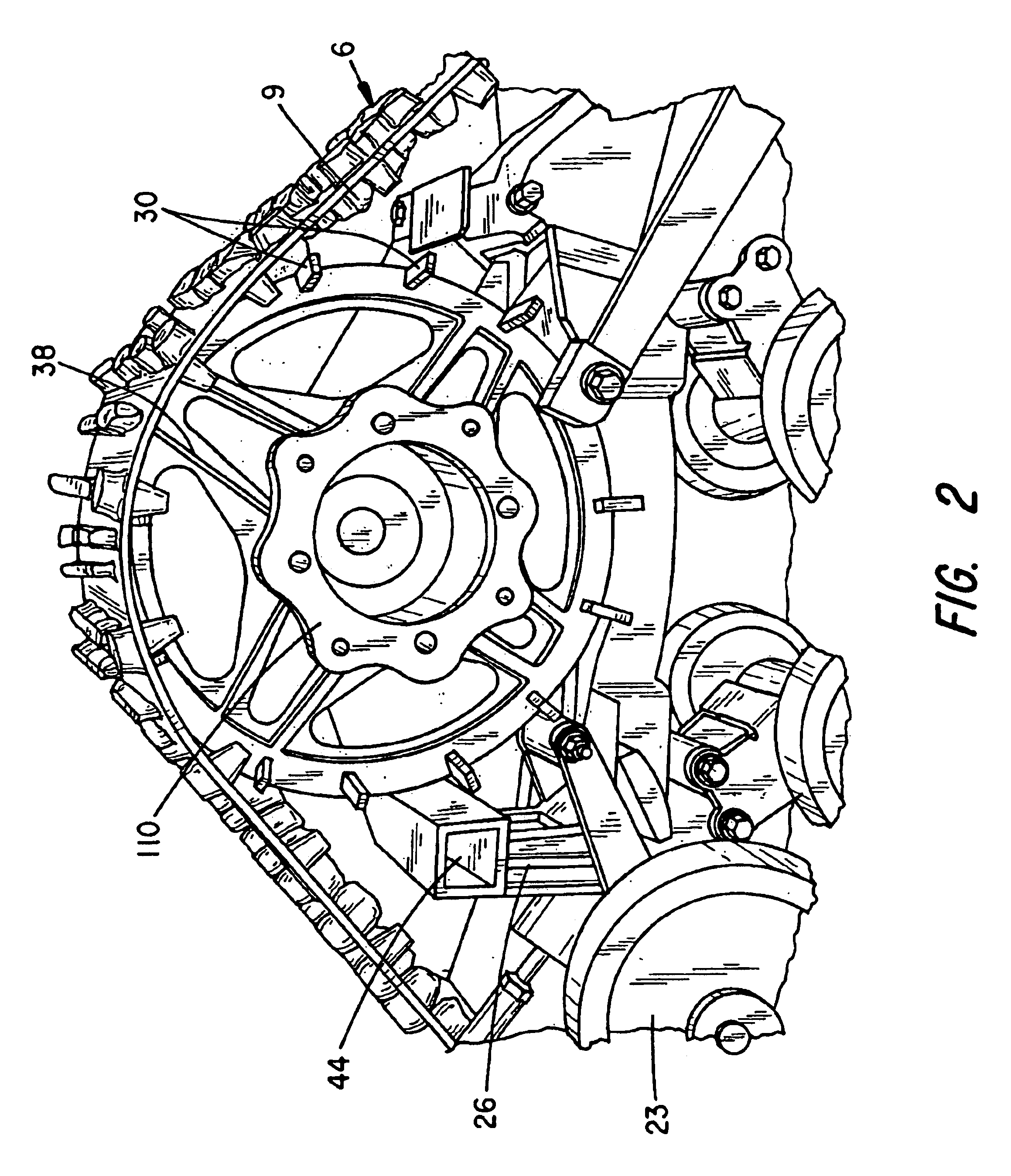
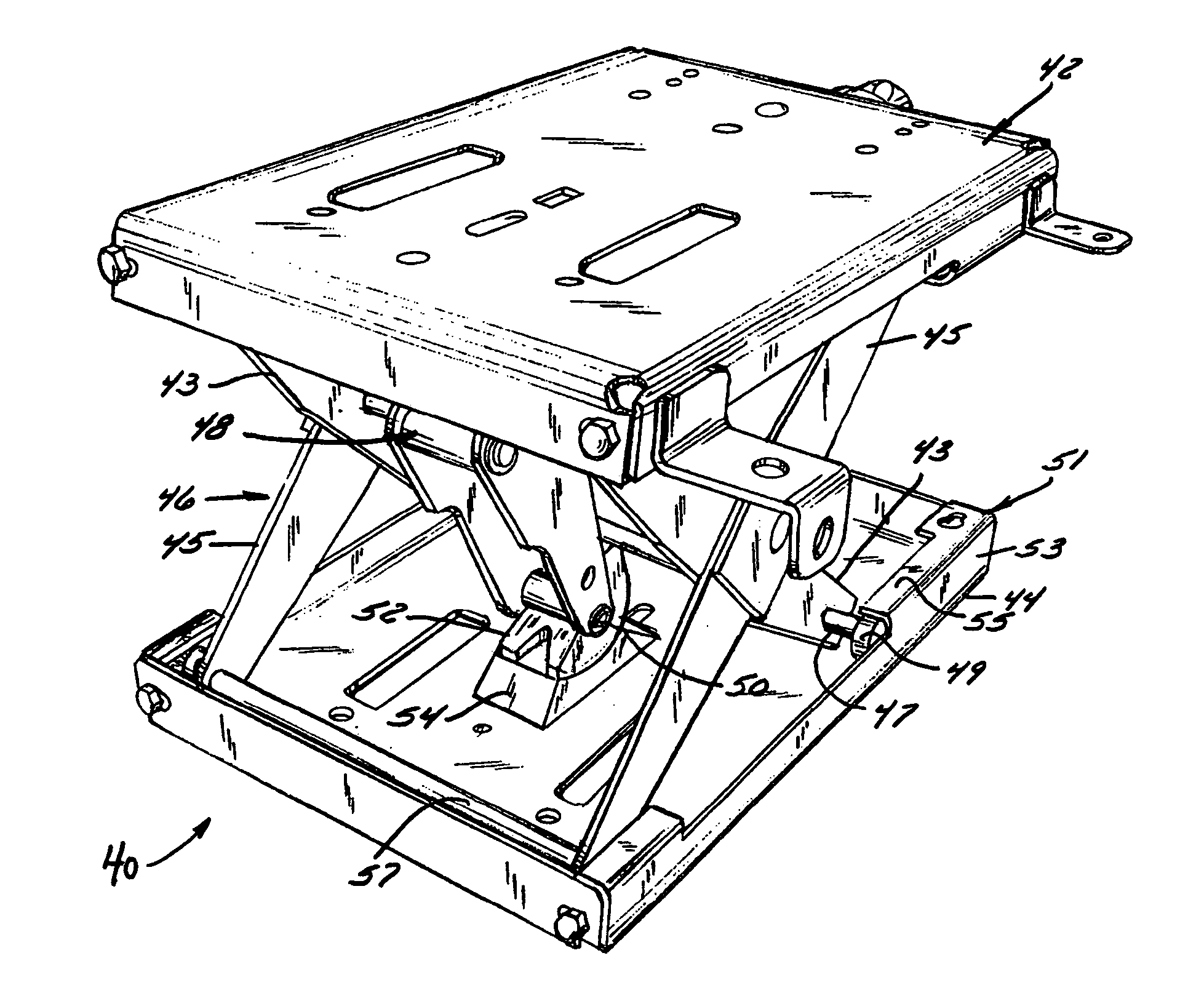
Terrain conforming track assembly
An endless track assembly that mounts to a wheeled vehicle. The assembly provides 1) a track suspension having fixed or adjustable, independently biased sets of idler wheels to vary the track contour without affecting track tension, 2) an eccentric bearing housing at a drive sprocket controls track tension, 3) a contoured peripheral edge at the drive sprocket prevents ice and mud buildup, 4) rubber-coated, plastic idler wheels facilitate track movement, 5) a multi-vehicle compatible adapter mounting plate accommodates a variety of vehicles, 6) a rotation limited torsion coupler and / or rotation limiting coupler arms prevent track contact with the vehicle, 7) a locking steering arm coupler prevents loss of steering control, and 8) shaped track lugs and channels clear and direct debris away from the track suspension and drive assembly. The improved suspension particularly supports sets of idler wheels in pivotal relation to the track support frame and resiliently biases a pre-tensioned rocker arm that links adjacent suspension arms mounted to the adjoining idler wheels. Suspension arm movement induces expansion and contraction of tension springs coupled to the rocker arms to augments shape changes at the track contact surface to optimize traction and steering control.
Owner:BRAZIER GLEN
Vehicle seat suspension and method
A vehicle seat suspension that includes a suspension cartridge which houses suspension components that includes one or more of the following: one or more biasing elements, a suspension arm arrangement, a damper arrangement, a height adjust assembly, and a weight adjust assembly. In one preferred embodiment, the cartridge includes all of these. The suspension can include a truncated roller that provides a larger effect of radius. The suspension can also include a cam upon which a suspension roller rides that increases maximum suspension stroke while minimizing collapsed suspension height. The suspension can also include a damper that is oriented so as to provide a nearly linear response over all regions of suspension stroke or travel.
Owner:MILSCO LLC
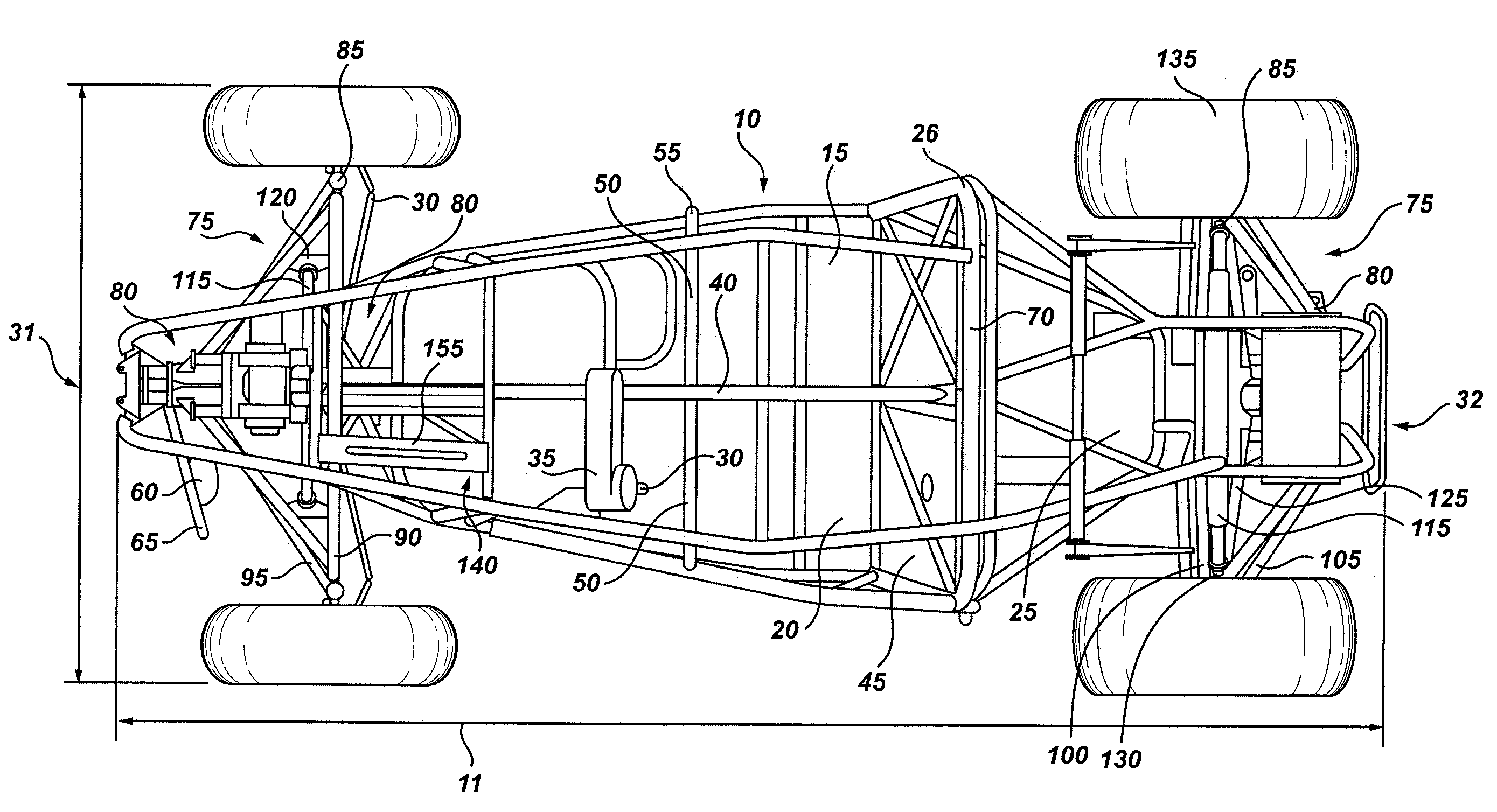
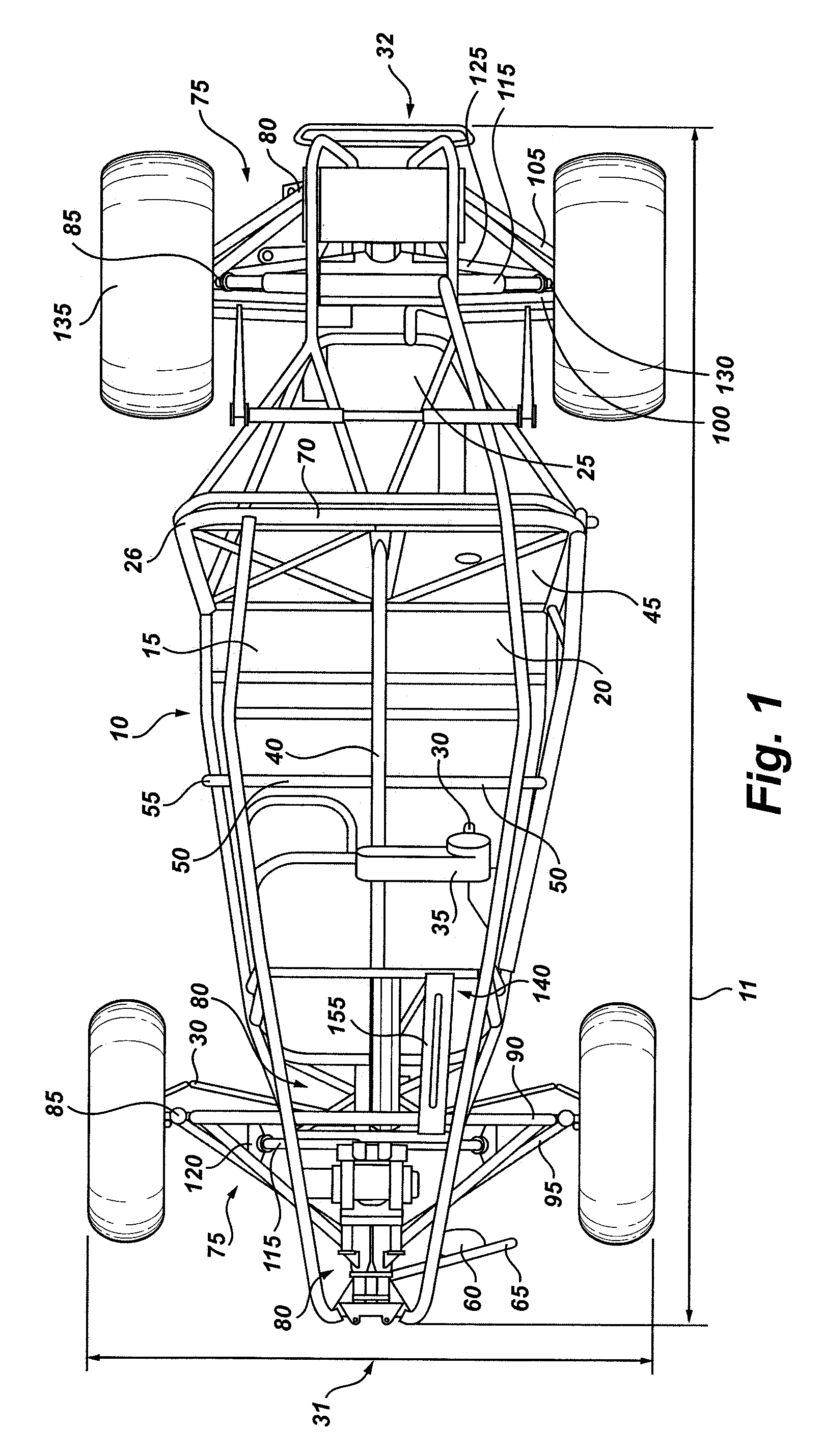
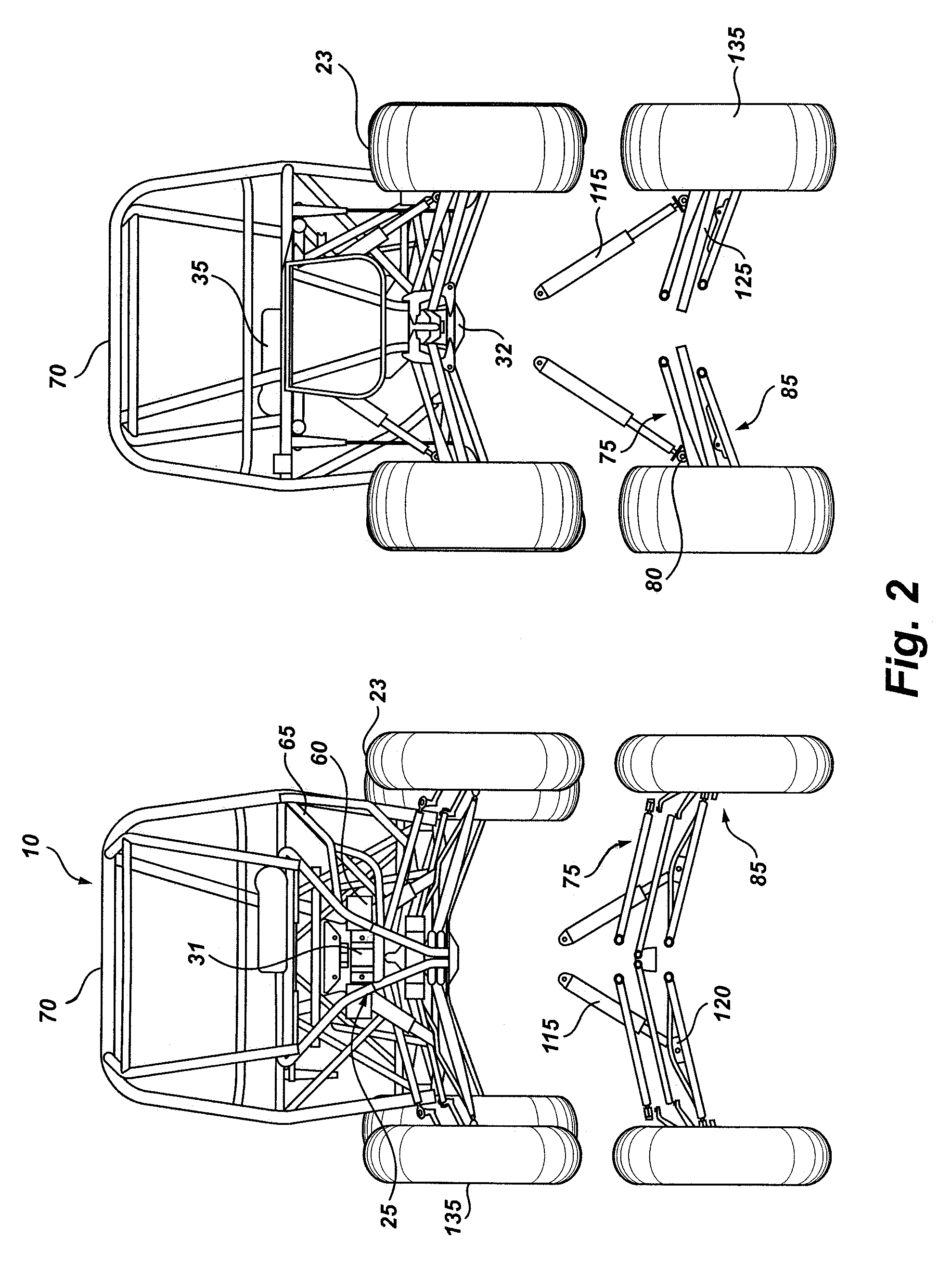
All terrain vehicle swept a-frame suspension and central support truss
The present invention features an all terrain, four-wheeled vehicle frame for carrying at least two passengers in a side-by-side riding configuration, comprising a rigid, tubular frame body which provides for a forward passenger compartment having structural support members for carrying a pair of seats for the side-by-side passengers and a rearward engine compartment configured for receiving an engine, power train, and transmission for driving wheels of the vehicle. The vehicle frame also includes a vertical, load-bearing truss member extending generally along a longitudinal, central axis of the vehicle within the passenger compartment, the truss member forming a load-bearing structural member between the pair of seats.
Owner:NORTH VAUGHN
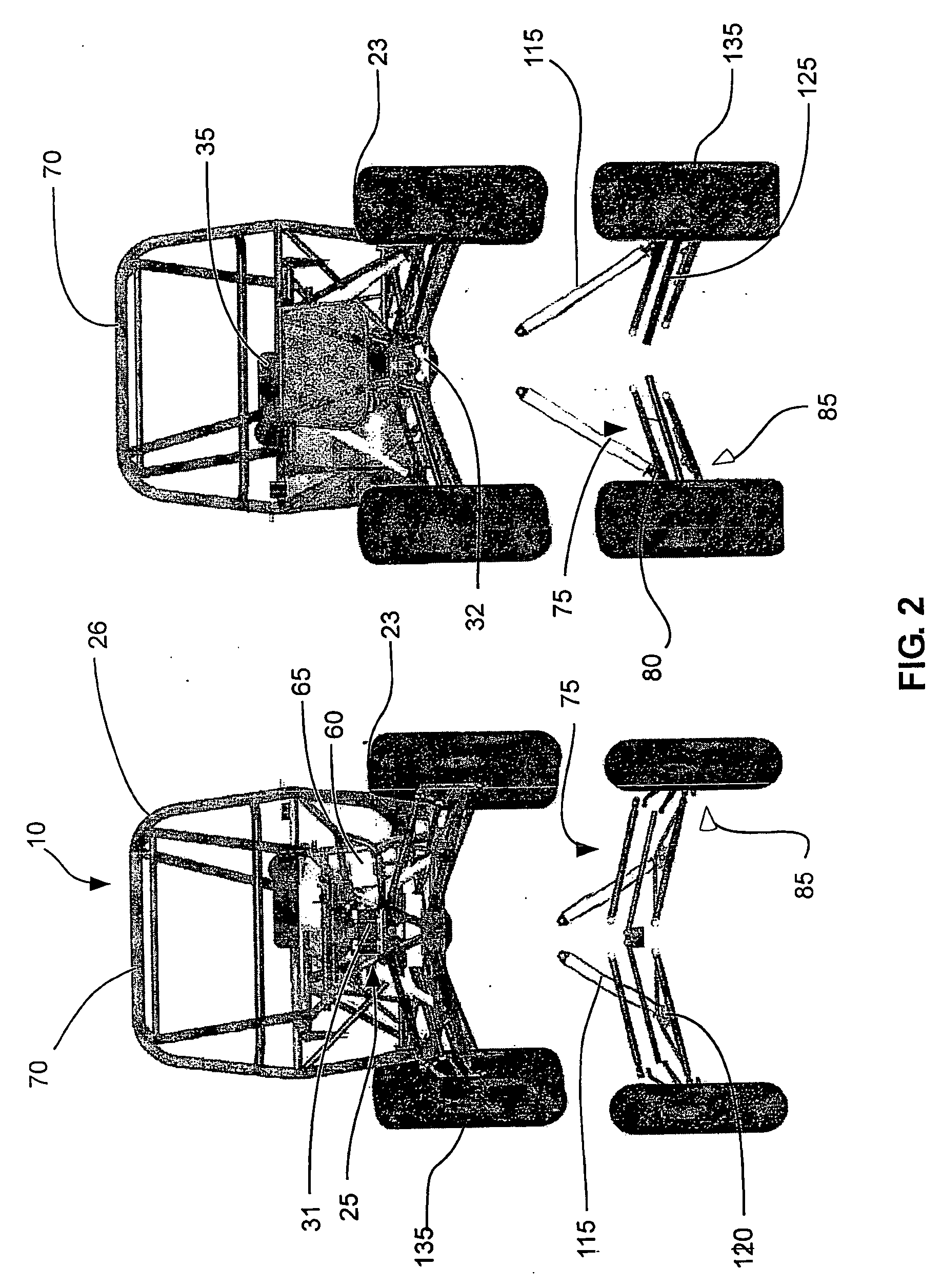
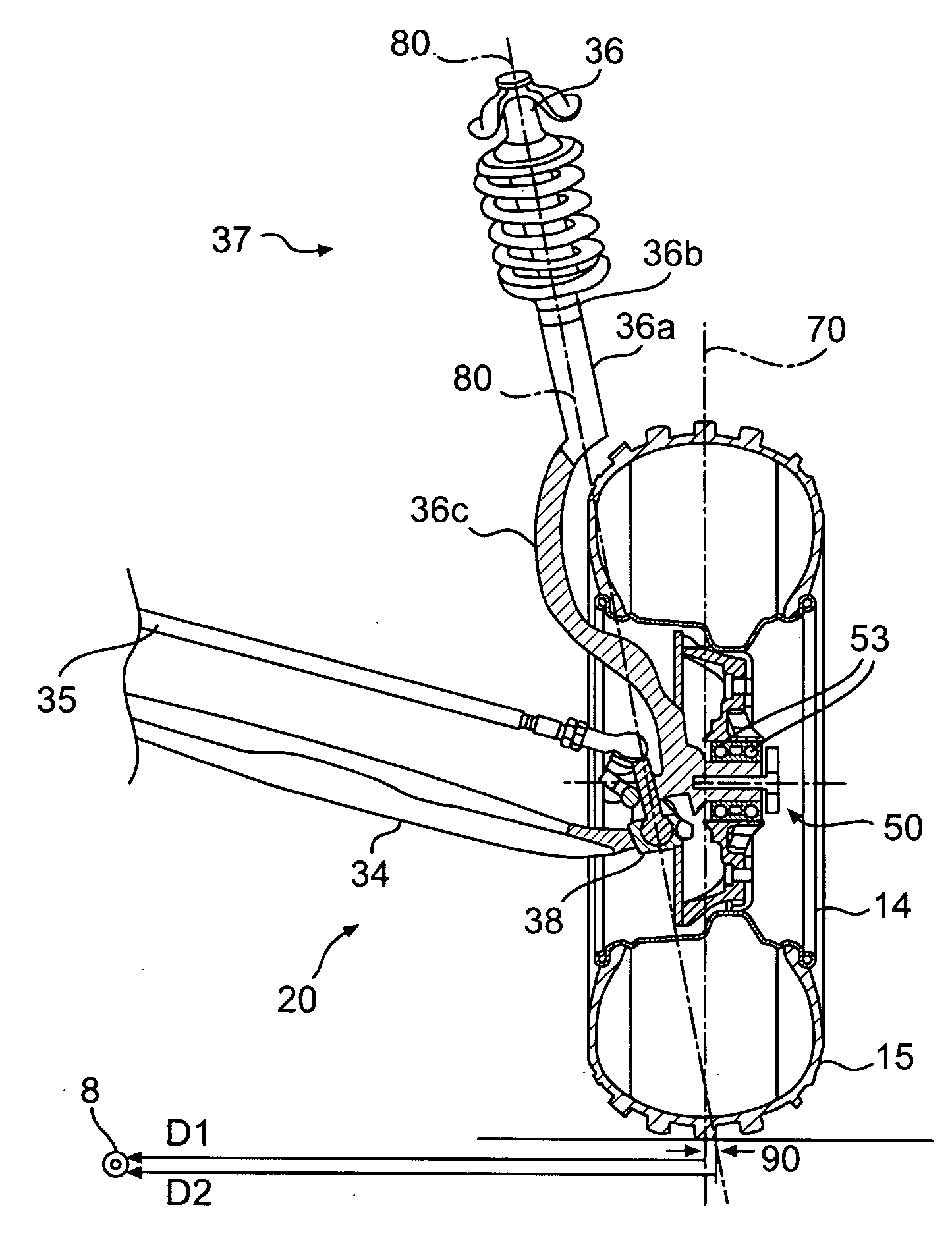
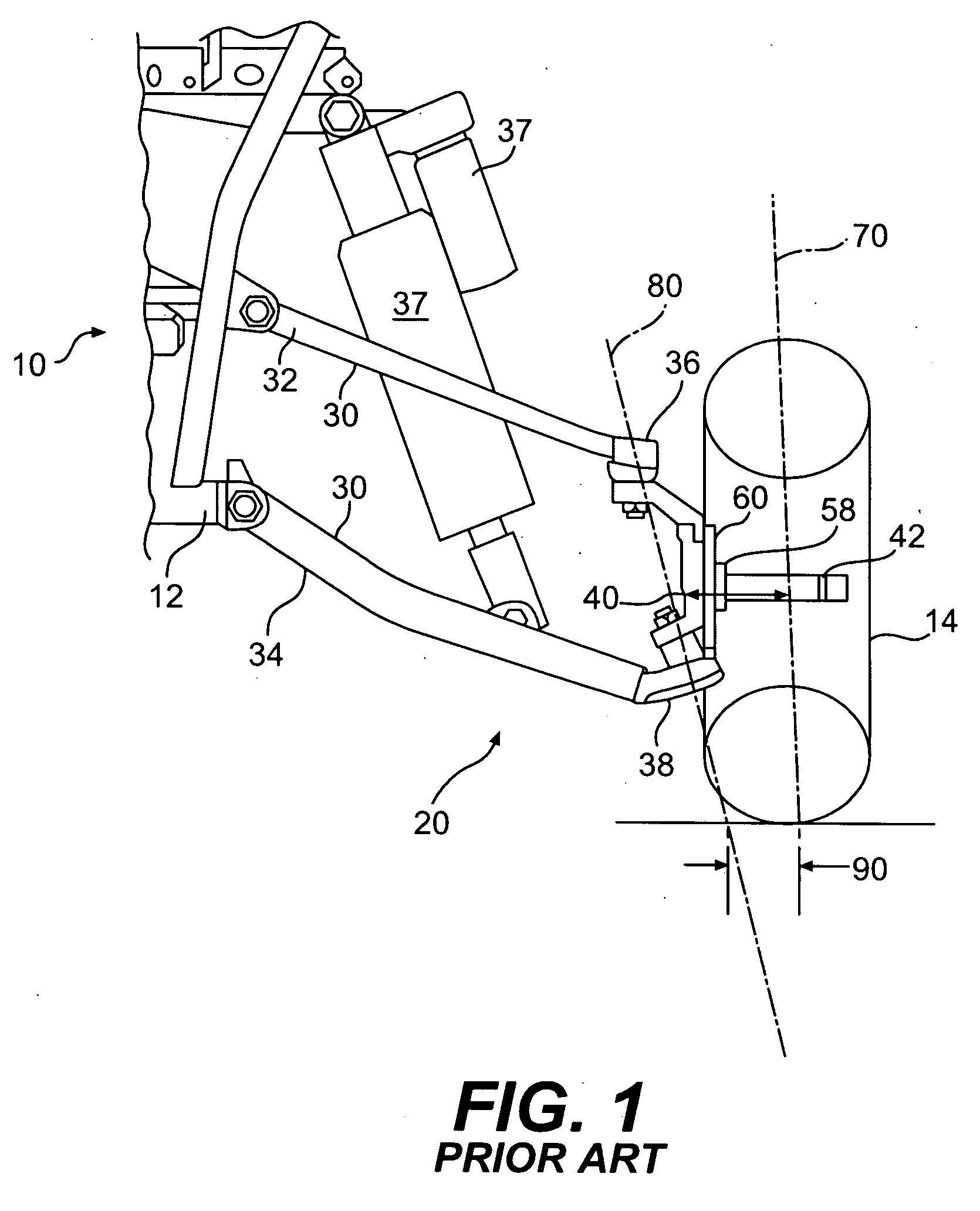
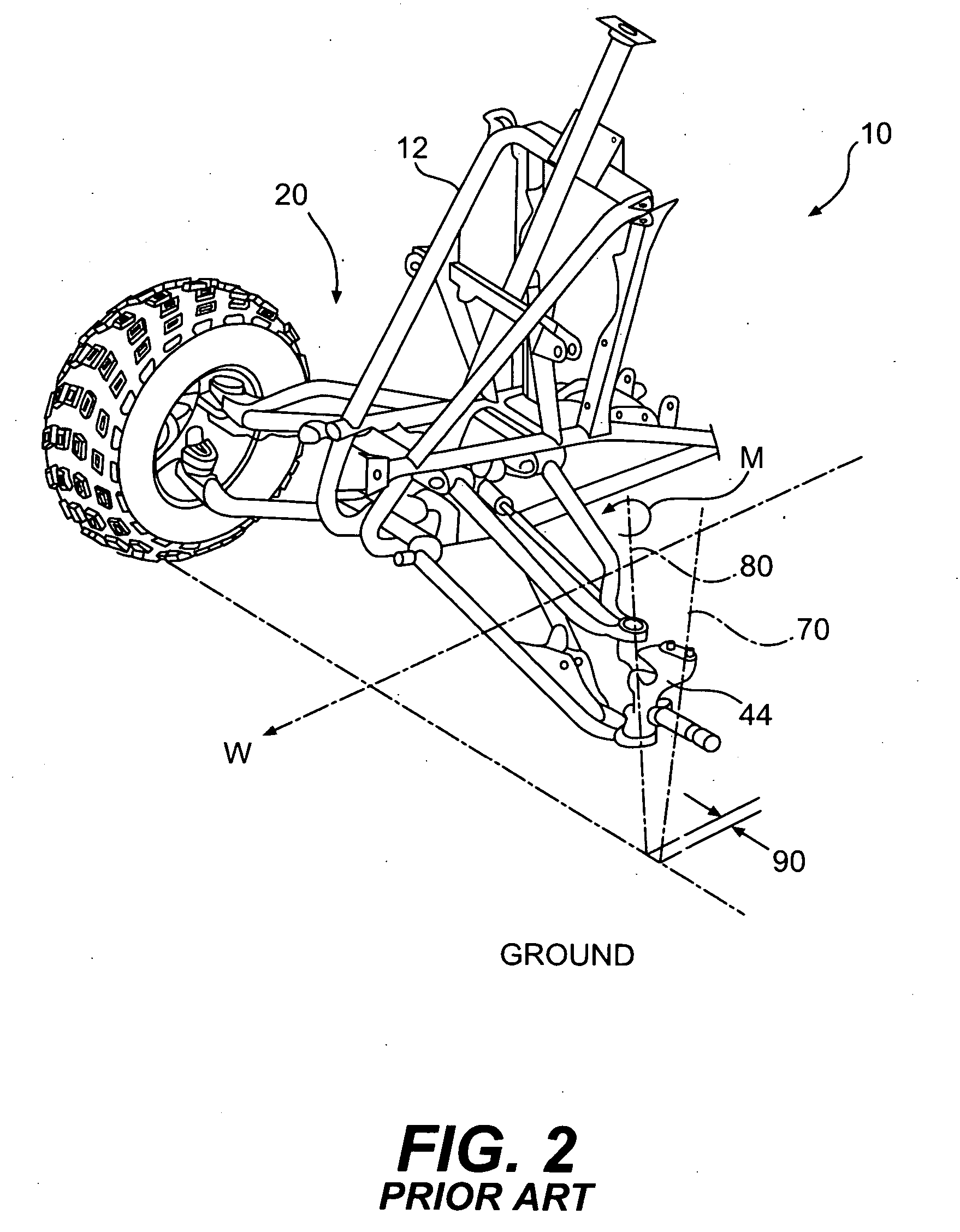
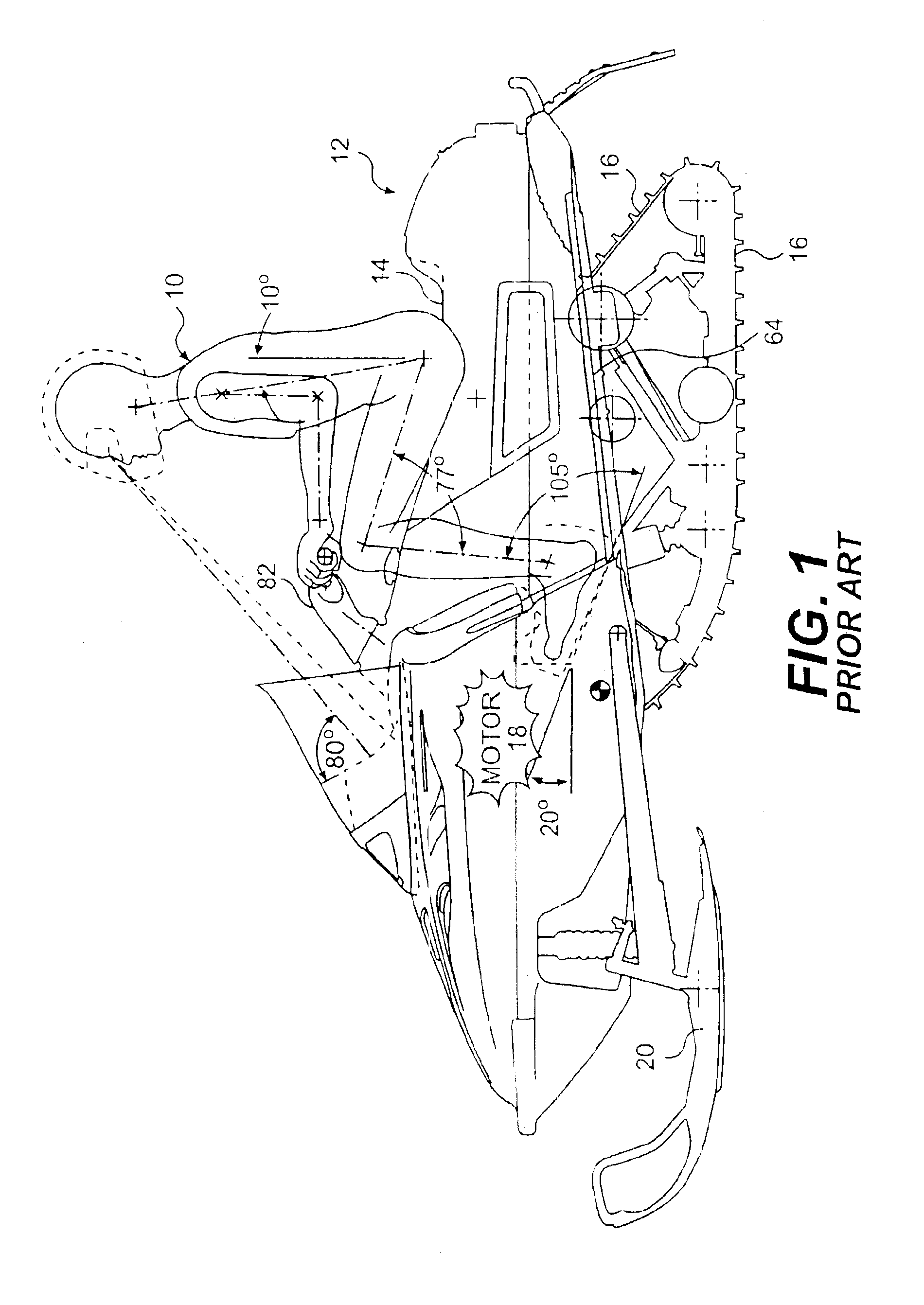
Front drive geometry for an all-terrain vehicle
InactiveUS20060006623A1Tightly packLow king pin axis angleCyclesSteering linkagesDisc brakePull force
A two-wheel-drive sport all-terrain vehicle (ATV) has a front drive geometry in which the scrub radius is zero or negative combined with a low king pin axis angle, which desirably reduces both steering kickback and lateral pull during braking. The scrub radius less than or equal to zero can be achieved by outwardly displacing the king pin axis, which is defined by the upper and lower pivotal joints of the upper and lower A-arms of the front suspension. To displace the king pin axis outwardly, the disk brake and associated caliper are inverted. The disk brake is supported by support arms extending inwardly from the wheel hub. The disk brake includes an aperture to accommodate both the lower pivotal joint, which protrudes through the plane of the disk, and the inverted caliper. The front suspension further includes a knuckle pivotally connected to the A-arms and an integral aluminum spindle. For further compactness, the wheel hub includes angular-contact bearings.
Owner:BOMBARDIER RECREATIONAL PROD INC
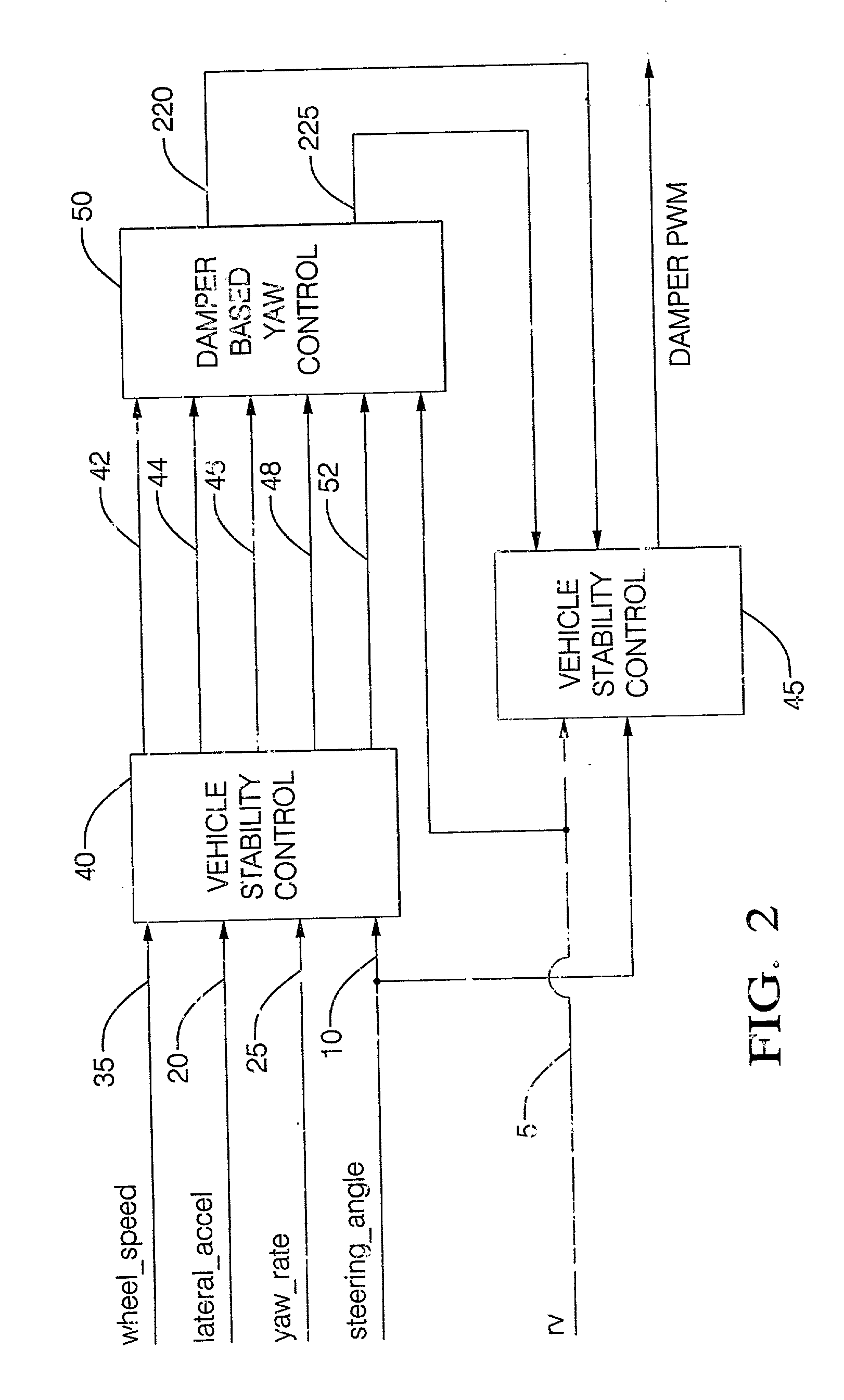
Control system for adjustable damping force damper
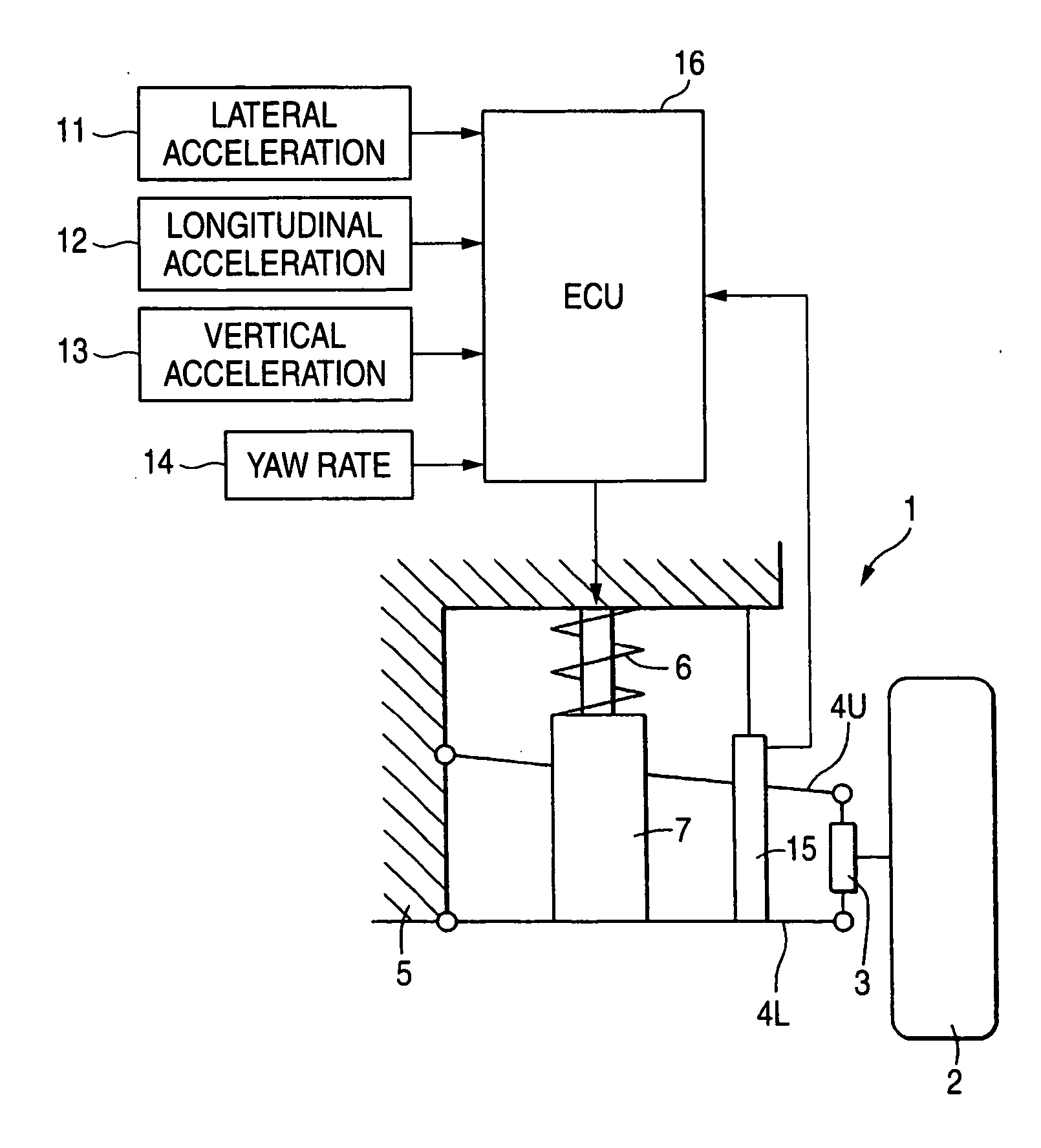
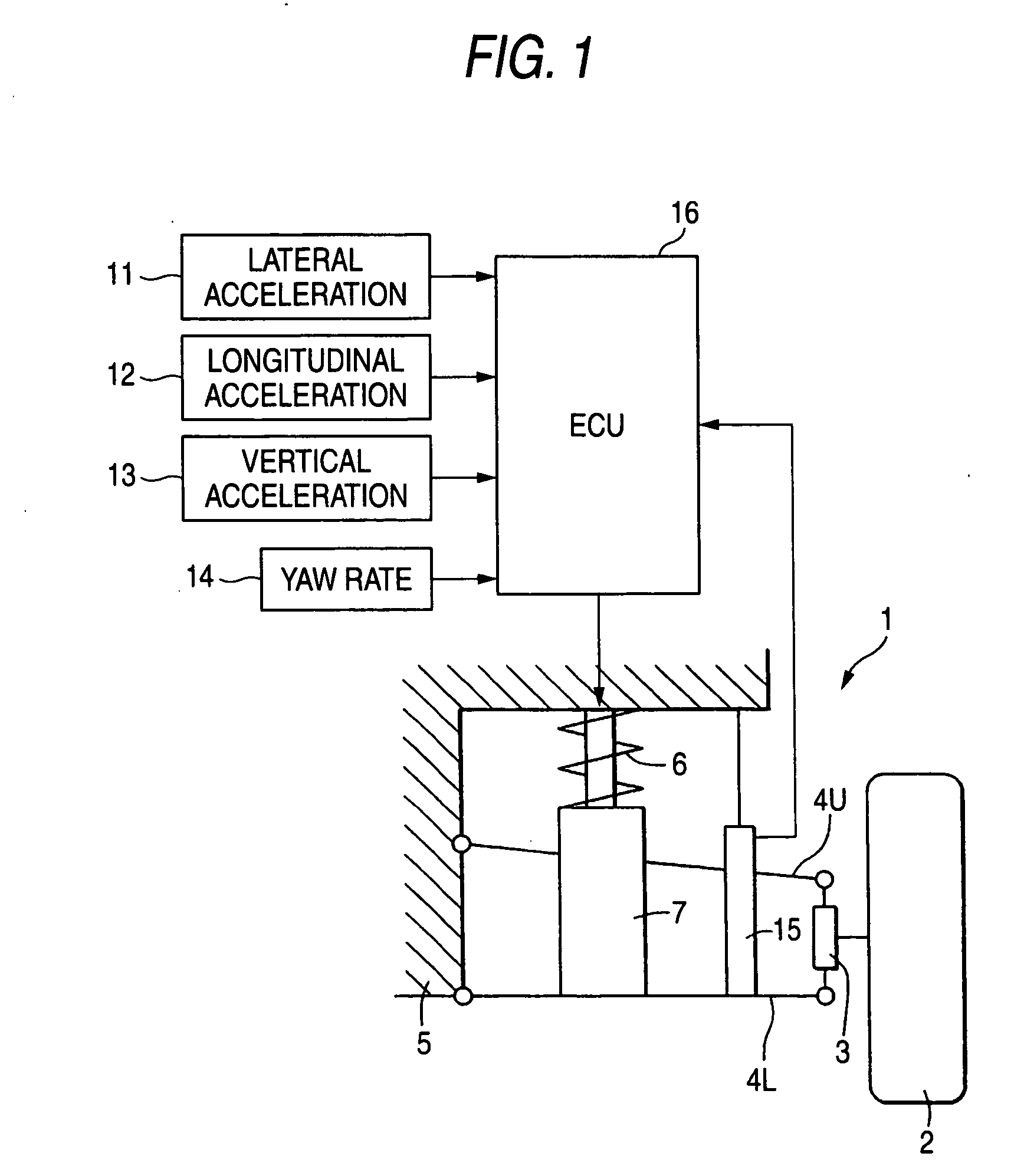
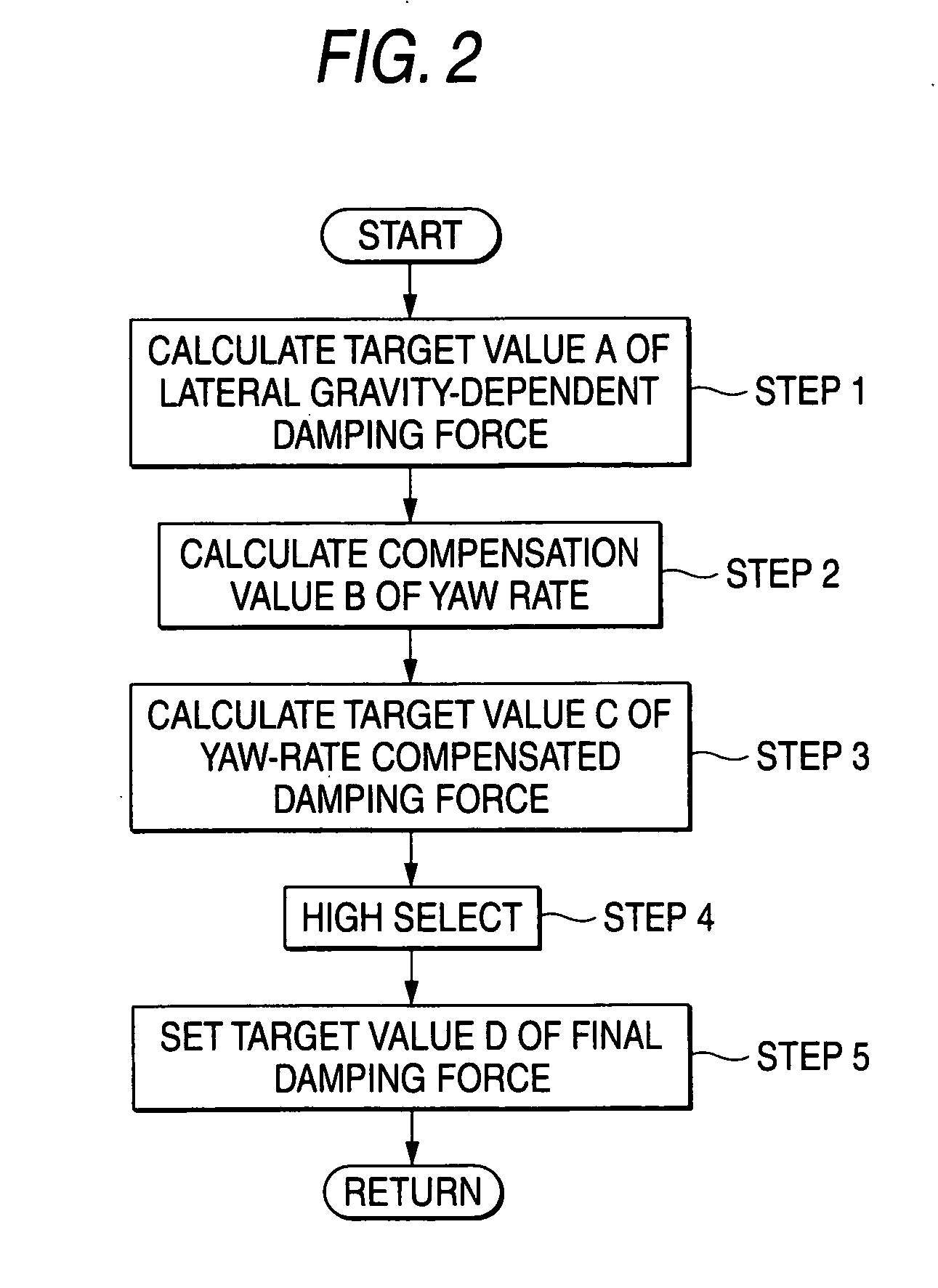
ActiveUS20060224287A1Good precisionWithout a deterioration of a high responsibilityVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesControl systemTarget control
A control system for an adjustable damping force damper of a suspension apparatus of a vehicle, includes a lateral acceleration detecting unit detecting a lateral acceleration of the vehicle at a gravity point thereof, a yaw rate detecting unit detecting a yaw rate of the vehicle and a control unit controlling a damping force of the damper. The control unit calculates a first target damping force based on an output of the lateral acceleration detecting unit, calculates a second target damping force based on a lateral acceleration at an axel position which is estimated by an output of the yaw rate detecting unit, compares an absolute value of the first target damping force with that of the second target damping force and sets a target controlling value of the damping force in accordance with the first or second target damping force which has a larger absolute value.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
All terrain vehicle swept A-frame suspension and central support truss
Owner:NORTH VAUGHN
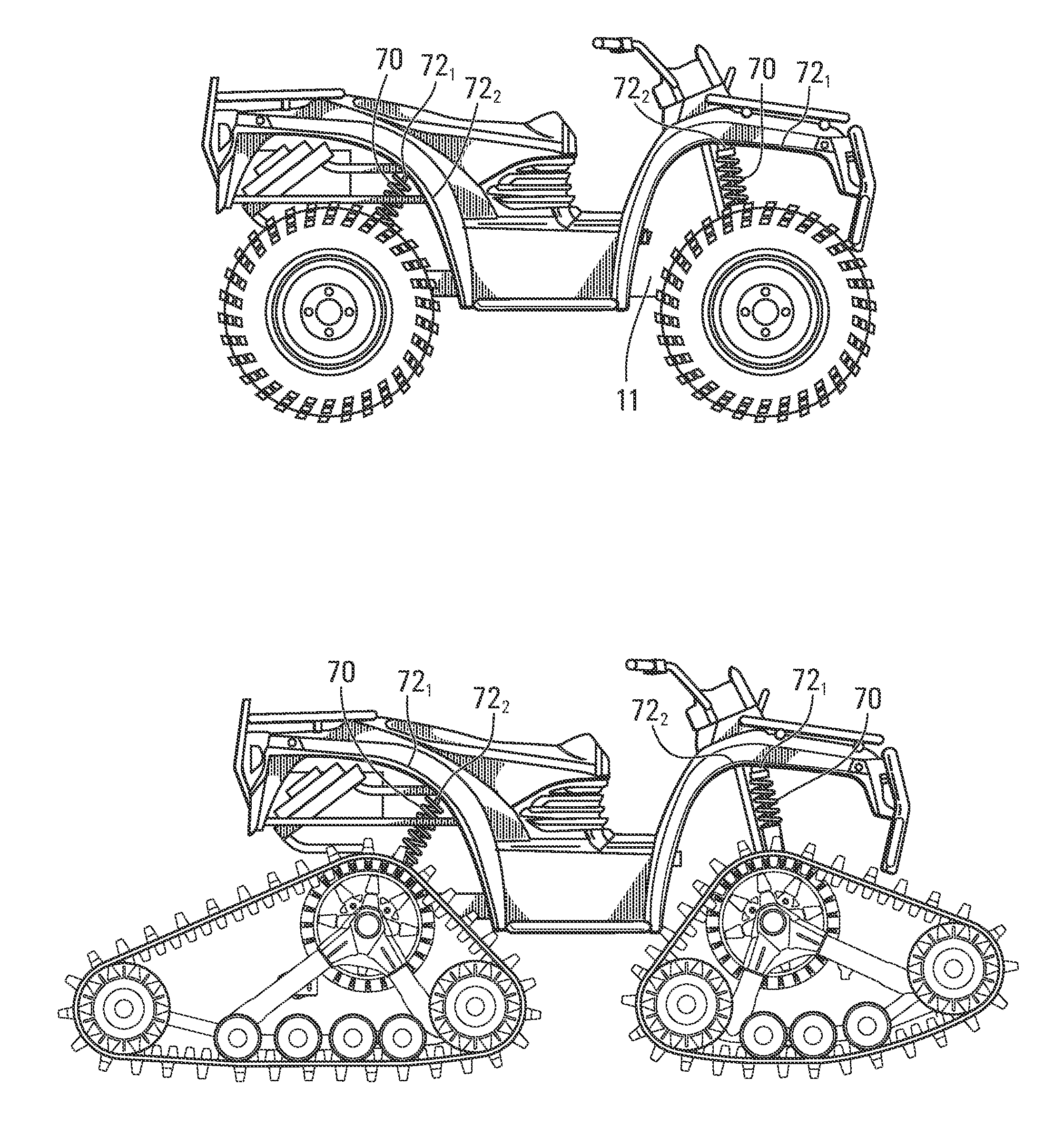
All-terrain vehicle (ATV) propellable on wheels or endless tracks
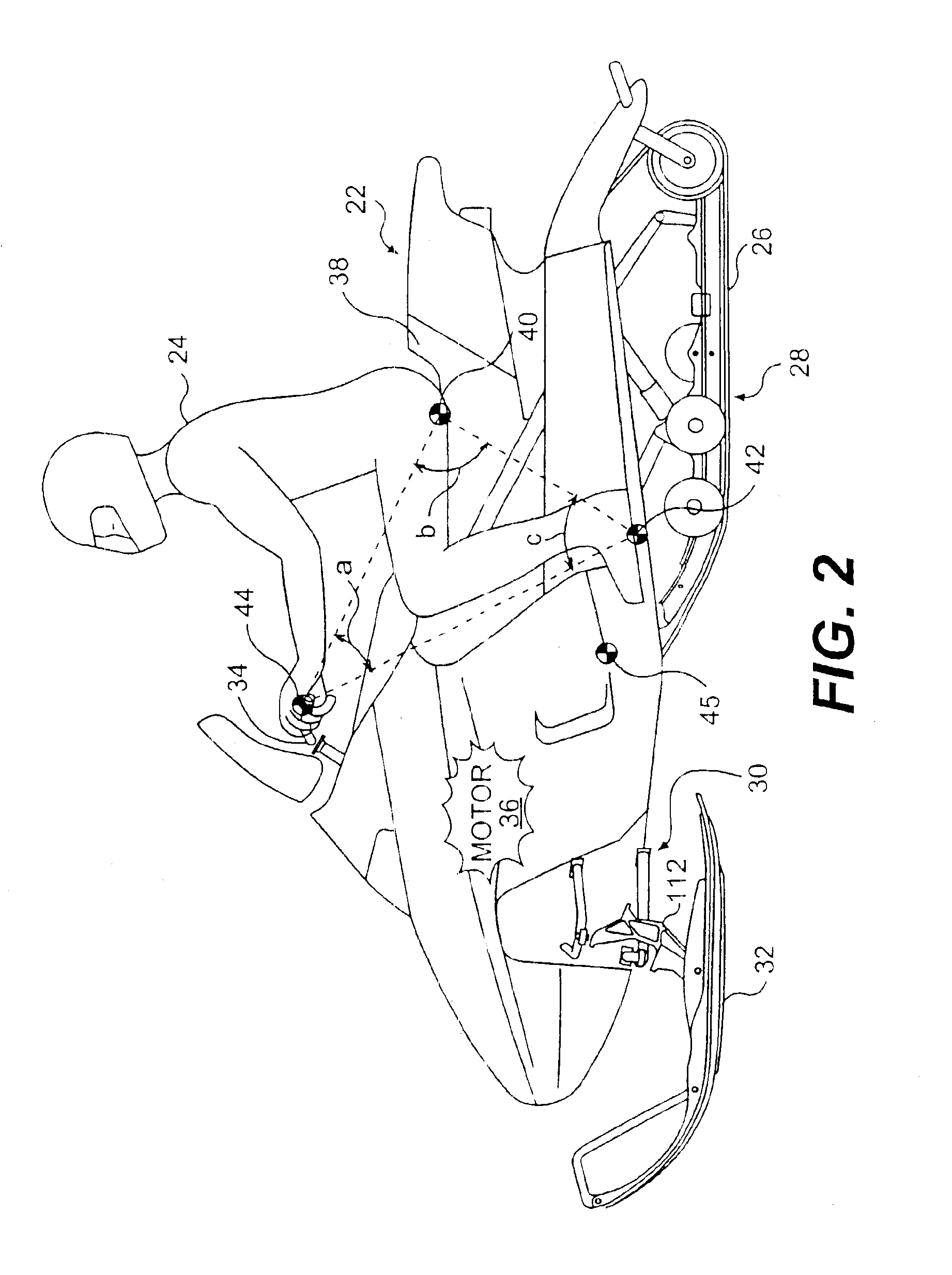
An all-terrain vehicle (ATV) equippable with a plurality of ground-engaging wheels or a plurality of ground-engaging track assemblies providing traction on the ground. The ATV is designed to facilitate its use whether it is equipped with the ground-engaging wheels or the ground-engaging track assemblies. A powertrain, a steering system, a suspension, a braking system, a body, and / or other components of the ATV have features which take into account that the ATV can be equipped with either the ground-engaging wheels or the ground-engaging track assemblies.
Owner:CAMOPLASY INC
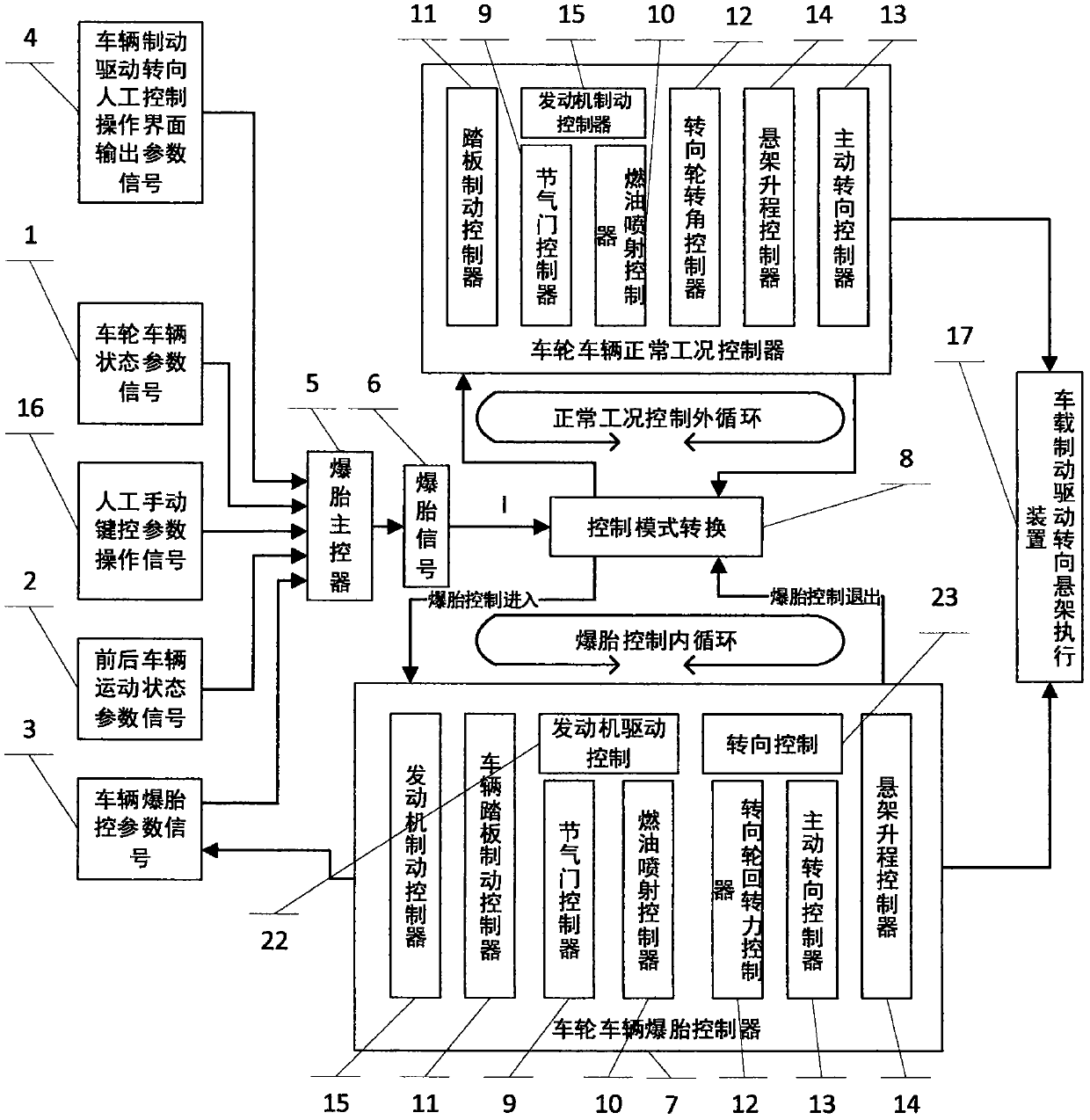
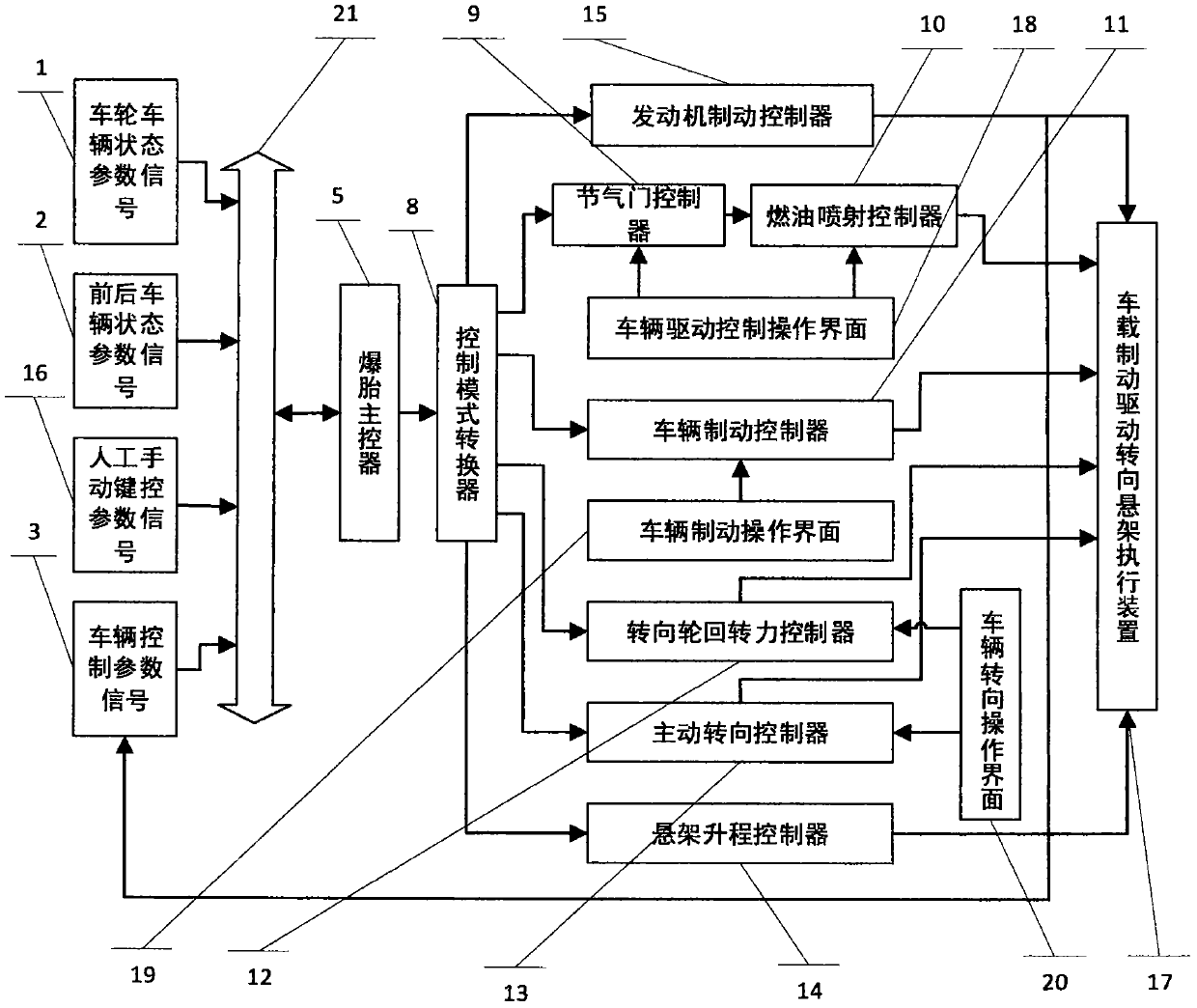
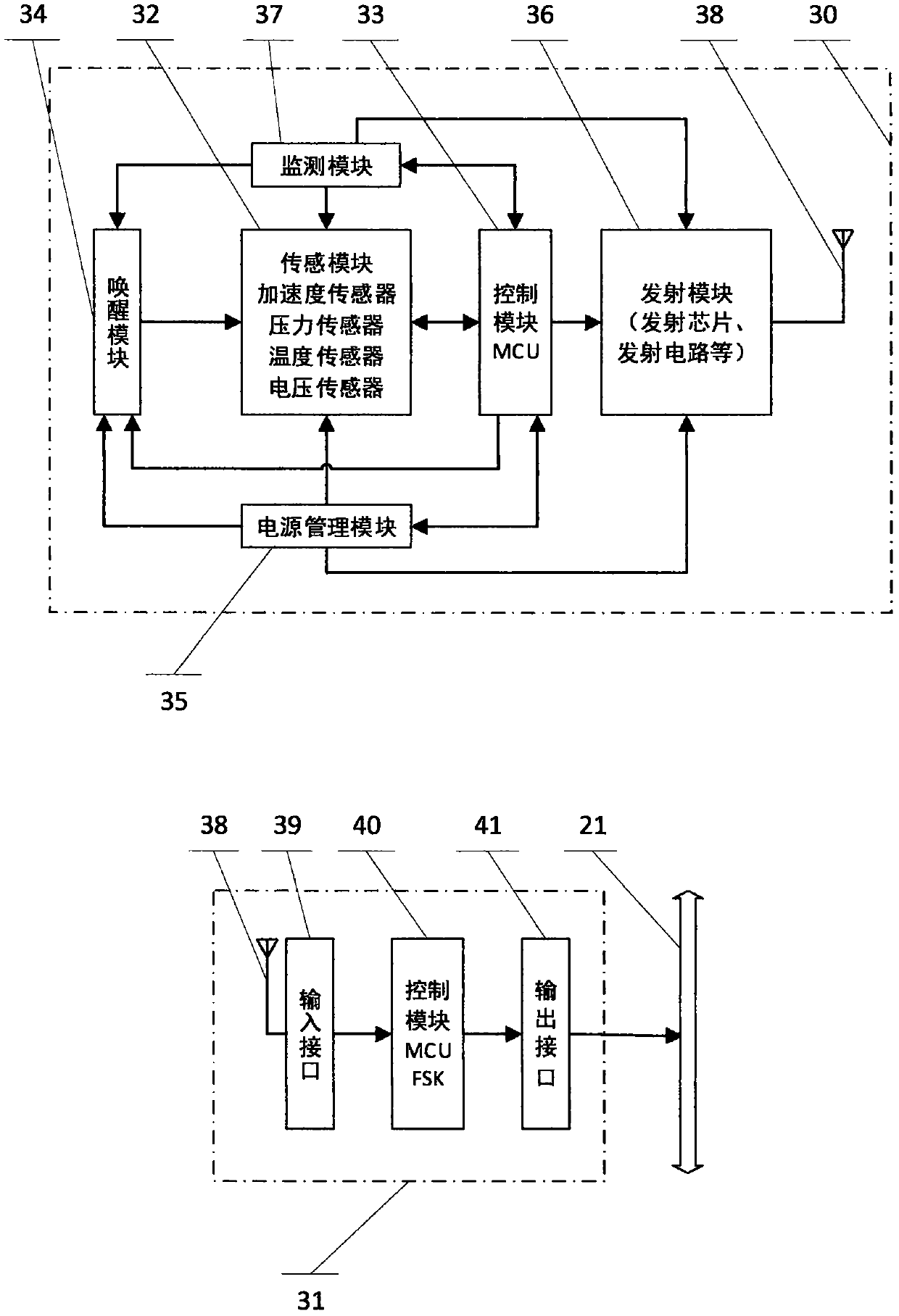
Automobile tire burst safety and stability control method
InactiveCN108501944ARealize staged tire blowout controlBlowout control normalSteering wheelControl mode
The invention provides an automobile tire burst safety and stability control method used for manned and unmanned vehicles and based on vehicle braking, driving, steering and suspension systems and belongs to the field of automobile tire burst safety. According to the automobile tire burst safety and stability control method, tire burst judgment using a tire pressure detection mode, a state tire pressure mode and a steering mechanical state mode are established; an automobile tire burst safety and stability control mode, an automobile tire burst safety and stability control mode model, an automobile tire burst safety and stability control mode algorithm, a control structure and a control process are adopted; through tire burst control entering and exiting as well as normal and tire burst control mode conversion, vehicle braking, driving, steering, steering wheel rotation force and suspension balancing control are carried out in a coordinated manner to realize real or unreal tire burst process overlapped tire burst control; and under a condition that a tire burst process state and a tire burst wheel and vehicle motion state are suddenly changed, important technical barriers that thewheel and the vehicle are seriously unstable due to tire burst, the tire burst extreme state is hard to control and so on are broken through to solve the important long-term problem which troubles theautomobile tire burst safety at present.
Owner:吕杉 +1
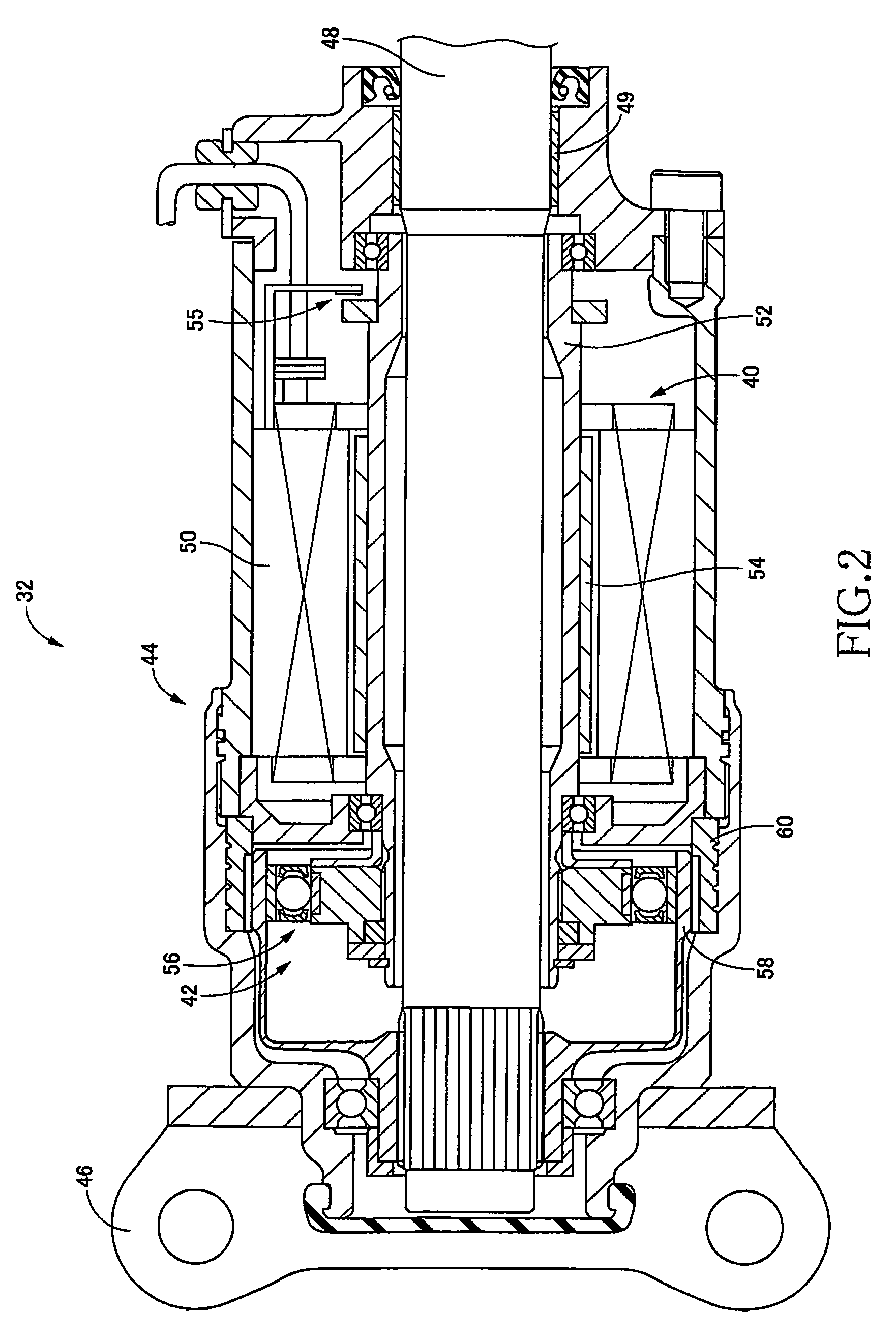
Suspension Apparatus for Vehicle
InactiveUS20080164111A1Simple structureReduce transmissionSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionControl theoryPiston rod
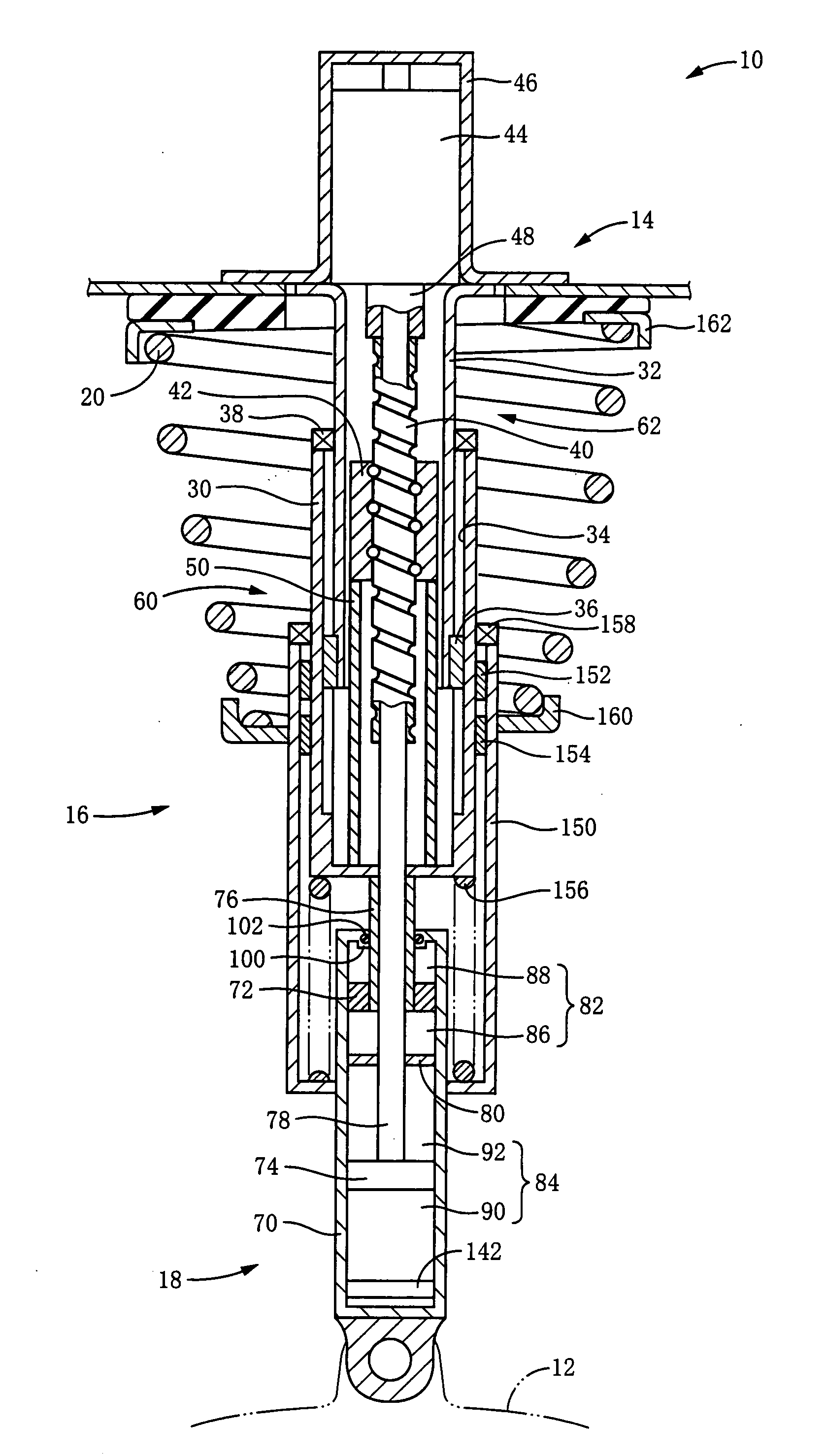
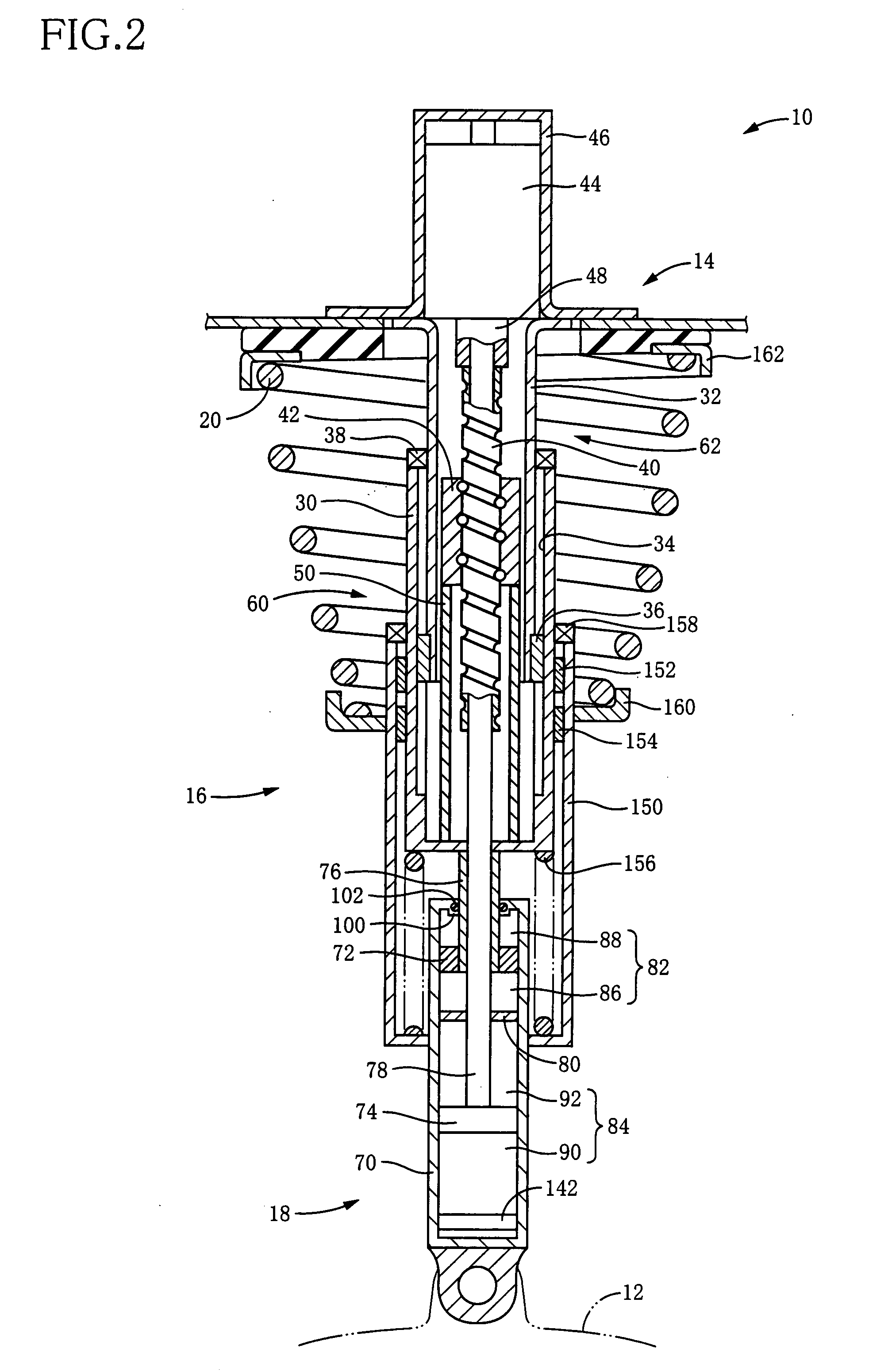
It is an object of the invention to improve utility in a suspension apparatus for a vehicle having an electromagnetic actuator and a hydraulic damper. In the suspension apparatus, a hydraulic damper is disposed between an electromagnetic actuator and a wheel-holding portion, and a cover tube is provided for accommodating a seal provided between a piston rod and a housing of the hydraulic damper. In the suspension apparatus according to the present invention wherein the hydraulic damper is disposed between the wheel-holding portion and the electromagnetic actuator, it is possible to effectively mitigate not only transmission of vibrations to the vehicle body from the wheel via the electromagnetic actuator but also transmission of vibrations to the electromagnetic actuator. Further, owing to the presence of the cover tube, entry of dust and the like into the hydraulic damper through the seal can be effectively prevented.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
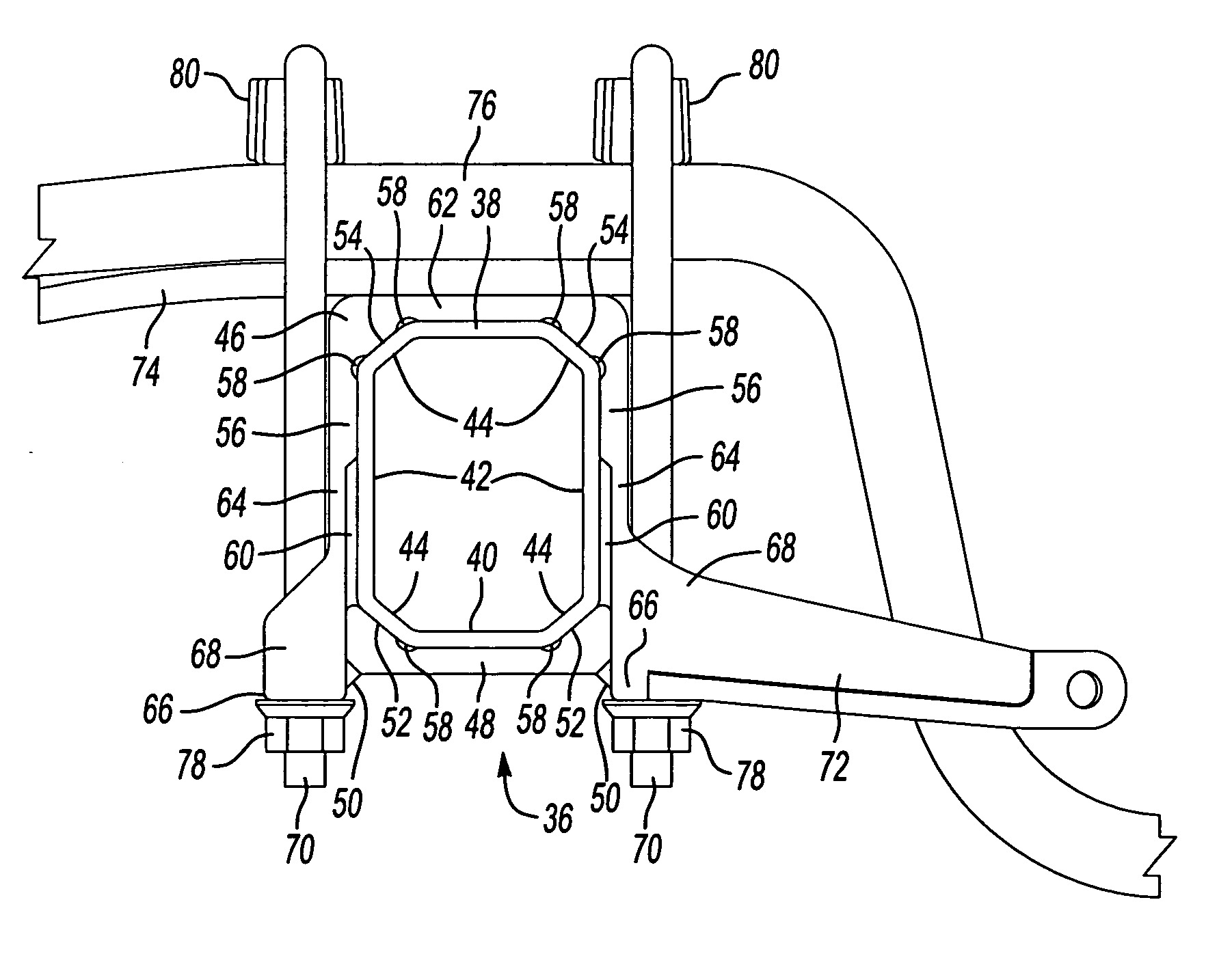
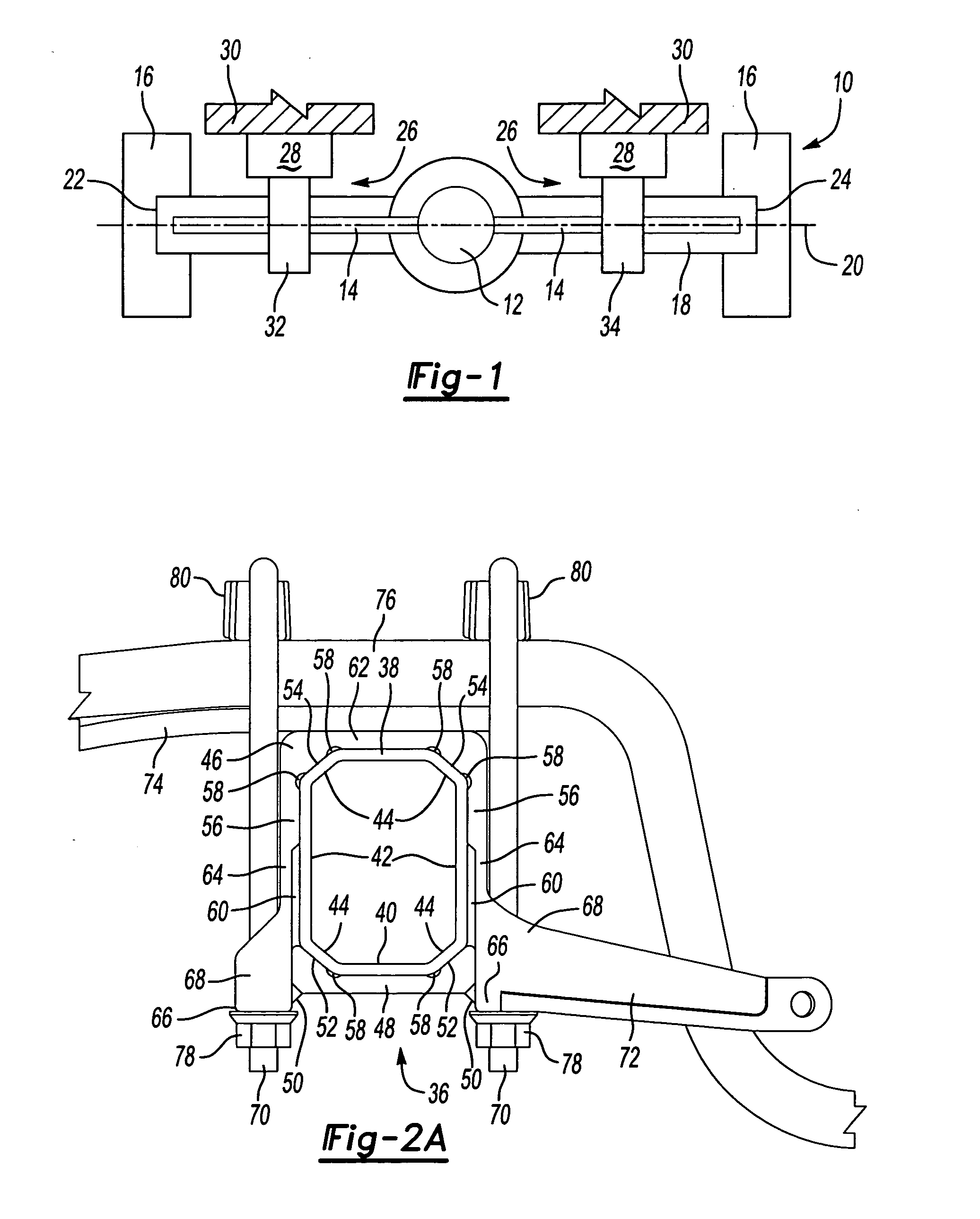
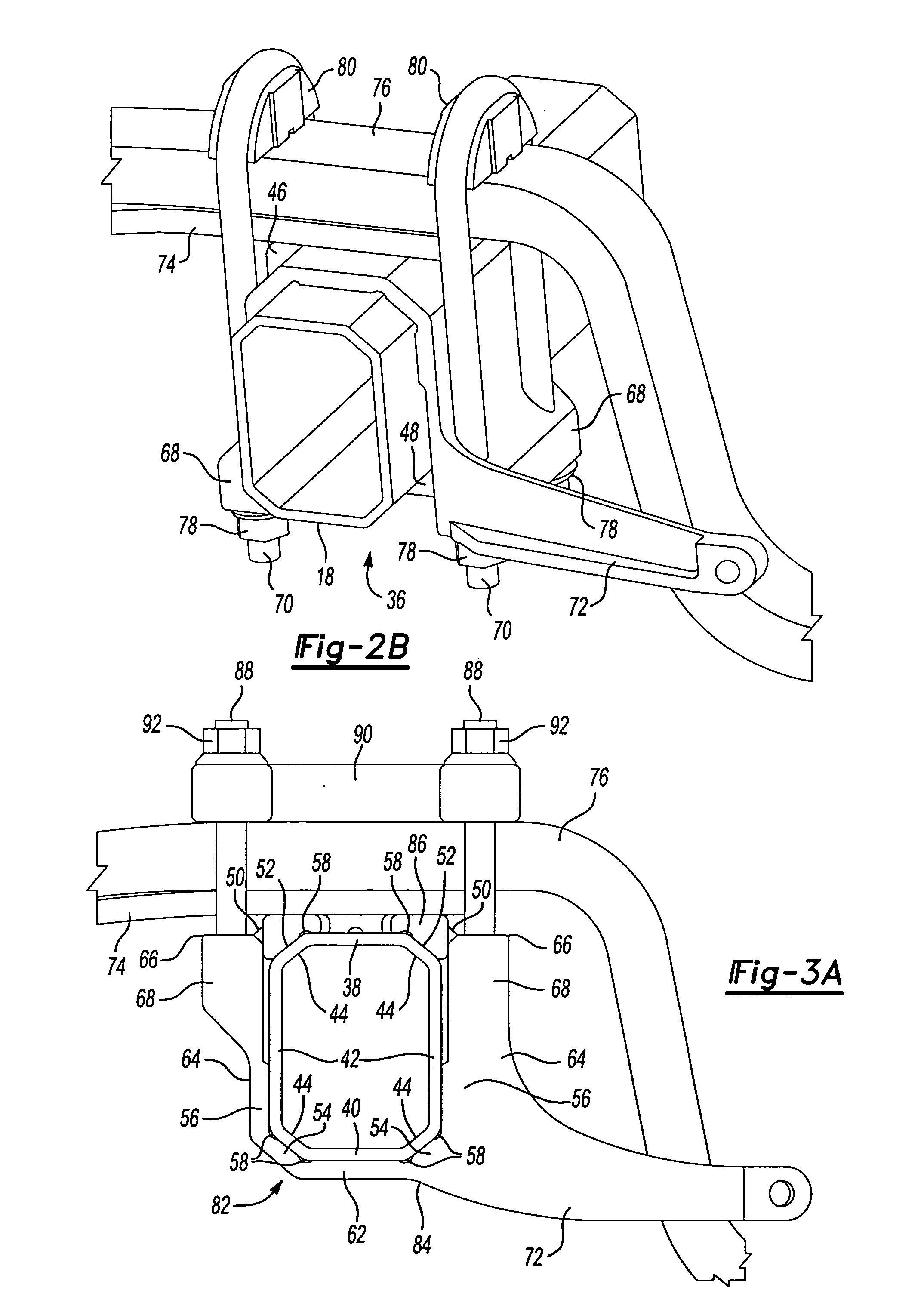
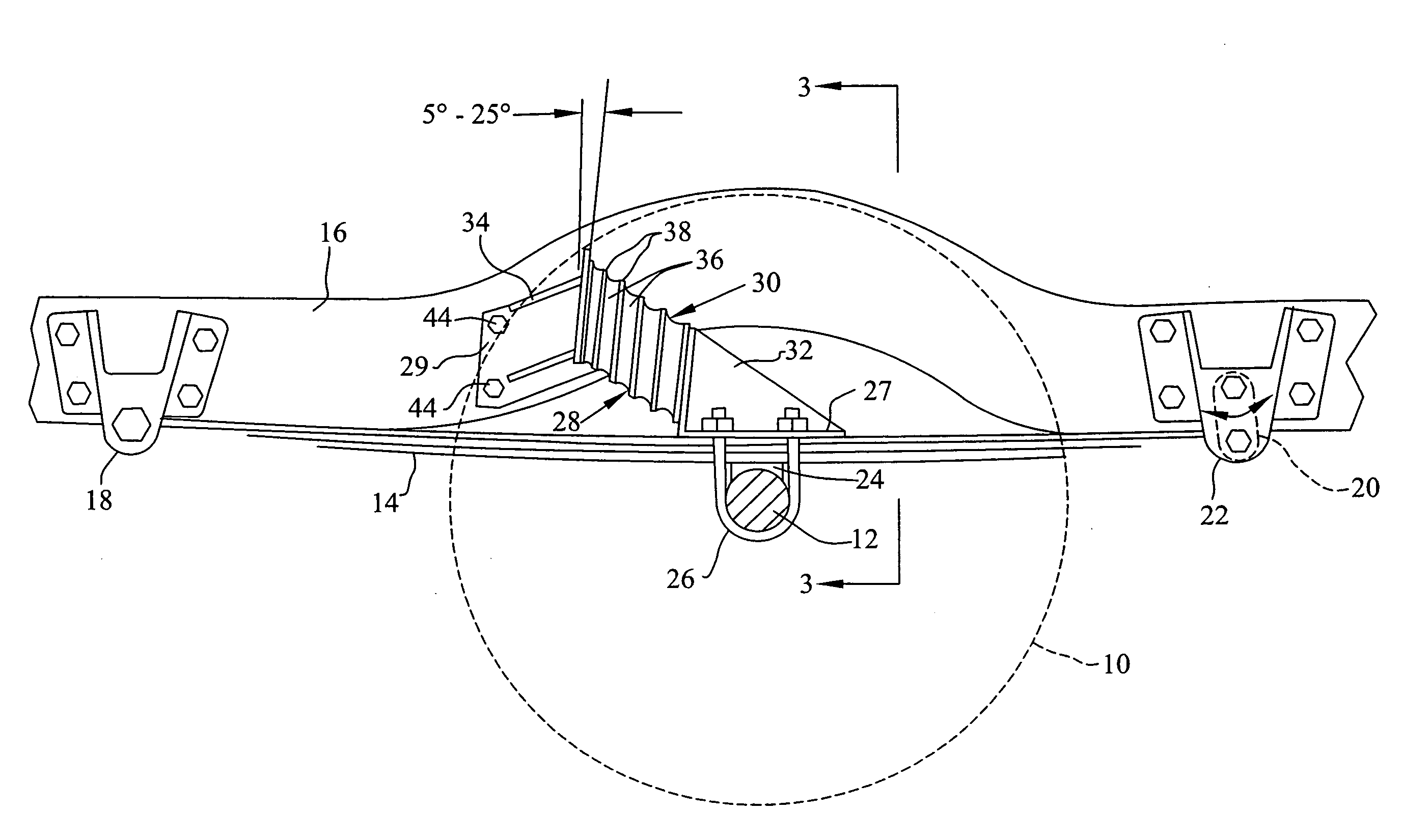
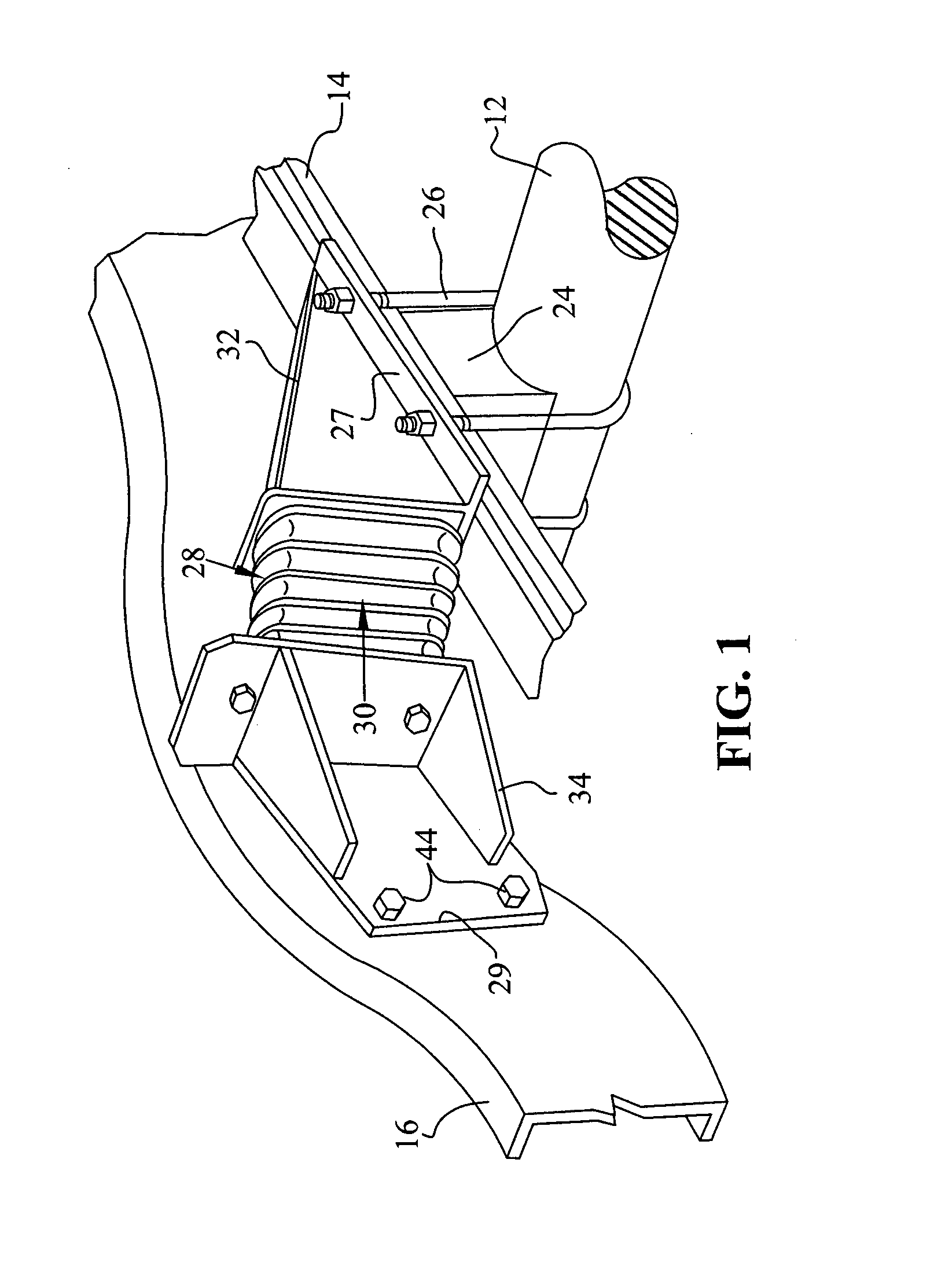
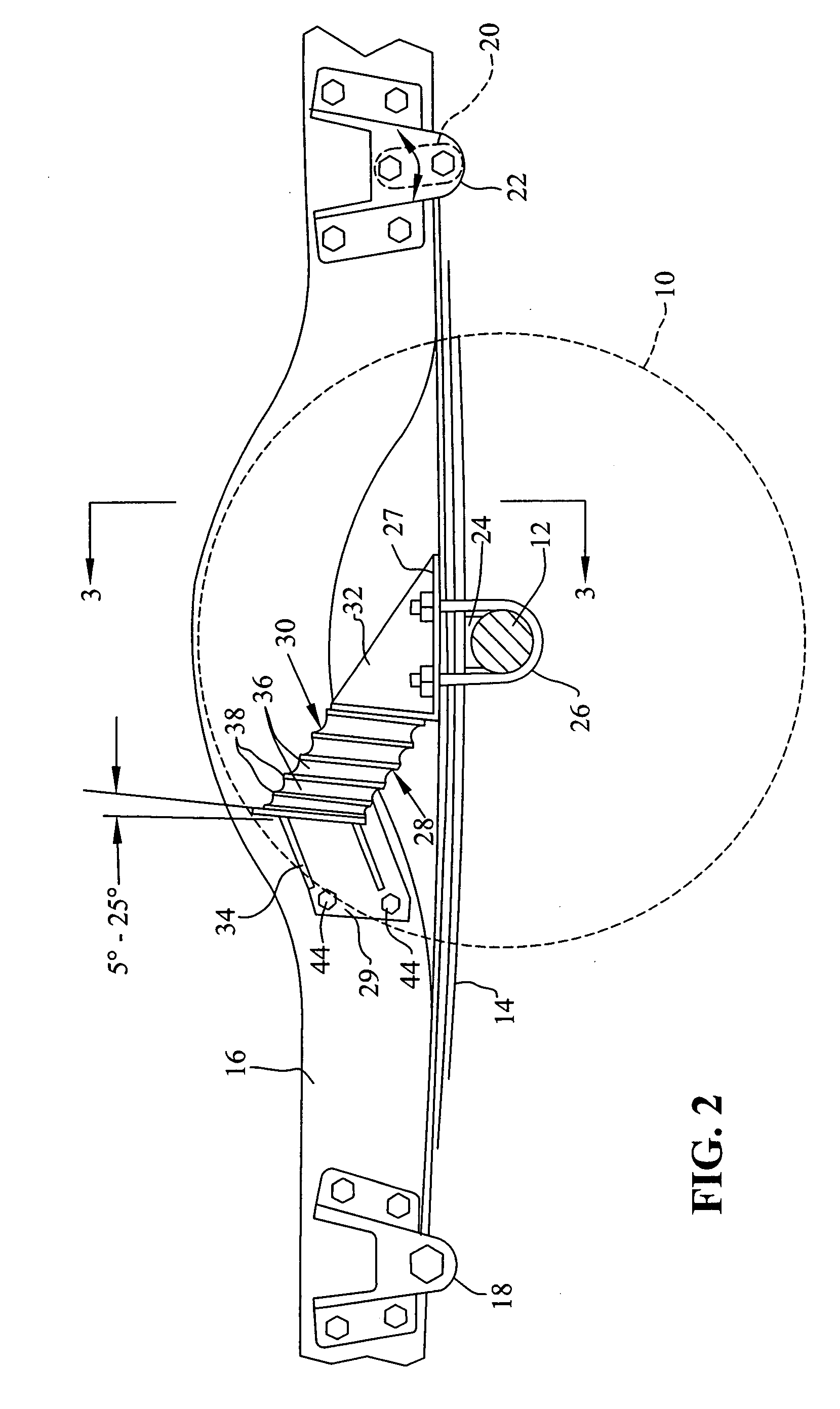
Preloaded suspension bracket assembly for axle housing
InactiveUS20050253351A1Easy to mergeSimple interfaceLeaf springsResilient suspensionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
An axle housing includes a suspension mount interface for mounting a vehicle suspension to the axle housing. The axle housing includes a first leg portion extending to a first wheel assembly and a second leg portion extending to a second wheel assembly. The first and second leg portions each include a suspension mount interface. Each suspension mount interface includes first and second bracket portions. The first and second bracket portions are clamped together prior to attachment to the axle housing to form a suspension bracket assembly. One clamped suspension bracket assembly is then slid over each axle housing leg portion. The first and second bracket portions are subjected to a preload force as they are welded or fastened to each other, providing a preload effect to define a suspension load path that has positive contact only at desired locations on the axle housing.
Owner:ARVINMERITOR TECH
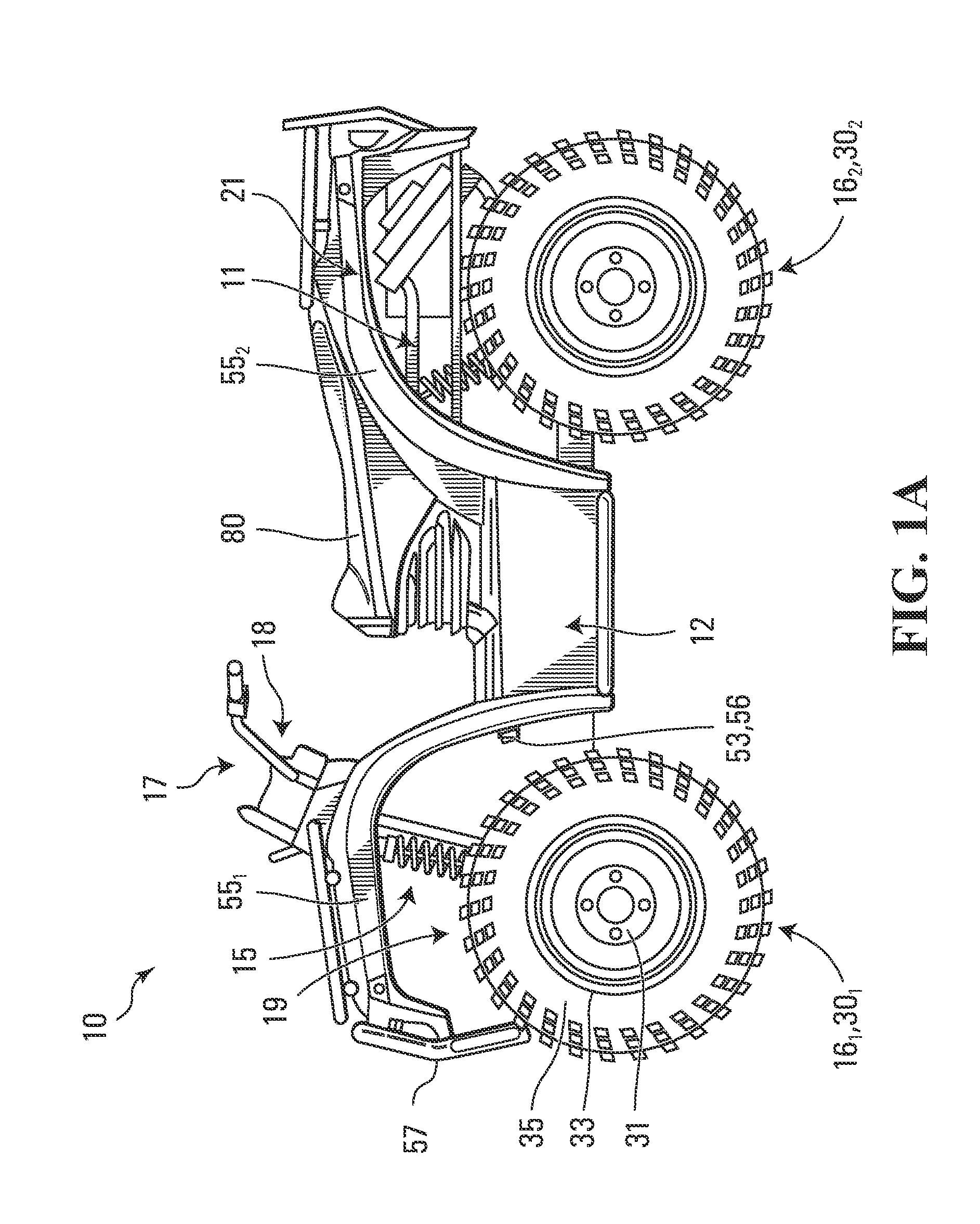
Front suspension with three ball joints for a vehicle
Owner:BOMBARDIER RECREATIONAL PROD INC
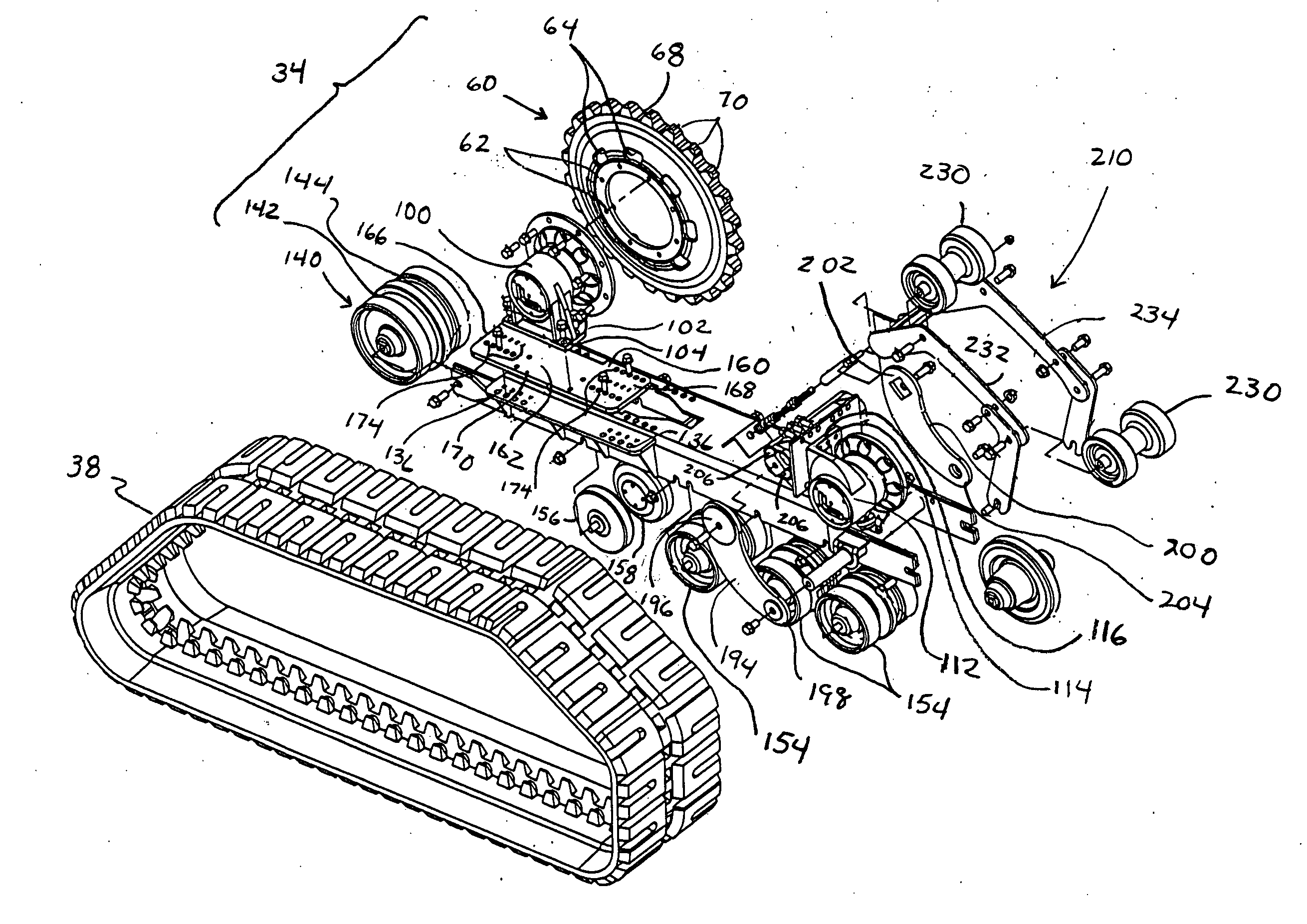
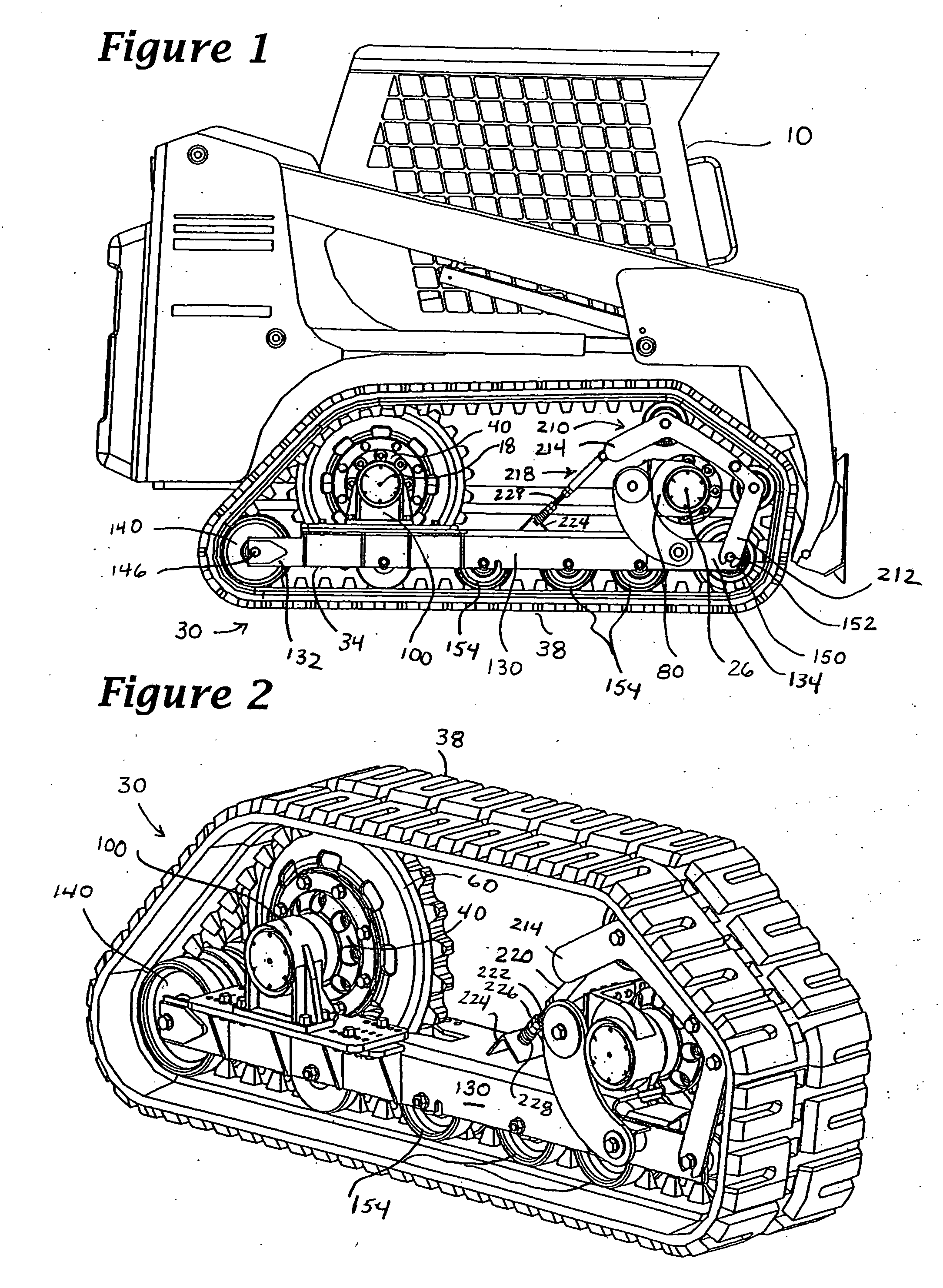
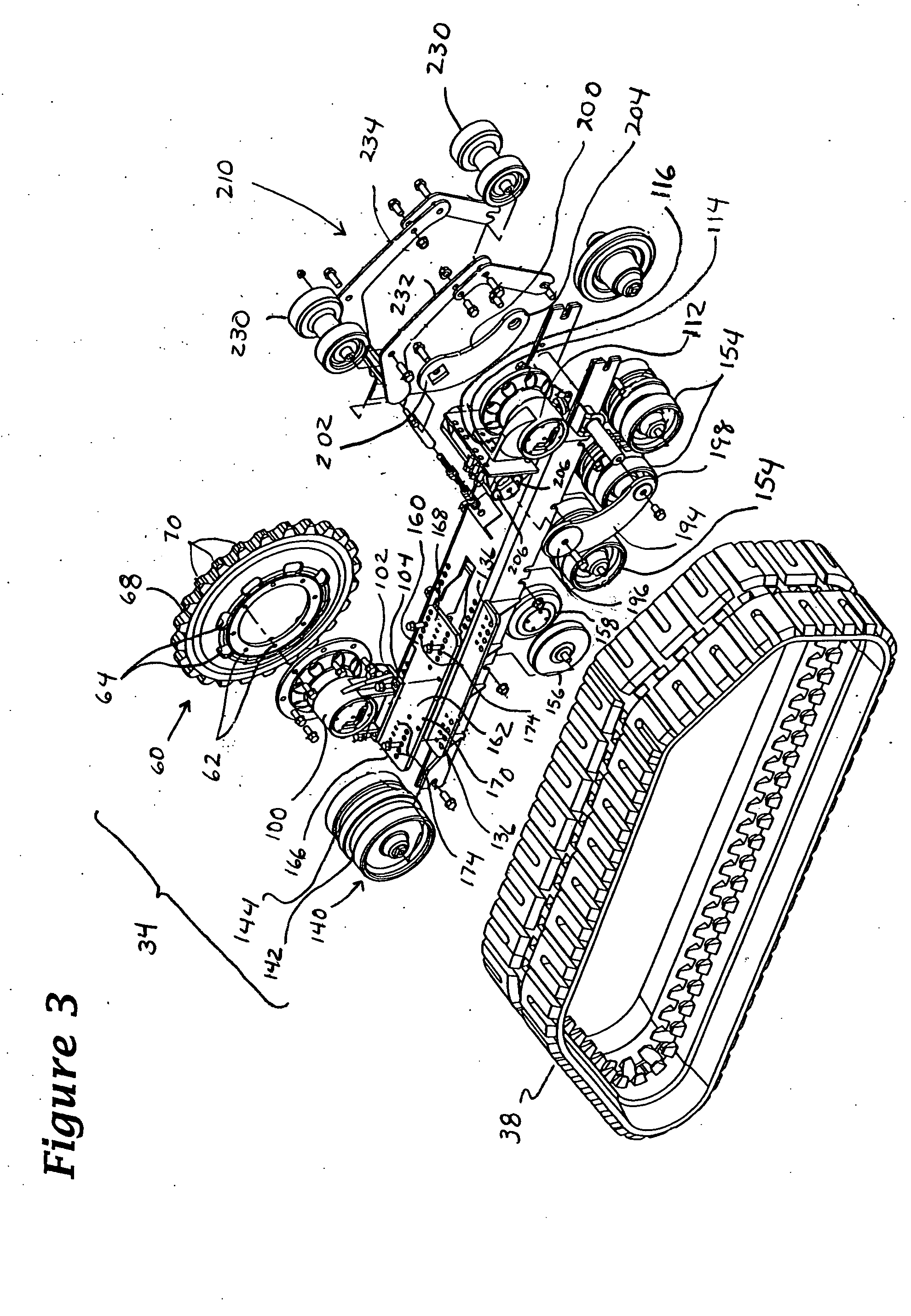
Track assembly
ActiveUS20050145422A1Improve stabilityGreat tractionGearingEndless track vehiclesBraced frameEngineering
A track assembly having first and second hub assemblies that are operatively connected to a support frame by first and second attachment members, respectively. The first and second attachment members include resilient or movable mounts that are configured so that the track assembly can be attached to vehicles whose axles or wheel flanges are misaligned or have irregular rotational movement such as runout or wobble. The attachment members may be adjustably positioned relative to the support frame to accommodate vehicles having different wheelbase lengths and axle lengths. An endless track encircles the first and second hub assemblies, and the support frame, and is drivingly engaged by one of the hub assemblies. First and second rollers, which define the longitudinal extent of the endless track, are positioned at either end of the support frame. A tensioning member, with at least one upper idler roller, positions the endless track so that it is spaced from one of the hub assemblies in a spaced relation. The track assembly increases traction and stability by providing a vehicle with an independent front suspension, a larger footprint, and a longer wheelbase. In use, each track assembly is bolted onto wheel flanges of a vehicle using existing wheel lugs and nuts.
Owner:ASV HLDG INC
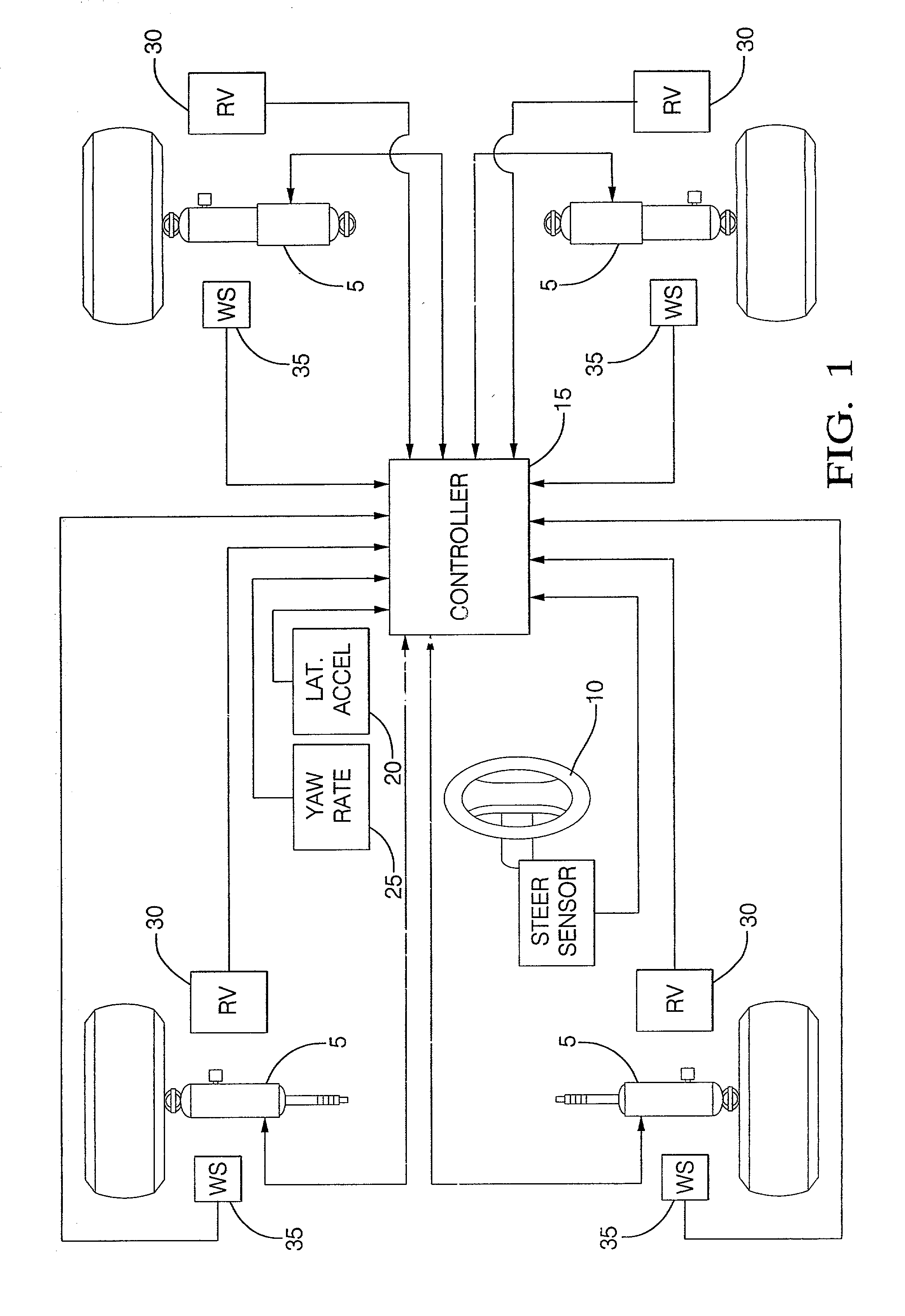
Damper based vehicle yaw control
InactiveUS20020128760A1Improve vehicle responseImprove stabilityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesTime derivativeYaw control
Controllable dampers are used to improve vehicle responses and stability during severe vehicle handling maneuvers. A total handling damping value for the vehicle is derived, preferably from the greatest of a yaw rate error value, a lateral acceleration value and a time derivative of lateral acceleration value. In addition, a control ratio of front axle roll damping to total roll damping is derived, preferably from the yaw rate error value, an oversteer / understeer indication and possibly vehicle speed. From these values, handling damping values are derived for each wheel of the vehicle and blended with damping values for the same wheels derived from suspension component movement to determine a corner damping command for each controllable damper. Preferably, the damping values derived from suspension component movement are shifted away from damping control of the vehicle body toward handling damping control when yaw rate error is large in magnitude.
Owner:BWI +1
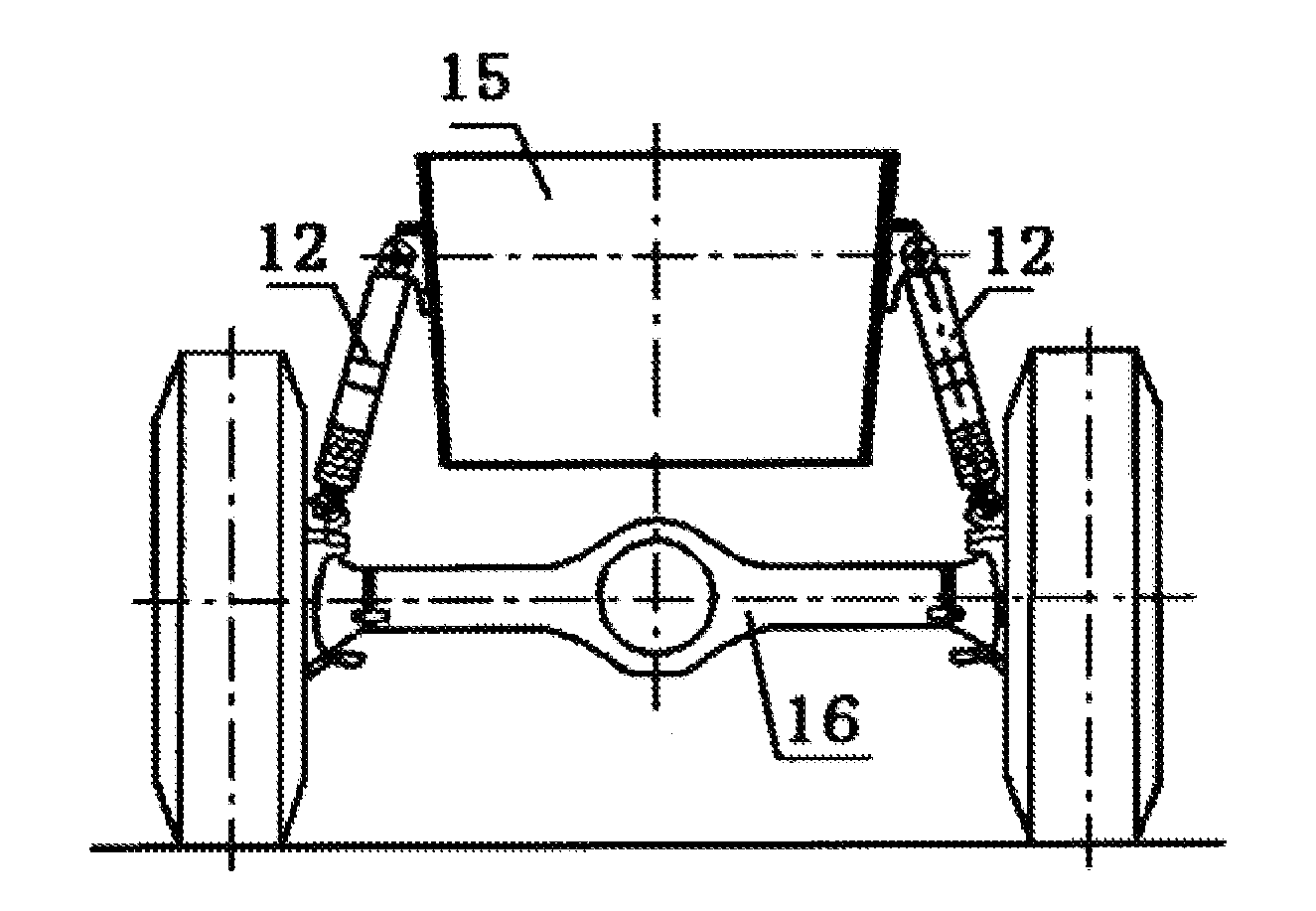
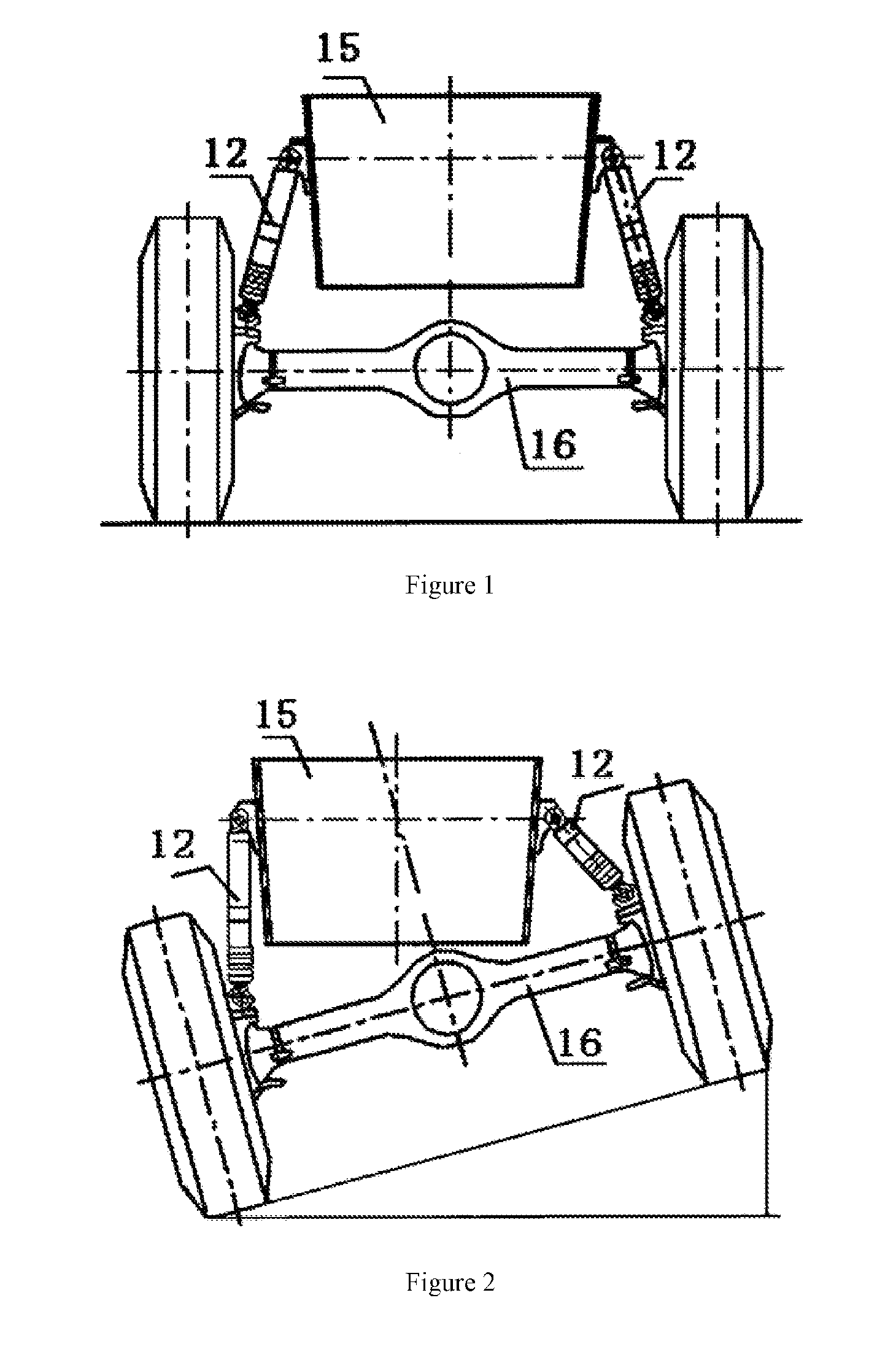
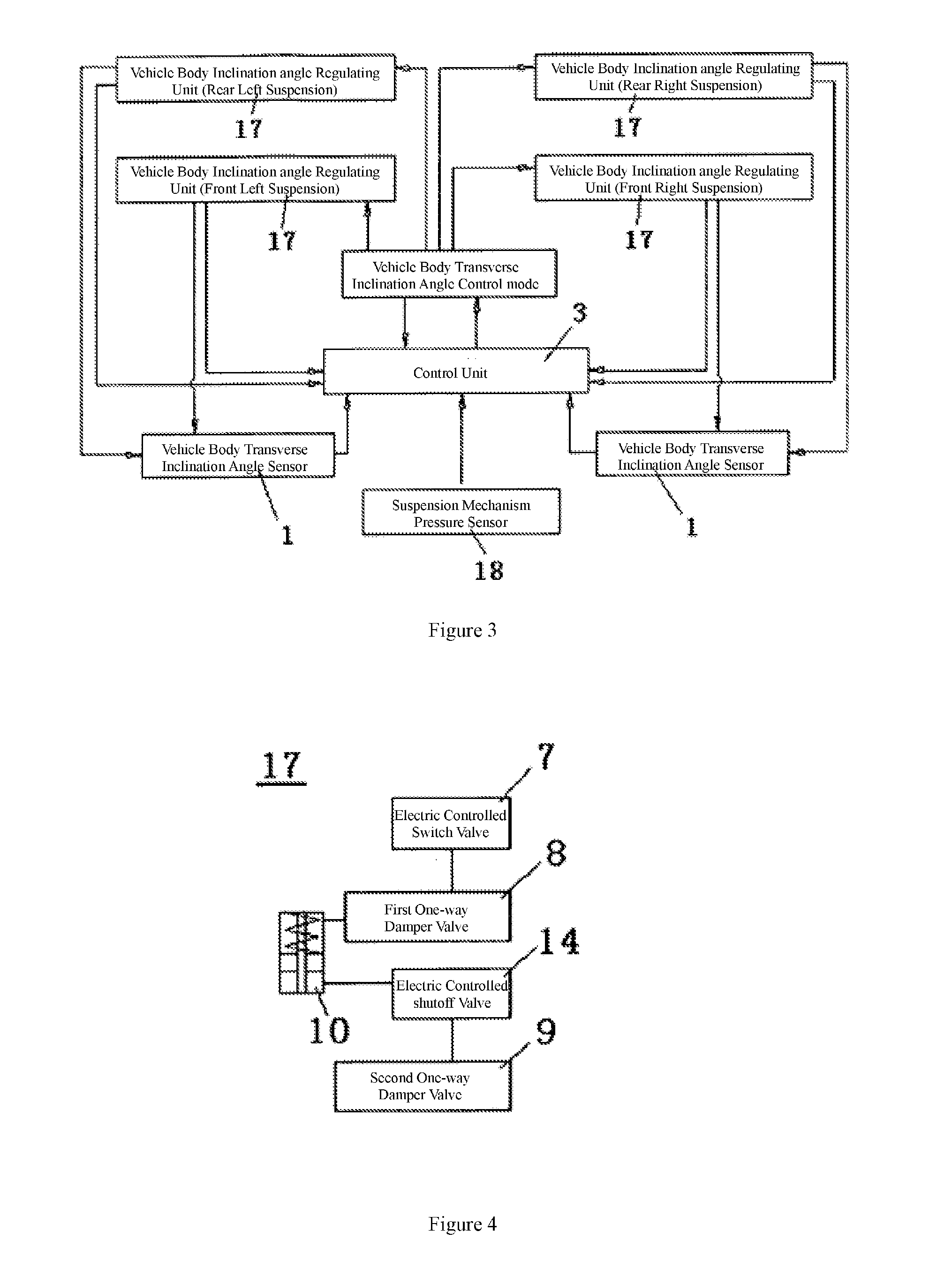
Vehicle body inclination-angle regulating uint, hydropneumatic suspension mechanism and mobile crane
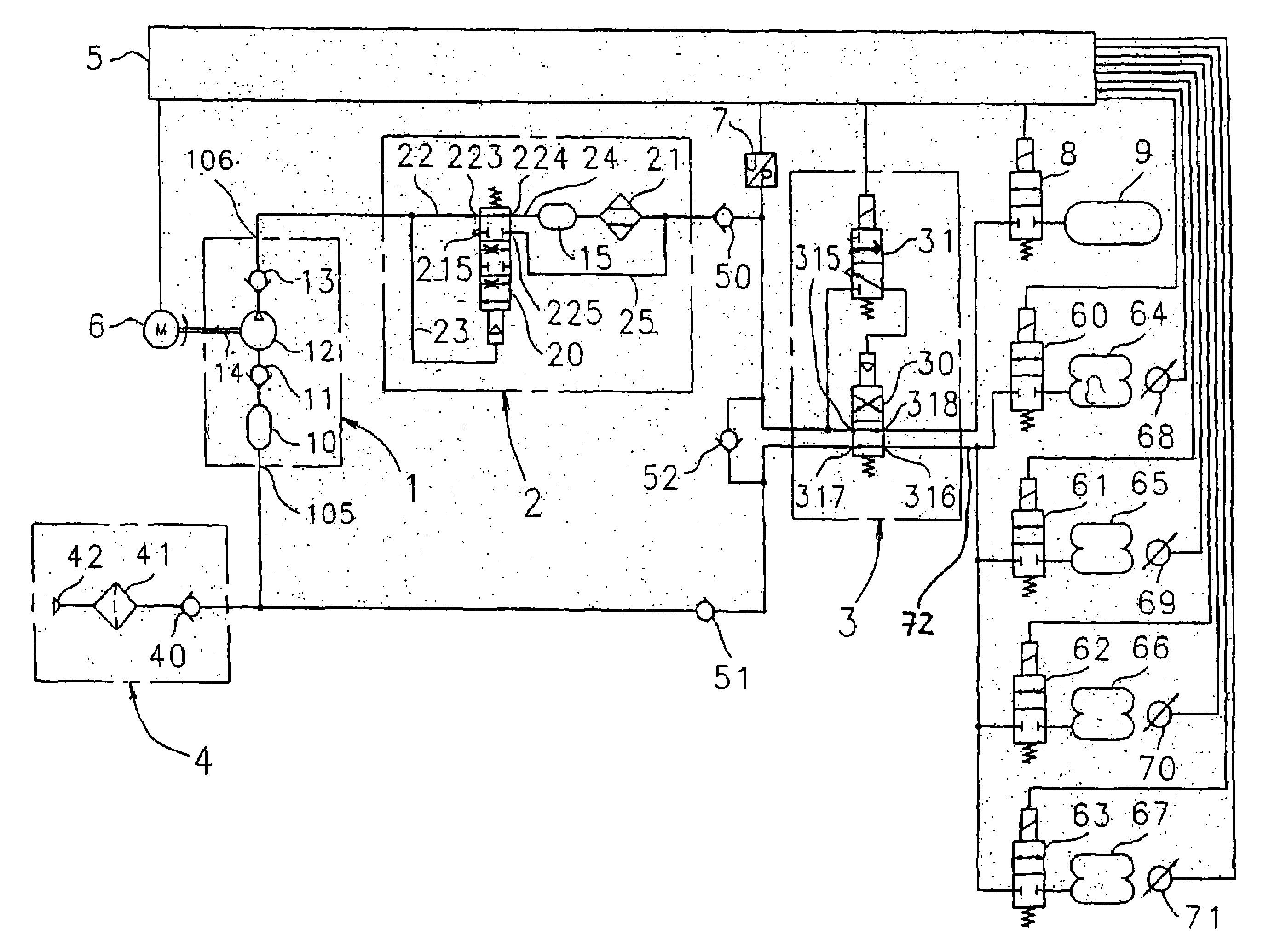
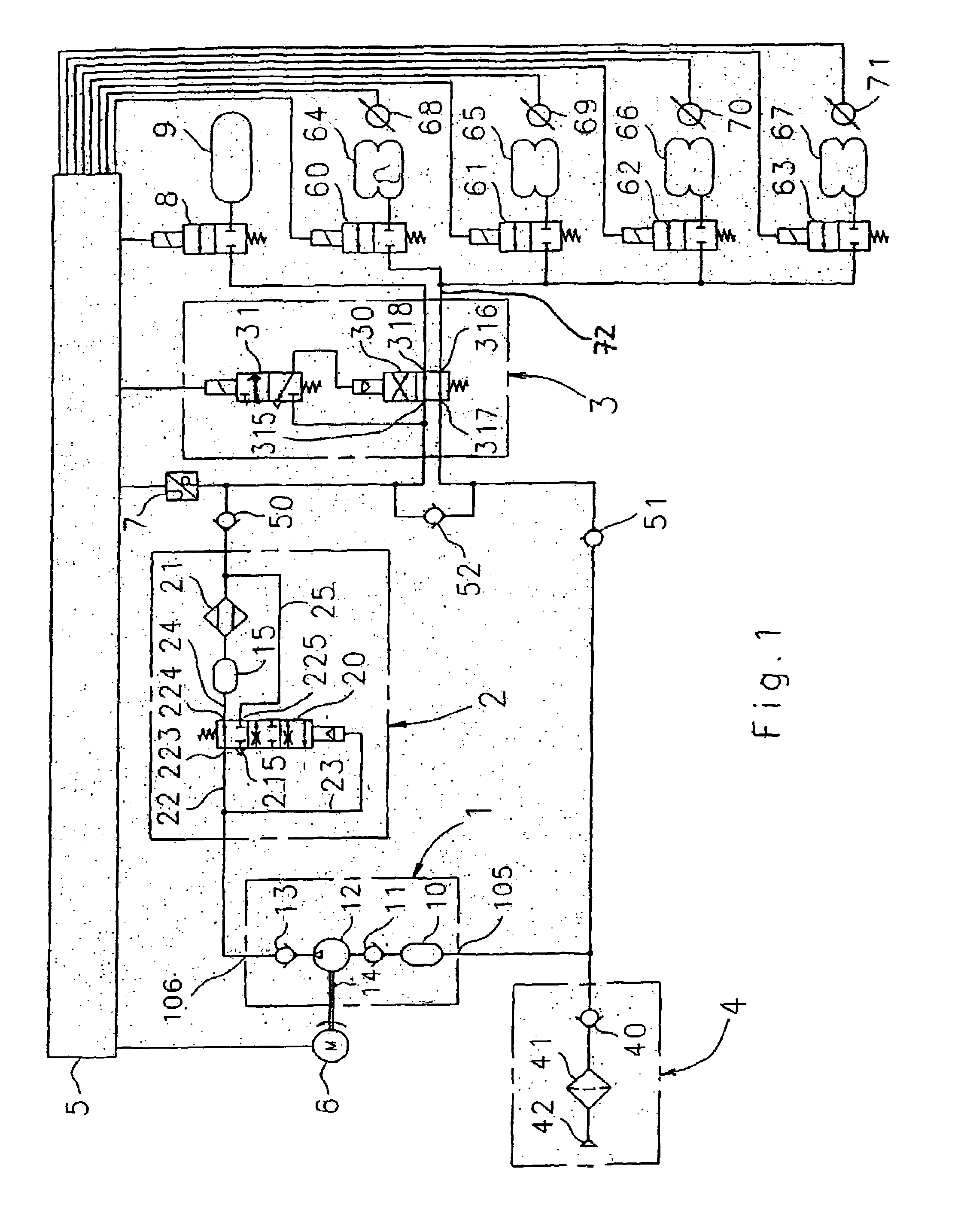
InactiveUS20130220110A1Improve securityIncrease dynamicsServomotor componentsInterconnection systemsHydropneumatic suspensionFuel tank
A vehicle body inclination angle regulating unit (17) includes a balancing oil cylinder (10). One chamber of the balancing oil cylinder (10) is connected with an oil tank (5) and an oil source for leveling operation via a first one-way damper valve (8) and an electric controlled switch valve (7), and the other chamber of the balancing oil cylinder (10) is connected with a non-rod chamber of a suspension oil cylinder via an electric controlled shutoff valve (14) and a second one-way damper valve (9). In addition, an automatically-leveling hydropneumatic suspension mechanism includes at least two pairs of suspension oil cylinders (12), vehicle body inclination angle regulating units (17), a vehicle body transverse inclination angle sensor (1) and a control unit (3). Each suspension oil cylinder (12) is correspondingly provided with the vehicle body inclination angle regulating unit (17) including the balancing oil cylinder (10). The present invention realizes effectively dynamic leveling function of different road conditions, especially transverse slopes, of the mobile crane. The mobile crane is provided with simple operation that are all automatically performed by the control unit, which improves driving safety remarkably and prevents an accident of vehicle overturning.
Owner:ZOOMLION HEAVY IND CO LTD +1
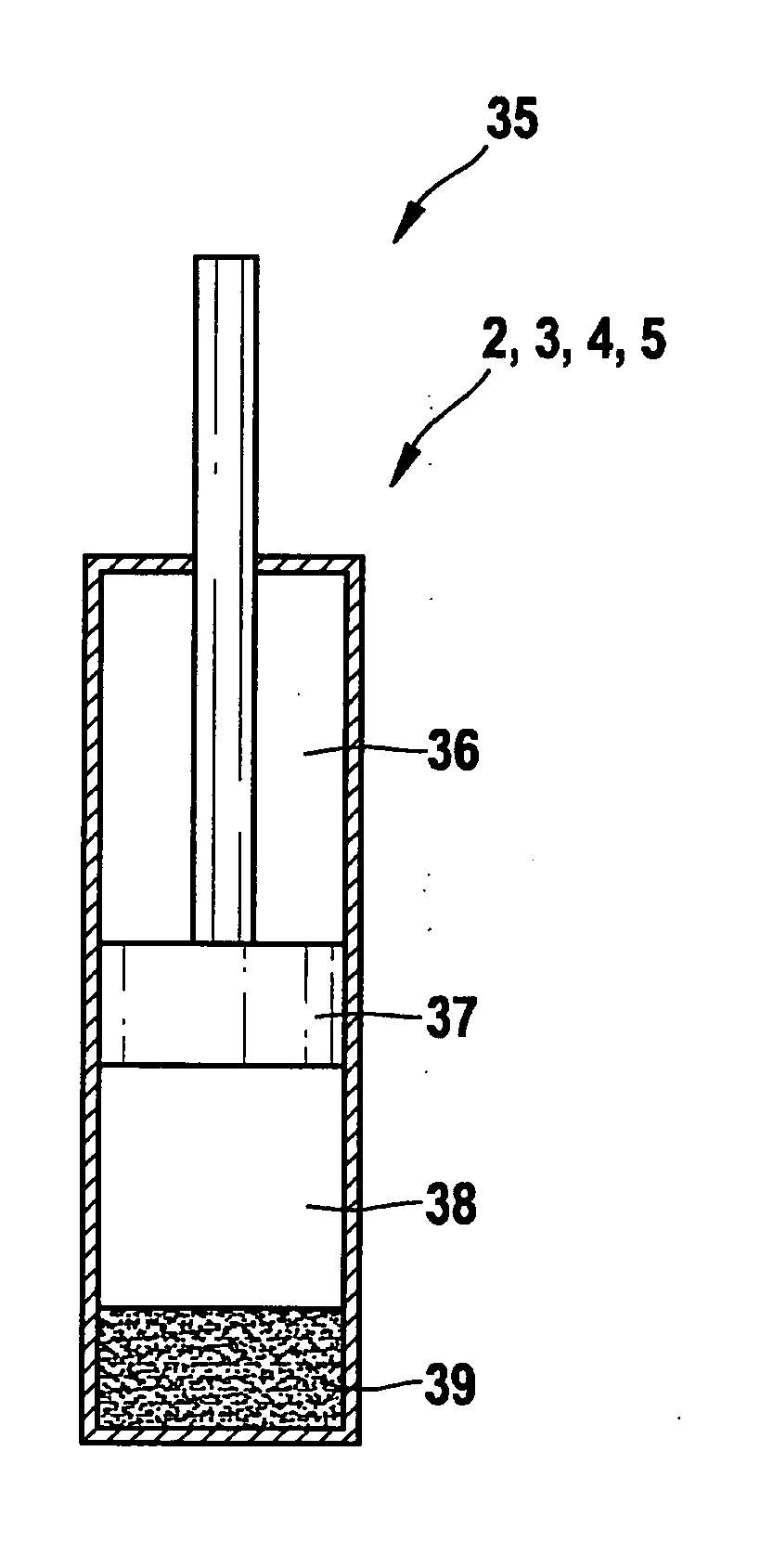
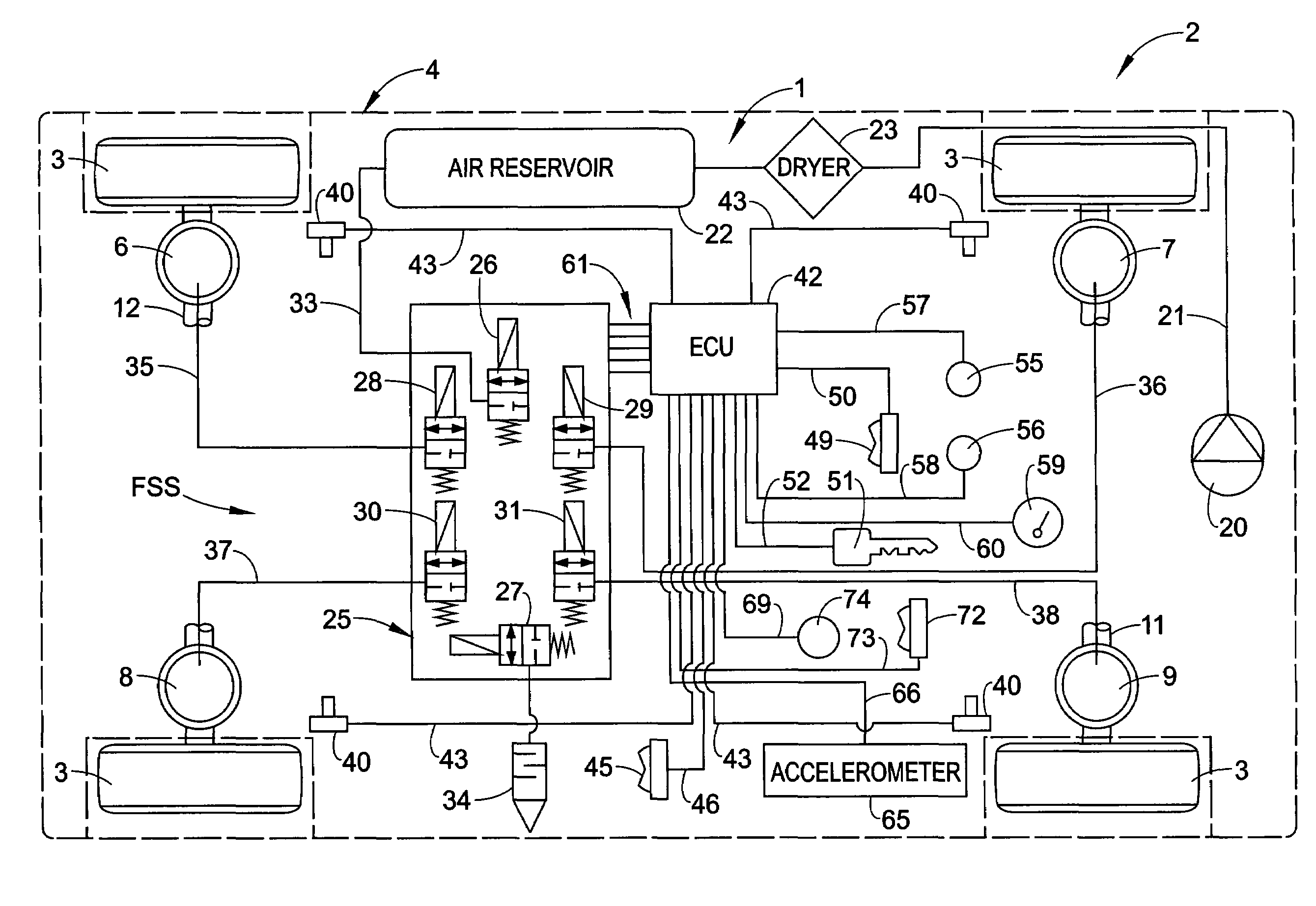
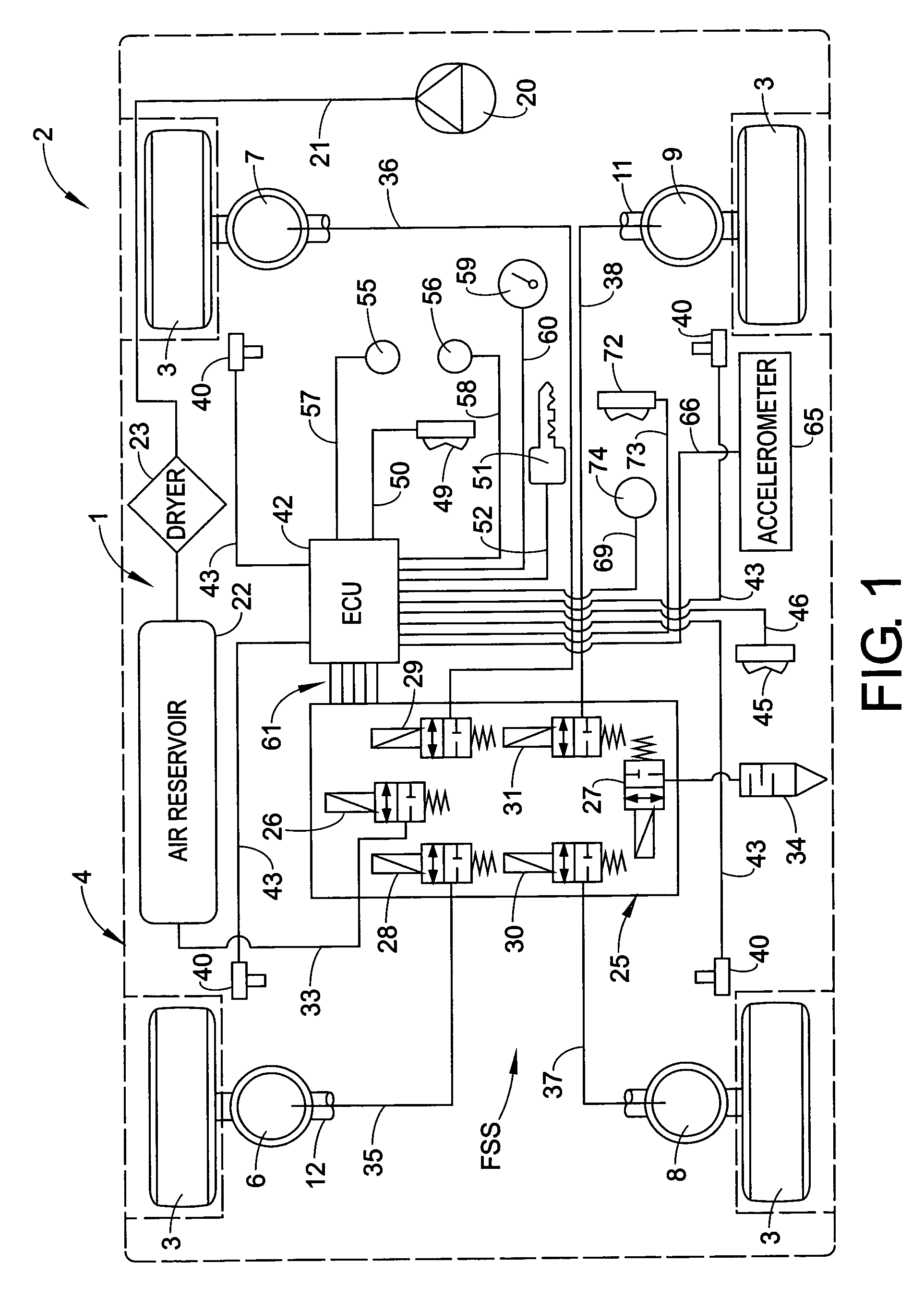
Pneumatic suspension system for a vehicle
ActiveUS7441789B2Inexpensive and compact constructionGood priceResilient suspensionsSuspension (vehicle)Control theory
A pneumatic suspension system for a vehicle includes a compressed air accumulator, a compressed air transport device, at least one pneumatic bellows and an electrically controllable reversing valve used to connect the compressed air accumulator to a suction connection of the compressed air transport device, in order to increase the amount of air in the pneumatic bellows in a first switching position, and to connect an outlet connection of the compressed air transport device to the pneumatic bellows, also used to connect the pneumatic bellows to the suction connection of the compressed air transport device and the outlet connection of the compressed air transport device to the pressure accumulator in a second switching position in order to reduce the amount of air in the pneumatic bellows. The reversing valve can be pre-controlled with the compressed air of the pneumatic suspension system.
Owner:WABCO GMBH
Electric power generation system for electric vehicles
An electrical power generating system is described for generating electrical energy for an electric vehicle, via the motion of the non-drive wheels, which converts kinetic energy to electrical energy to replenish the batteries of said vehicle. The preferred version places one or more alternator / generator(s) at the non-driven wheels of the vehicle. Each alternator / generator is unitarily formed with respect to a mounting plate unitarily formed with respect to said mounting plate and said vehicle's suspension, and each alternator / generator includes a rotating field means integrated with the rotating mounting plate attached to the wheel and a stationary stator means stationarily attached to the frame through the suspension. Conventional electrical contact means attached to between said rotating field means and said stationary stator means for generating electrical current for said vehicle. Since the mechanical loading on the spindle bearing assemblies has been substantially increased, the bearing assemblies of the invention are of a heavy-duty design. That is, such bearing assemblies are large enough to handle the weight of said vehicle, including that of the alternator, as well as the weight of the wheel assembly, including tire and brakes. As the vehicle moves forward or backward, the rotational force applied to the vehicle's wheels will rotate the integrated rotating field means relative to the stationary stator means to produce alternating current (AC). Alternating current is converted to direct current (DC) either by a diode bridge, transformer, or controller, for distribution to the EV's electrical system. DC electricity is used to recharge storage batteries, provide electricity for the drive motor and operate the vehicle's electrical equipment. Thus, the regenerative system, does not add any additional load on the drive motor. Wheel bearing assemblies are usually used for all wheels on vehicles and the very nature of bearing assemblies are to reduce friction. By the incorporation of alternators into the wheel bearing assemblies, a vehicle can generate electricity when moving, without additional workload to the drive train; since wheel bearing assemblies are a necessary and integral part of any rolling vehicle and by their very nature reduce friction and resistance.
Owner:SMITH VINCENT A +2
Bolster spring suspension assembly
ActiveUS7234723B2Reduce bumpsSmooth rideNon-rotating vibration suppressionLoad securingSuspension (vehicle)Control theory
A bolster spring assembly is adapted for securement to a vehicle having a primary suspension system for securing an axle to the vehicle. The bolster spring assembly is located and secured between the leaf spring over the axle and the undercarriage of the vehicle as a supplement to the primary suspension system.
Owner:LIPPERT COMPONENTS MFG INC
Stabilizer bar
InactiveUS20060243355A1Reduce manufacturing costHigh hardnessFurnace typesInterconnection systemsTemperingClassical mechanics
A tubular stabilizer bar for a vehicle suspension is formed from an as-quenched steel material that is not subjected to a tempering process, and which has a hardness of at least 40 Rockwell C. The stabilizer bar includes an ultimate tensile strength that is greater than 200 ksi with a ratio of yield strength to ultimate tensile strength that is no more than 0.9. The stabilizer bar is significantly harder and has significantly improved fatigue life without compromising ductility, when compared with prior designs.
Owner:MERITOR SUSPENSION SYST U S
Device for changing distance between wheel and vehicle body, and system including the device
InactiveUS20070290473A1Reduce spacingAdjustable distanceVehicle cleaning apparatusLoading/unloading vehicle arrangmentEngineeringActuator
An adjuster device includes (a) a shaft held by a vehicle body; (b) an arm extending from the shaft in a direction intersecting an axial direction of the shaft; (c) an actuator causing one of rotation of the shaft and axial movement of the shaft in the axial direction; and (d) a motion converter converting the one of the rotation of the shaft and the axial movement of the shaft, into the other of the rotation of the shaft and the axial movement of the shaft. The arm is connected at a distal end portion thereof to one of at least one suspension arm, so as to enable the rotation of the shaft to cause change in a vertical distance between a wheel and the vehicle body. The shaft is connected to one of the at least one suspension arm and / or to an axle carrier, so as to enable the axial movement of the shaft to cause change in an alignment of the wheel. Also disclosed is an adjusting system including the adjuster device.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Retractable wheel fairings for motor vehicles
ActiveUS8979102B1Reduce air resistanceLower the volumeVehicle seatsVehicle body stabilisationSupporting systemAerodynamic drag
A retractable wheel fairing device for decreasing the aerodynamic drag and / or increasing downforce of a vehicle is described. The device includes a fairing body with a suspension-mounted support system such that the fairing body, when deployed, reciprocates up and downwardly with the corresponding wheel of the vehicle. The suspension-mounted support system is adapted to functionally or physically disengage the wheel fairing device from the suspension of the vehicle upon lifting of the wheel fairing device with a separate retraction system.
Owner:PRENTICE MICHAEL
Hydro-pneumatic suspension control loop, multi-axle vehicle hydro-pneumatic suspension system and crane
ActiveCN101618669AImprove mobilityImprove roll stiffnessResilient suspensionsHydropneumatic suspensionAutomotive engineering
The invention discloses a hydro-pneumatic suspension control loop. The design key point of the invention comprises that: a communication relationship between a suspension oil cylinder rodless cavity and an energy accumulator at the same side is controlled by a two position two-way valve to realize rigid and flexible conversion of a suspension system; each suspension oil cylinder rod cavity is communicated with an energy accumulator at the opposite side so as to obtain relatively strong side tilting rigidity; and communication relationships between a pressure oil line and the suspension oil cylinder rodless cavity and between an oil return oil line and the suspension oil cylinder rodless cavity are controlled by a two position two-way valve, respectively so as to control the lifting of a vehicle body. In the multi-axle vehicle hydro-pneumatic suspension system provided by the invention, all the middle axle hydro-pneumatic suspension control loops and rear axle hydro-pneumatic suspension control loops form a lifting control group so as to level the vehicle body. The hydro-pneumatic suspension control loop provided by the invention has reasonable and reliable design and higher comprehensive performance of the suspension system, and is suitable for a multi-axle vehicle, particularly for a multi-axle construction crane. The invention also provides a crane using the hydro-pneumatic suspension control loop.
Owner:XUZHOU HEAVY MASCH CO LTD
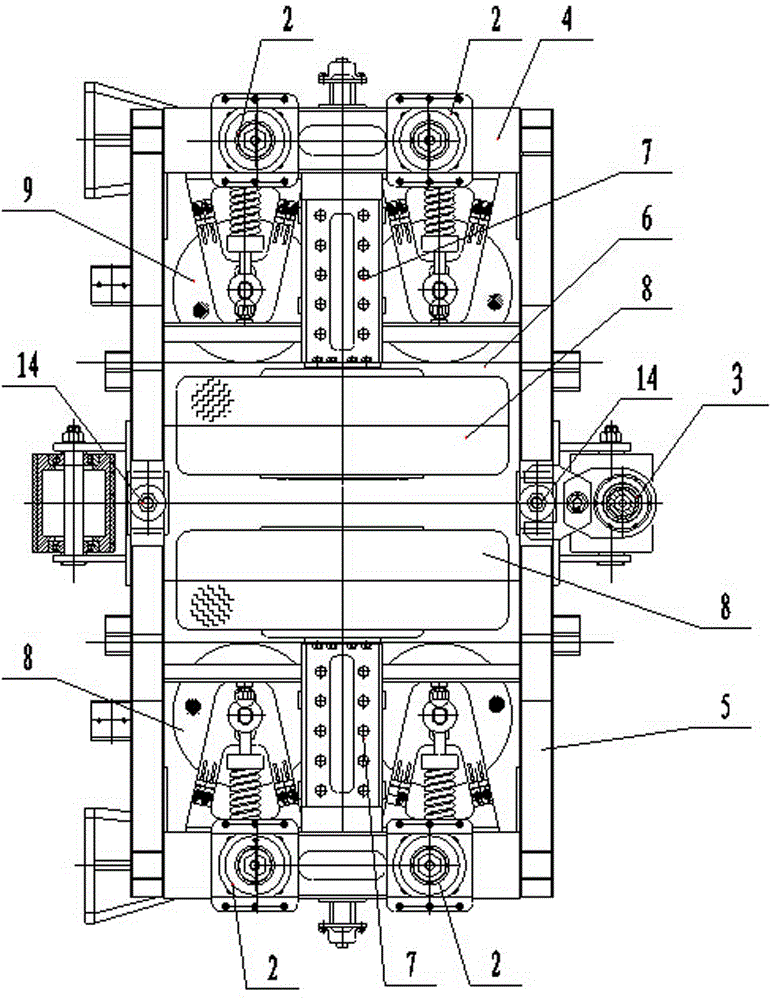
Straddle type monorail operation vehicle with structure comprising two pairs of wheels
ActiveCN104554323AEnsure stabilityFree up spaceRail-engaging wheelsIC reciprocating piston engine transmissionBogieTransfer case
The invention relates to an urban rail operation vehicle and in particular relates to a straddle type monorail operation vehicle with a structure comprising two pairs of wheels. The straddle type monorail operation vehicle comprises a carriage, a steering frame, an engine, a transfer case and a walking pump, wherein the steering frame is connected with an underframe of the carriage through a central pin dragging device; the steering frame comprises a framework, a secondary suspension device and a dragging device; the overall framework is of an II-shaped full-steel installed and welded plate type box structure and comprises a side beam, end beams connected to two ends of the upper part of the side beam and two vertical beams which are connected between the end beams; a motor bracket is fixed between the upper part of the side beam and the corresponding vertical beam; two independently-driven walking wheel assemblies are mounted on two motor brackets; four guide wheel assemblies are mounted on two sides of the middle part of the side beam; two stabilizing wheel assemblies are mounted on two sides of the lower part; the secondary suspension device adopts a secondary steel coil spring assembly. The straddle type monorail operation vehicle can reasonably meet the circuit requirements of monorail PC beams and is high in safety coefficient, excellent in dragging performance, simple and compact in structure, easy to maintain, stable in running and excellent in brake performance.
Owner:太原中车时代轨道工程机械有限公司
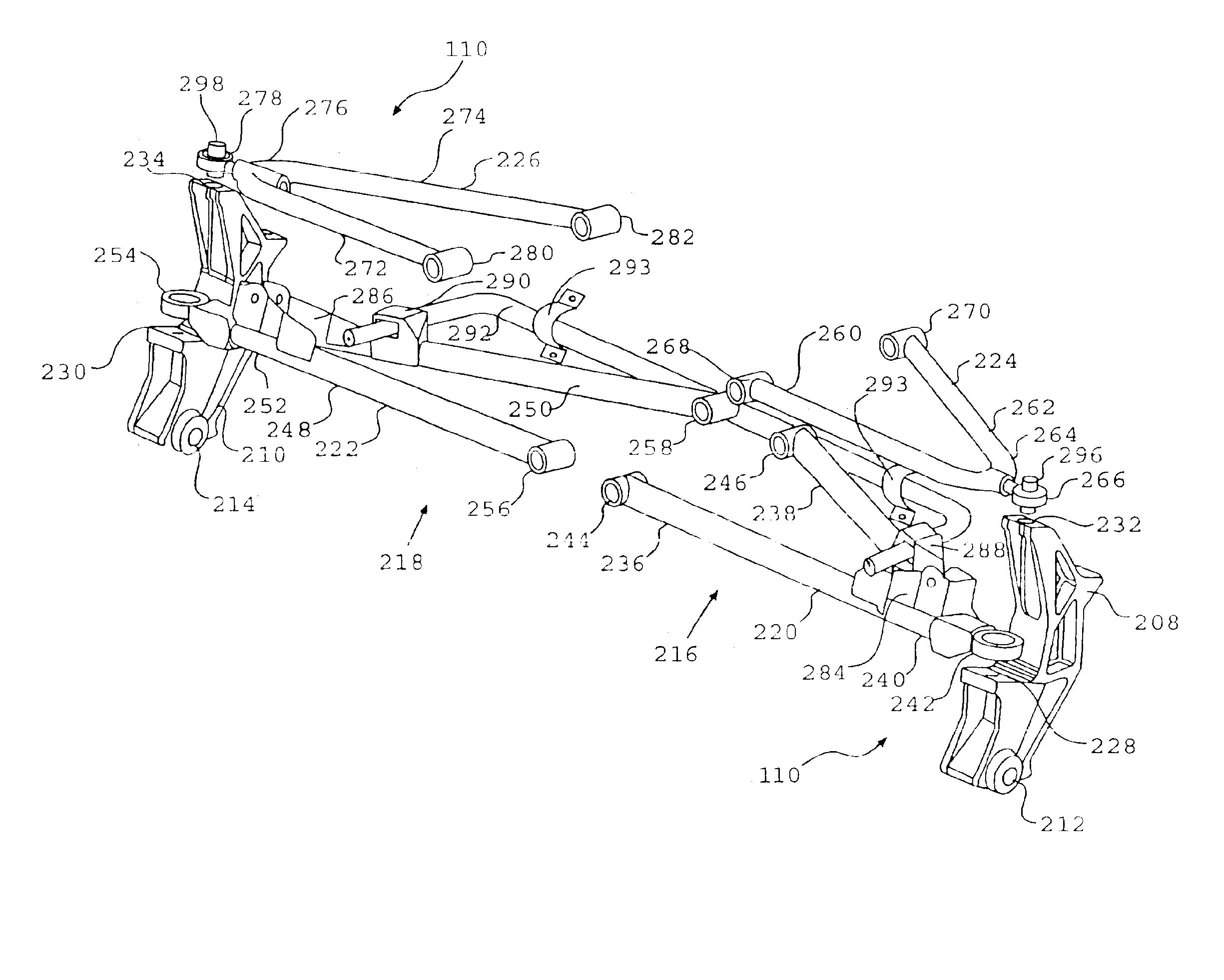
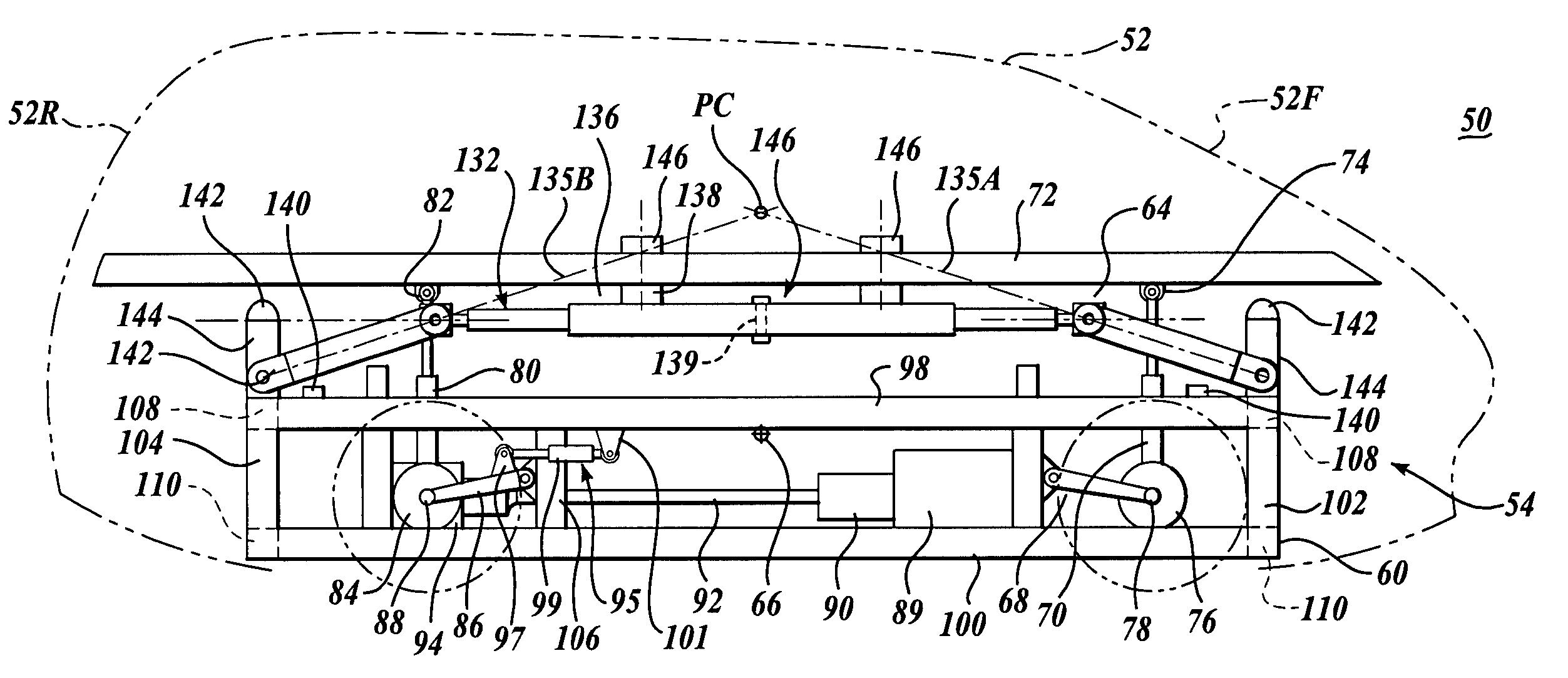
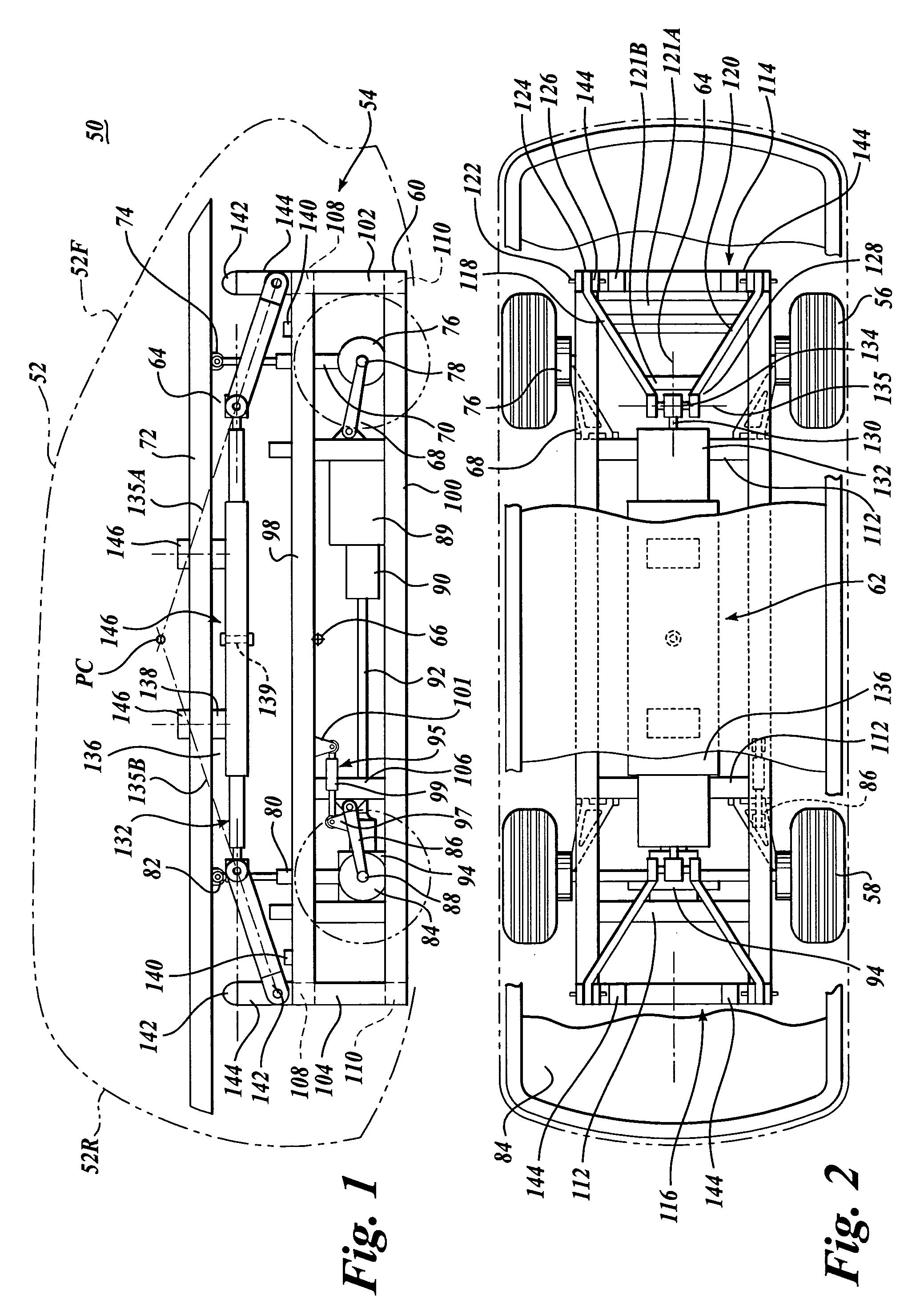
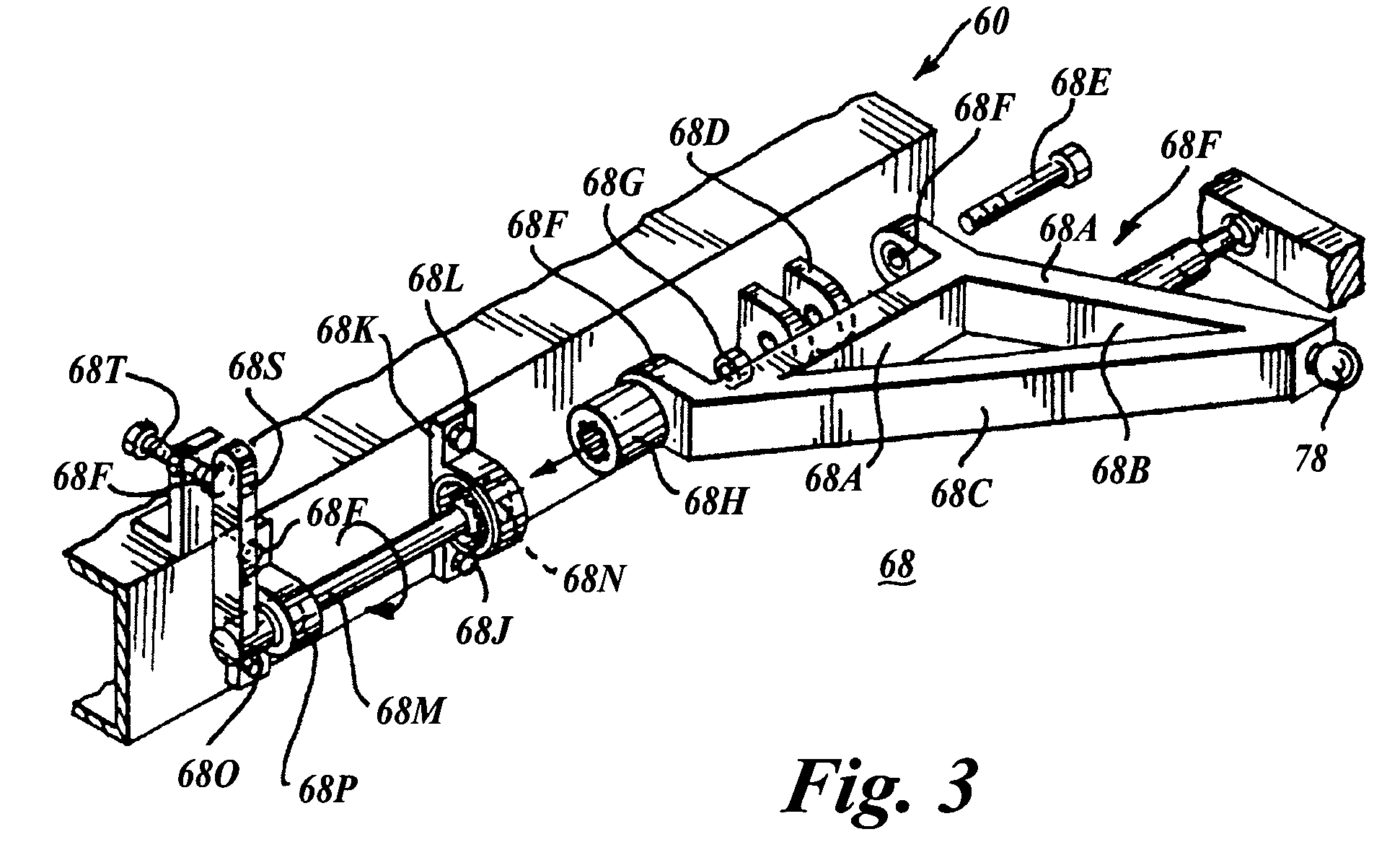
Vehicle with movable and inwardly tilting safety body
ActiveUS7377522B2Reduce the detrimental effects on vehicle handlingImprove vehicle handlingPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementRigid suspensionsStructural engineeringSuspension (vehicle)
A suspension system for a vehicle (50c) having a body (52c) and a plurality of wheel support assemblies (56c, 58c) includes a tie structure (60c) interposed between the body and the wheel support assemblies. A first interconnection system (68c) interconnects the tie structure to the wheel support assemblies, and the second interconnection system (302) interconnects the tie structure and the body. The second interconnection system includes a plurality of link structures (304, 320) pivotally connected at one end to the tie structure, and pivotally connected at the opposite end to the body. Such link structures are oriented relative to the tie structure to extend towards a common point along a longitudinal axis (33B) of the tie structure.
Owner:MACISAAC WILLIAM L
Method for Chassis Control of a Motor Vehicle, and Device for the Performance Thereof
ActiveUS20120055745A1Increase stiffnessAdjust stiffnessSpringsResilient suspensionsCompressive loadMotorized vehicle
In a method for chassis control of a motor vehicle which has at least one wheel suspension, a vehicle body, and a shock absorber having a rebound stage, whose stiffness is adjustable, and a compression stage, whose stiffness is adjustable, the stiffness of the compression stage is changed for a compressive load of the shock absorber generated by a specific vehicle body movement, and the stiffness of the rebound stage is additionally changed for a subsequently following tensile load of the shock absorber generated by the specific vehicle body movement, or the stiffness of the rebound stage is changed for a tensile load of the shock absorber generated by a specific vehicle body movement, and the stiffness of the compression stage is additionally changed for a subsequently following compressive load of the shock absorber generated by the specific vehicle body movement.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
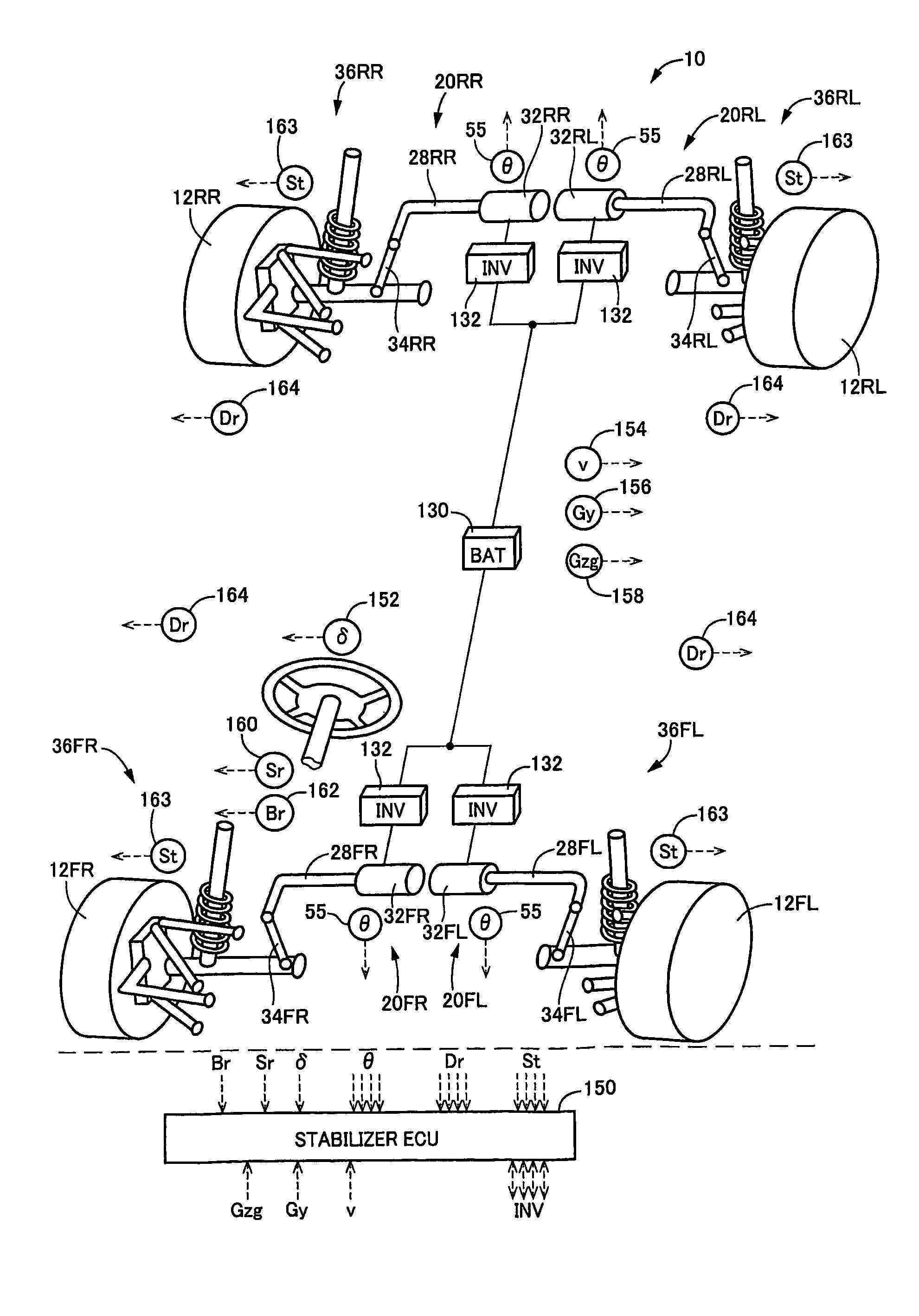
Vehicle stabilizer system
InactiveUS7896360B2Improve applicabilityImprove featuresSteering partsInterconnection systemsEngineeringSuspension (vehicle)
A vehicle stabilizer system including: (a) a stabilizer bar (28) including (a-1) a torsion bar portion (90), and (a-2) an arm portion (92) that extends from the torsion bar portion in a direction not parallel to the torsion bar portion; (b) an actuator (32) configured to rotate the stabilizer bar about an axis of the torsion bar portion; and (c) a link rod (34) interconnecting the suspension arm (78) and one of opposite ends of the arm portion that is remote from the torsion bar portion. The stabilizer bar generates a stabilizing force which is dependent on a reaction that is generated as a result of torsion of the torsion bar portion, and which forces the wheel (12) and the body in a selected one of a direction toward each other and a direction away from each other. The actuator allows the stabilizer bar to generate the stabilizing force whose magnitude is changeable by operation of the actuator. The link rod is inclined with respect to the suspension arm to which the link rod is connected, such that an angle defined by the link rod and the suspension arm is not 90°.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method and system for aligning a stationary vehicle with an artificial horizon
ActiveUS7104547B2Reduce consumptionWork lessVehicle cleaning apparatusLoading/unloading vehicle arrangmentHorizonData storing
A method of positioning a vehicle chassis of a stationary vehicle in approximate alignment with a predetermined datum is provided. The vehicle has an axle and a fluid suspension system. The fluid suspension system includes a control device, a pressurized fluid source and an exhaust passage. The pressurized fluid source and the exhaust passage are in fluid communication with the plurality of fluid suspension members through the control device. The vehicle also includes an electronic control unit operatively associated with the control device. The method including steps of providing an alignment sensor supported on the chassis for outputting a signal indicative of the orientation of the chassis to the electronic control unit and acquiring a signal output by the alignment sensor. Another step includes comparing the signal from the alignment sensor to alignment data stored in the electronic control unit. A further step includes selectively operating the control device to permit fluid communication between one or more of the fluid suspension members and one of the pressurized fluid source and the fluid exhaust until the signal from the alignment sensor approximately corresponds to the alignment data. A system for performing the method is also discussed.
Owner:DRIVERIGHT HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com