Patents
Literature
43results about How to "Improve vehicle handling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
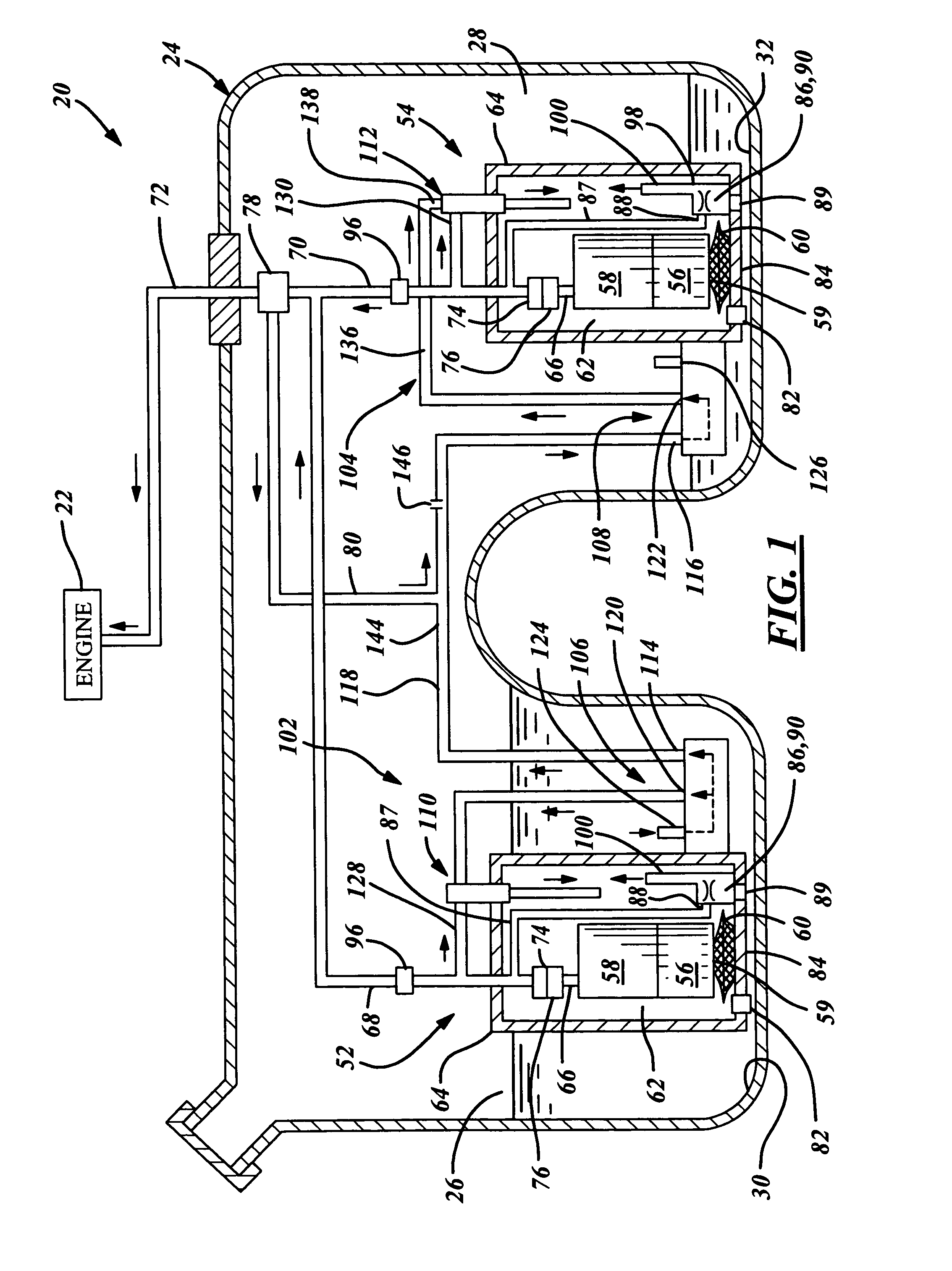
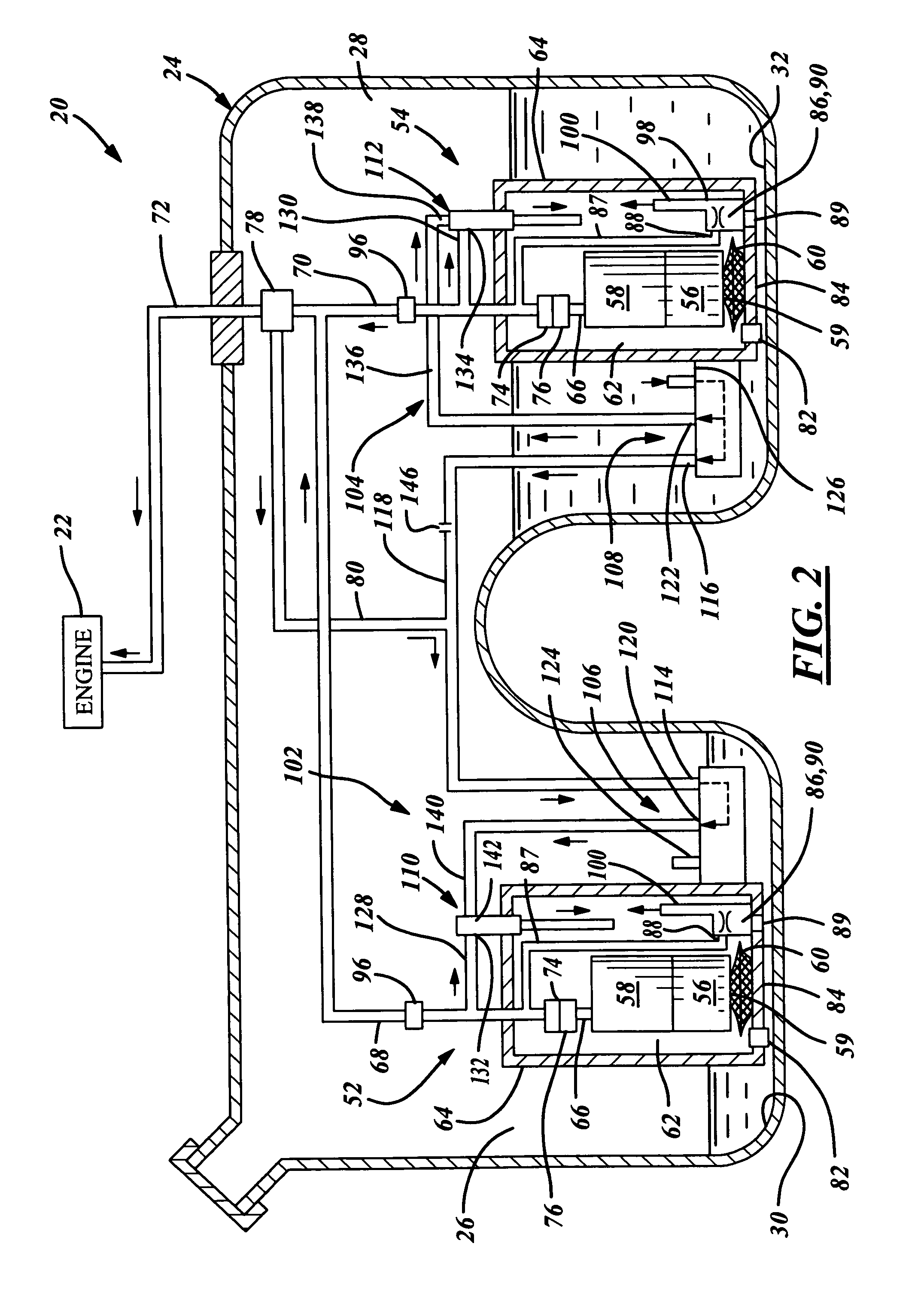
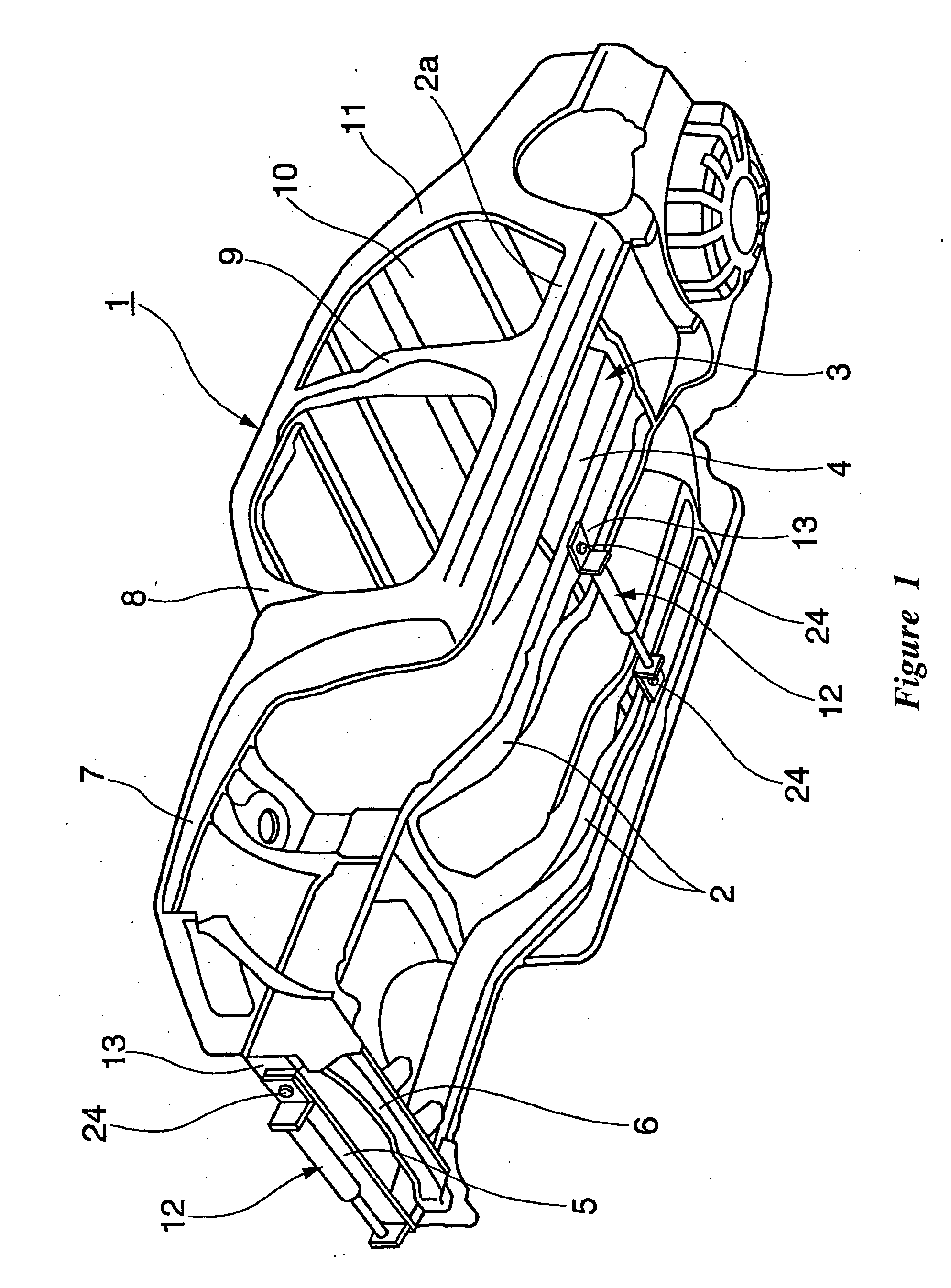
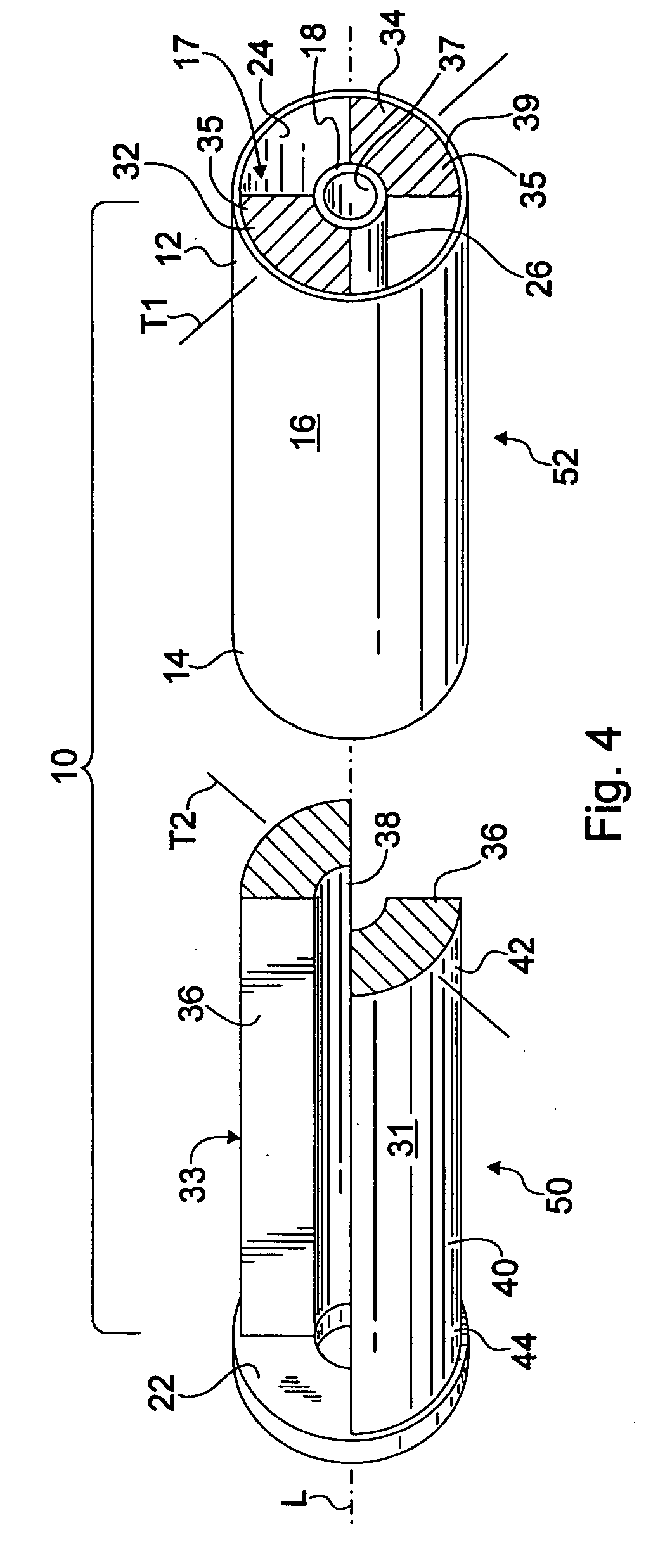
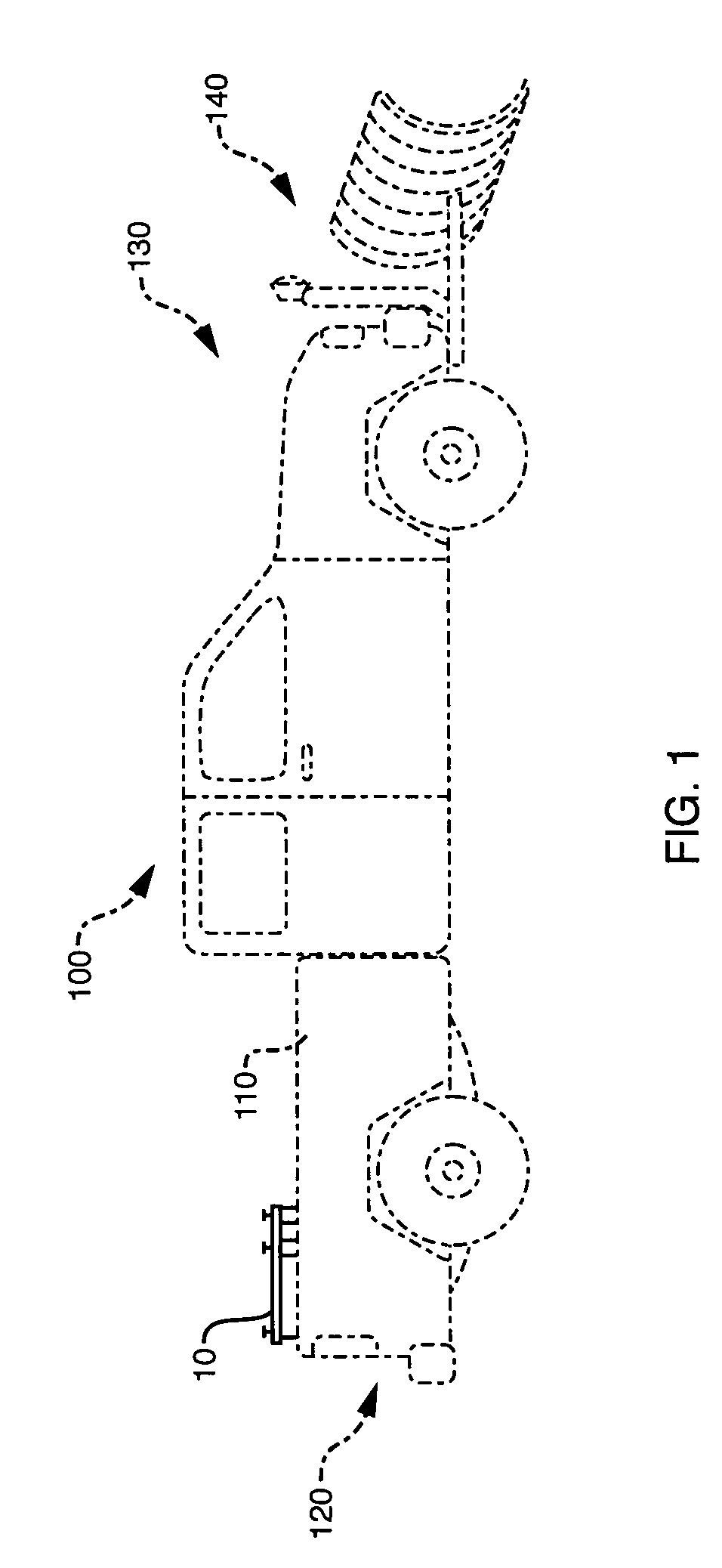
Vehicle with movable and inwardly tilting safety body
ActiveUS20050275181A1Reduce the detrimental effects on vehicle handlingImprove vehicle handlingVehicle body stabilisationVehicle cleaning apparatusEngineeringInterconnection
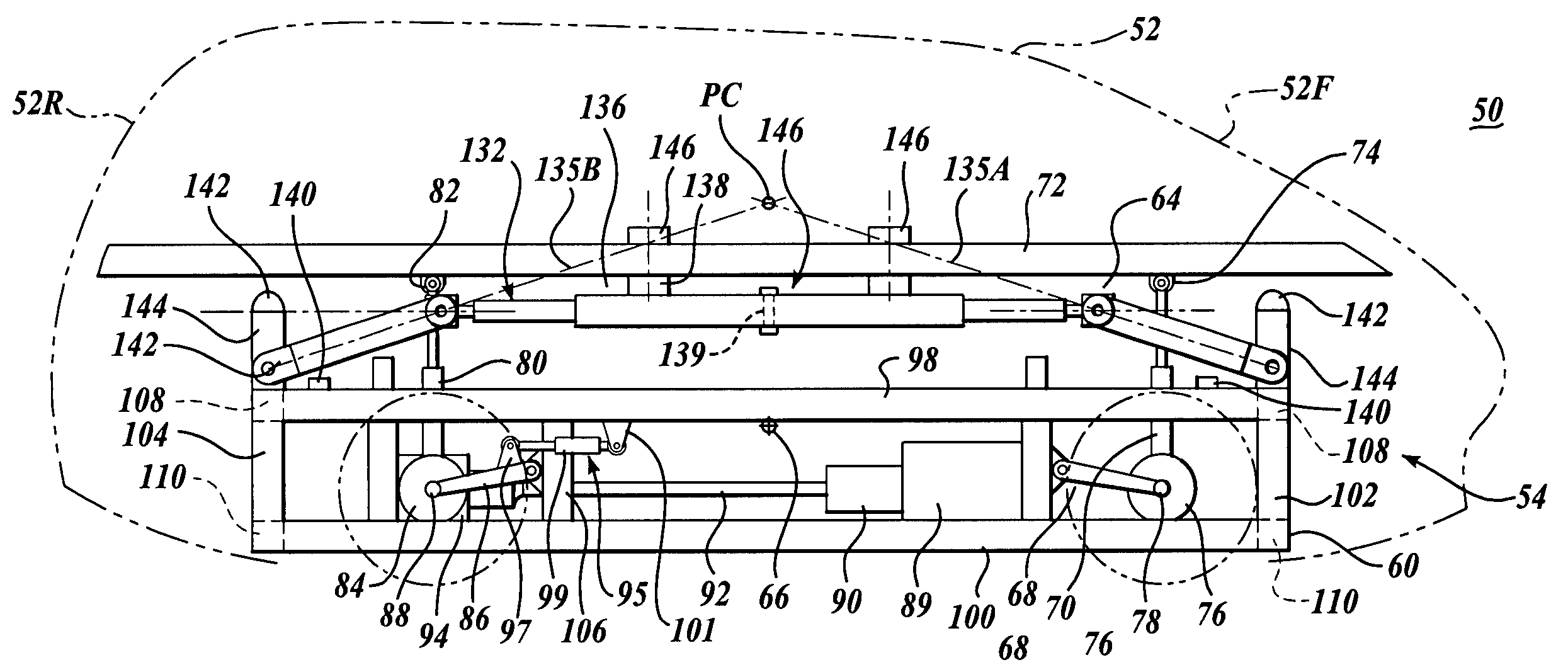
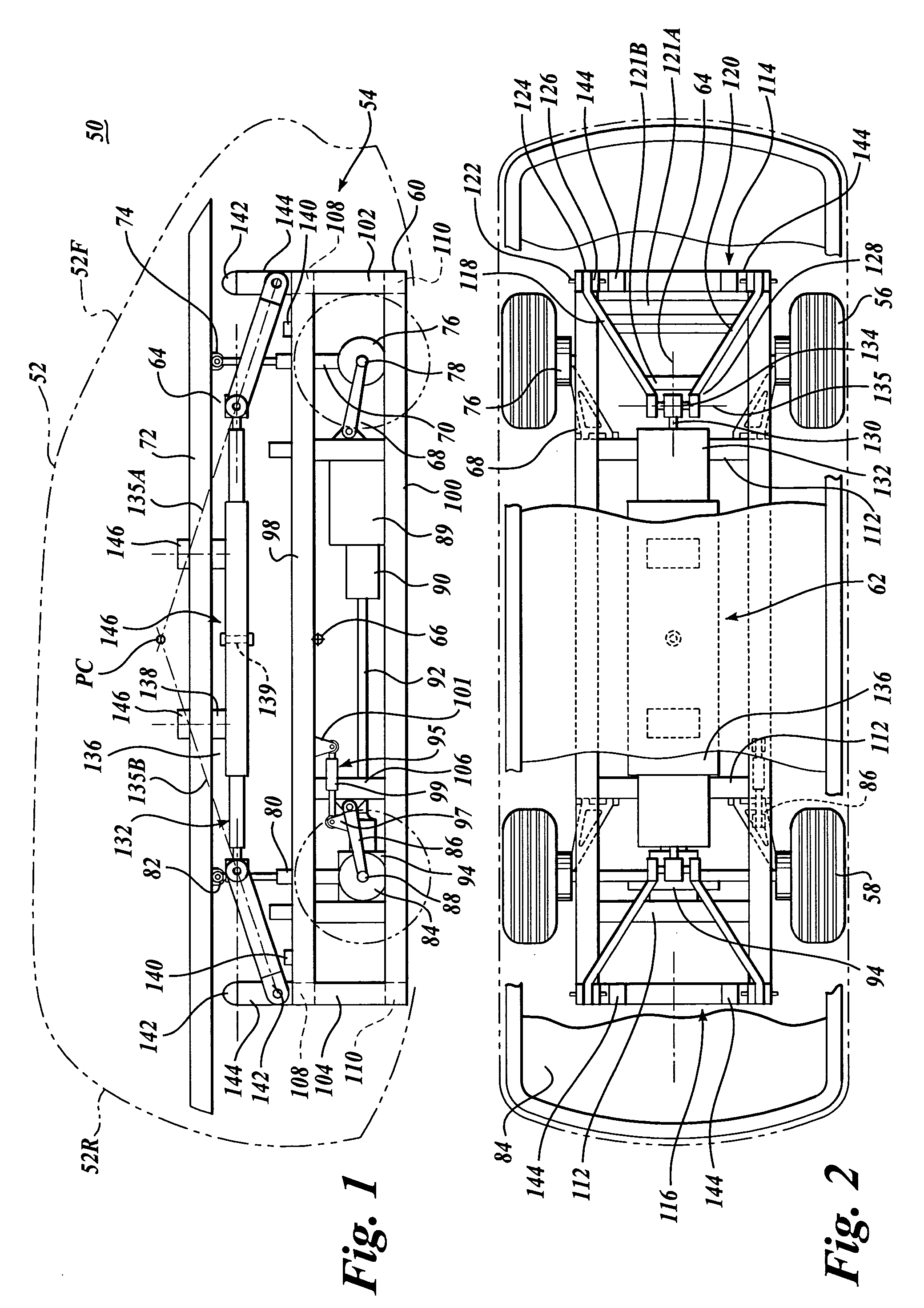
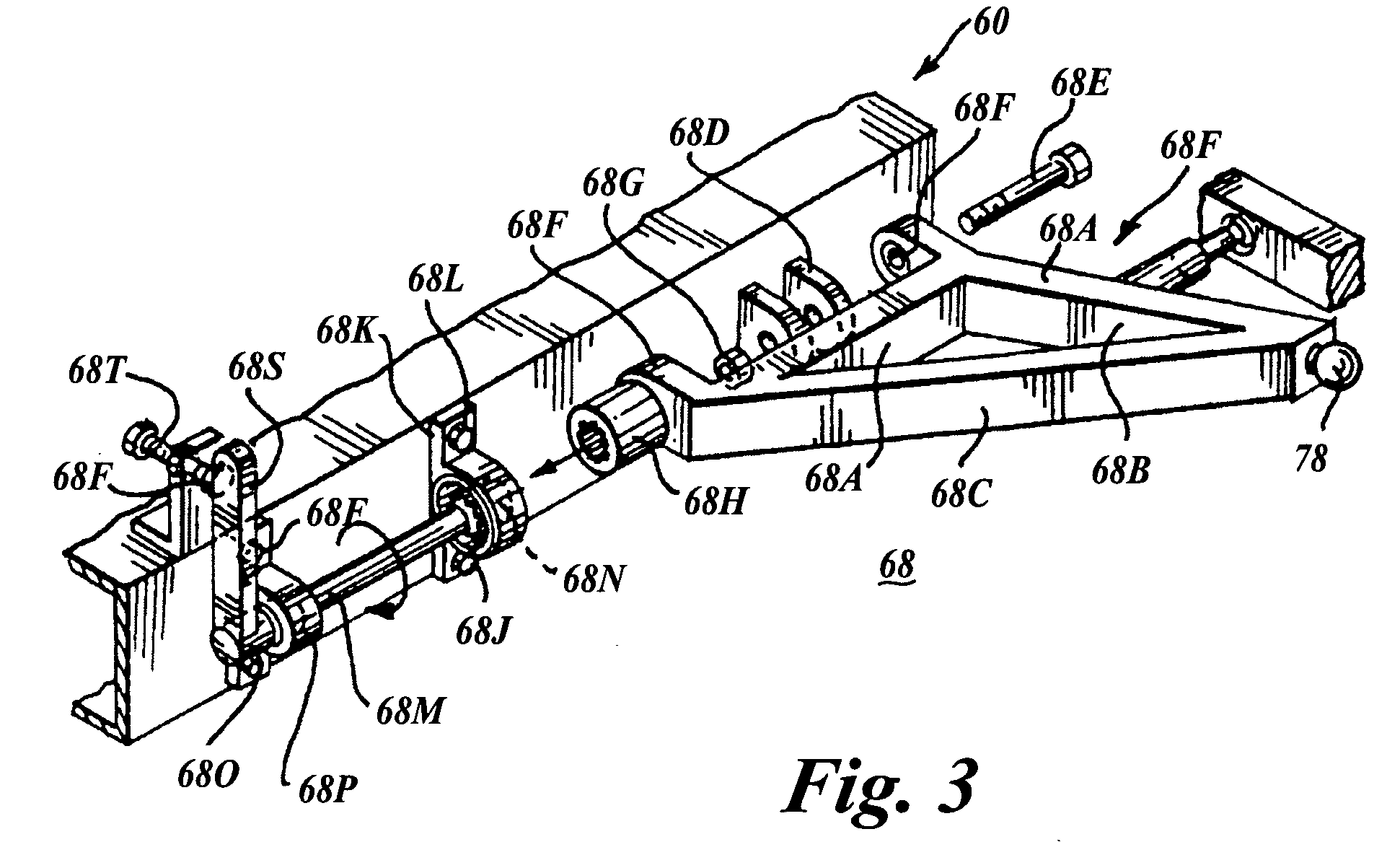
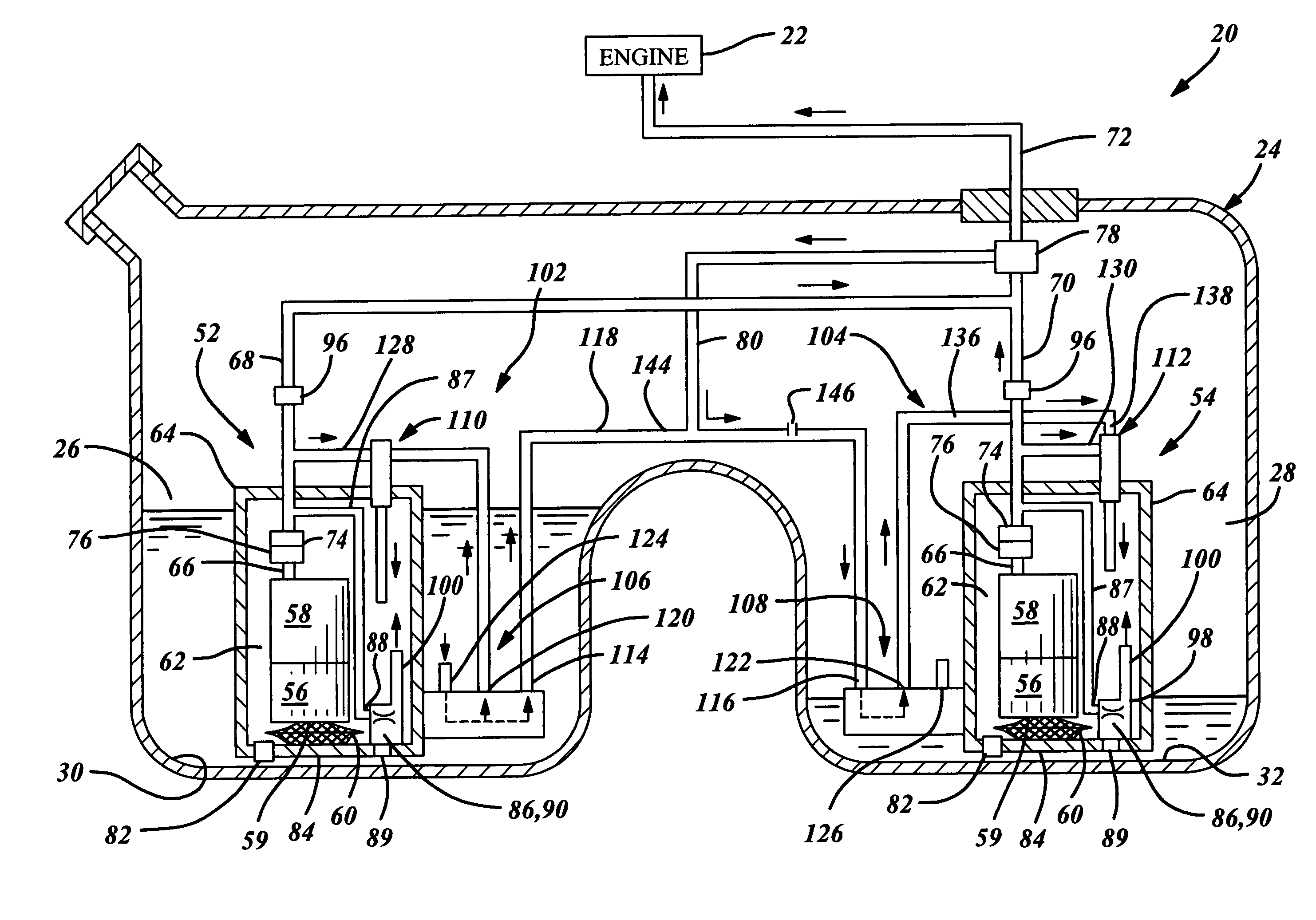
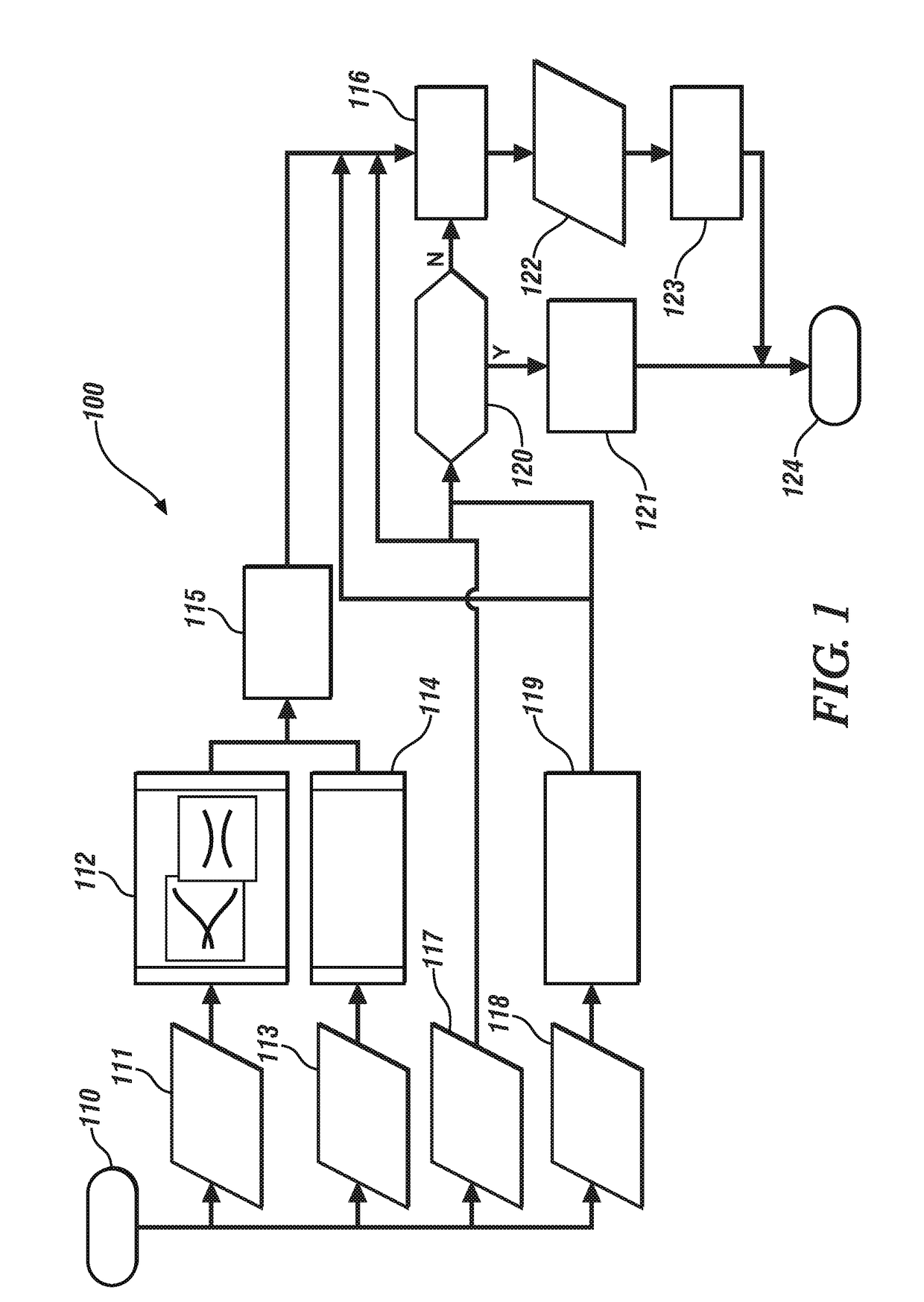
A suspension system for a vehicle (50c) having a body (52c) and a plurality of wheel support assemblies (56c, 58c) includes a tie structure (60c) interposed between the body and the wheel support assemblies. A first interconnection system (68c) interconnects the tie structure to the wheel support assemblies, and the second interconnection system (302) interconnects the tie structure and the body. The second interconnection system includes a plurality of link structures (304, 320) pivotally connected at one end to the tie structure, and pivotally connected at the opposite end to the body. Such link structures are oriented relative to the tie structure to extend towards a common point along a longitudinal axis (33B) of the tie structure.
Owner:MACISAAC WILLIAM L
Fuel delivery system for a combustion engine
InactiveUS7069913B1Increase fuel consumptionEconomical and robust fuel deliveryMachines/enginesLiquid fuel feedersCombustionFuel tank
A fuel delivery system with at least one fuel tank and at least two fuel chambers has a fuel transfer assembly preferably integrated into an in-tank fuel pump module for controlling fuel levels between the at least two fuel chambers. The fuel transfer assembly has a transfer jet which receives pressurized fuel from a fuel pump of the module and at least two control valves for dictating the source of low pressure fuel flowing into the transfer jet and discharged therefrom preferably into a fuel reservoir of the module. Preferably, one control valve is located in each fuel chamber. The control valve opens upon a pre-established high fuel level and closes upon low fuel level. The fuel chamber containing the open control valve is generally the source of fuel for the fuel pump module.
Owner:TI GRP AUTOMOTIVE SYST LLC
Vehicle with movable and inwardly tilting safety body
ActiveUS7377522B2Reduce the detrimental effects on vehicle handlingImprove vehicle handlingPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementRigid suspensionsStructural engineeringSuspension (vehicle)
A suspension system for a vehicle (50c) having a body (52c) and a plurality of wheel support assemblies (56c, 58c) includes a tie structure (60c) interposed between the body and the wheel support assemblies. A first interconnection system (68c) interconnects the tie structure to the wheel support assemblies, and the second interconnection system (302) interconnects the tie structure and the body. The second interconnection system includes a plurality of link structures (304, 320) pivotally connected at one end to the tie structure, and pivotally connected at the opposite end to the body. Such link structures are oriented relative to the tie structure to extend towards a common point along a longitudinal axis (33B) of the tie structure.
Owner:MACISAAC WILLIAM L
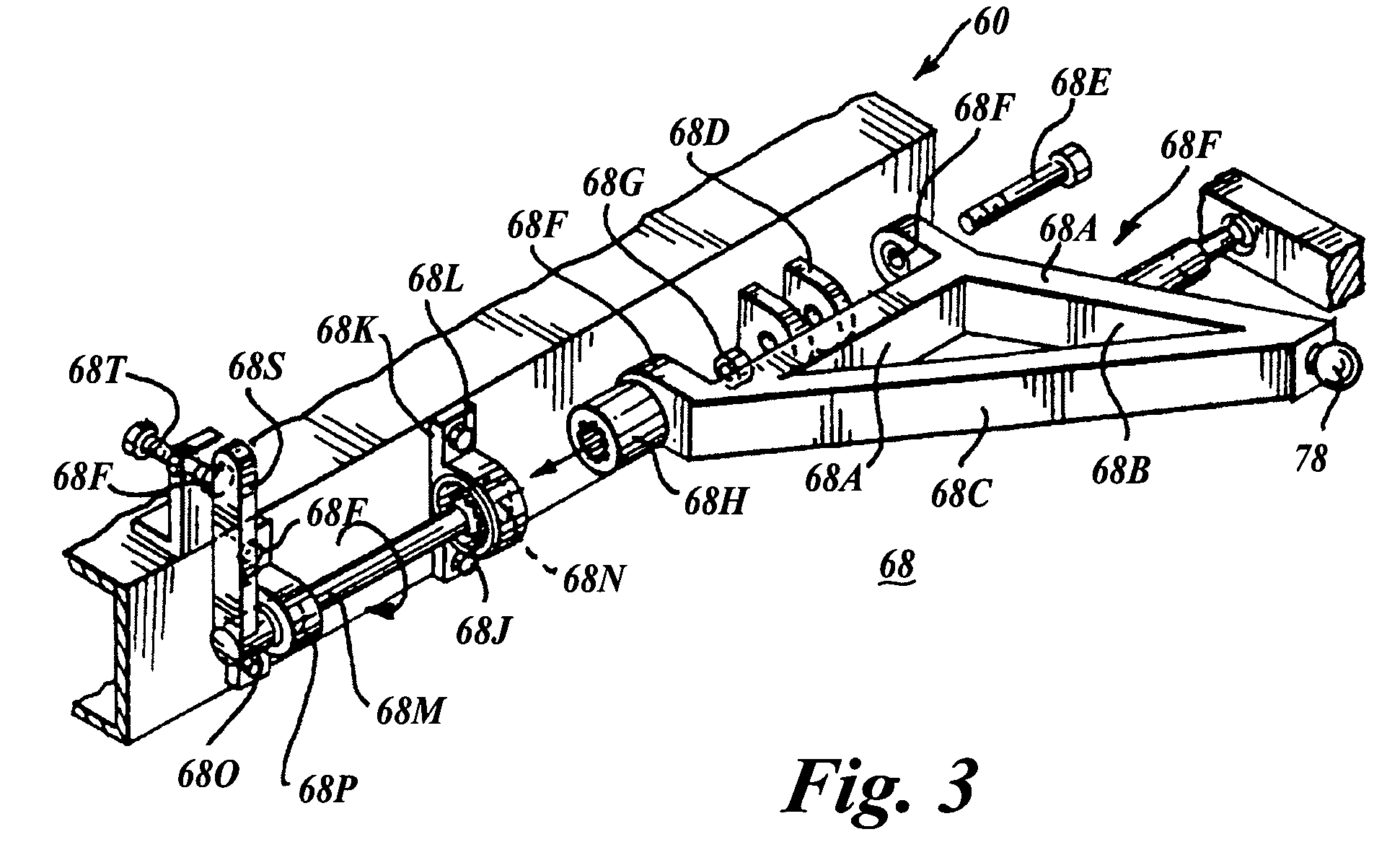
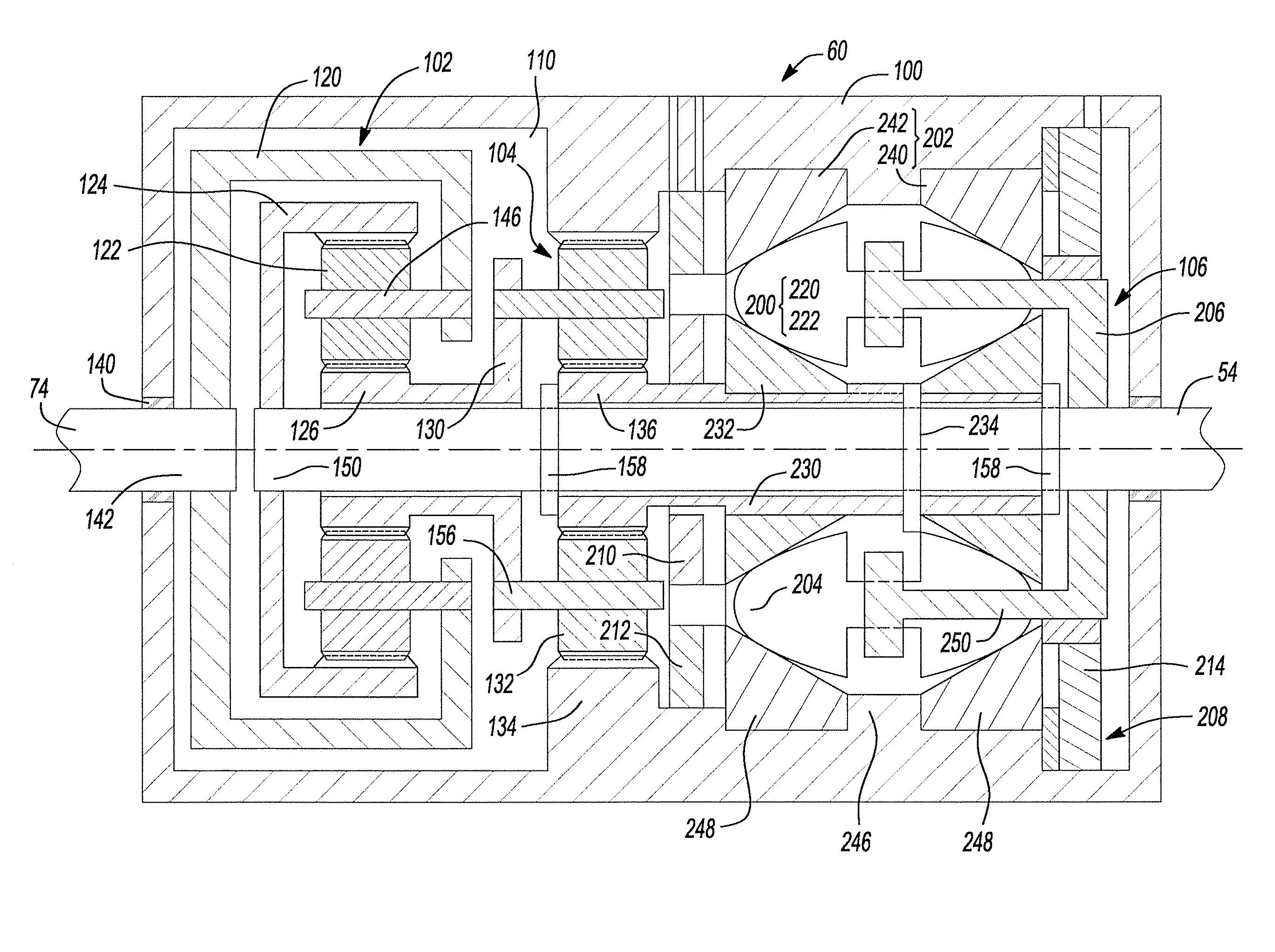
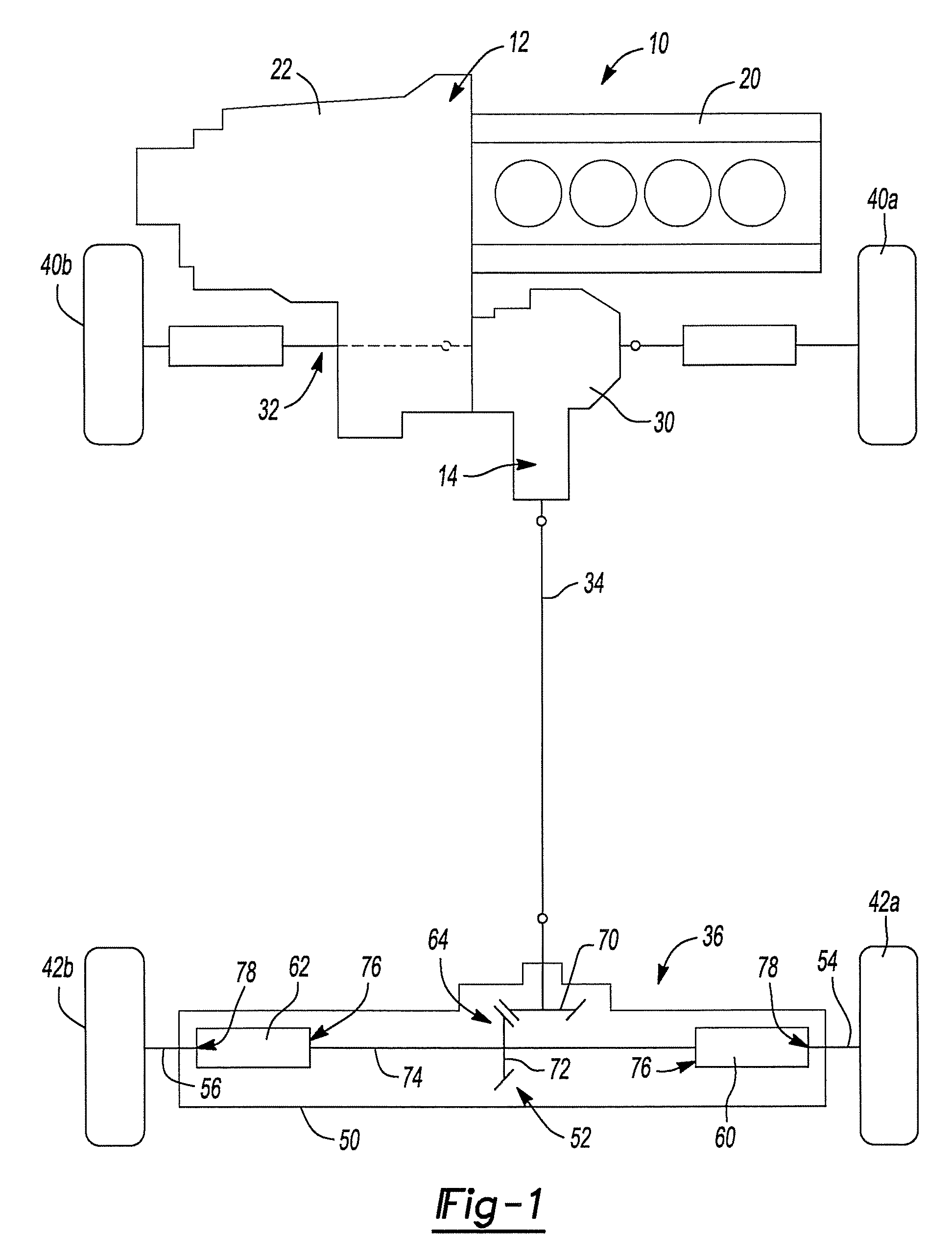
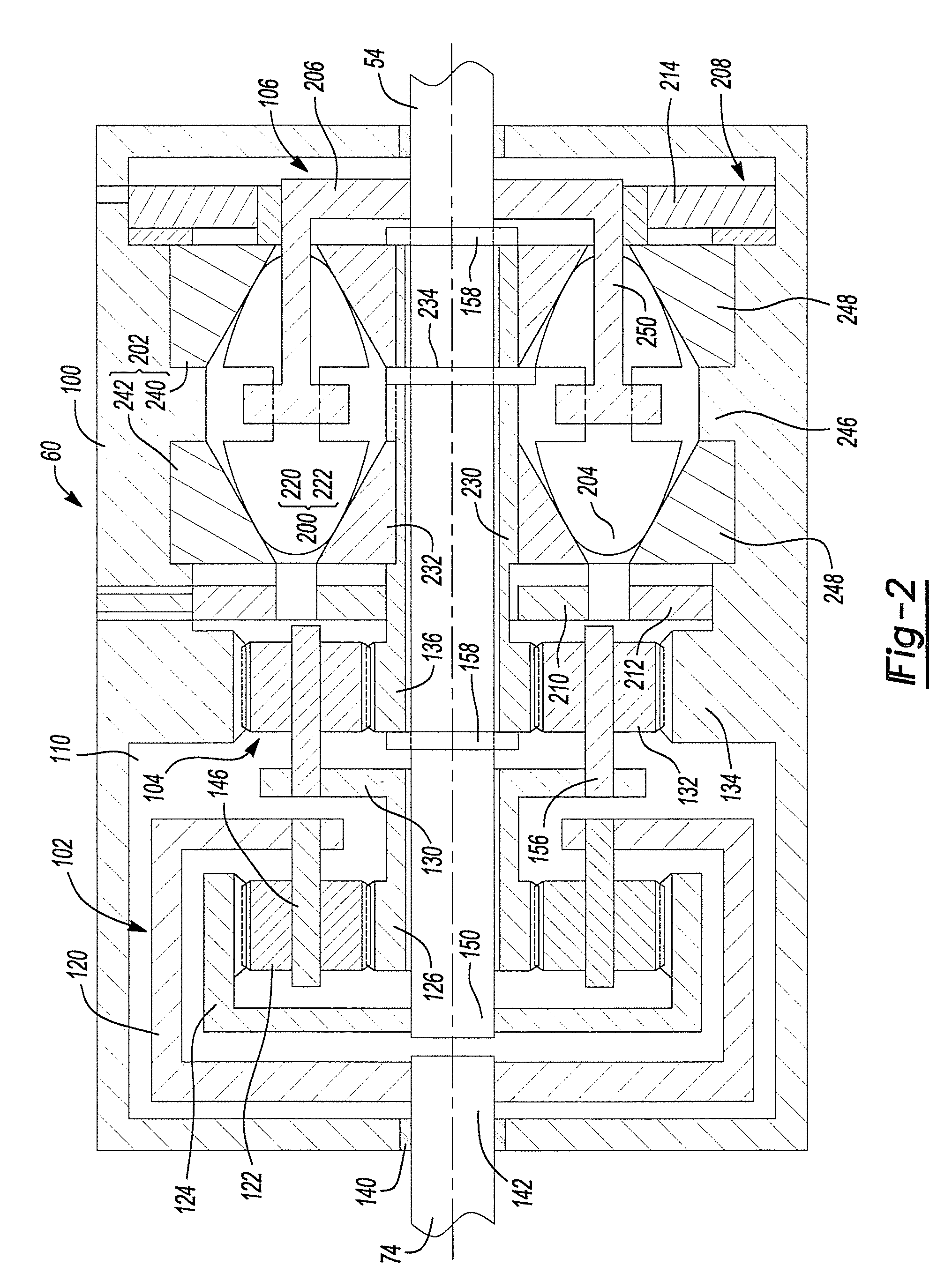
Continuously variable torque vectoring axle assembly
ActiveUS7951035B2Improve vehicle handlingTransmission elementsDifferential gearingsGear wheelDistribution power system
A vehicle driveline having an axle assembly with an input pinion, which is configured to receive a rotary input, a input ring gear, which is meshingly engaged with the input pinion, a first output member, a second output member and a power distribution system. The first output member is configured to drive a first vehicle wheel on a first side of a vehicle. The second output member is configured to drive a second vehicle wheel on a second side of the vehicle opposite the first side. The power distribution system is driven by the input ring gear and distributes drive torque between the first and second output members. The power distribution system includes a first continuously variable transmission. A method for operating a vehicle driveline is also provided.
Owner:AMERICAN AXLE & MFG
Lubrication system for a four cycle engine
InactiveUS6848528B2Improve cylinder chargingSimple wayInternal combustion piston enginesClosed-circuit pressure lubricating systemsEngineeringDry sump
A dry sump lubrication system for a four cycle engine is disclosed. The dry sump lubrication system has at least two lubricant storage chambers. A first lubricant storage chamber stores a first volume of lubricant. The first lubricant storage chamber may be located in a lower part of the crankcase. A second lubricant storage chamber is an oil tank and stores a second volume of lubricant. The oil tank may be secured to the output end of the crankcase. The first lubricant storage chamber is capable of storing at least 30% of a total volume of lubricant within the dry sump lubrication system.
Owner:BRP ROTAX
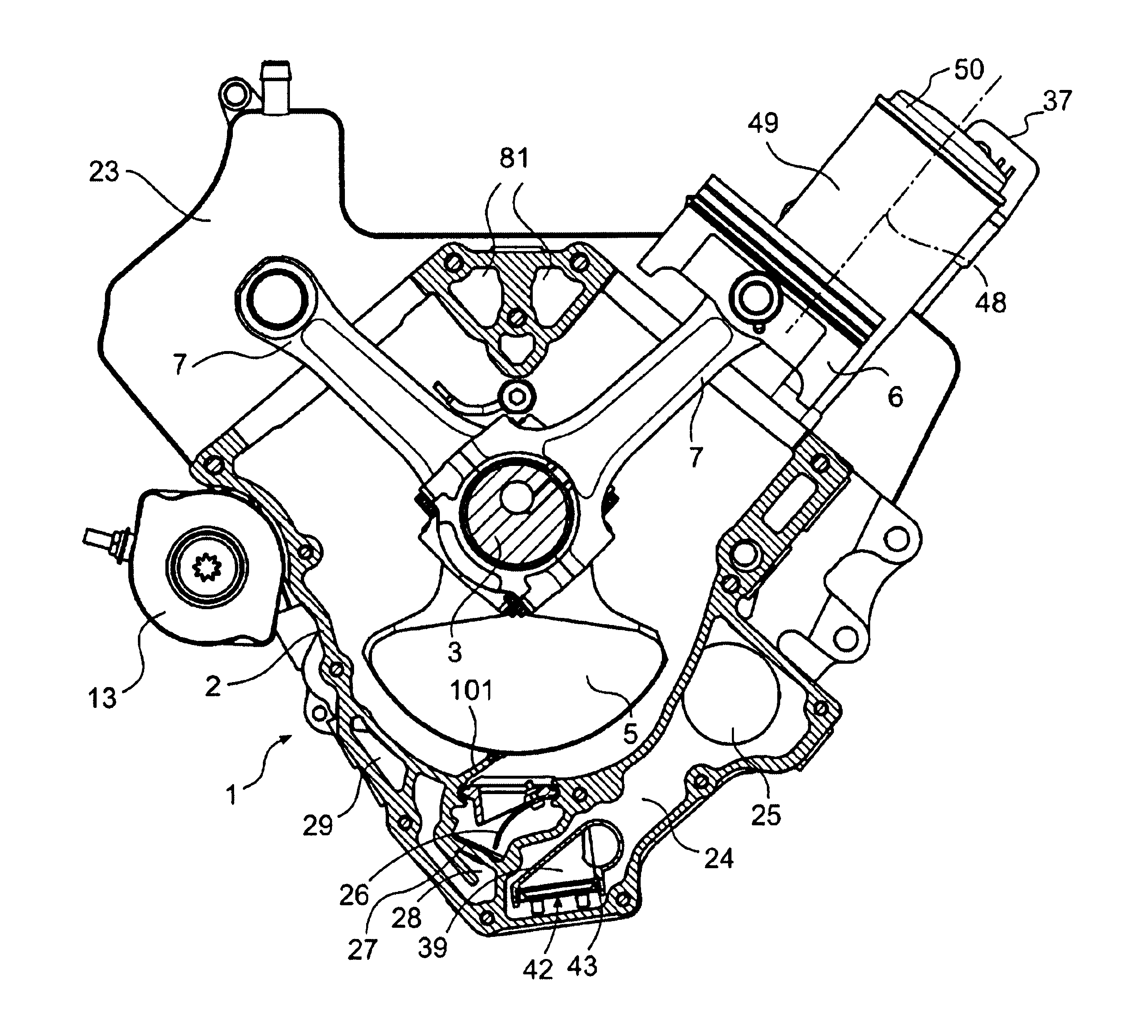
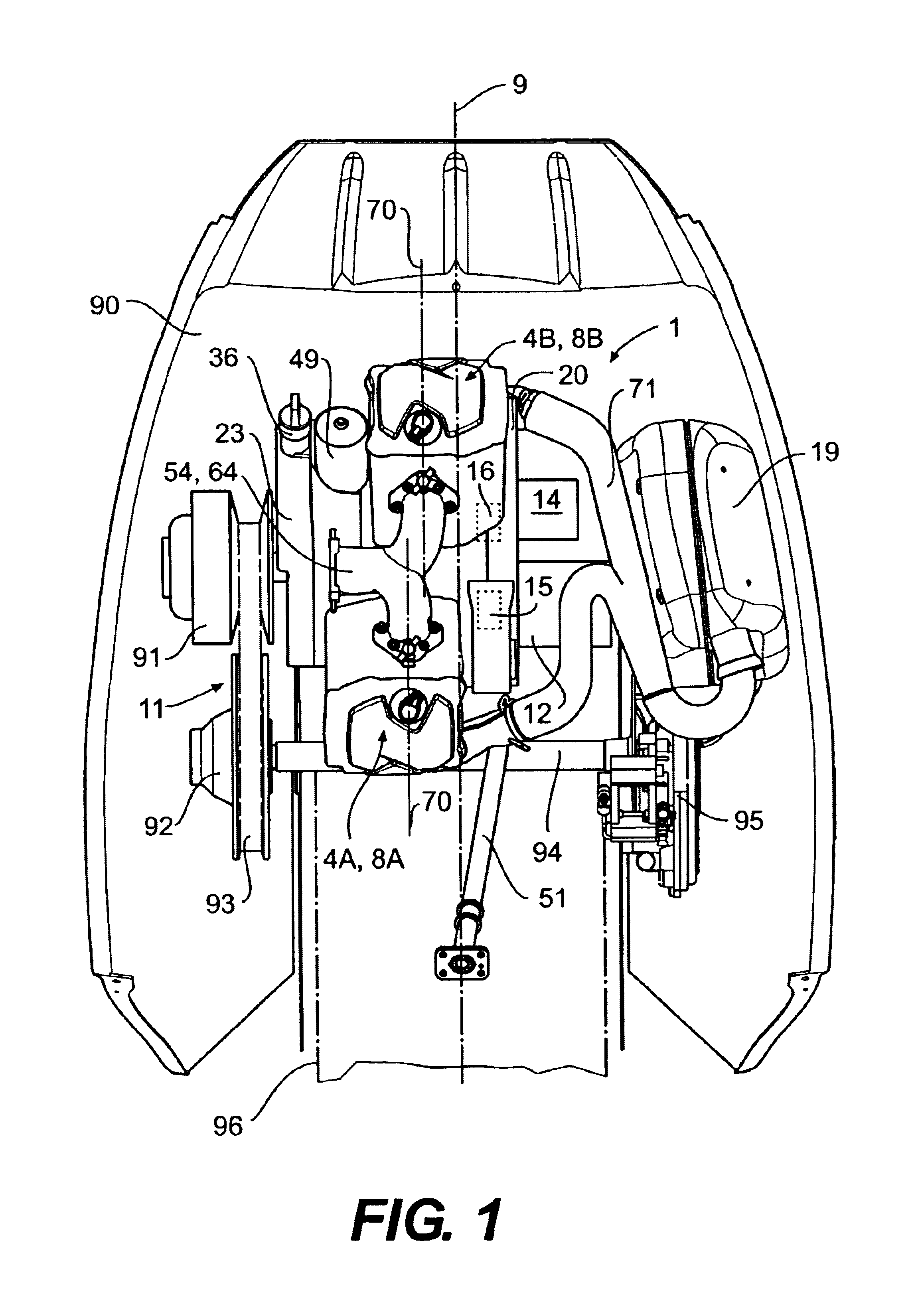
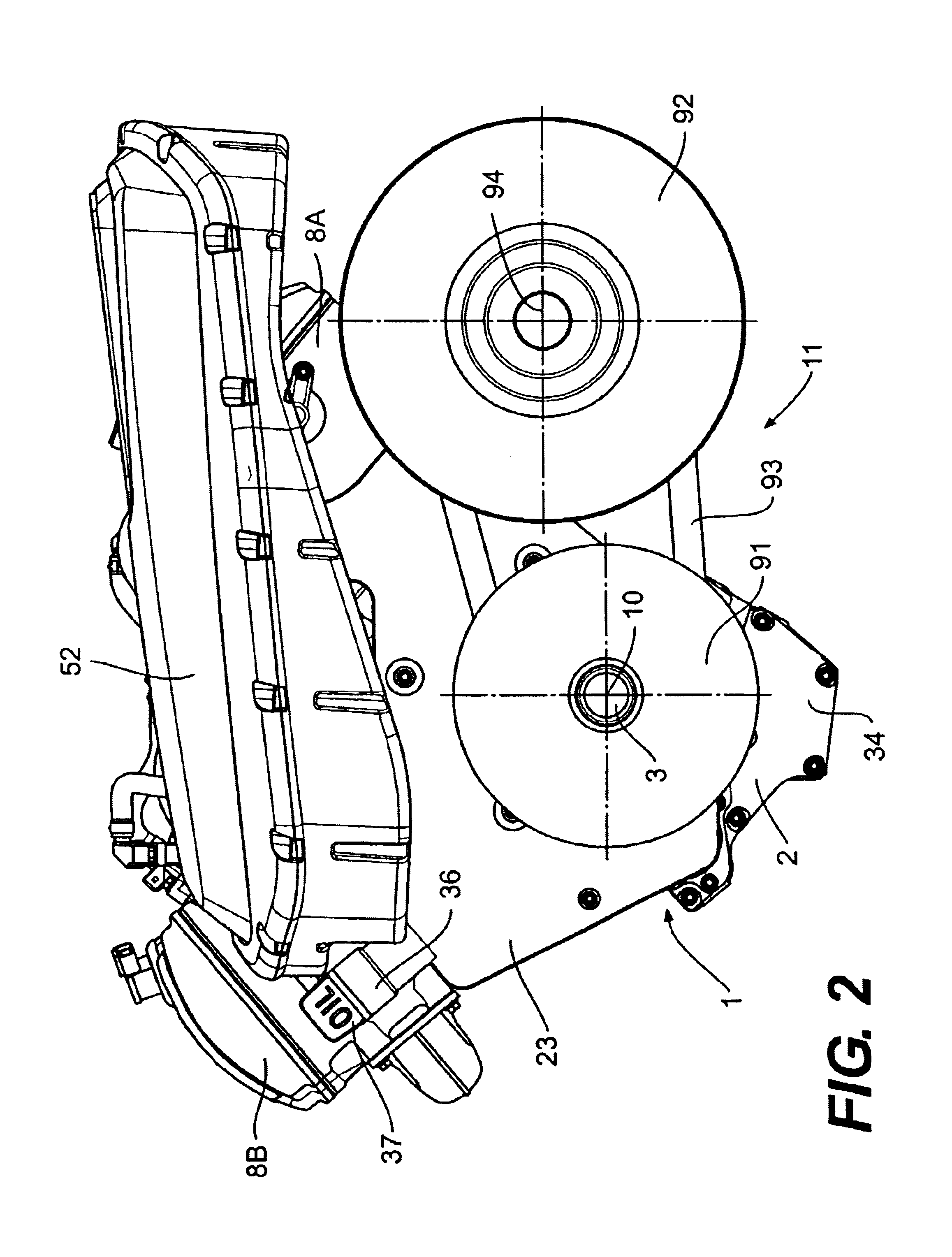
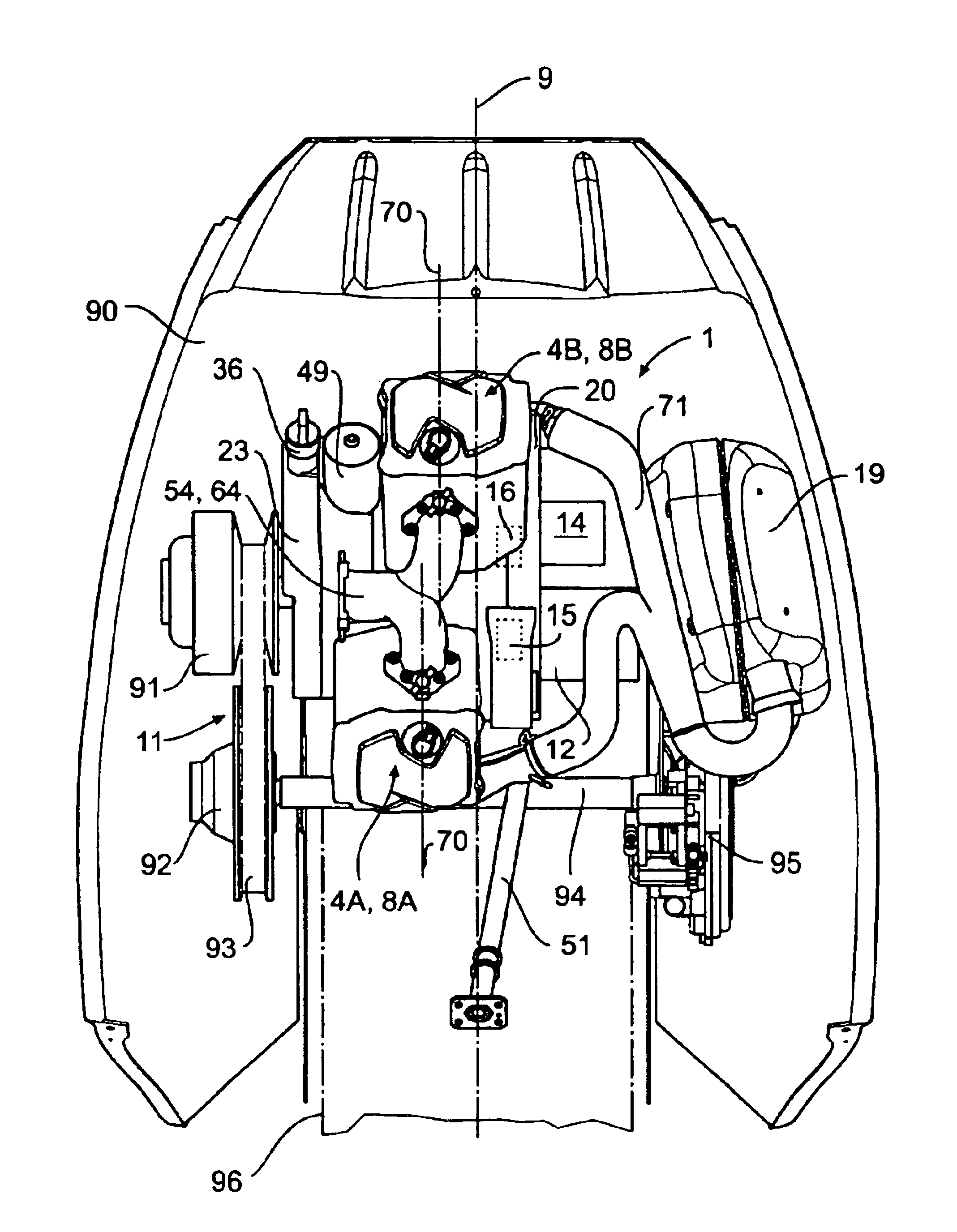
Engine arrangement for a four cycle engine
InactiveUS6929081B2Improve vehicle handlingLower center of gravityInternal combustion piston enginesClosed-circuit pressure lubricating systemsCrankshaftGravitation
An arrangement of a four cycle engine is disclosed for use in a vehicle providing a relatively low center of gravity for improved handling and maneuverability. The engine components are located on opposing sides of the longitudinal axis of the vehicle and behind the axis of the crankshaft to move the center of gravity to the middle of the vehicle.
Owner:BRP ROTAX
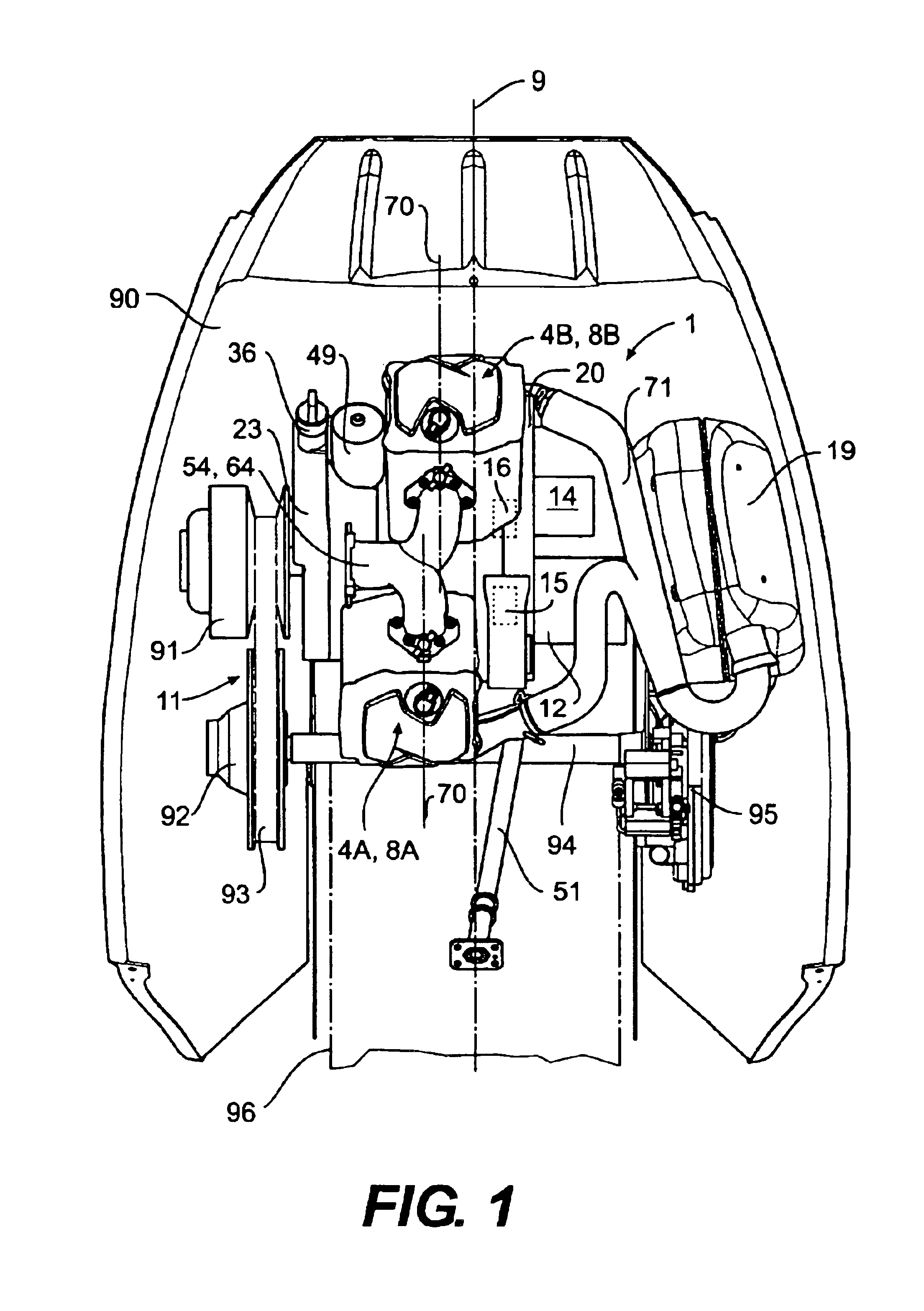
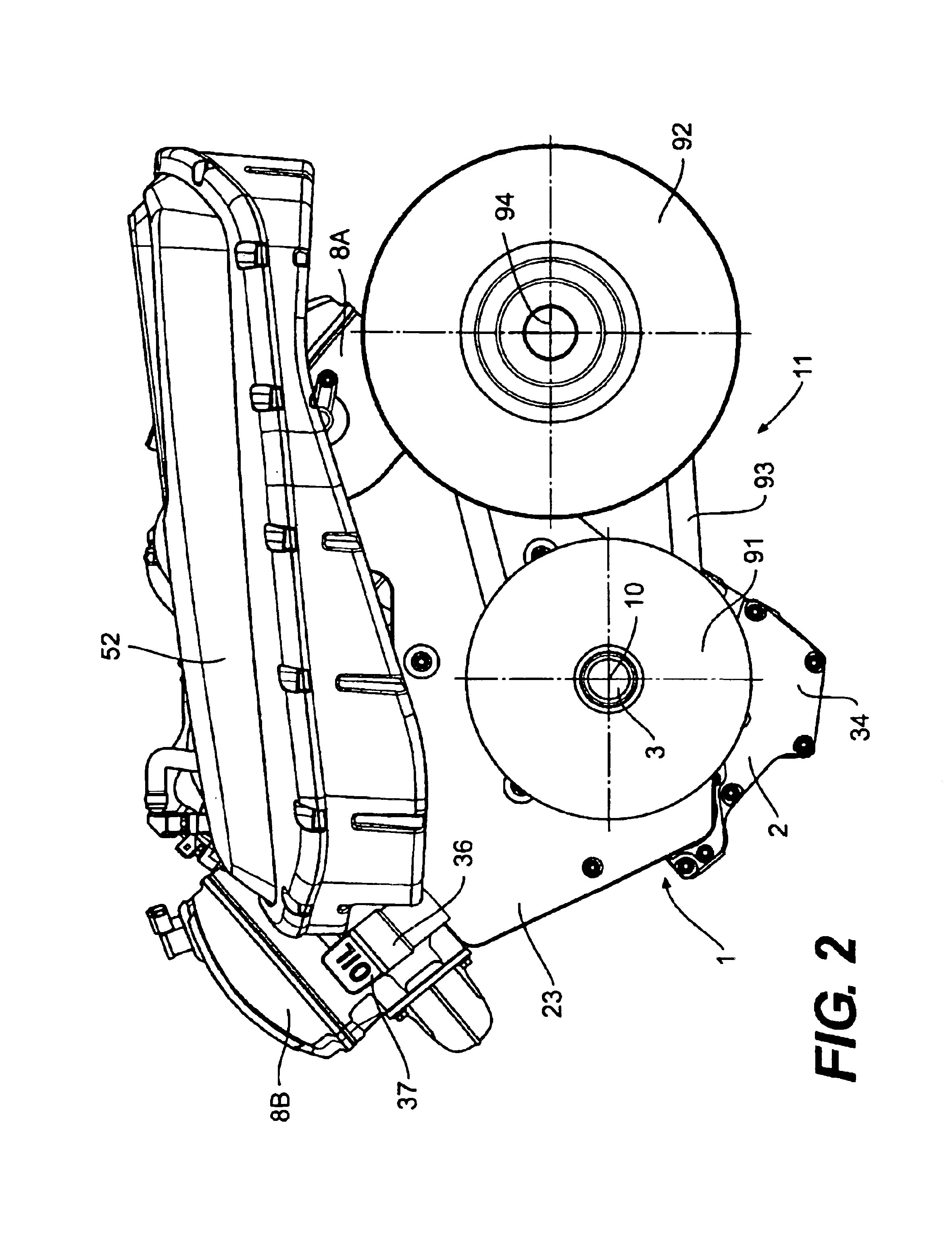
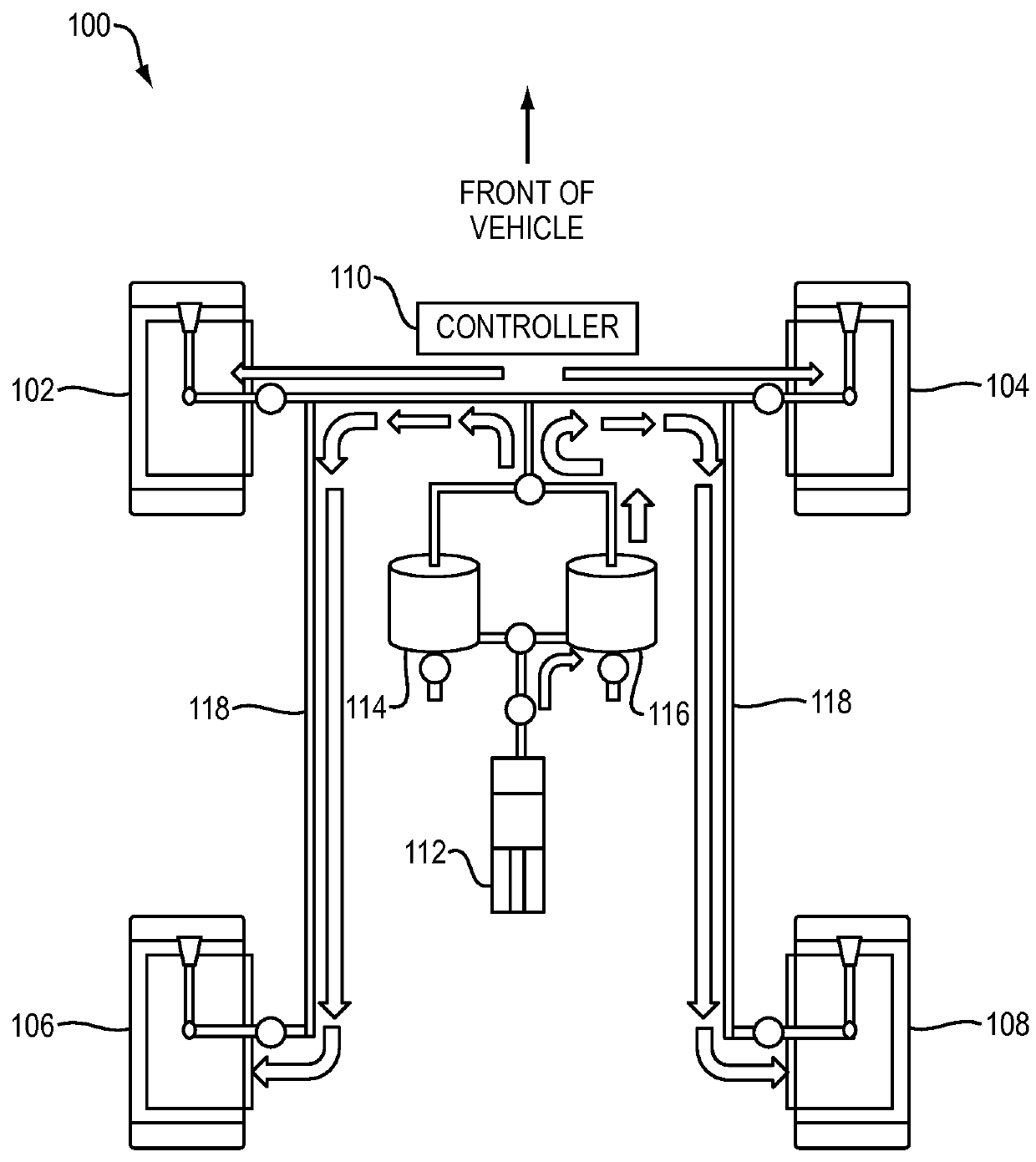
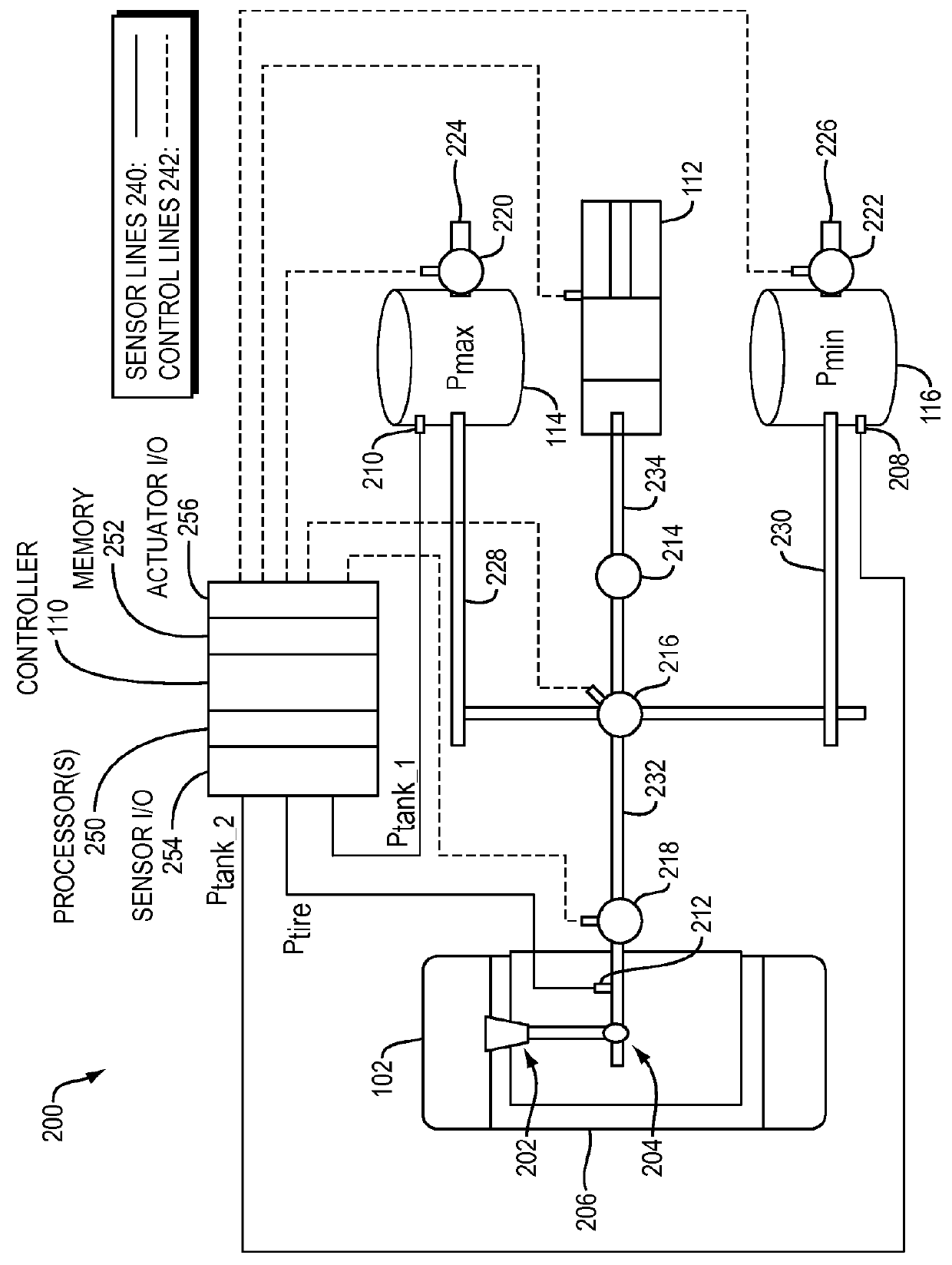
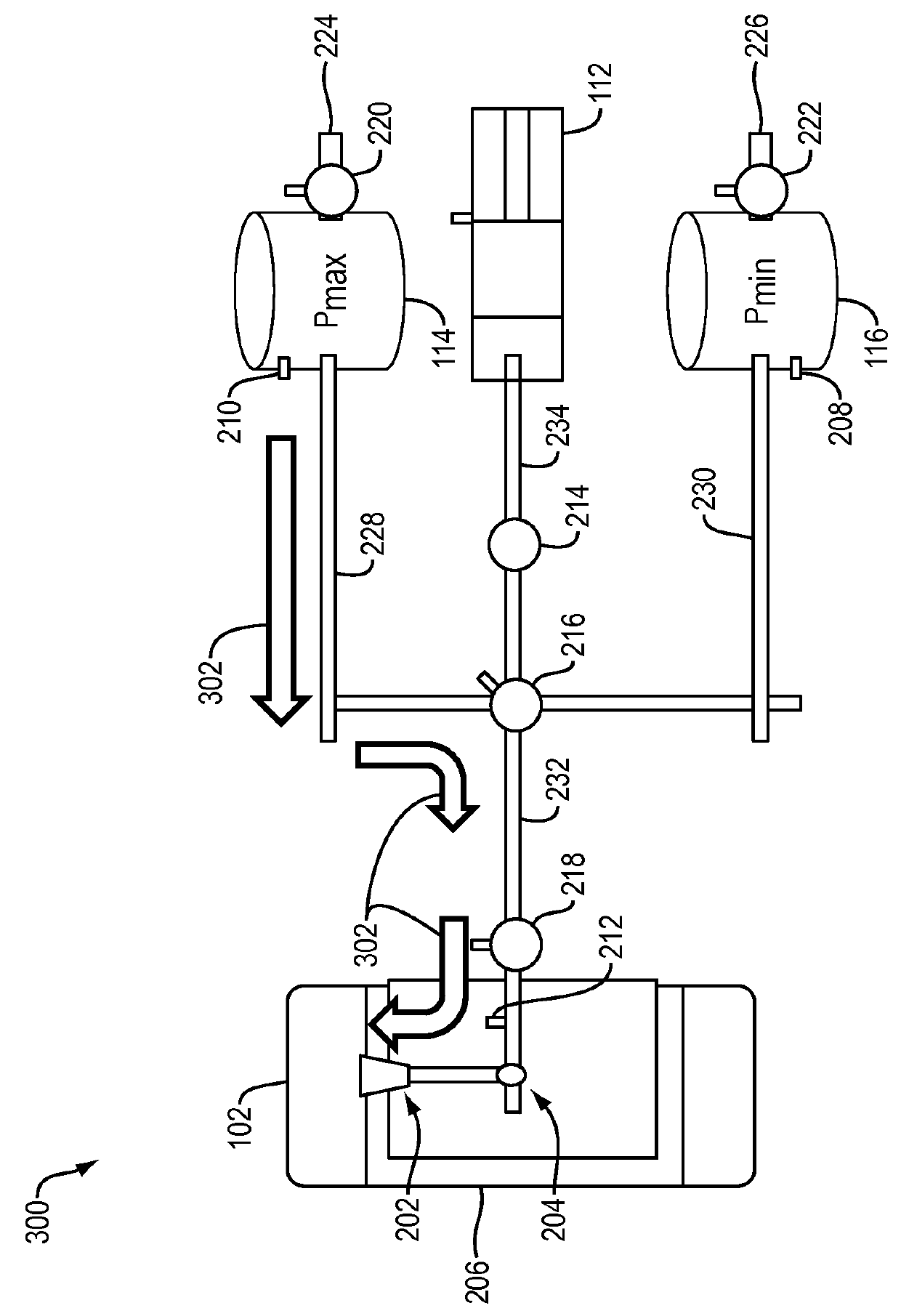
Dynamic tire air pressure system
ActiveUS20160052351A1Easy rideImprove fuel economyDigital data processing detailsCheck valvesPressure systemHigh pressure
In one embodiment, a dynamic tire air pressure system for a vehicle is disclosed. The system includes a tire pressure sensor that measures an air pressure of a tire. The system also includes a first reservoir tank maintaining a lower air pressure than the measured air pressure of the tire. The system further includes a second reservoir tank maintaining a higher air pressure than the measured air pressure of the tire. The system additionally includes one or more valves that control deflation and inflation of the tire by selectively coupling the tire to the first or second reservoir tanks.
Owner:HYUNDAI AMERICA TECHN CENT +2
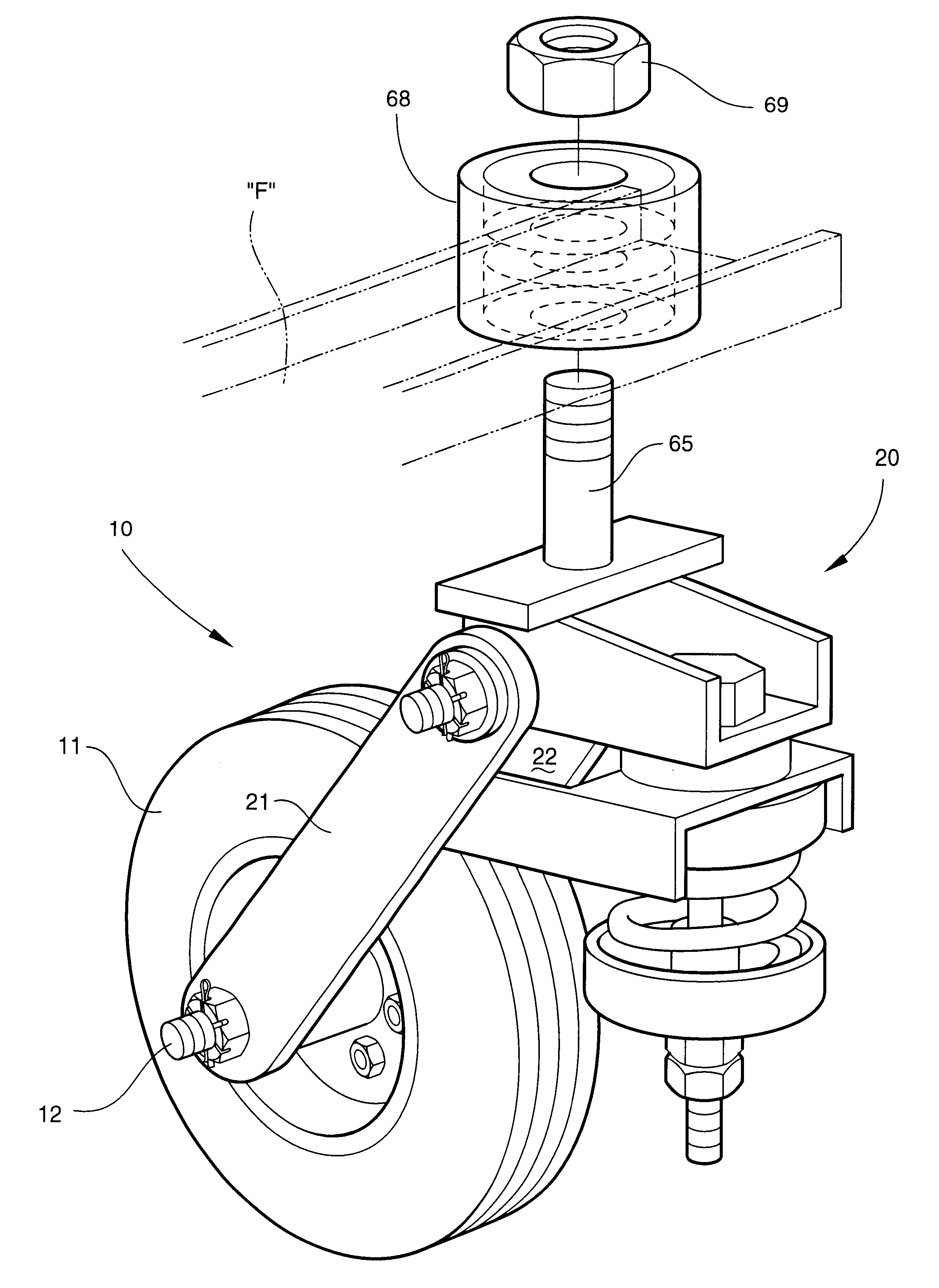
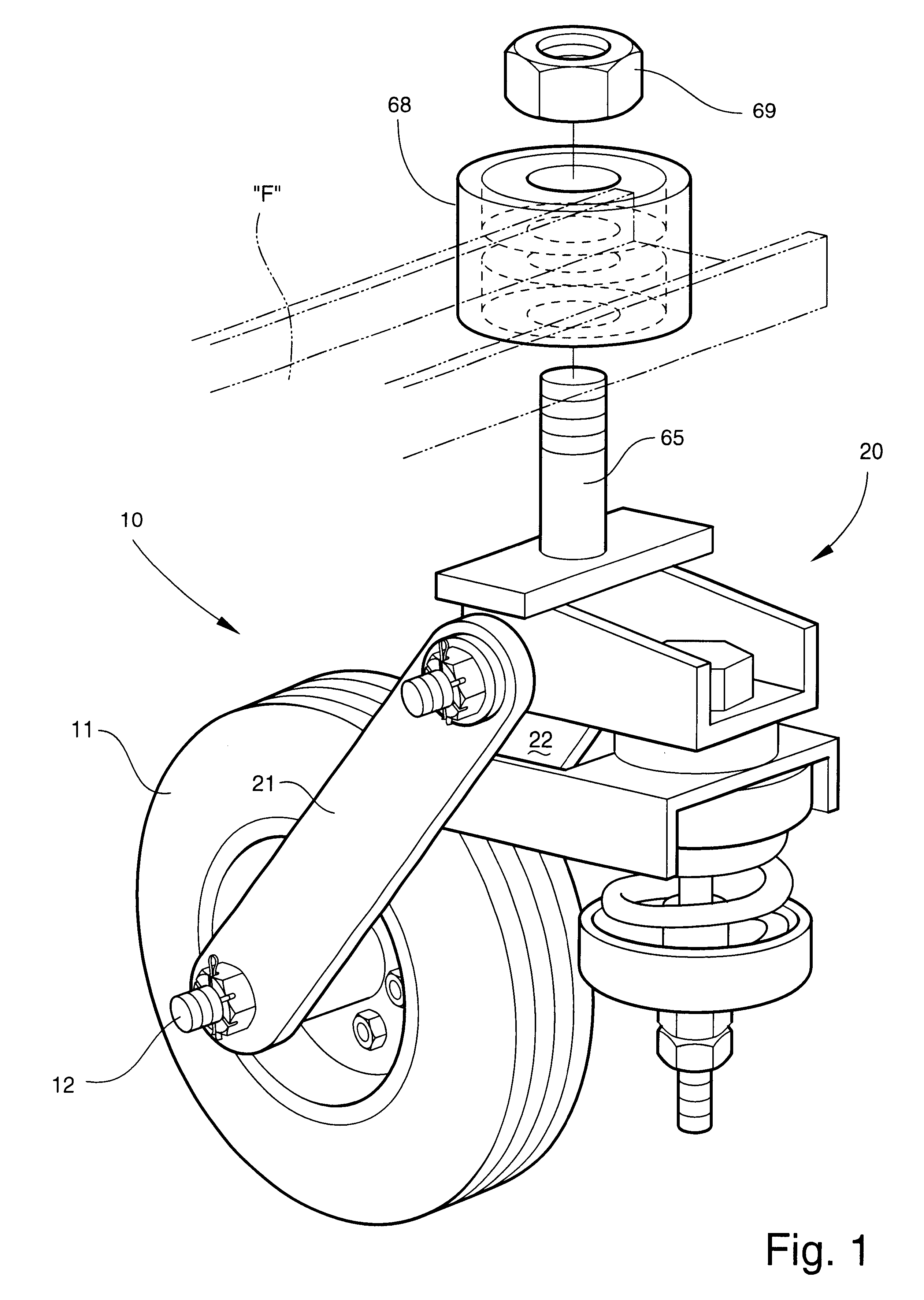
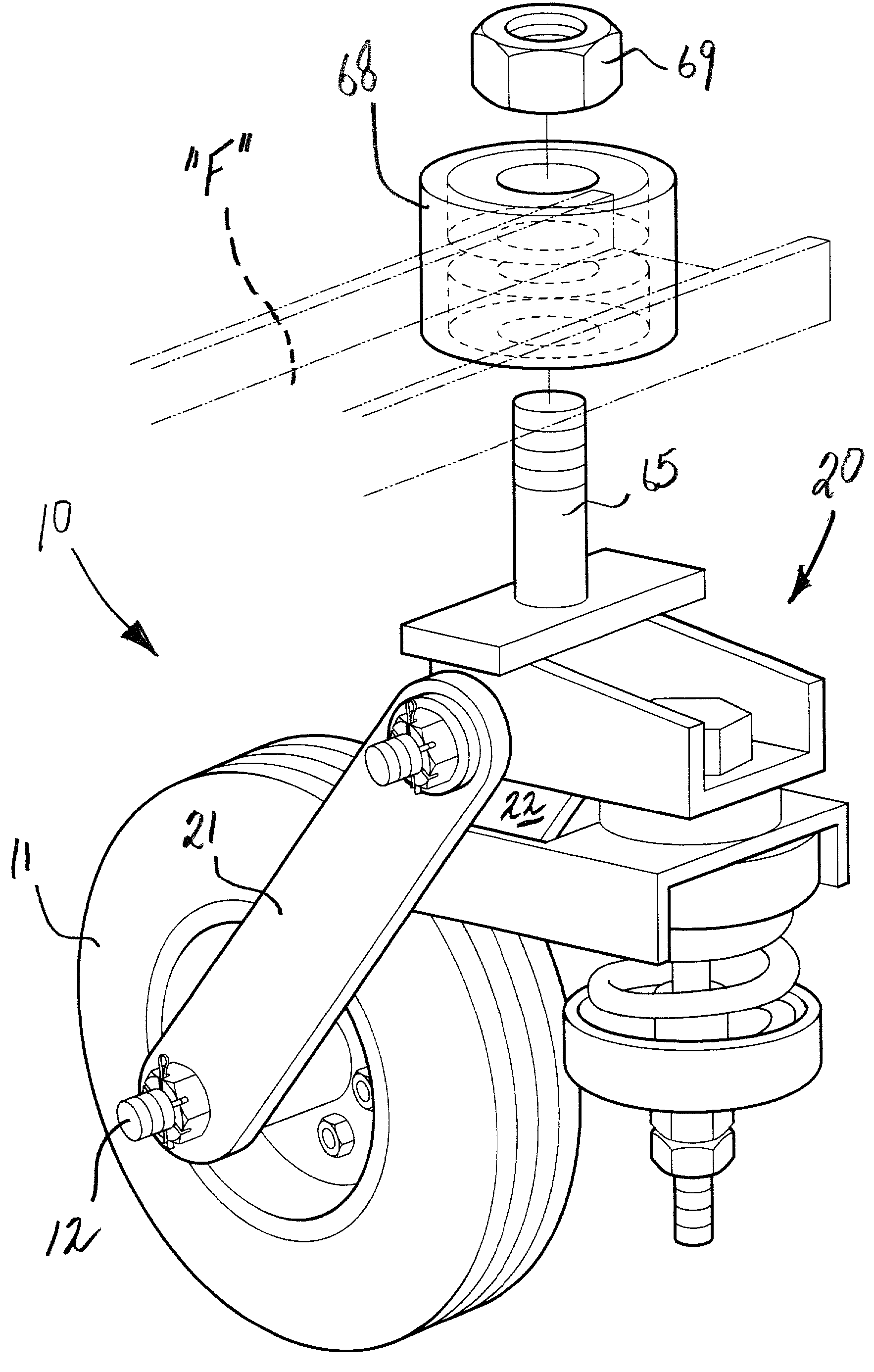
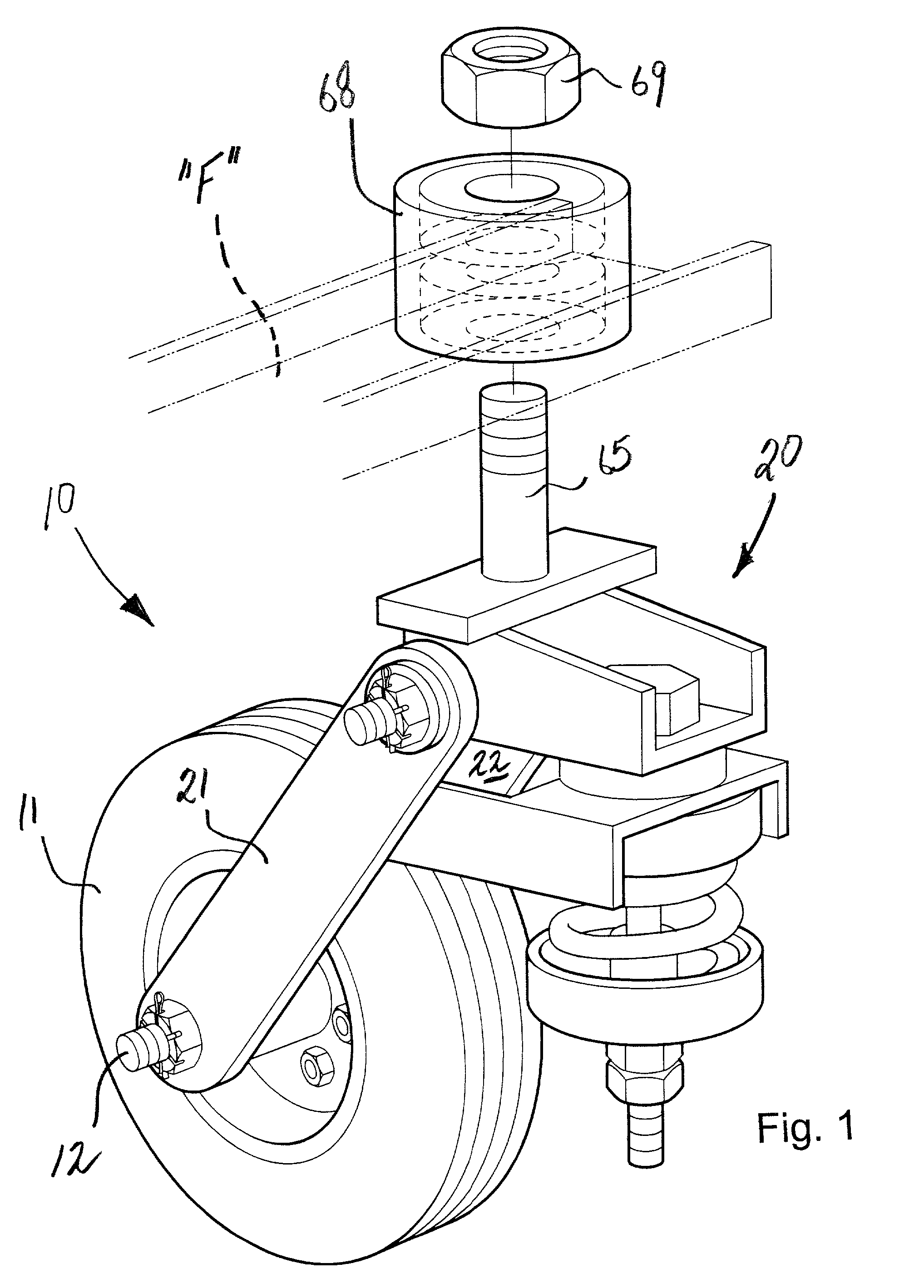
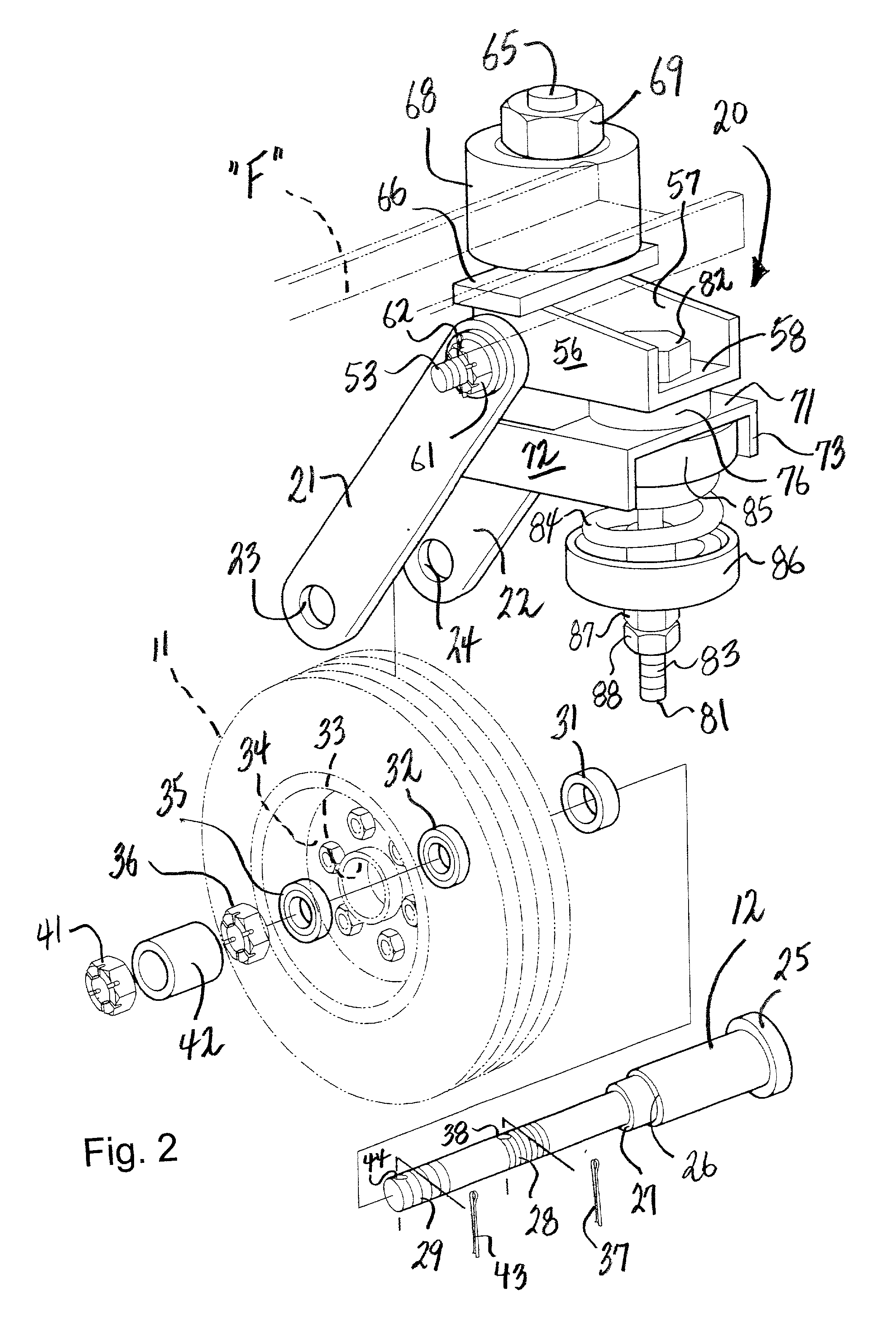
Swivel wheel assembly with adjustable shock absorption
InactiveUS6607201B2Improve efficiencyImprove vehicle handlingCarriage/perambulator with single axisCastorsShock absorberWheel and axle
A swivel wheel assembly includes a wheel axle, and a vehicle wheel rotatably mounted on the wheel axle. A shock-absorbing wheel fork is secured to opposite ends of the wheel axle and includes first and second elongated spaced-apart support arms. A pivot pin extends through pin openings formed with proximal ends of the first and second support arms. A base is carried by the pivot pin, and is adapted for pivoting movement about an axis defined by the pivot pin. An adjustable shock absorber dampens pivoting movement of the base relative to the vehicle wheel, thereby absorbing the energy of sudden shocks to the vehicle wheel during use.
Owner:MARSHBURN BILL W
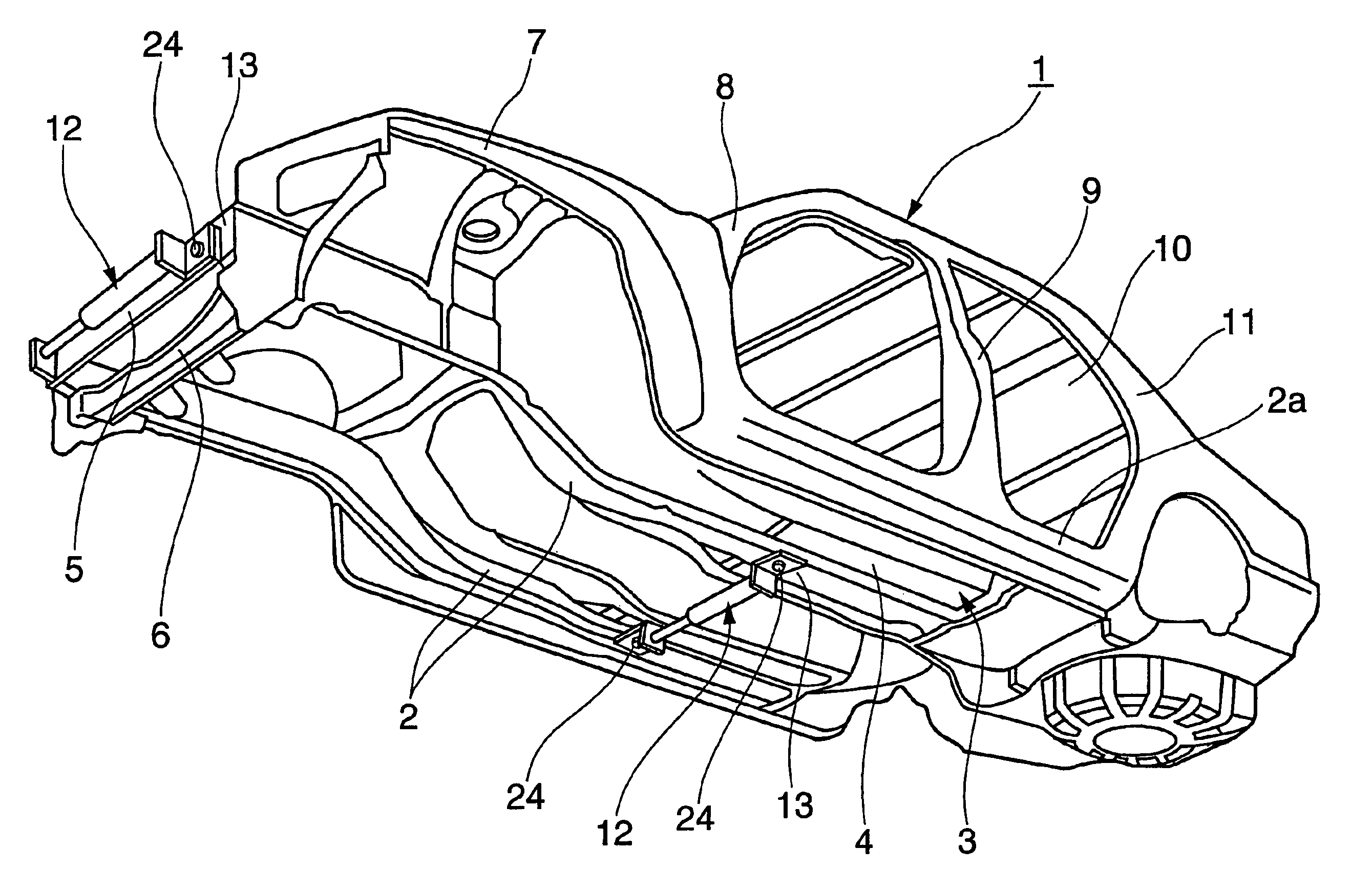
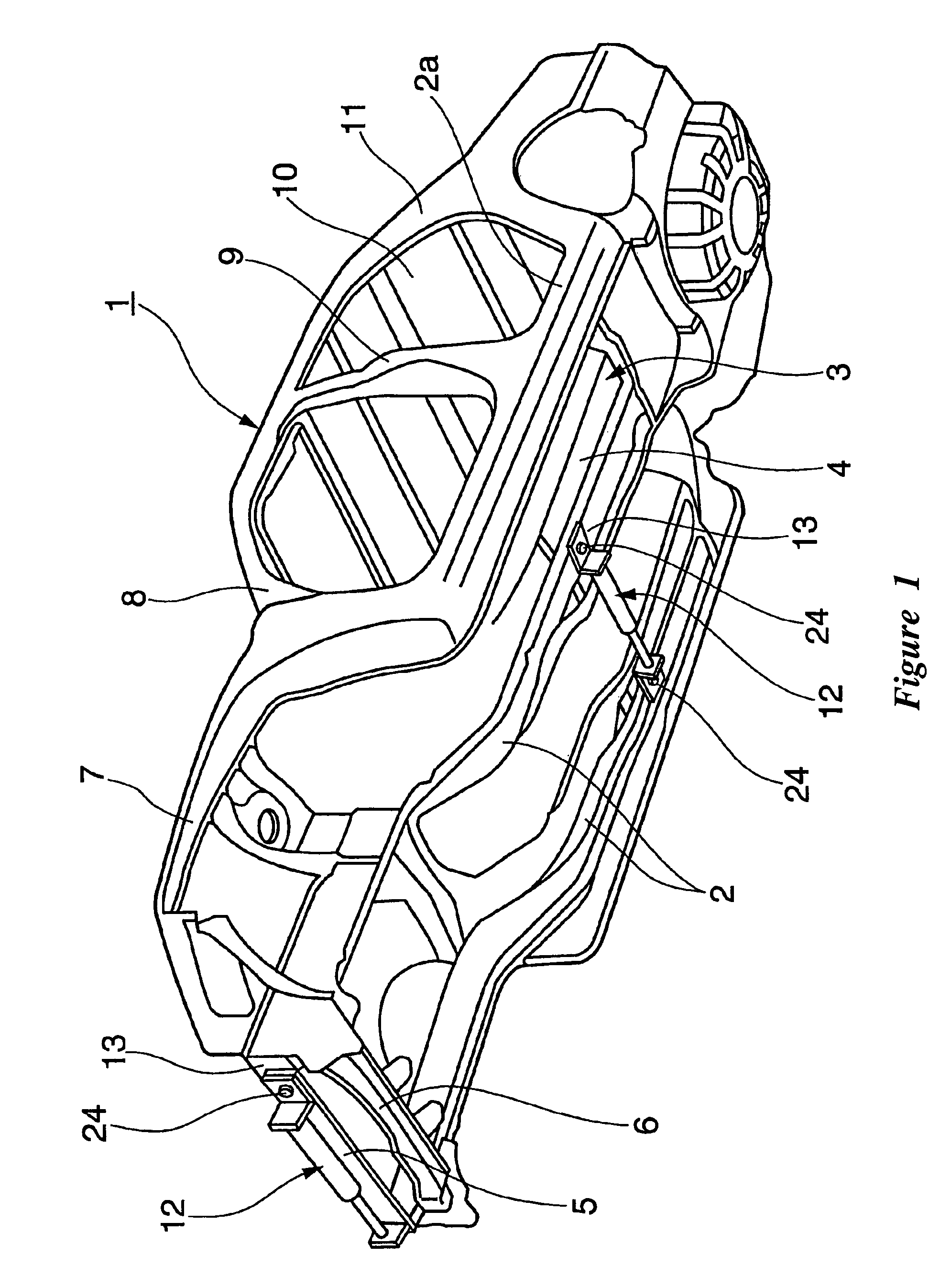
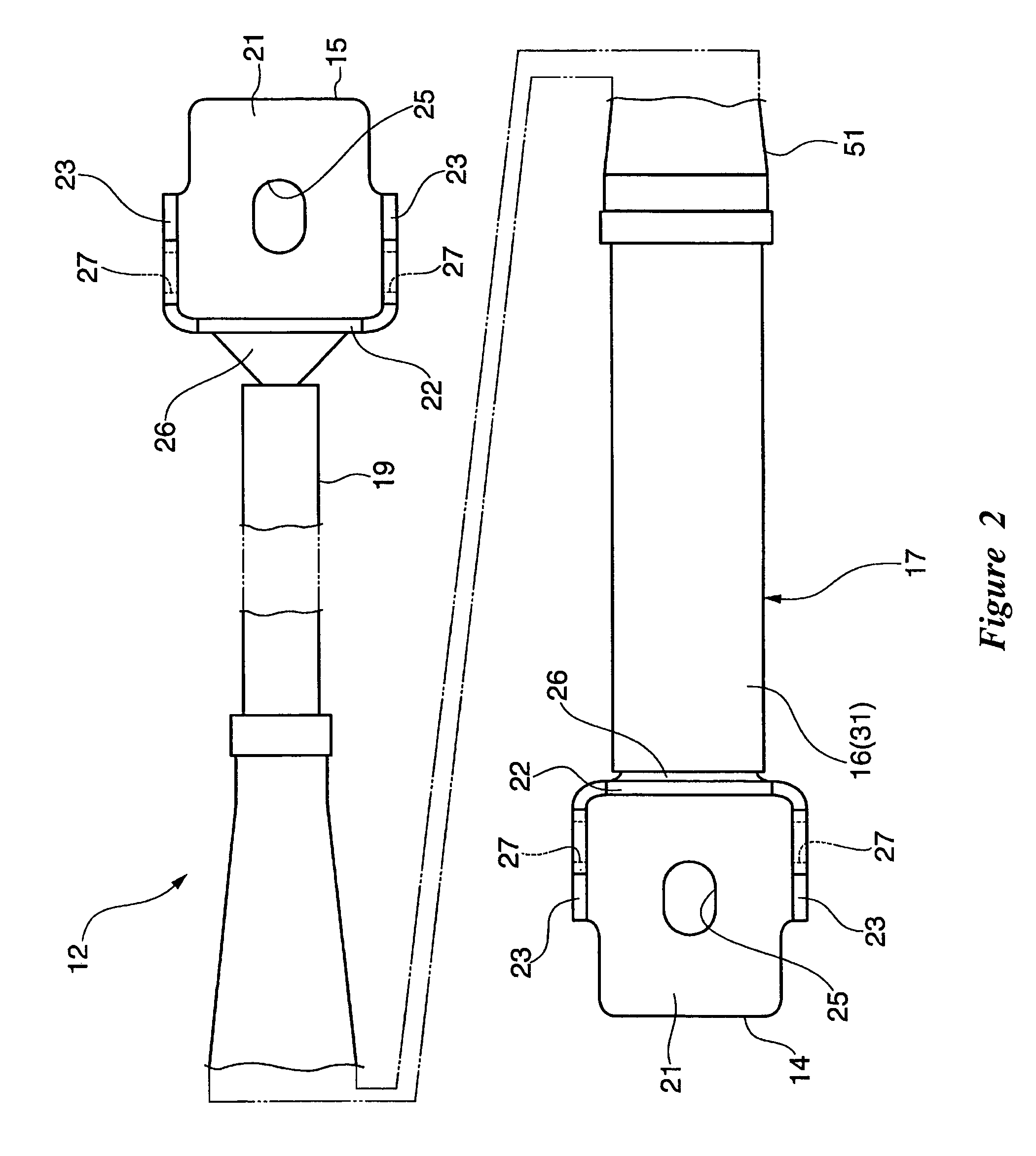
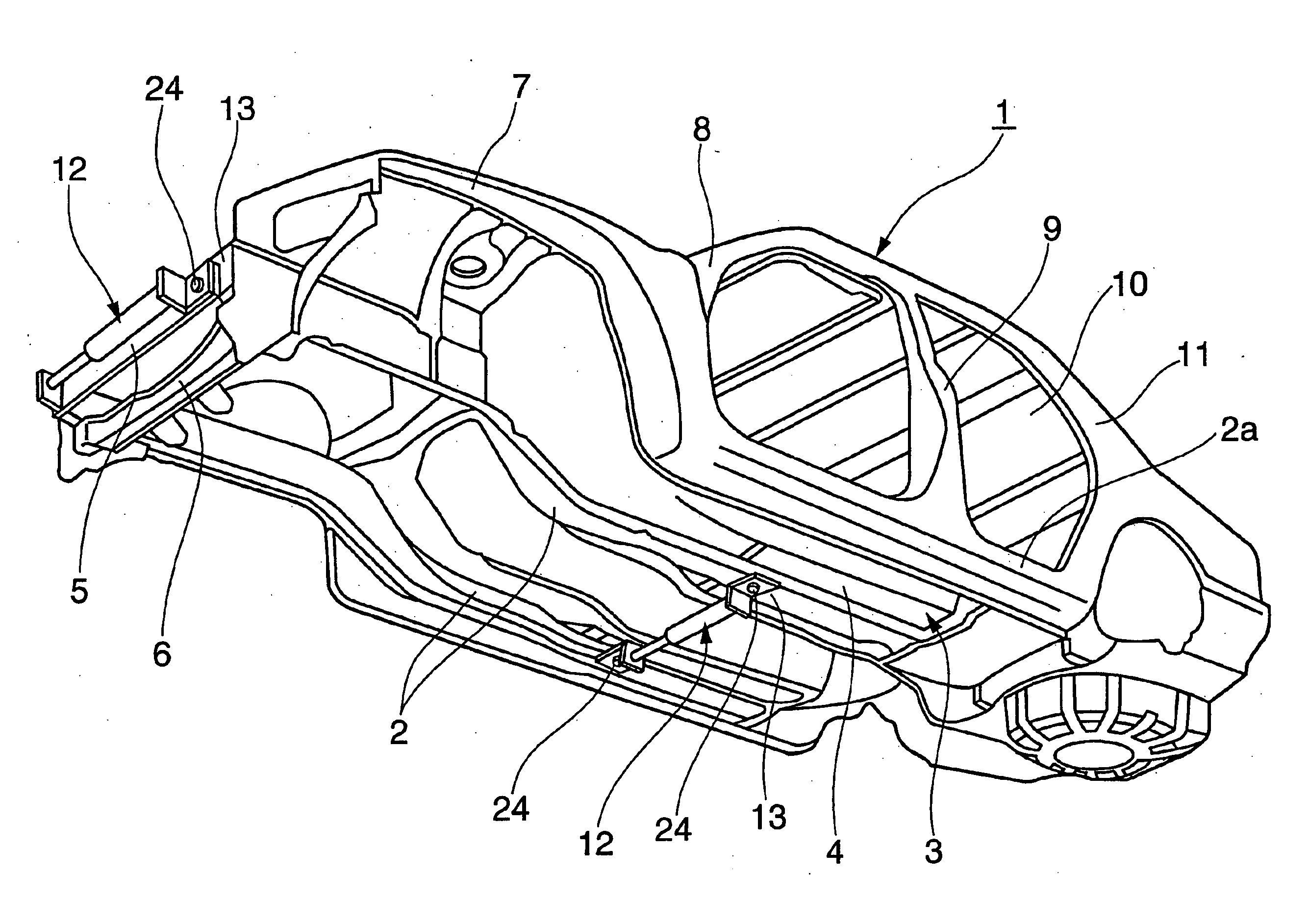
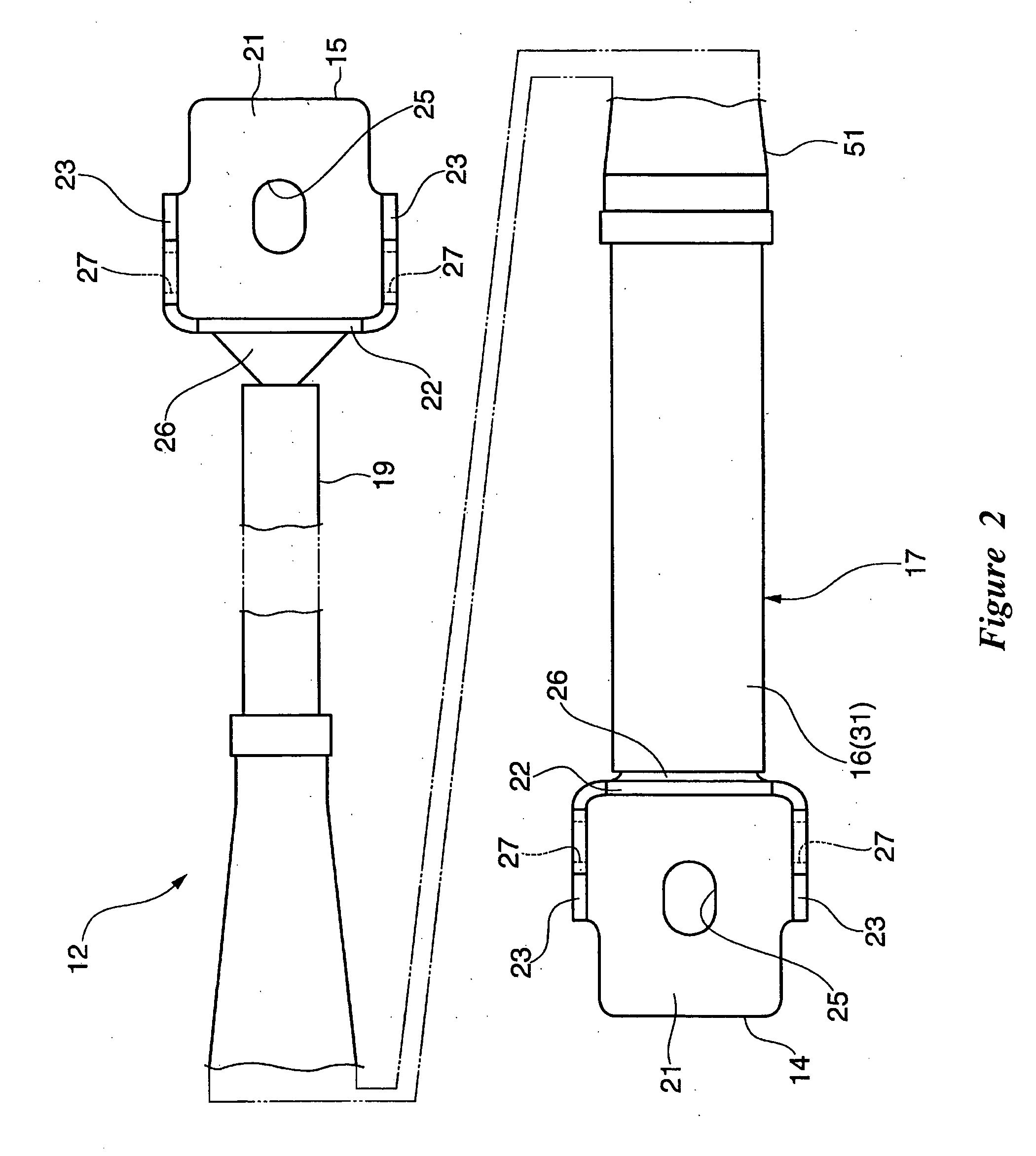
Reinforcement device for vehicle
ActiveUS7845661B2Reduces available leg roomImprove vehicle handlingVehicle seatsSteering linkagesEngineering
A reinforcement device for a vehicle is formed in a slender shape and comprises a medial region with a hydraulic damper. The damper generates a damping force against deformation in the longitudinal direction. The longitudinal direction is defined as a lateral direction of the associated vehicle body. The reinforcement device is removably mounted at both ends to a frame of the vehicle.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Reinforcement device for vehicle
ActiveUS20060125225A1Reduces available leg roomImprove vehicle handlingVehicle seatsVehicle body-frame connectionsEngineeringShock absorber
A reinforcement device for a vehicle is formed in a slender shape and comprises a medial region with a hydraulic damper. The damper generates a damping force against deformation in the longitudinal direction. The longitudinal direction is defined as a lateral direction of the associated vehicle body. The reinforcement device is removably mounted at both ends to a frame of the vehicle
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
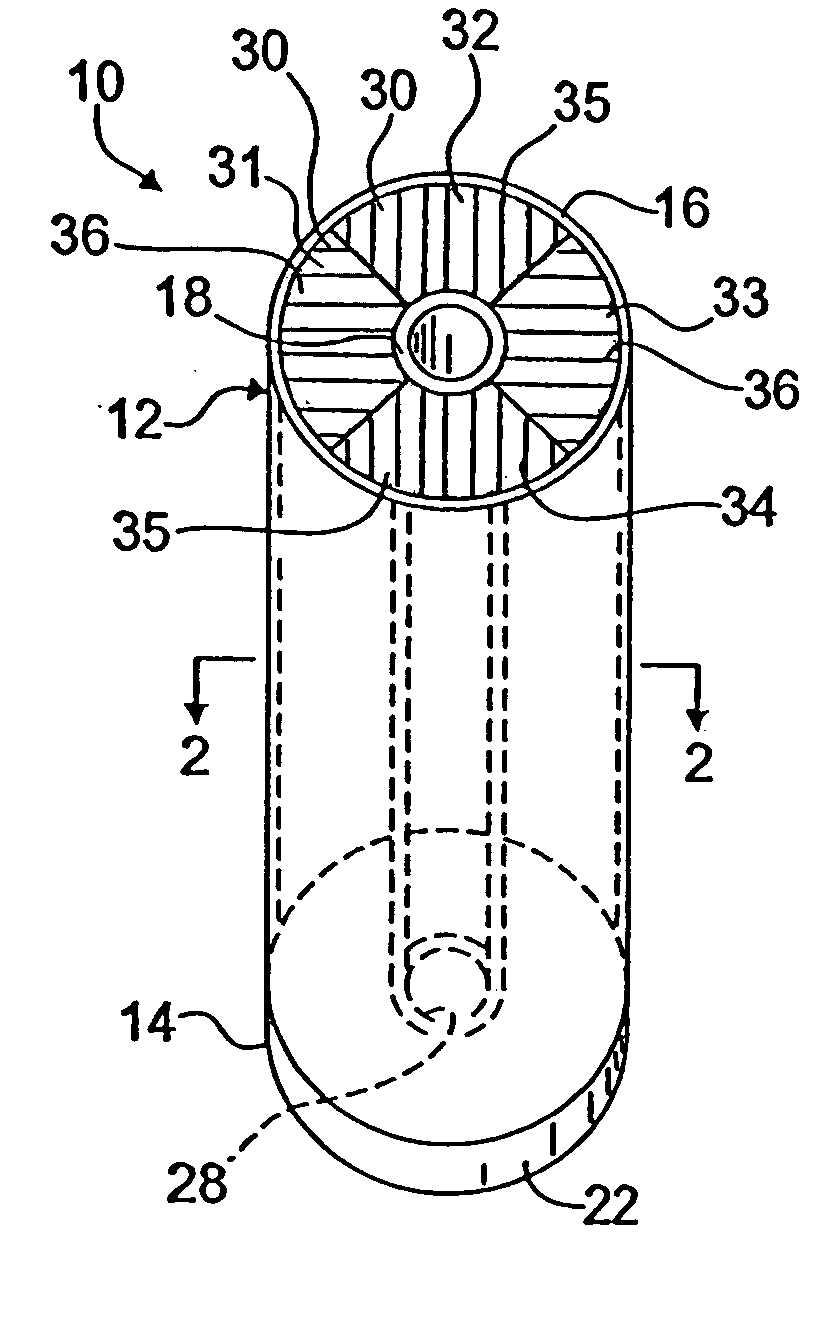
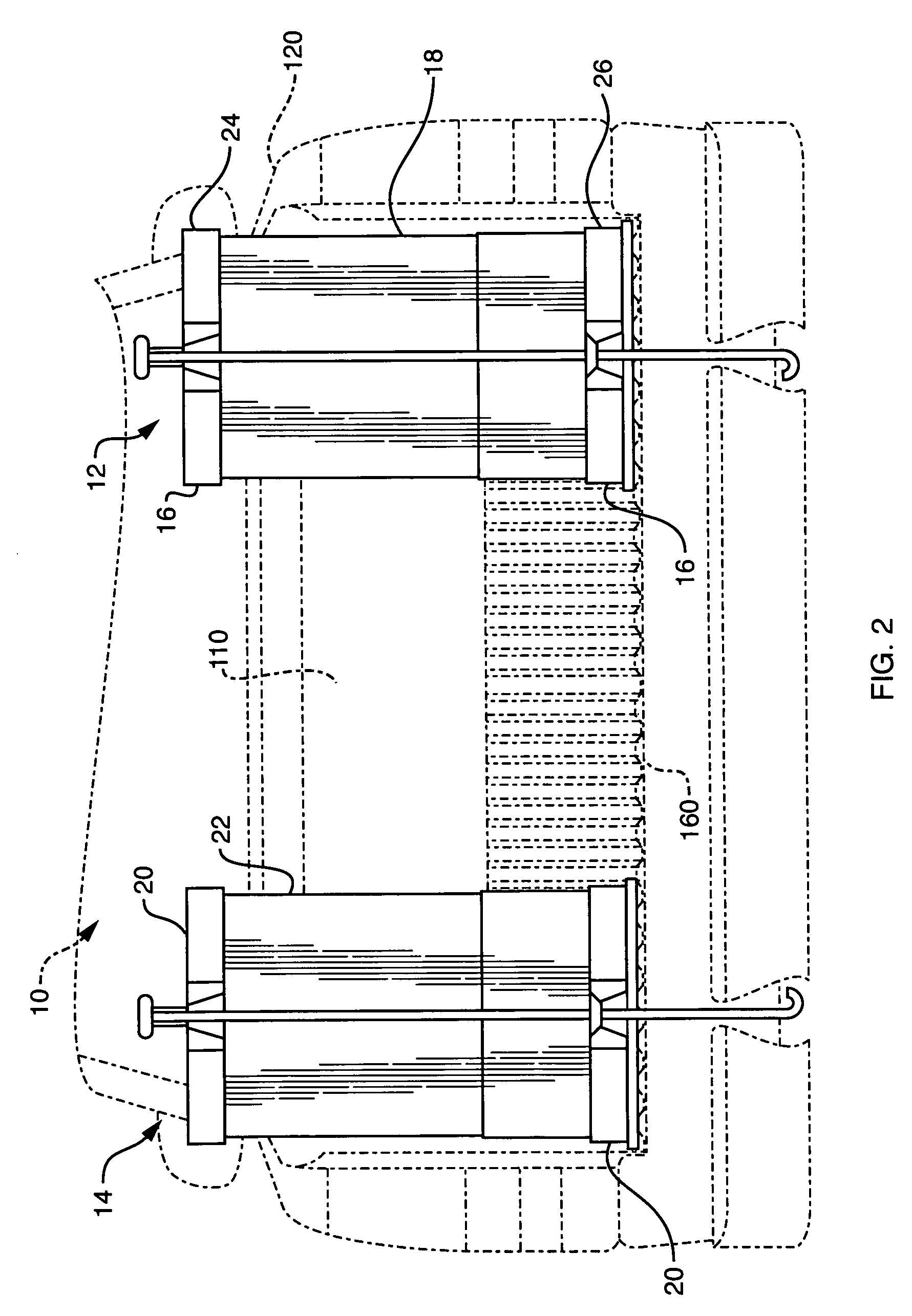
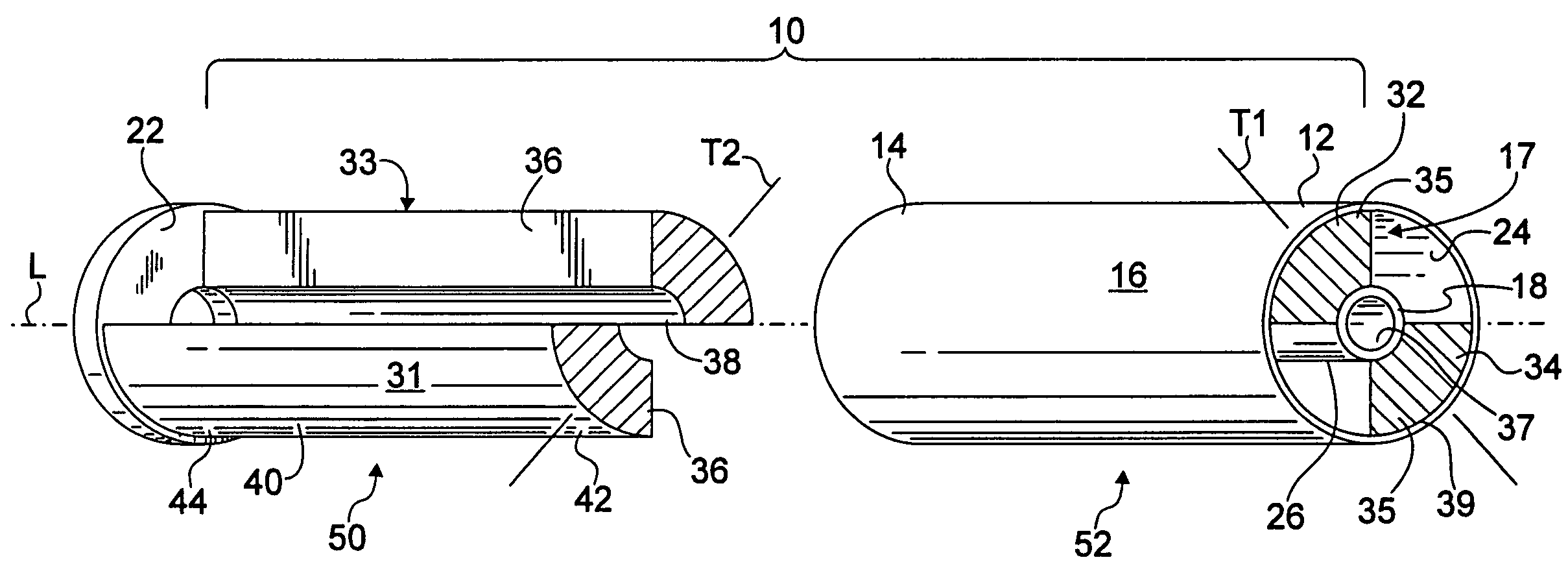
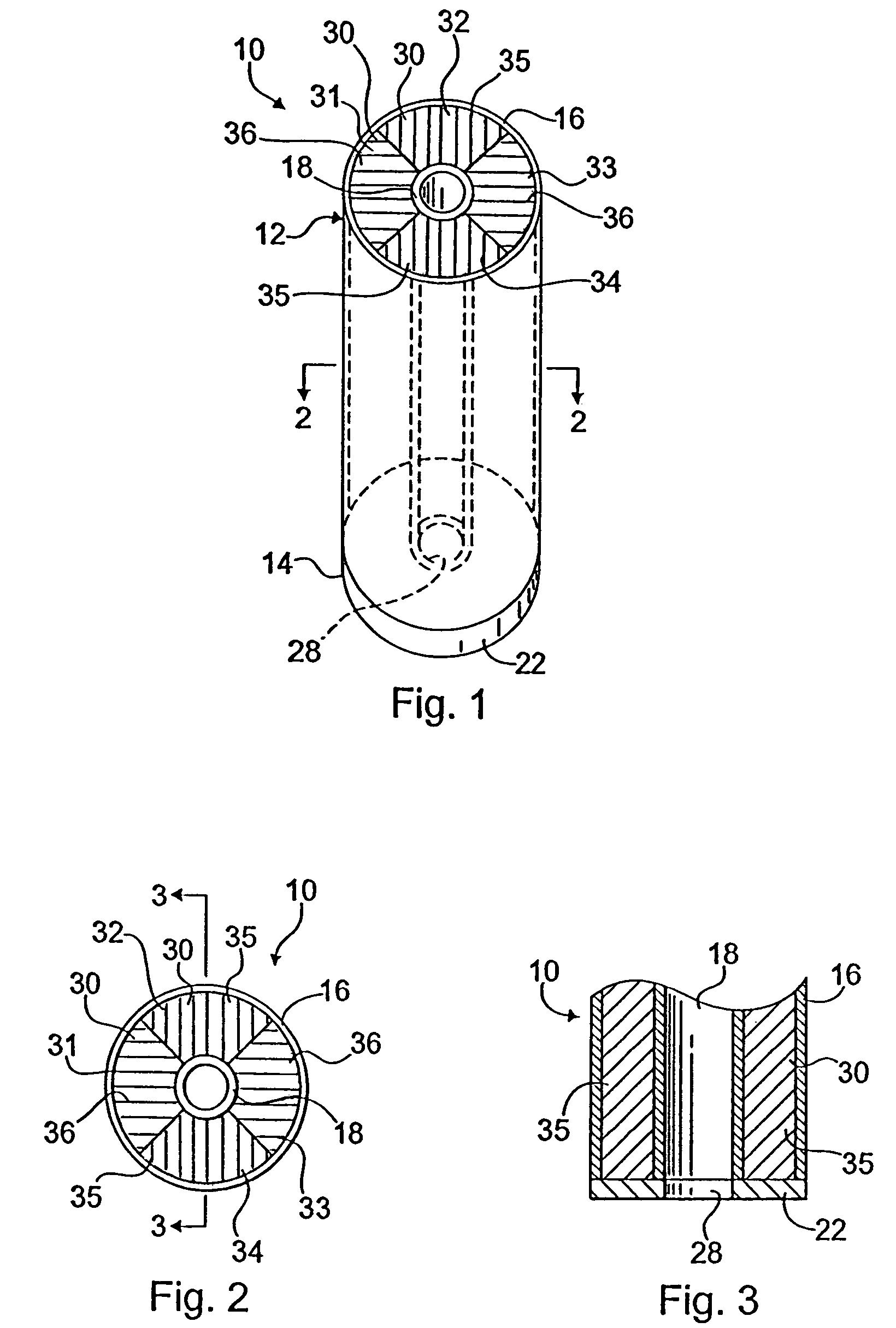
Composite bushing having dual damping capability
InactiveUS20060108727A1Variable resistanceImprove vehicle handlingPortable framesMultiple spring combinationsElastomerEngineering
A composite bushing including an outer sleeve coaxially surrounding an inner sleeve, and including an elastomeric body extending between the outer sleeve and the inner sleeve. The elastomeric body is provided with circumferentially alternating wedge sections having different physical characteristics, so as to provide a bushing having directional differences in resistance to deflection. The resiliency in a first radial direction appreciably differs from the resiliency in a second radial direction, where the second radial direction is at an angle to the first radial direction. The resulting bushing configuration can be used to attenuate vibration and noise in a vehicle, and thereby contribute to improved vehicle handling and ride comfort.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
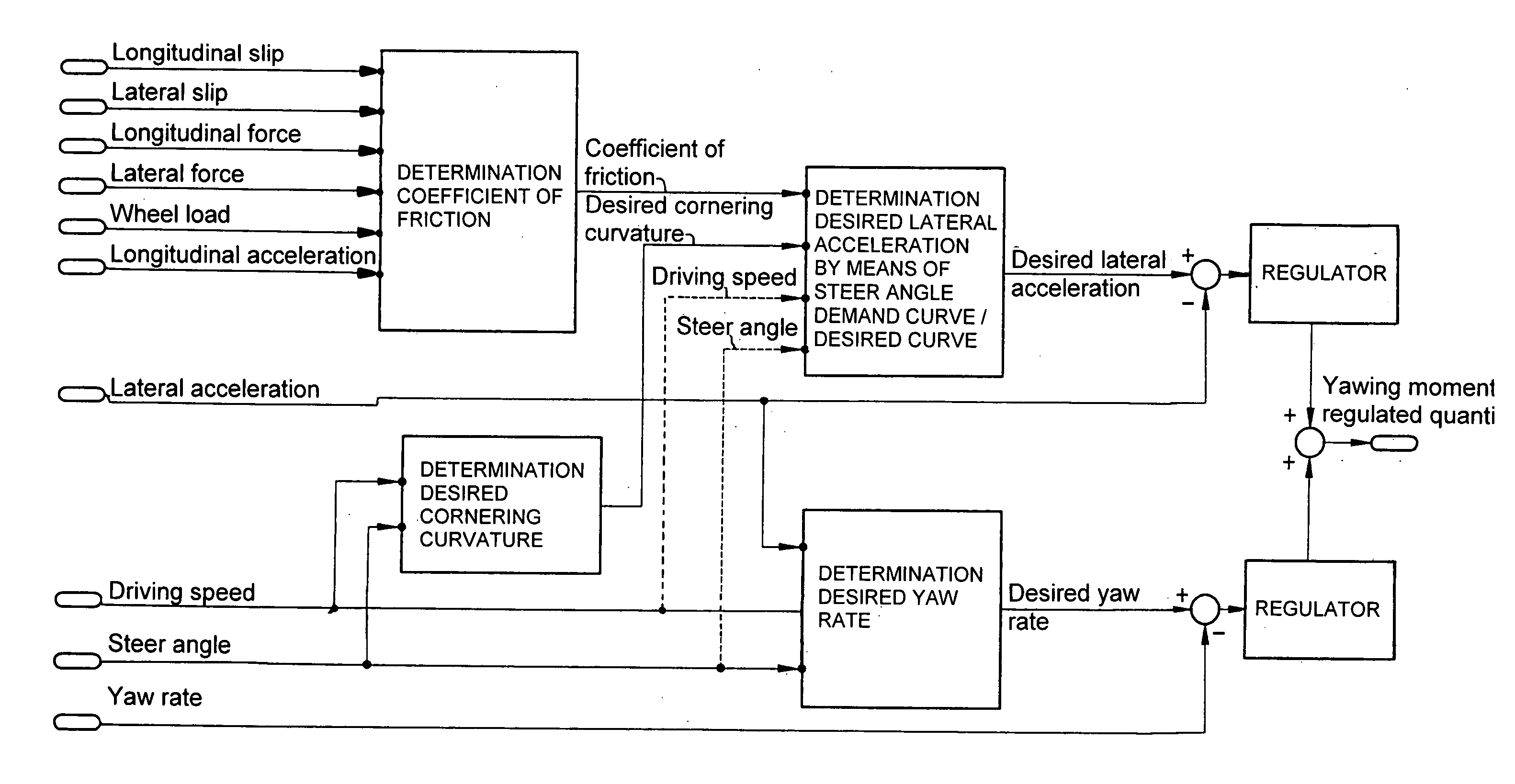
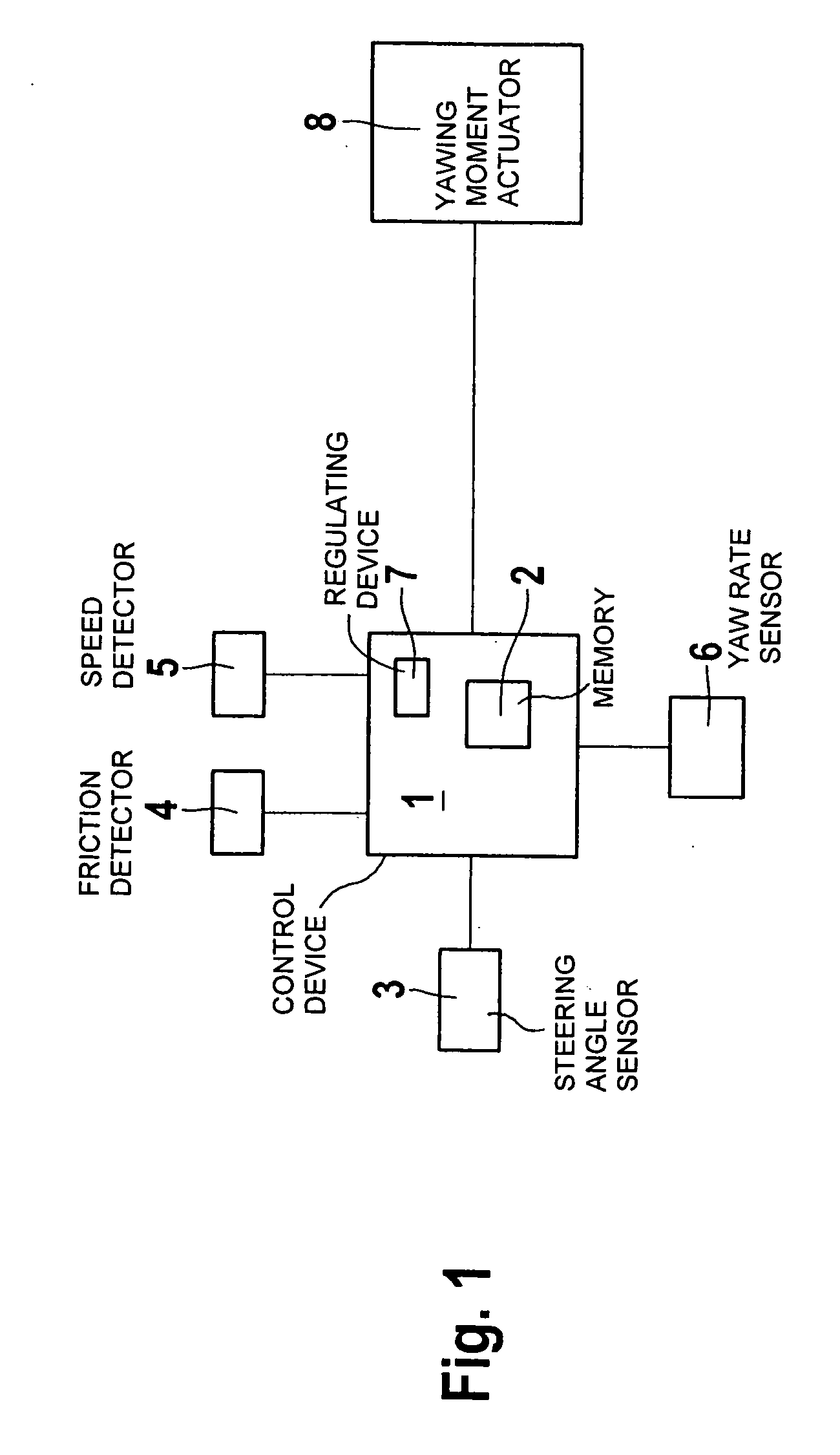
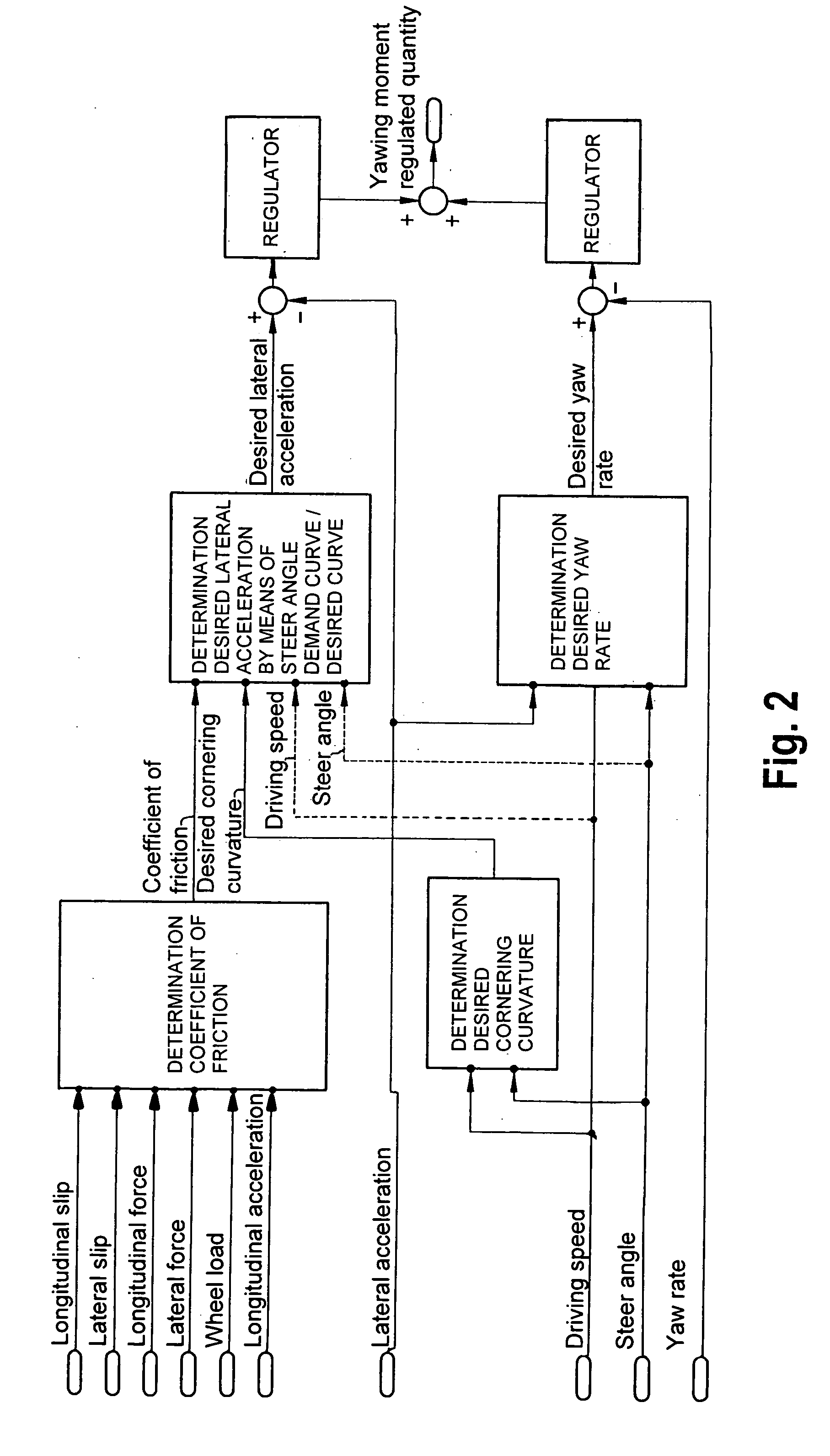
Method and system for controlling a yawing moment actuator in a motor vehicle
InactiveUS20070021887A1Expand rangeEasy and cost-effectiveVehicle body stabilisationDigital data processing detailsSteering angleActuator
Owner:DR ING H C F PORSCHE AG
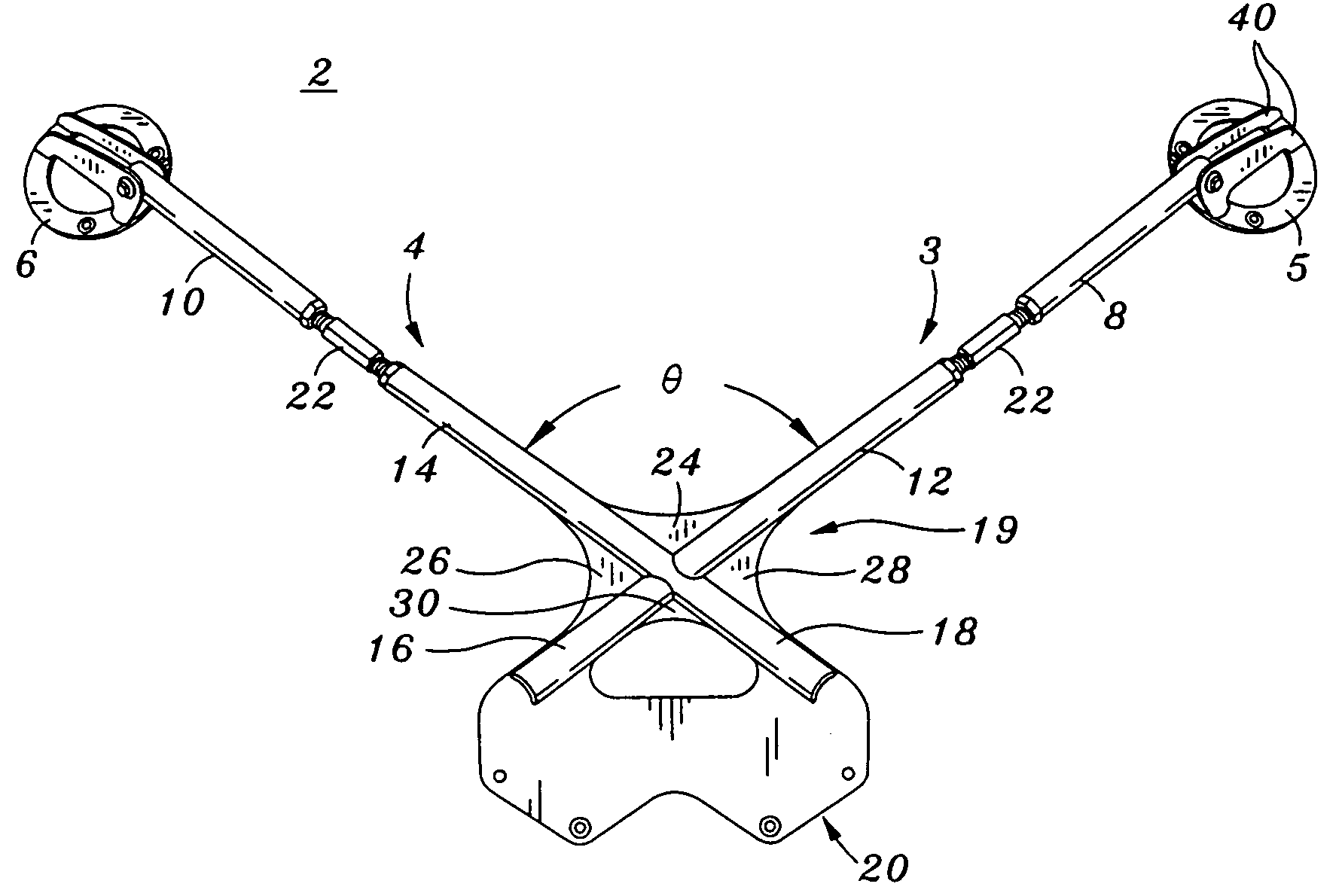
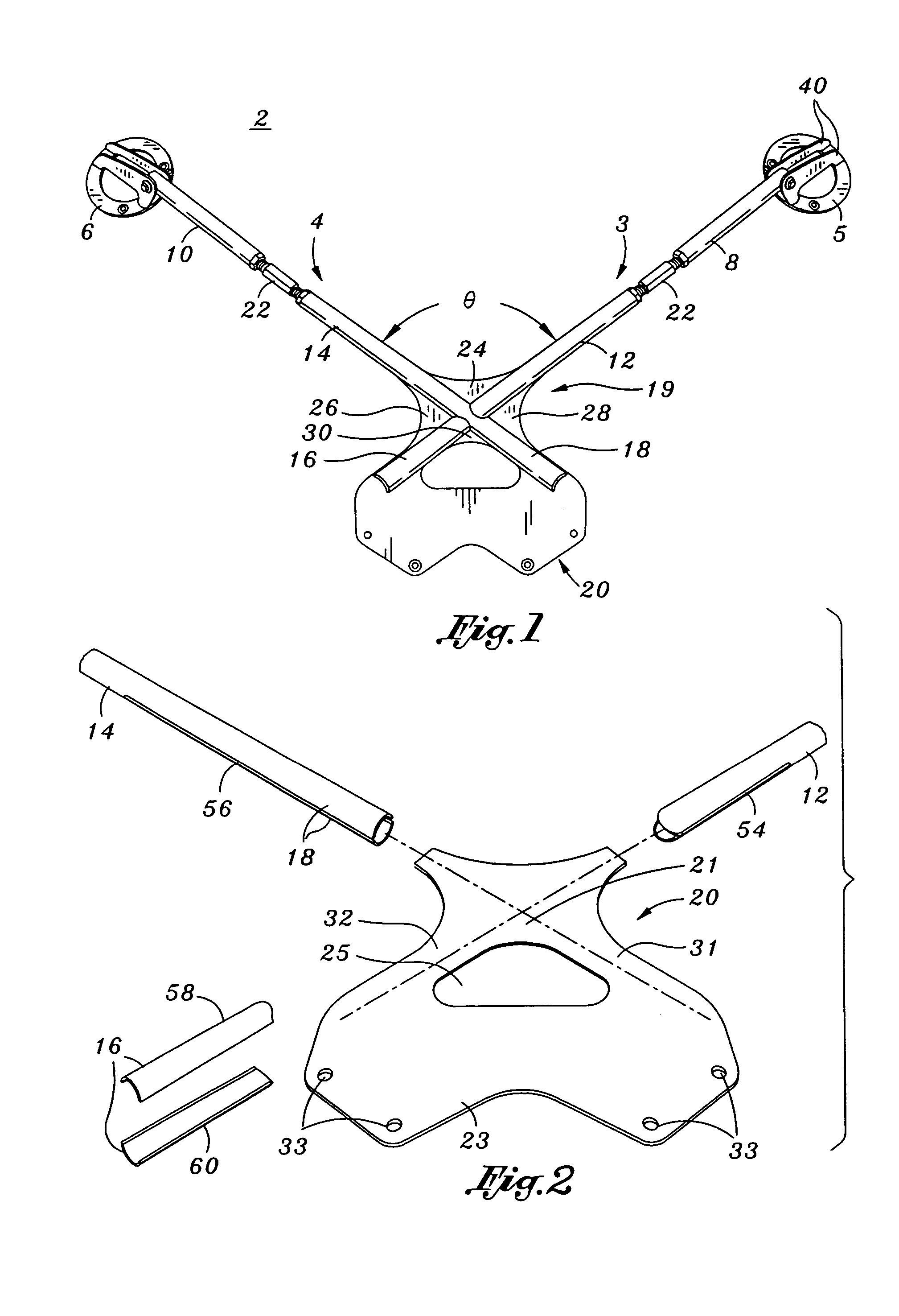
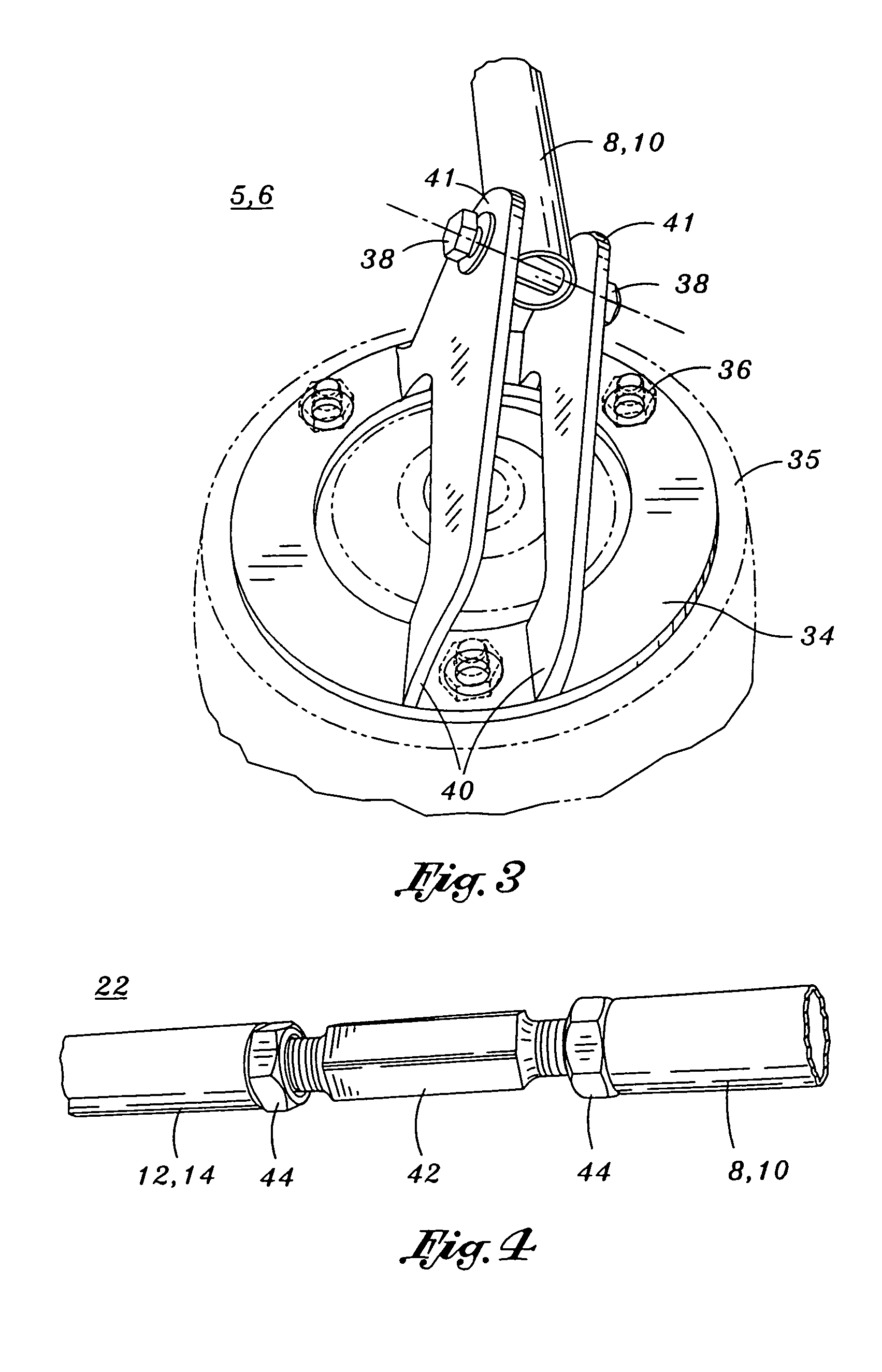
Strut/shock crossmember
ActiveUS7055837B2Increase stiffnessImprove vehicle handlingUnderstructuresSuperstructure subunitsInterconnectionEngineering
A crossmember device is provided which is adapted to be installed between a pair of strut / shock towers of a vehicle. The crossmember device includes a left brace and right brace each having an upper, intermediate and lower portion. The left and right brace are interconnected in a X configuration, wherein the center of the interconnection is between the intermediate and lower portions of the left and right brace. A planar body mounting flange provides gusseting structure to interconnect the left and right brace. A strut / shock tower flange assembly is swivel attached to each distal end of the upper portions of the left and right brace.
Owner:NOBLE ERIC
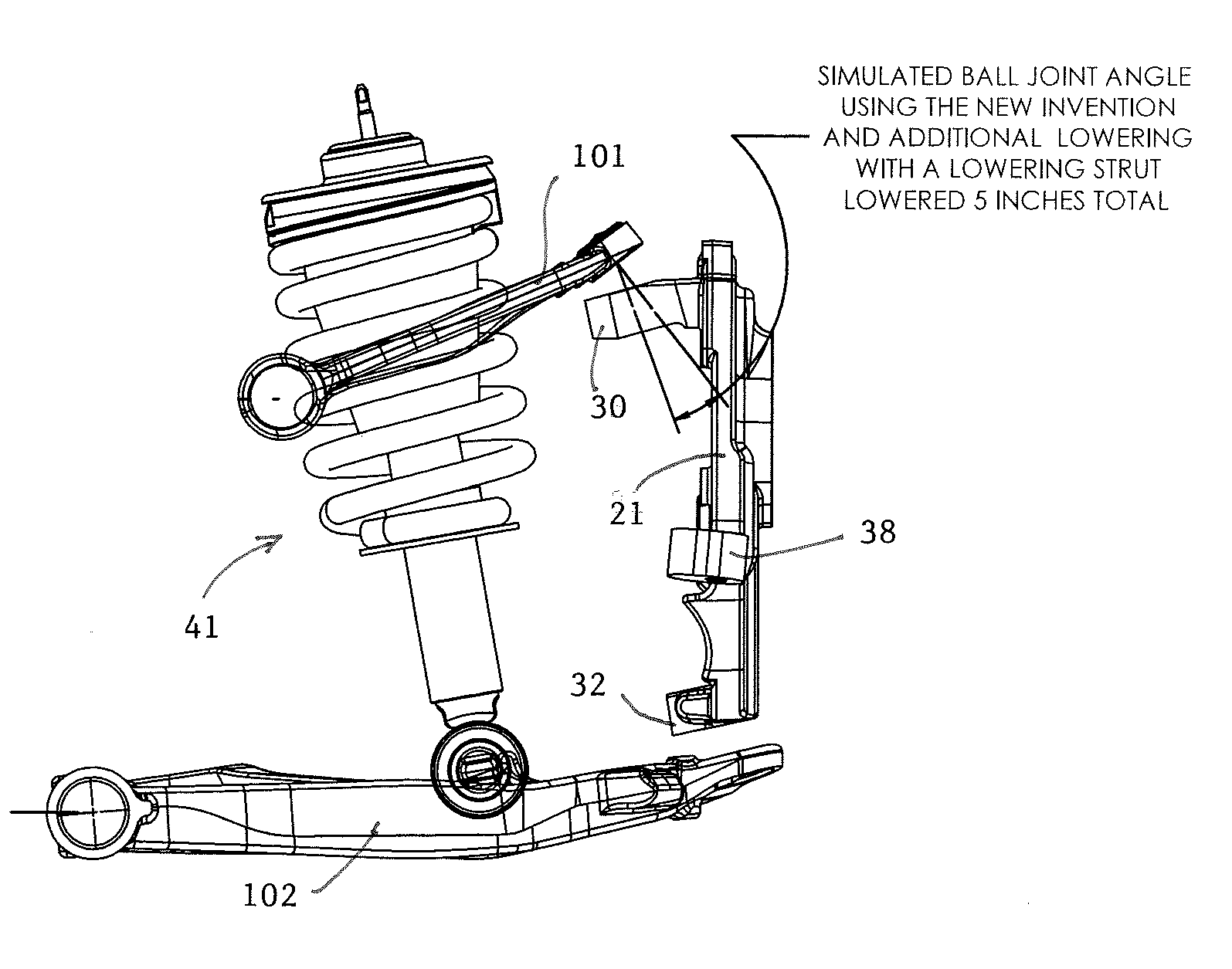
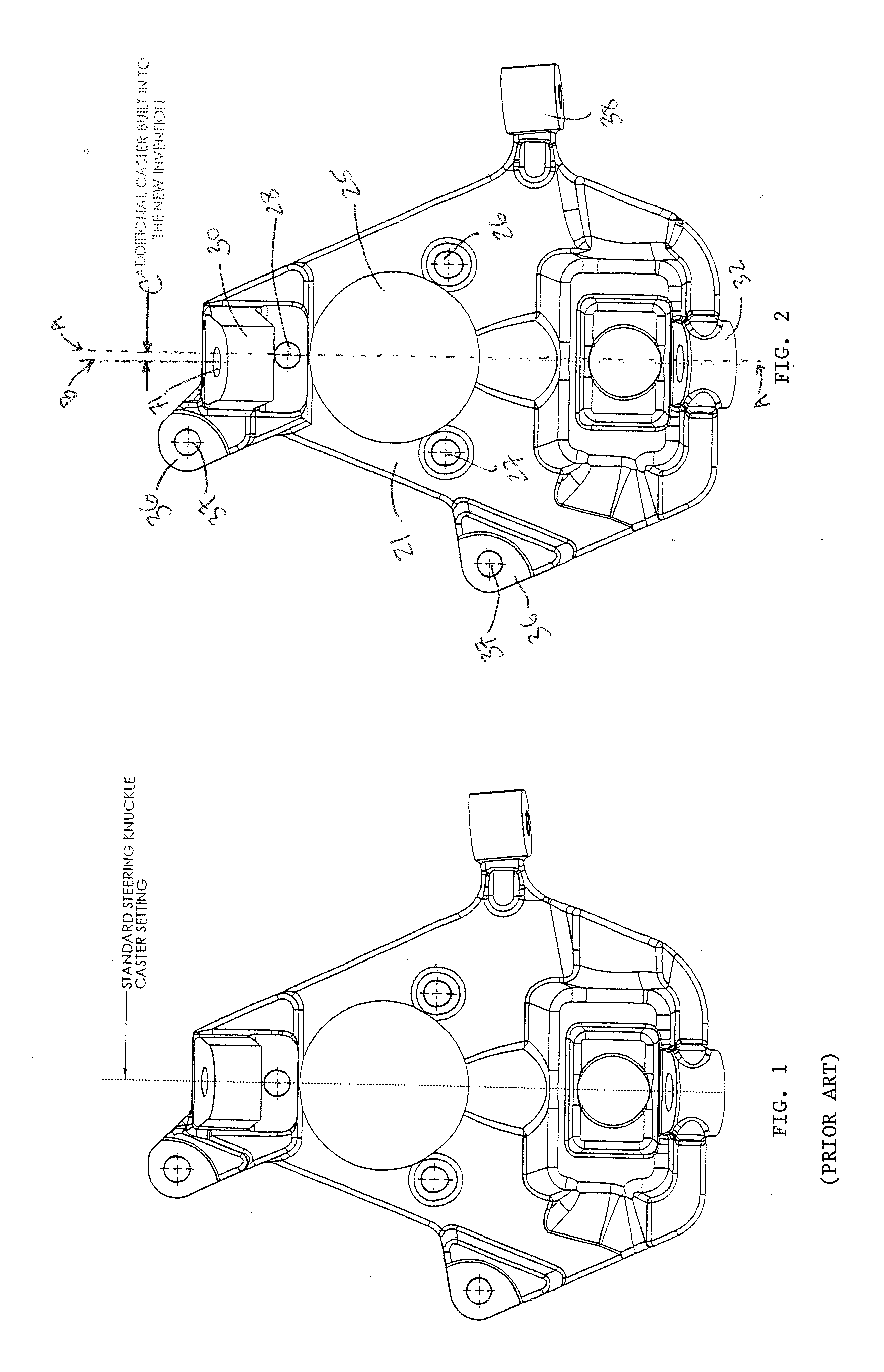
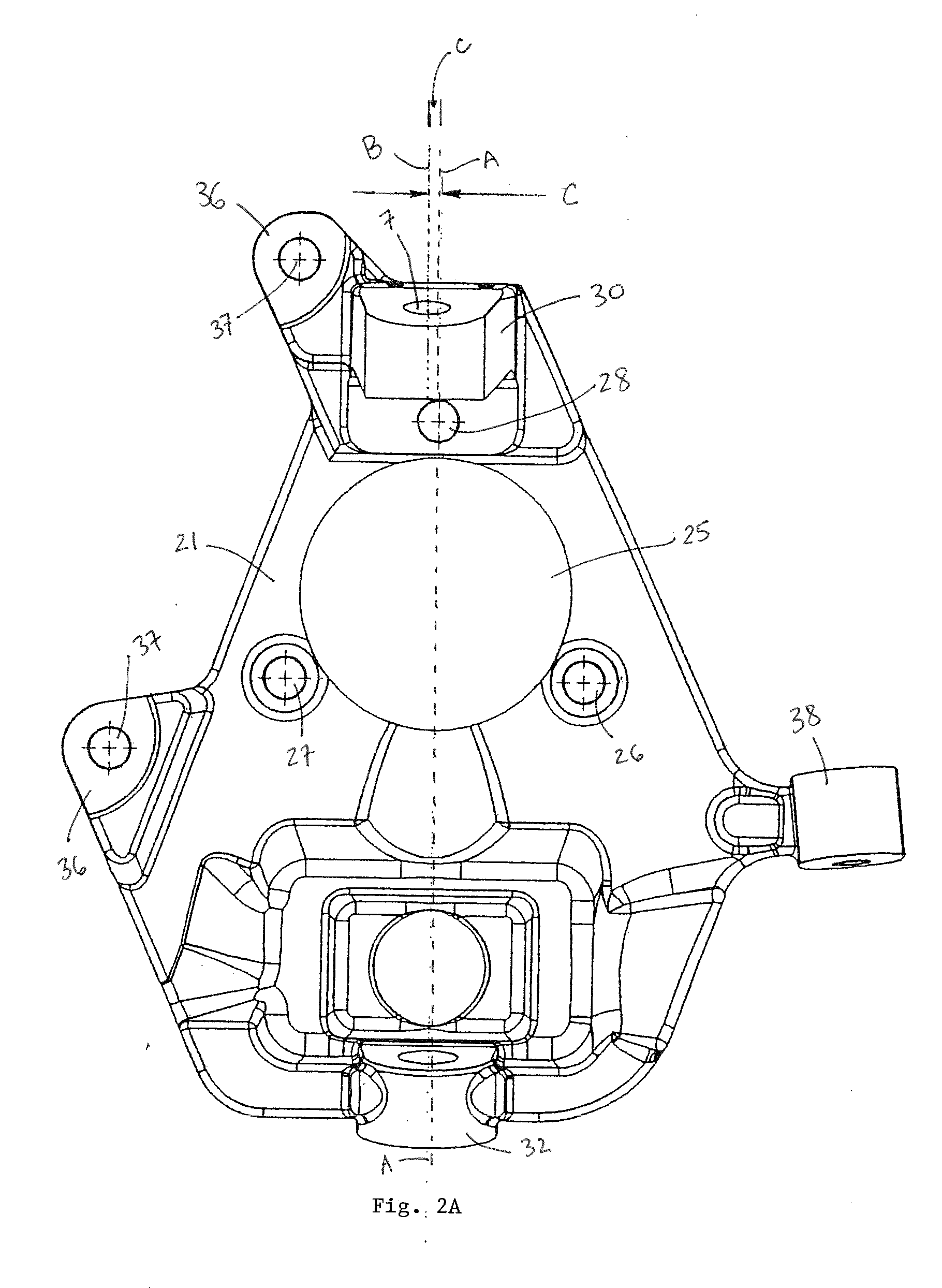
Steering knuckle
InactiveUS20140265202A1Improve vehicle handlingIncreasing casterSteering linkagesResilient suspensionsCaster angleEngineering
The present invention provides improved aftermarket vehicle lowering steering knuckles that are superior to existing aftermarket steering knuckles because they are capable of lowering a vehicle while maintaining or improving vehicle handling, increasing caster, and improving alignment capabilities. Embodiments of the vehicle lowering steering knuckles of the present invention improve handling characteristics by adding caster angle into the steering knuckle, allowing the original caster specifications to be increased without changing the forward or aft locations of the vehicle wheels. This is achieved by adjusting the mounting location of the upper ball joint laterally so that the mounting points are adjusted without affecting the front wheel placement. Embodiments of the vehicle lowering steering knuckles of the present invention also increase vehicle lowering capacity by increasing the downward angle of the upper ball joint mount.
Owner:KW AUTOMOTIVE NORTH AMERICA
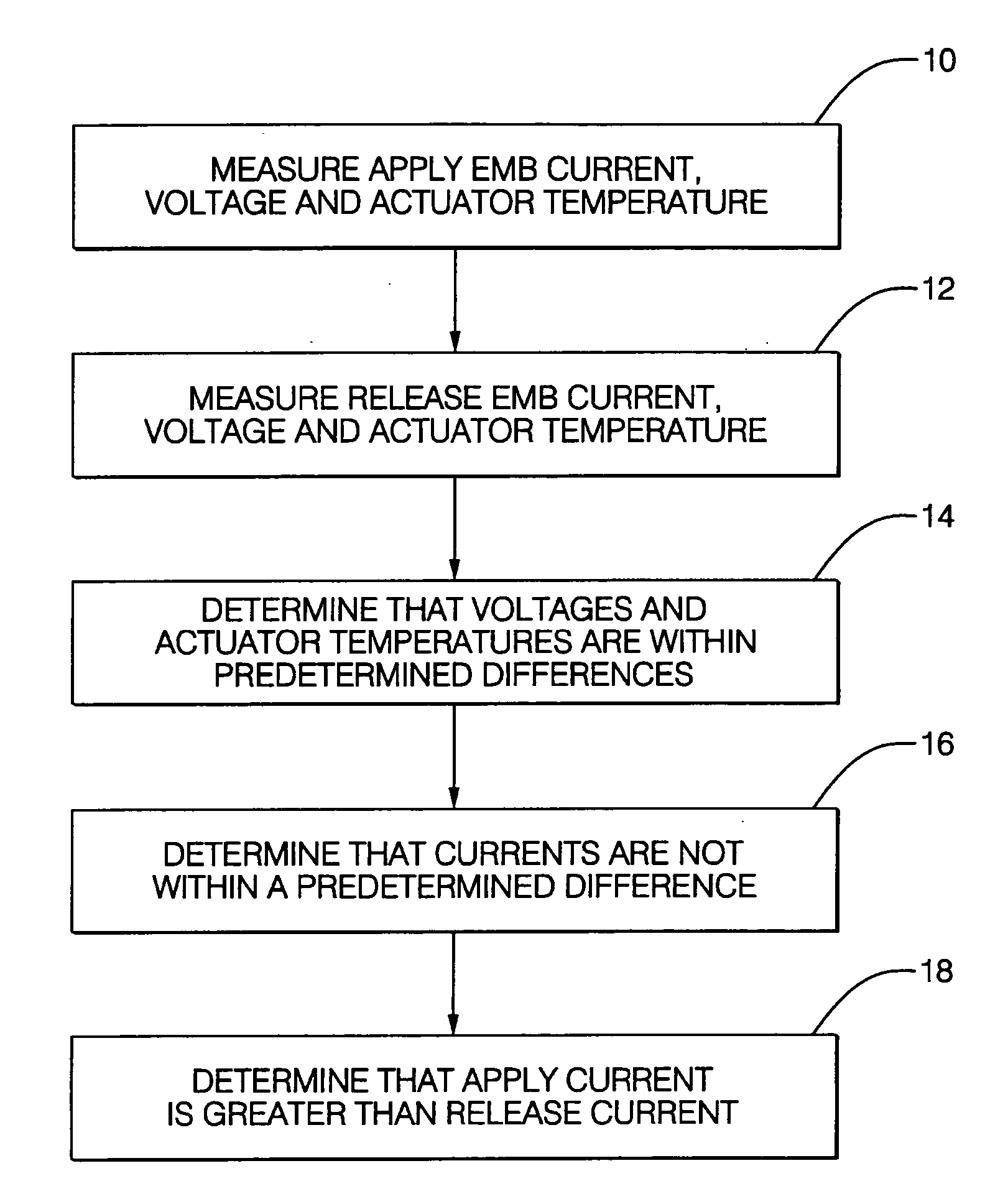
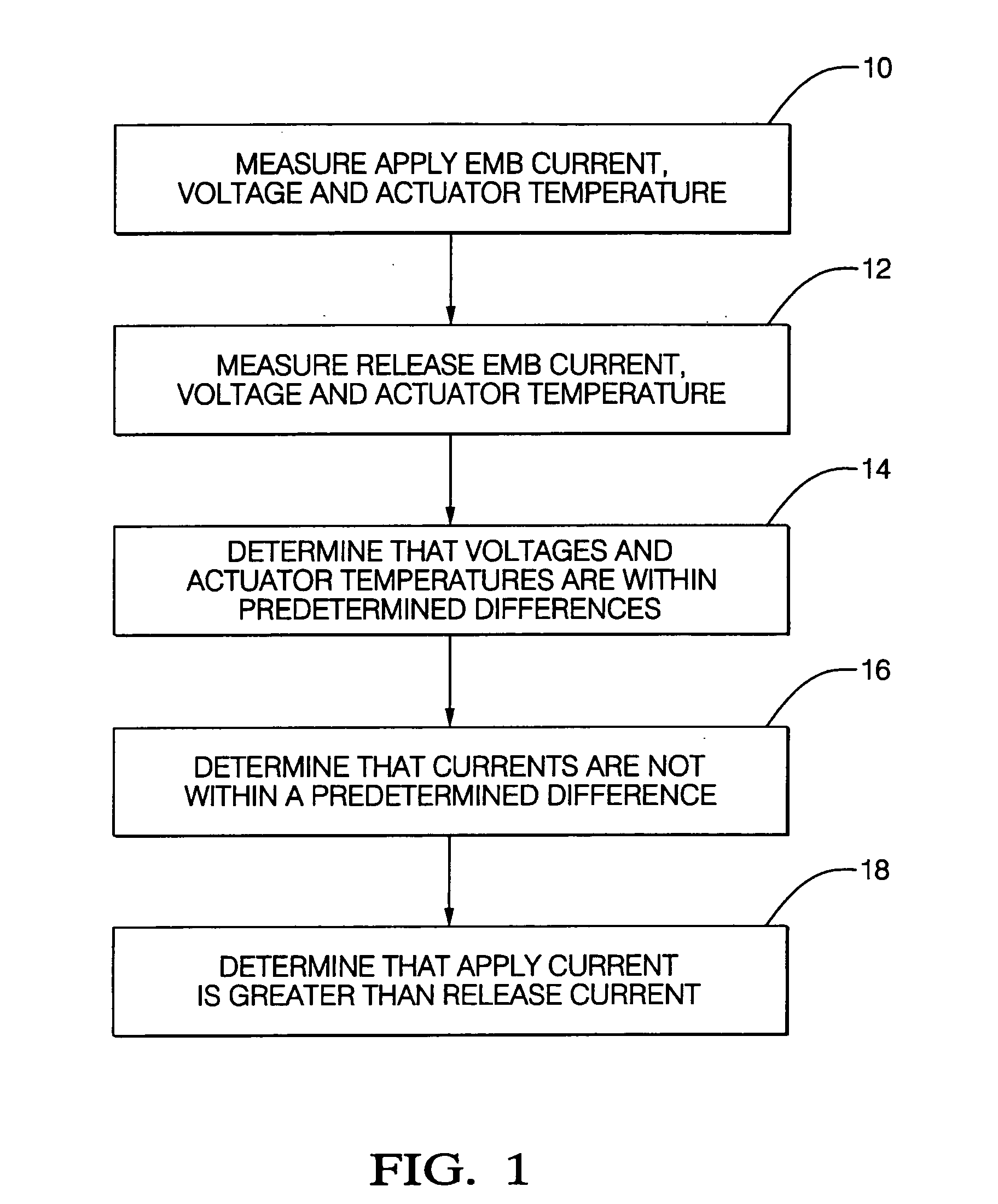
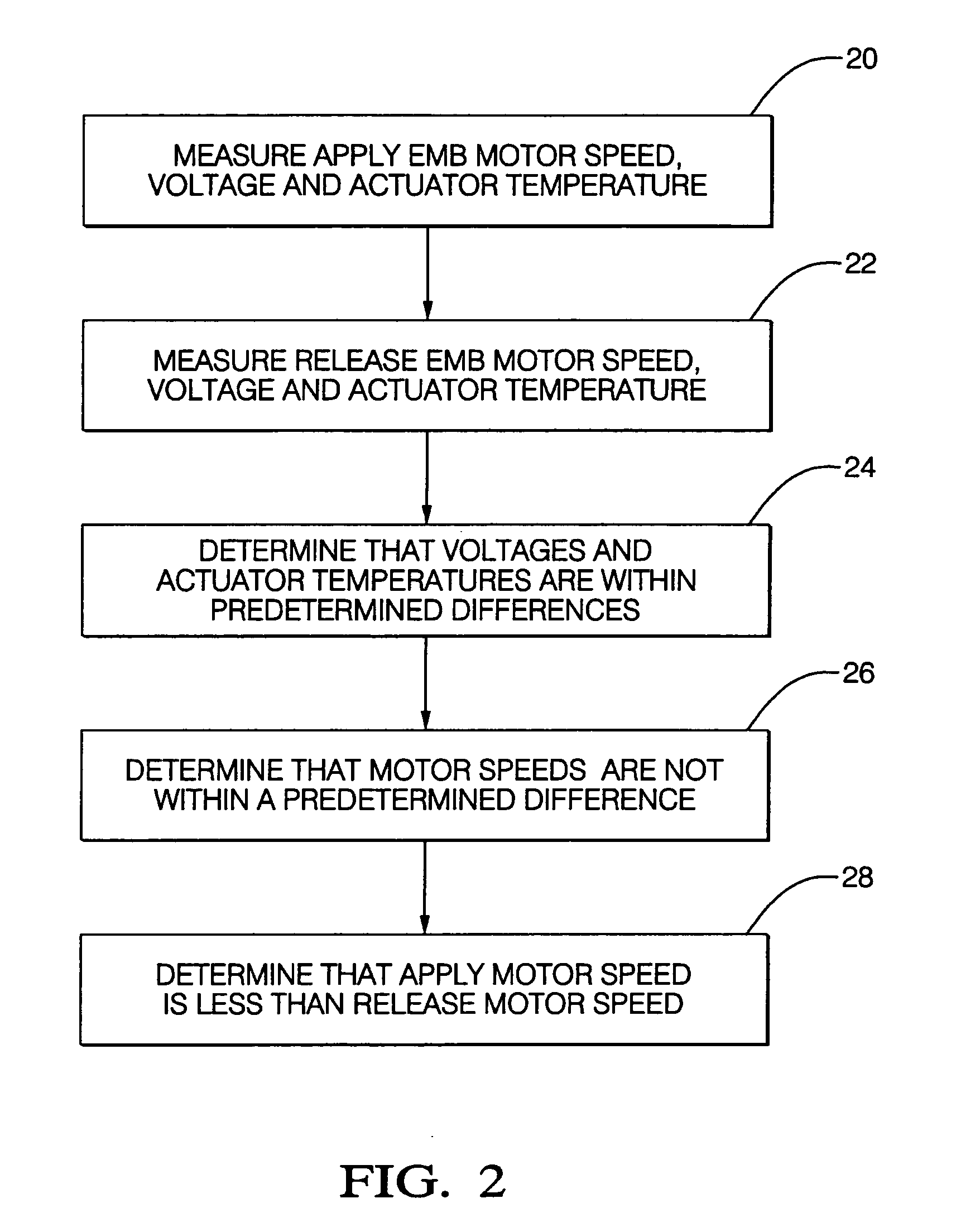
Method for detecting electric-mechanical-brake pad drag and/or calculating actuator efficiency
InactiveUS20050216160A1Increase fuel consumptionImprove vehicle handlingSafety arrangmentsAnalogue computers for trafficMotor speedElectric machine
Electric-mechanical-brake (EMB) pad drag is determined from measurements (which can include estimations) of EMB voltage, EMB actuator temperature, and either EMB current or EMB motor speed during an open-loop apply of the EMB pad and during an open-loop release of the EMB pad. An open-loop EMB actuator efficiency is calculated when certain conditions of the same measurements apply, whereupon the EMB actuator efficiency is calculated using at least the apply or release EMB current and a corresponding apply or release preselected (such as a nominal) EMB current or is calculated using at least the apply or release EMB motor speed and a corresponding apply or release preselected (such as a nominal) EMB motor speed.
Owner:BWI CO LTD SA +1
Wheel suspension with centrally pivoted transverse leaf spring
ActiveUS20170305222A1Improve the level ofReduce manufacturing costBusesResilient suspensionsControl armEngineering
A wheel suspension arrangement is provided for a vehicle having a longitudinal direction, a transverse direction and a vertical direction. The wheel suspension arrangement includes a wheel holder for supporting a vehicle wheel. A first vertical end region of the wheel holder is pivotally attached to a vehicle support structure by a rigid control arm and a second vertical end region of the wheel holder is attached to the vehicle support structure by a leaf spring. A longitudinal direction of the leaf spring is arranged substantially in the transverse direction of the vehicle. The leaf spring is pivotally attached to the vehicle support structure at a transverse centre region of the vehicle, and a centre of the leaf spring in the transverse direction is located vertically offset from a pivotal attachment location of the leaf spring. The pivotal attachment location of the leaf spring is vertically offset towards the side of the rigid control arm.
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
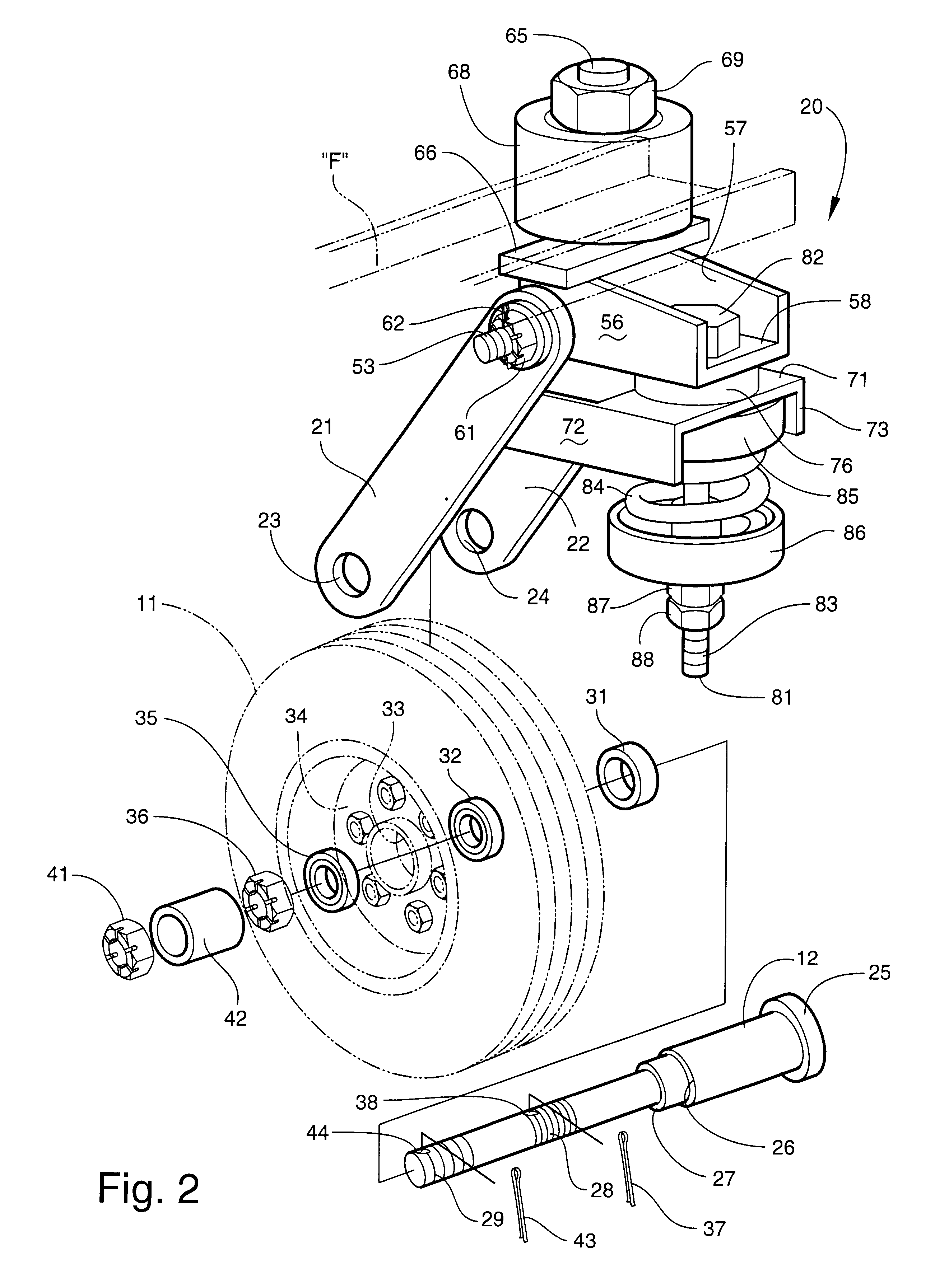
Swivel wheel assembly with adjustable shock absorption
InactiveUS20020084608A1Quick disassemblyImprove efficiencyCastorsDeflectable wheel steeringRotational axisControl theory
A swivel wheel assembly includes a wheel axle, and a vehicle wheel rotatably mounted on the wheel axle. A shock-absorbing wheel fork is secured to opposite ends of the wheel axle. The wheel fork includes first and second elongated spaced-apart support arms located on opposite sides of the vehicle wheel. The support arms have respective distal and proximal ends. The distal ends define respective axle openings receiving the wheel axle. The proximal ends extend beyond a periphery of the vehicle wheel and define respective pin openings. A pivot pin extends through the pin openings formed with proximal ends of the first and second support arms. A base is carried by the pivot pin, and is adapted for pivoting movement about an axis defined by the pivot pin. A vertical swivel shaft is mounted on the base, and is adapted for connecting to an underframe of a vehicle to provide swivel movement of the vehicle wheel about an axis defined by the swivel shaft. An adjustable shock absorber is operatively connected to the base for dampening pivoting movement of the base relative to the vehicle wheel, thereby absorbing the energy of sudden shocks to the vehicle wheel during use.
Owner:MARSHBURN BILL W
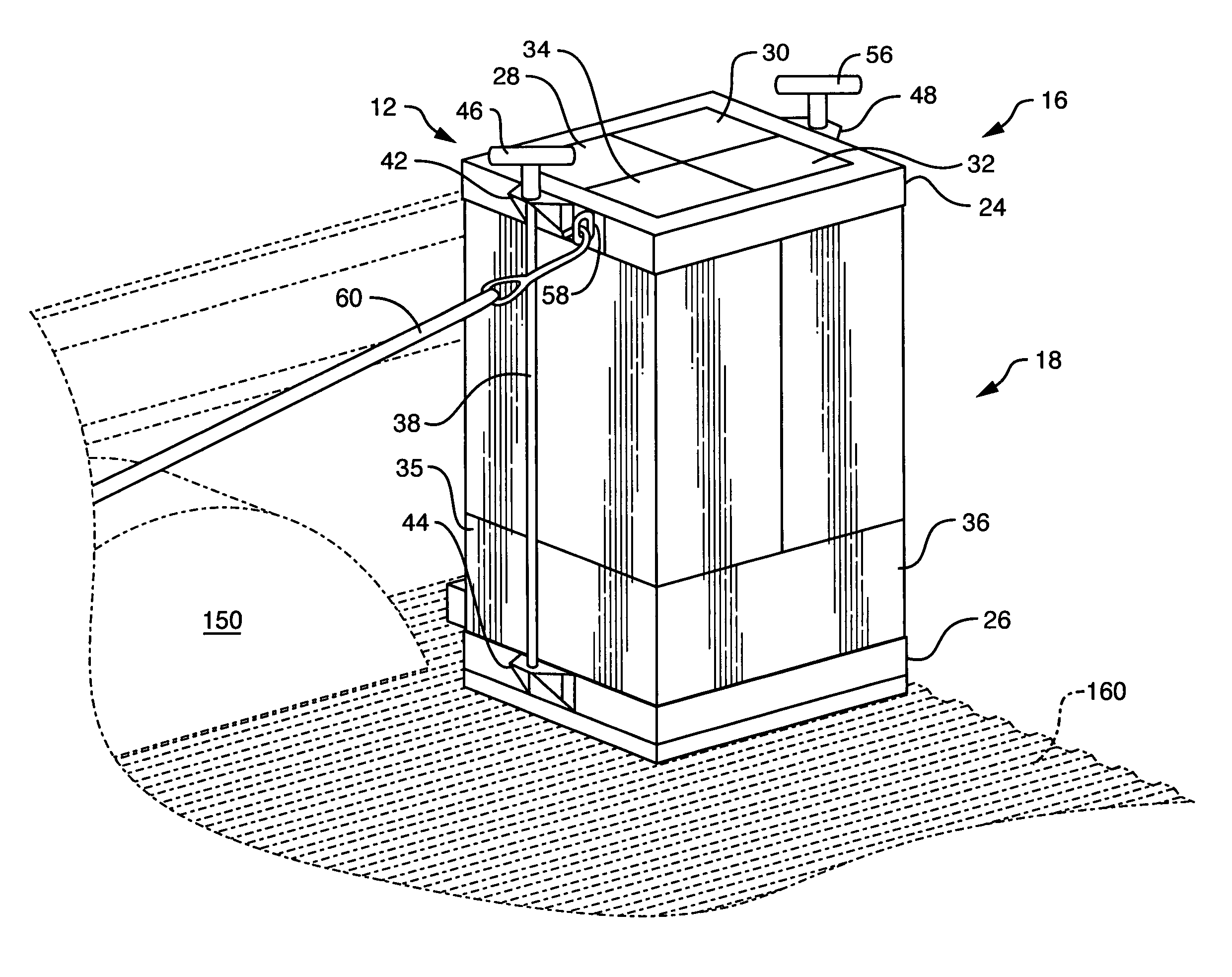
Vehicle ballast system
InactiveUS7175201B2Easily inserted into and removedMinimize impactVehicle cleaning apparatusTractorsPickup truckBallast
A vehicle ballast system for improving the balance of a vehicle. The system is particularly well suited for use in the bed of a pickup truck but is not limited to that deployment. The system includes one or more ballast units. Each ballast unit includes a frame set and a ballast element. The frame set retains the ballast element therein. The ballast element may be one or more concrete blocks. The frame set includes an upper frame and a lower frame. The respective frames are connected together in a manner to contain the ballast element using a front retaining rod and a rear retaining rod is preferably affixable to a bracket secured to the rear of the vehicle. A tether may be removably connected between the upper frame and a securing point of the vehicle. A shock-absorbing lanyard may be employed at the rear of the system as a restraint upon sudden deceleration of the vehicle.
Owner:CHILDS THOMAS +2
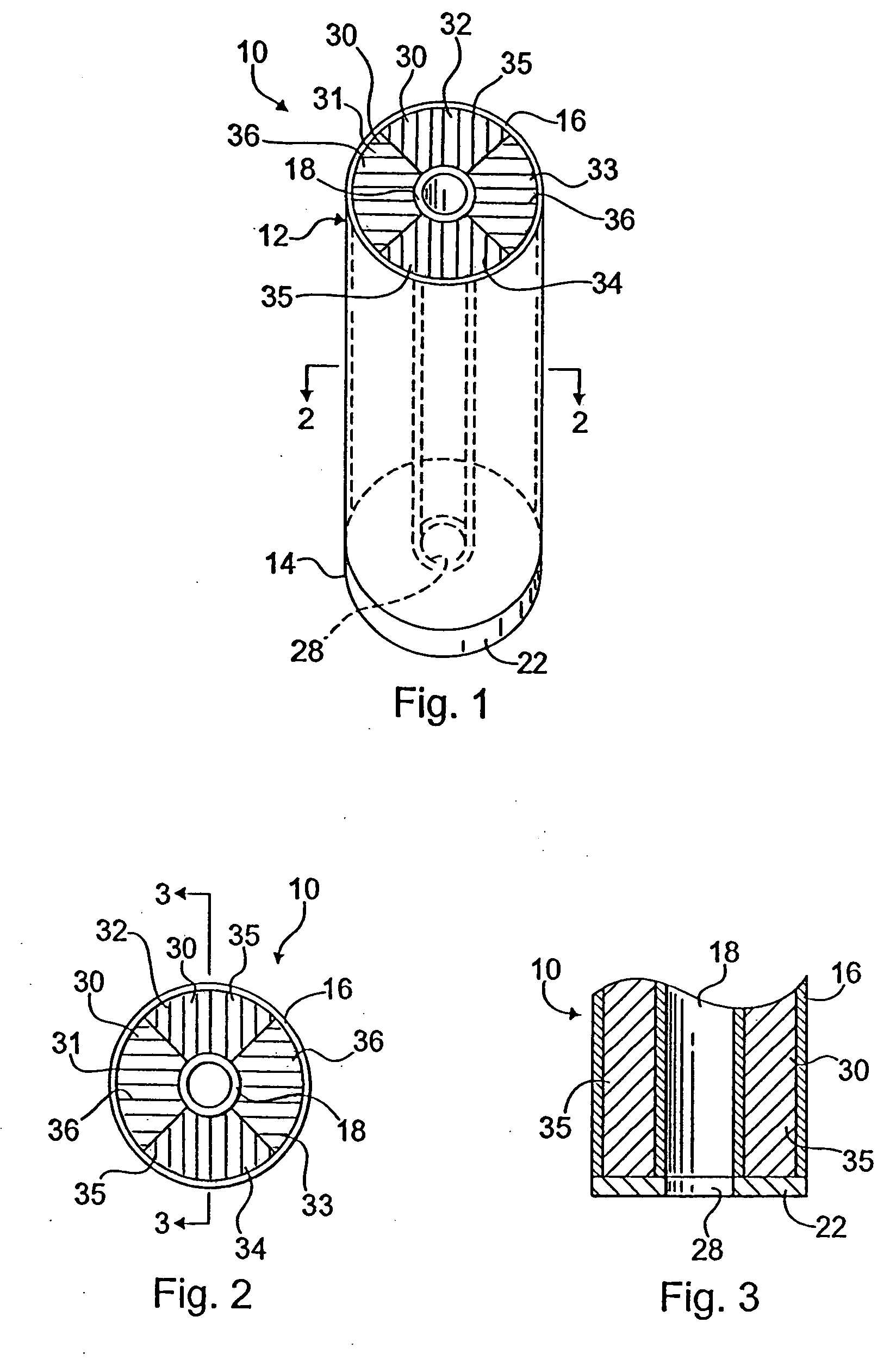
Composite bushing having dual damping capability
InactiveUS7296786B2Improve vehicle handlingPortable framesMultiple spring combinationsElastomerEngineering
A composite bushing including an outer sleeve coaxially surrounding an inner sleeve, and including an elastomeric body extending between the outer sleeve and the inner sleeve. The elastomeric body is provided with circumferentially alternating wedge sections having different physical characteristics, so as to provide a bushing having directional differences in resistance to deflection. The resiliency in a first radial direction appreciably differs from the resiliency in a second radial direction, where the second radial direction is at an angle to the first radial direction. The resulting bushing configuration can be used to attenuate vibration and noise in a vehicle, and thereby contribute to improved vehicle handling and ride comfort.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
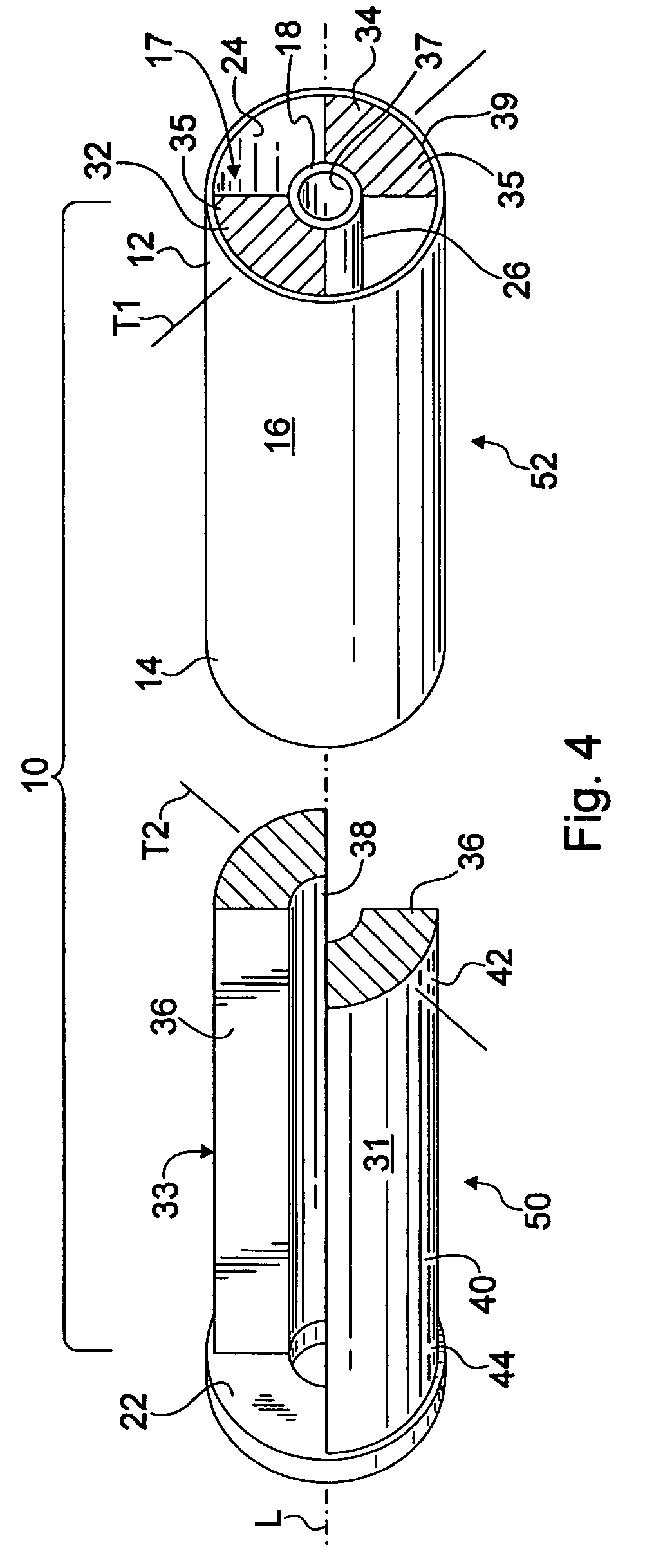
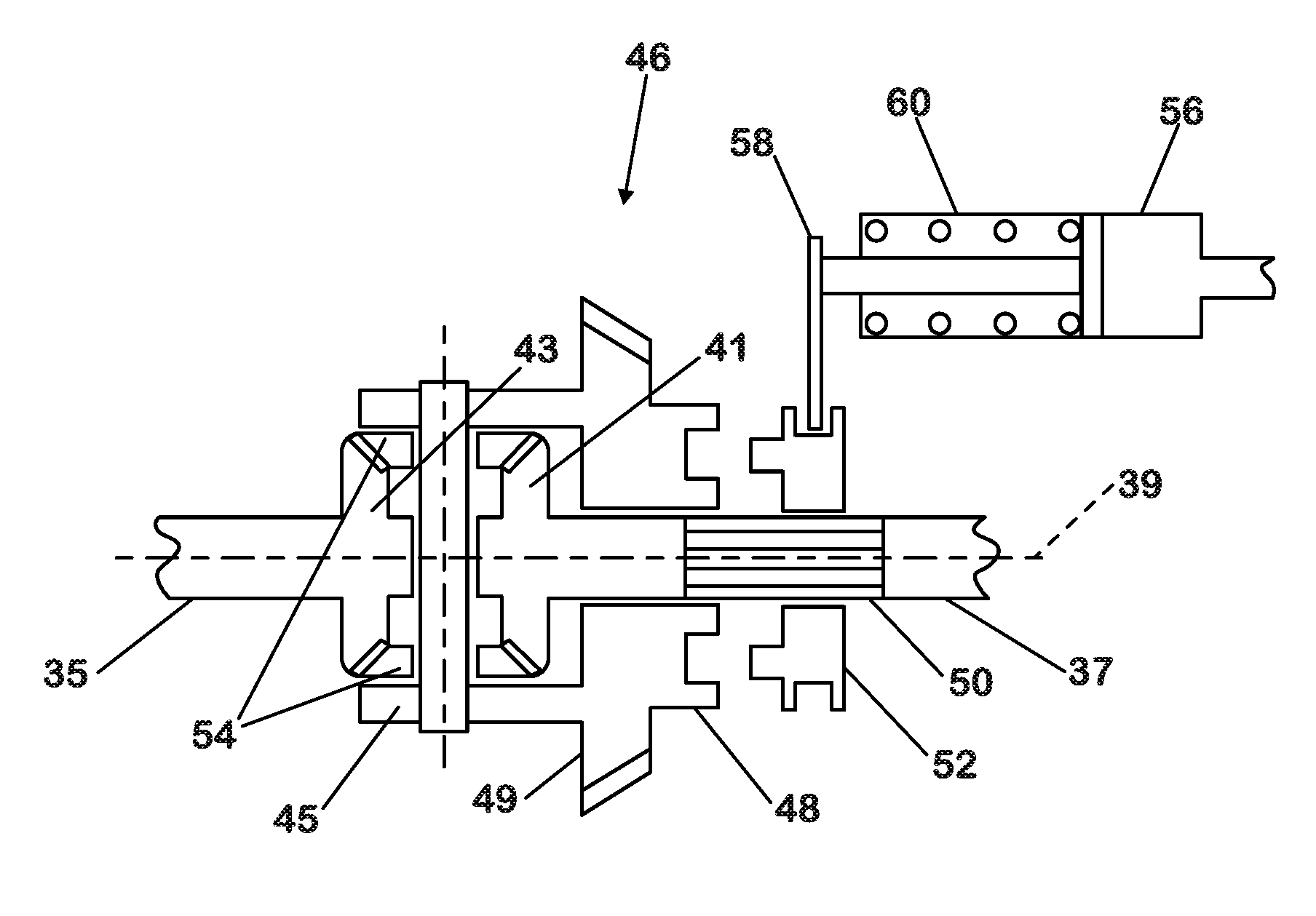
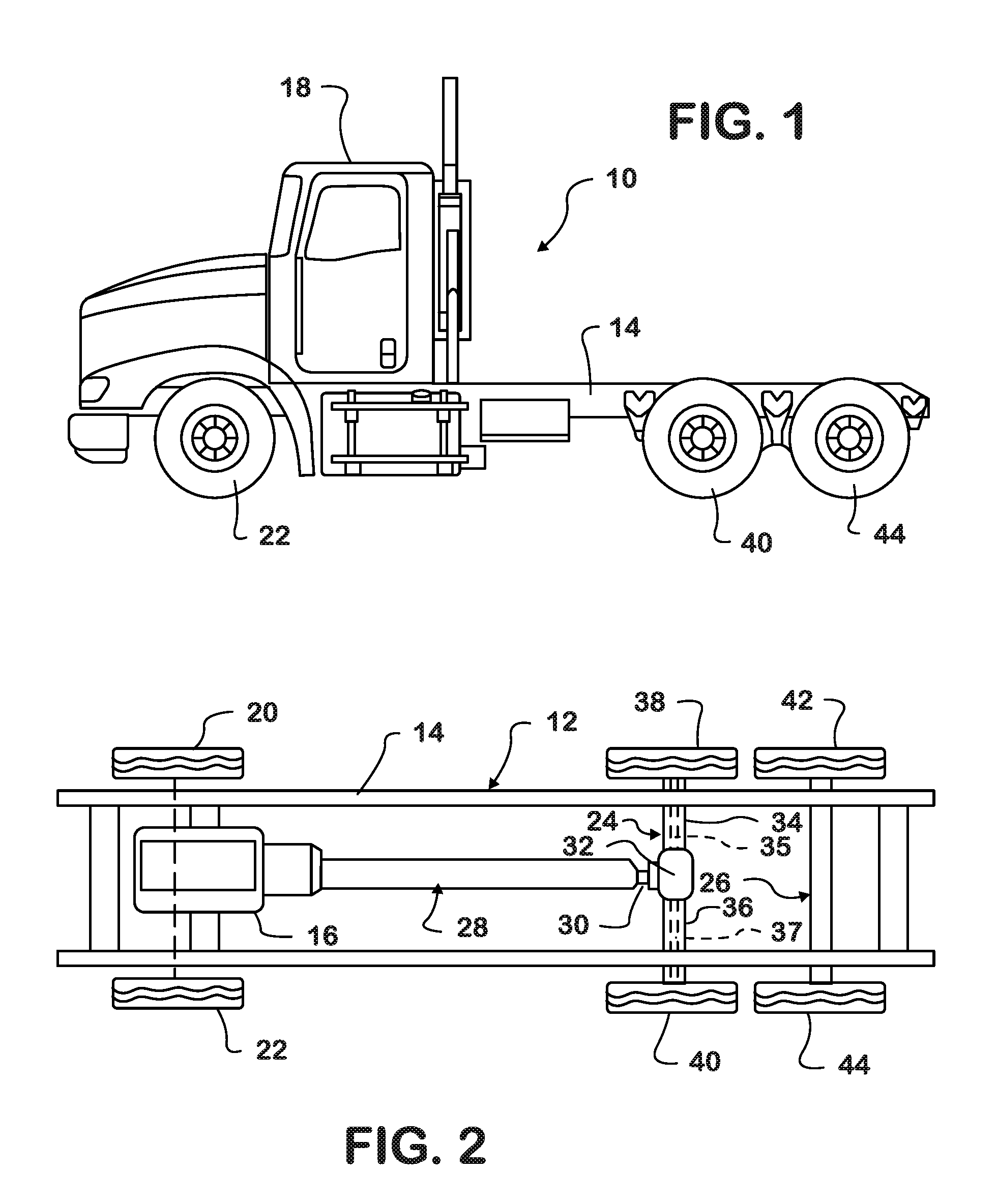
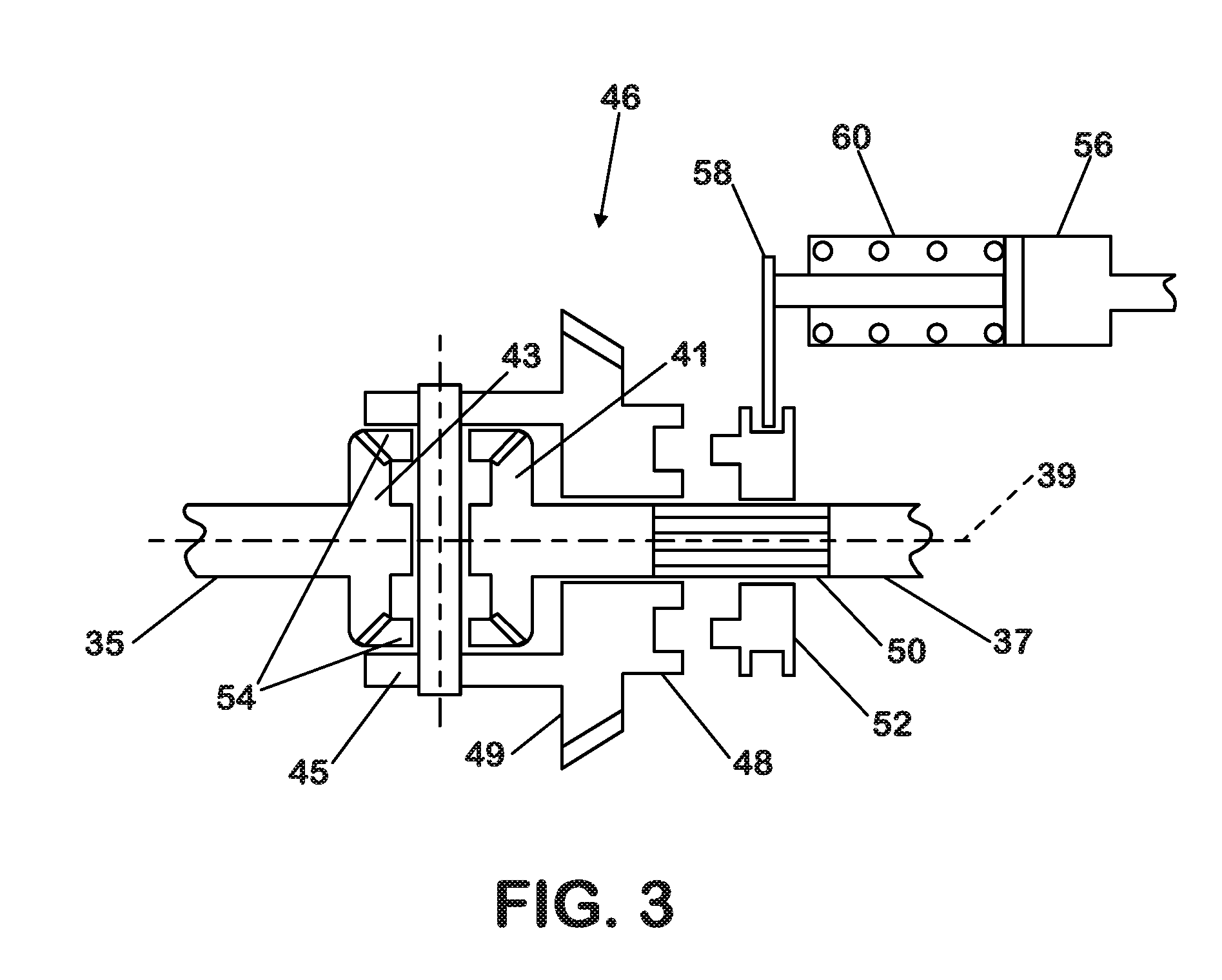
Automated differential lock
ActiveUS20160272177A1Improve vehicle handlingIncreasing longitudinalPropulsion unit safety devicesBraking systemsControl systemAutomotive engineering
A differential locking axle control system that can cause the axle to automatically lock and unlock at any vehicle speed, up to a predetermined maximum speed, or any wheel spin rate up to a predetermined maximum, when a vehicle is being steered either in a straight line or around a curve while taking traction and global positioning factors into account.
Owner:INT TRUCK INTPROP LLC
Method and system for generating steering commands to cancel out unwanted steering moments
ActiveUS20190084616A1Improve driving experienceImprove vehicle handlingSteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlSteering angle
A system and method for generating steering commands to cancel out unwanted steering moments is disclosed. The method includes determining, by a controller of a vehicle, an amount of suspension displacement that is caused as a result of driving the vehicle on an uneven road. The suspension displacement induces an unwanted steering moment. The method also includes determining a steering angle command based at least on the amount of suspension displacement. The method also includes performing the steering angle command. Performing the steering angle command cancels out the unwanted steering moment.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Vehicle steering system
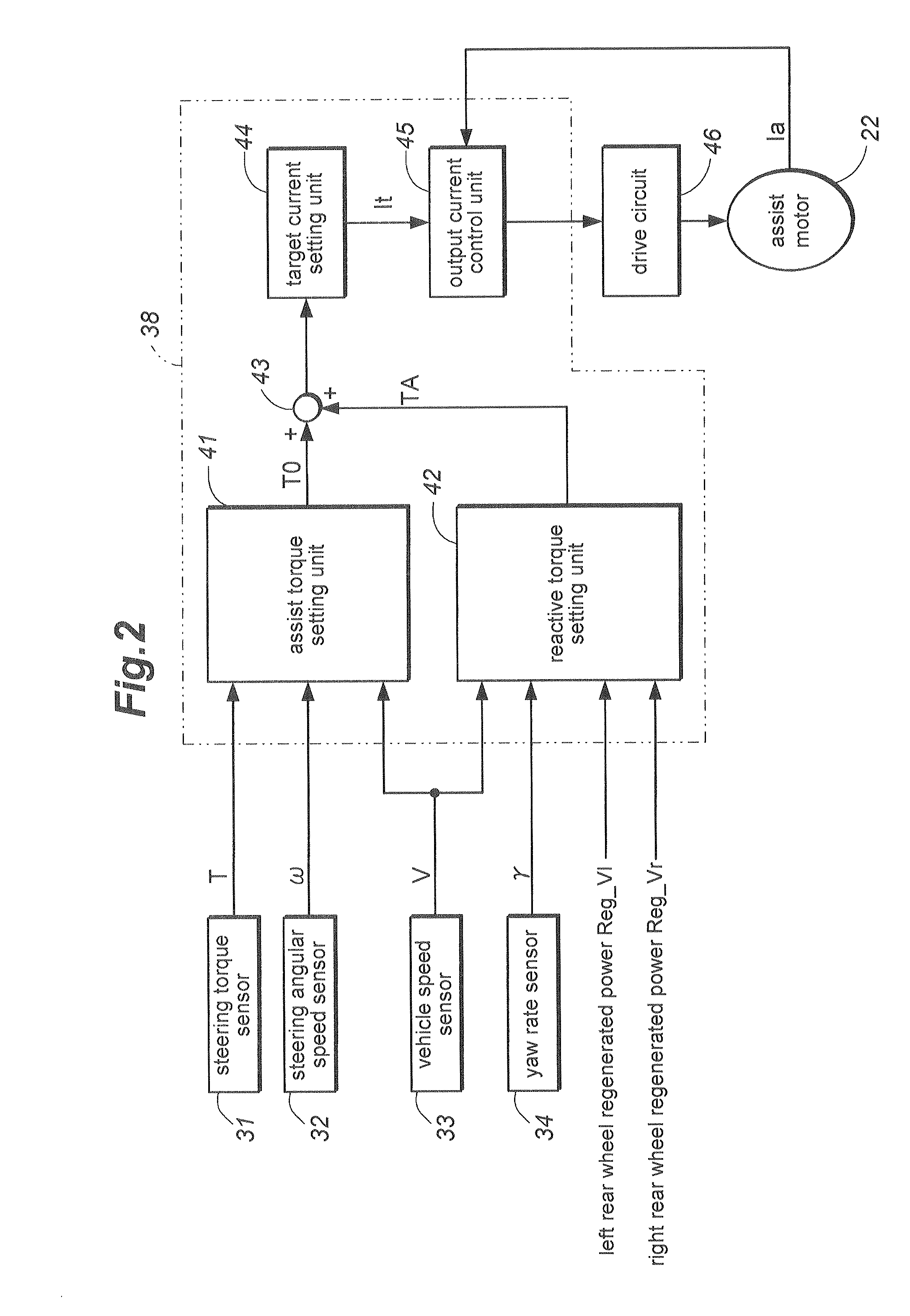
InactiveUS20100252355A1Improve vehicle handlingAvoid changeHybrid vehiclesSteering initiationsRegenerative brakePower steering
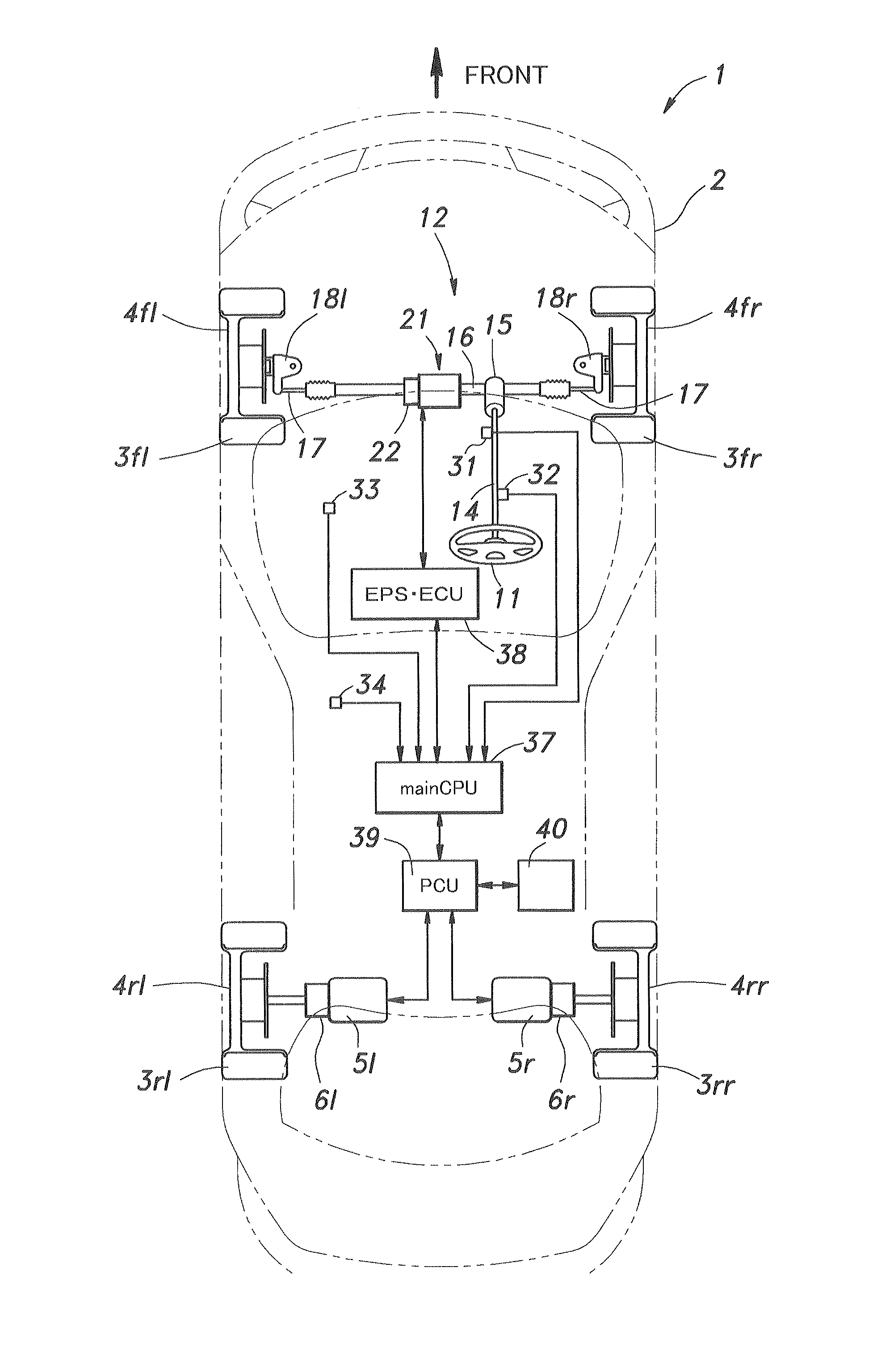
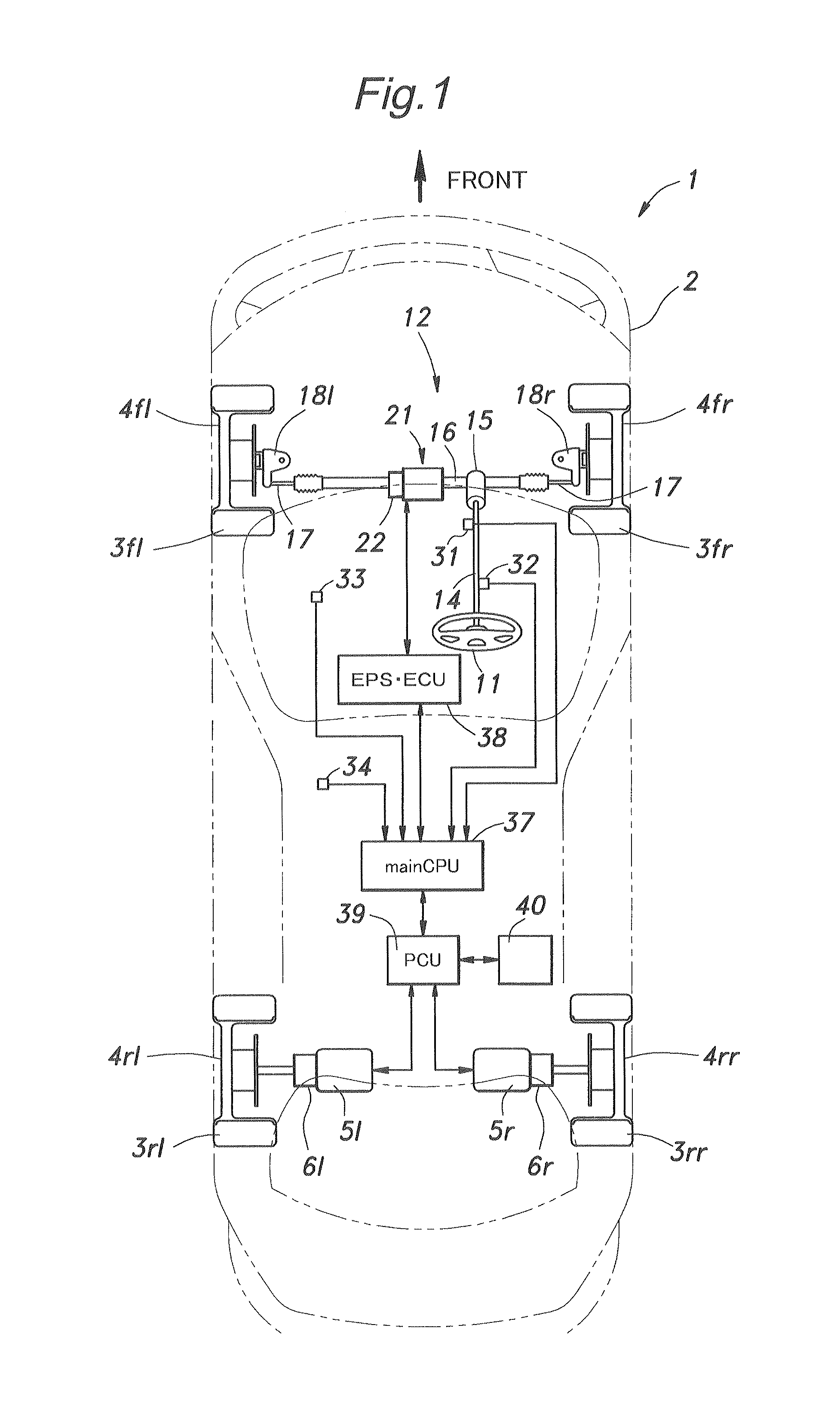
In a steering system for a vehicle incorporated with a rear drive electric motor (5) for driving a pair of rear wheels (3rl, 3rr) that can function as a regenerative brake for the rear wheels, a steering torque control unit (38) reduces a steering assist torque provided by the power steering assist unit (21) when the rear drive electric motor is providing a regenerative braking. When the rear wheels are braked by a regenerative braking action without substantially applying a brake to the front wheel, the vehicle may acquire a temporal oversteer tendency. However, by increasing the effort required to steer the front wheels, such a tendency can be canceled or compensated, and the vehicle operator is enabled to control the vehicle without experiencing any unfamiliar feeling or discomfort. The effort required to steer the front wheels can be increased by decreasing the assist steering torque or providing a reactive steering torque at such a time.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
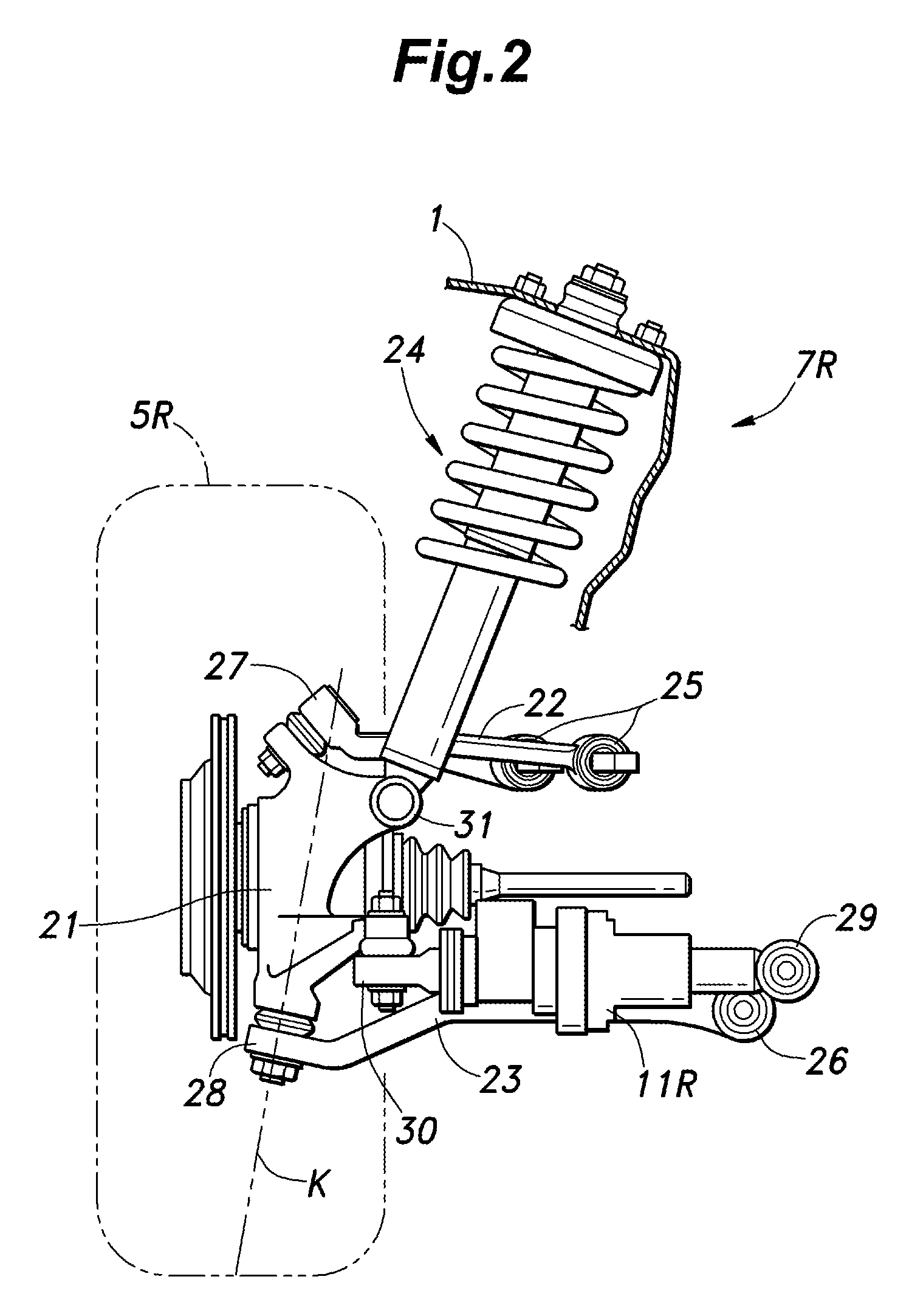
Lower arm mounting structure of vehicle suspension
InactiveUS7458594B2Displacement minimizationReducing and eliminating phenomenonUnderstructuresResilient suspensionsIn vehicleMechanical engineering
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Rear wheel toe angle control system for a vehicle
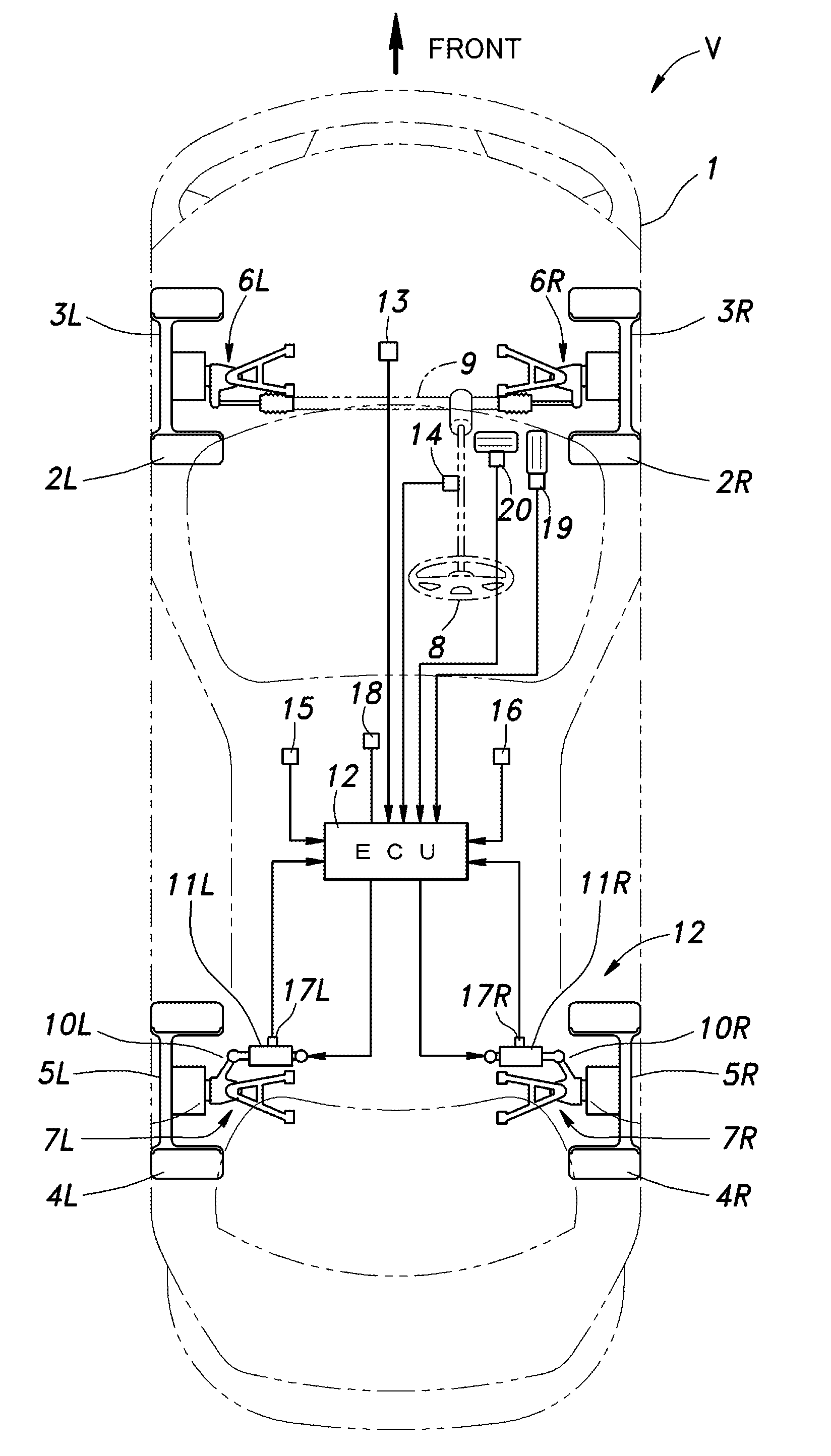
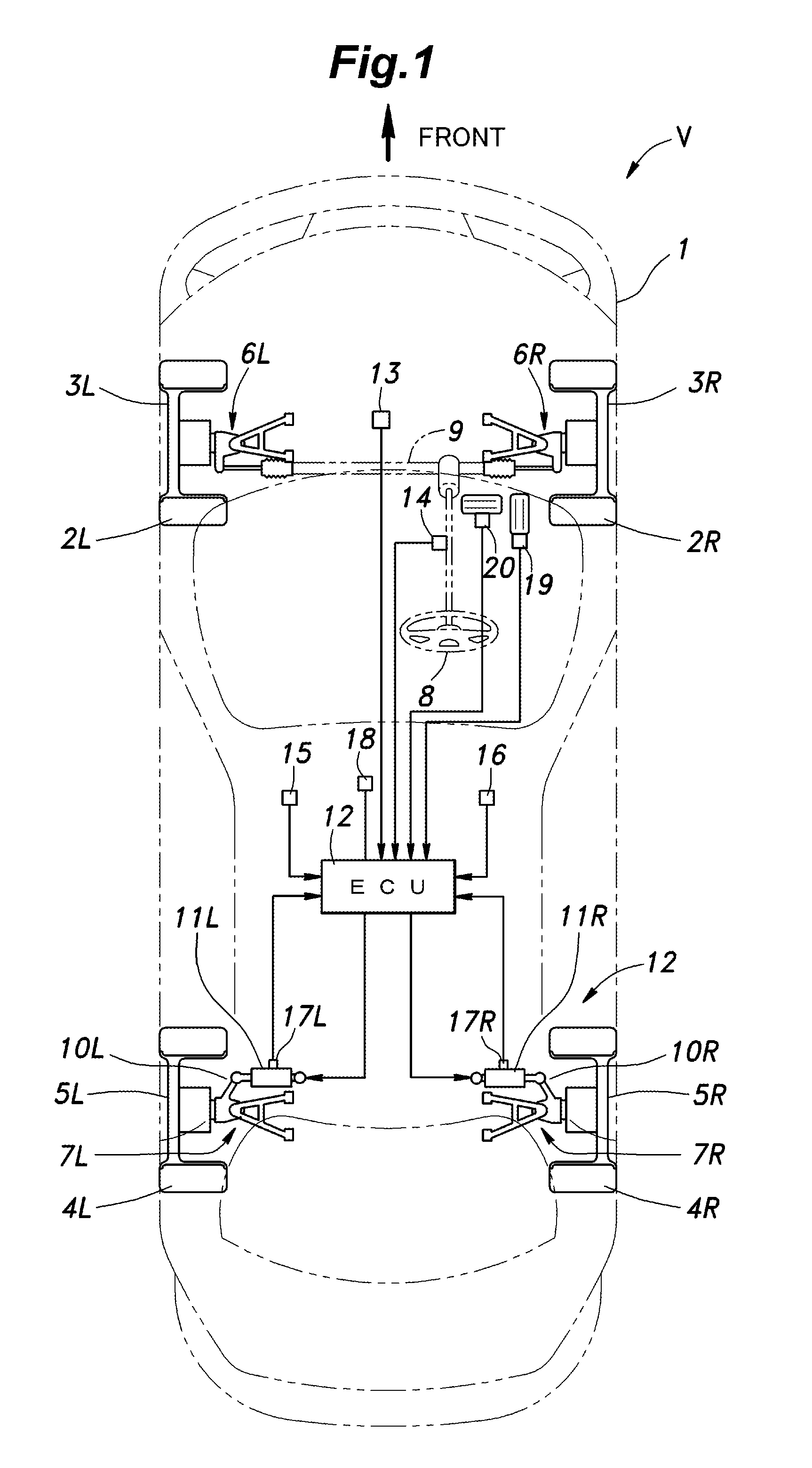
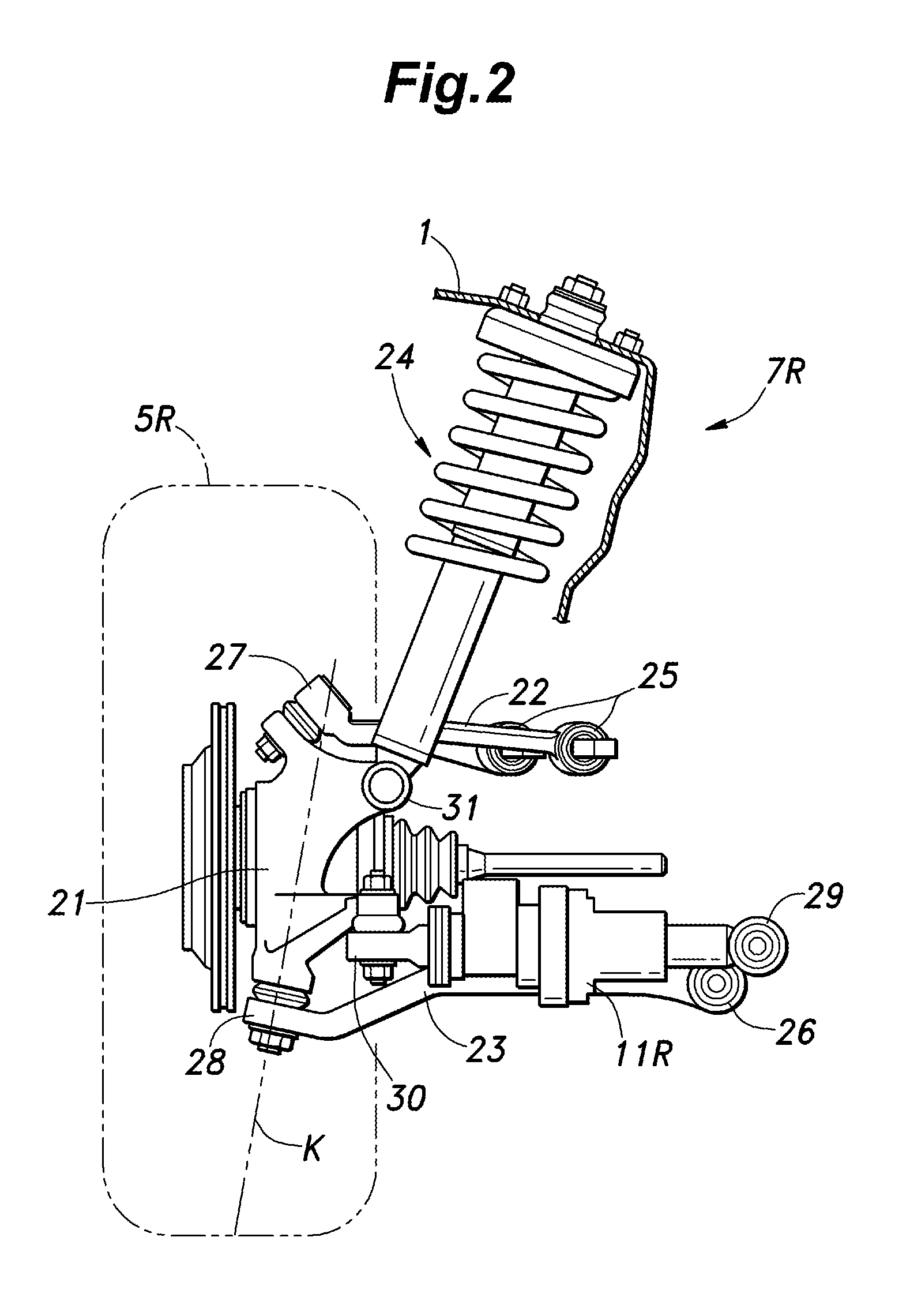
ActiveUS20120253608A1Improve vehicle handlingEasy to handleDigital data processing detailsSteering linkagesControl systemEngineering
In a rear wheel toe angle control system, the toe angle response properties of the right and left wheels are prevented from differing from each other depending on the operating condition of the vehicle, and the handling of the vehicle can be improved. The rear wheel toe angle control system (10) comprises a control command angle computing unit (83) for setting a target toe angel for each rear wheel (5) according to an operating condition of the vehicle (V), an angle-length conversion unit (87) for setting a target operating amount of each electric actuator (11) according to the target toe angle, a stroke sensor (17) for detecting an actual operating amount of each electric actuator (11), a motor position feed back duty computation unit (89) for setting a control value of each electric actuator (11) according to the difference between the actual operating amount and the target operating amount, and a compensating unit (90) for compensating the control value according to a value such as the lateral acceleration of the vehicle body (1) which is associated with the axial force of each electric actuator (11).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
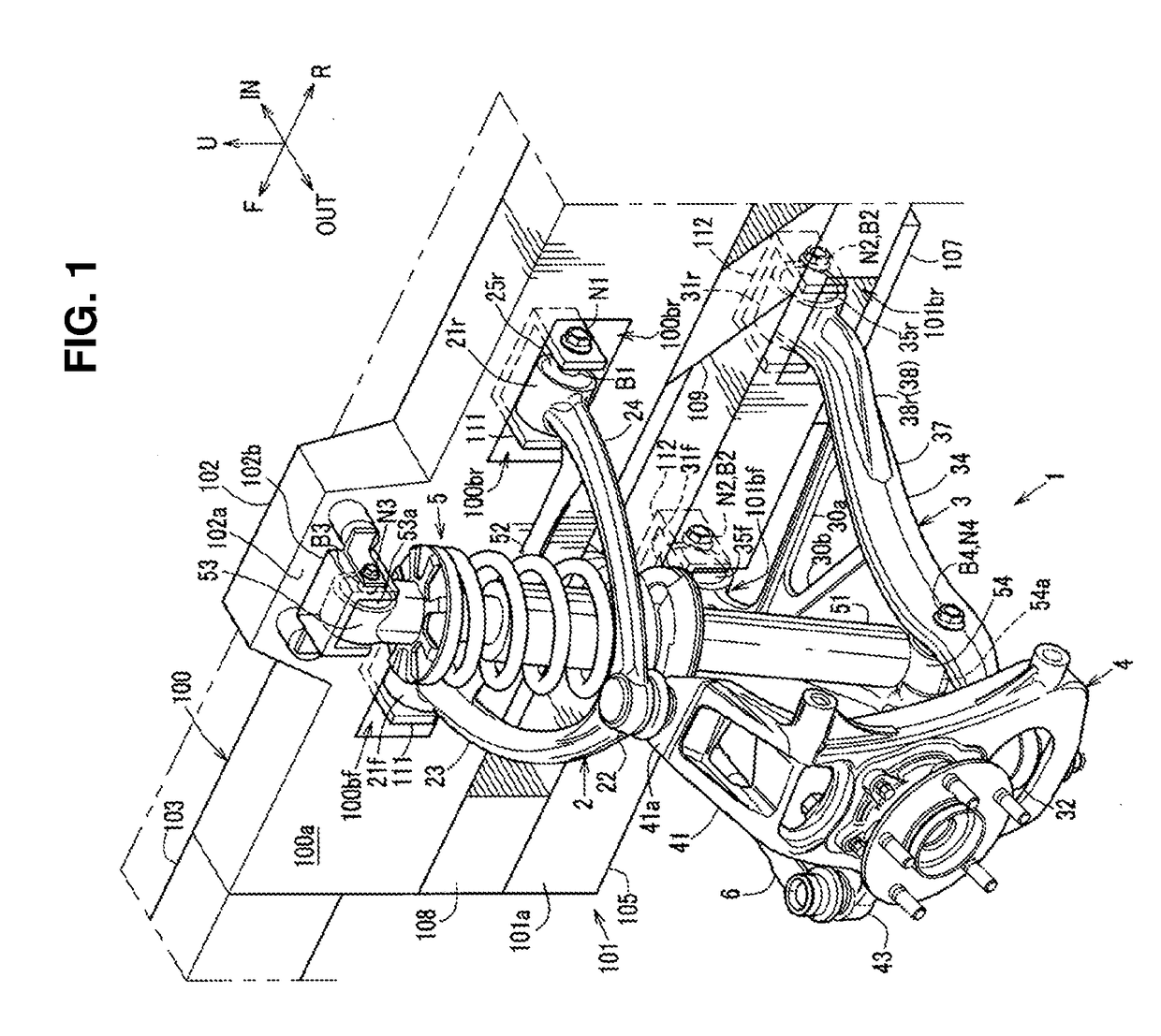
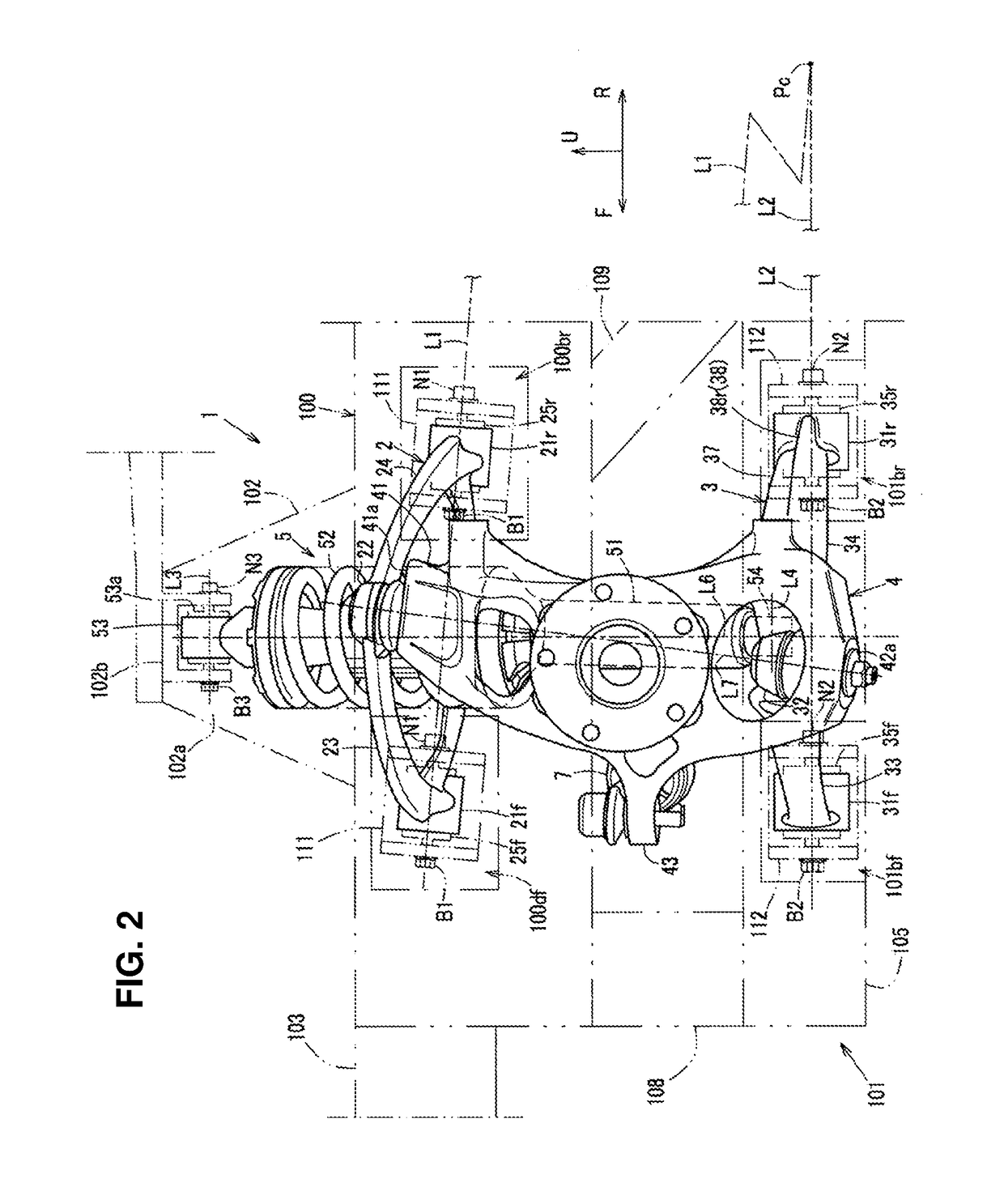
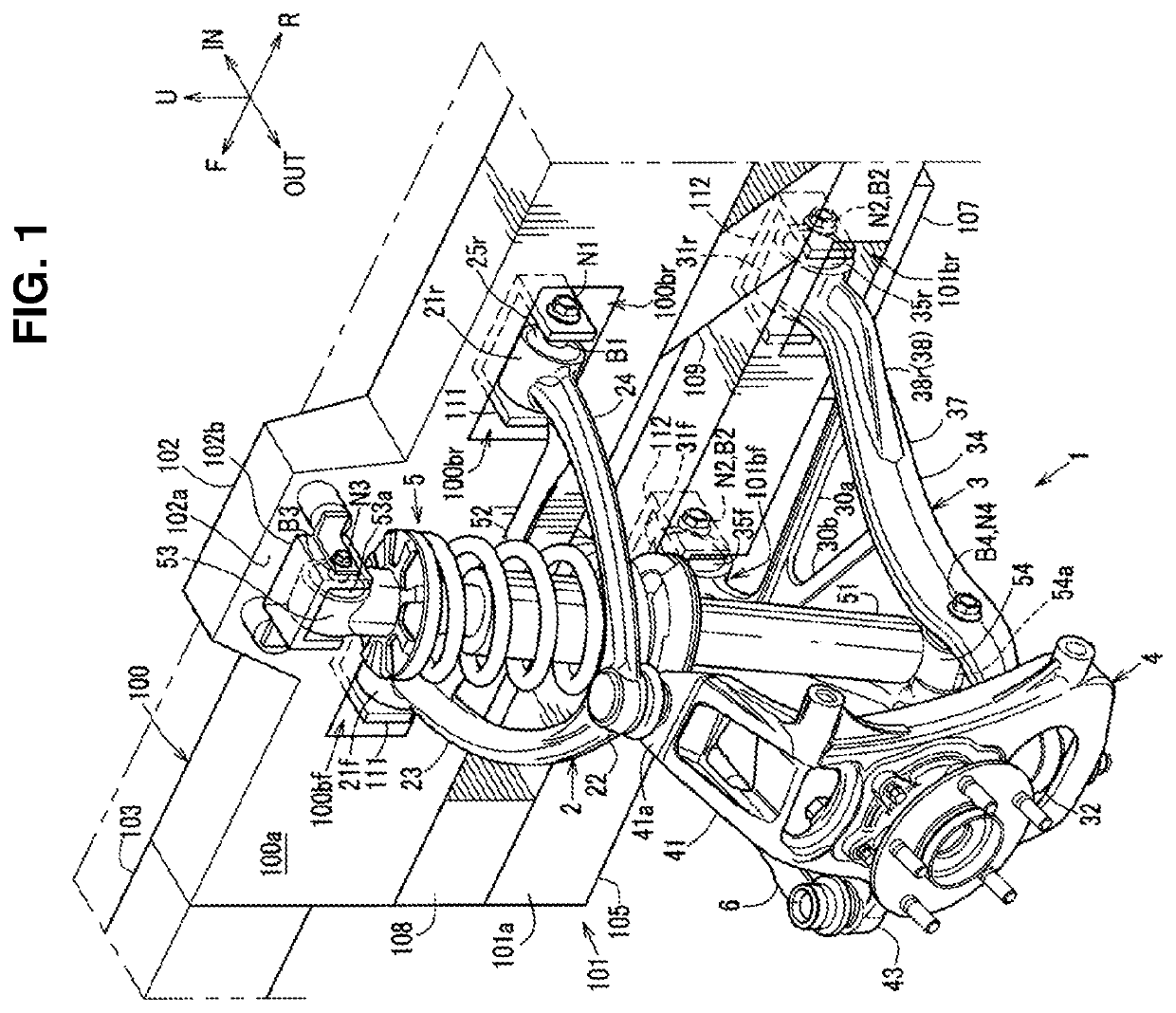
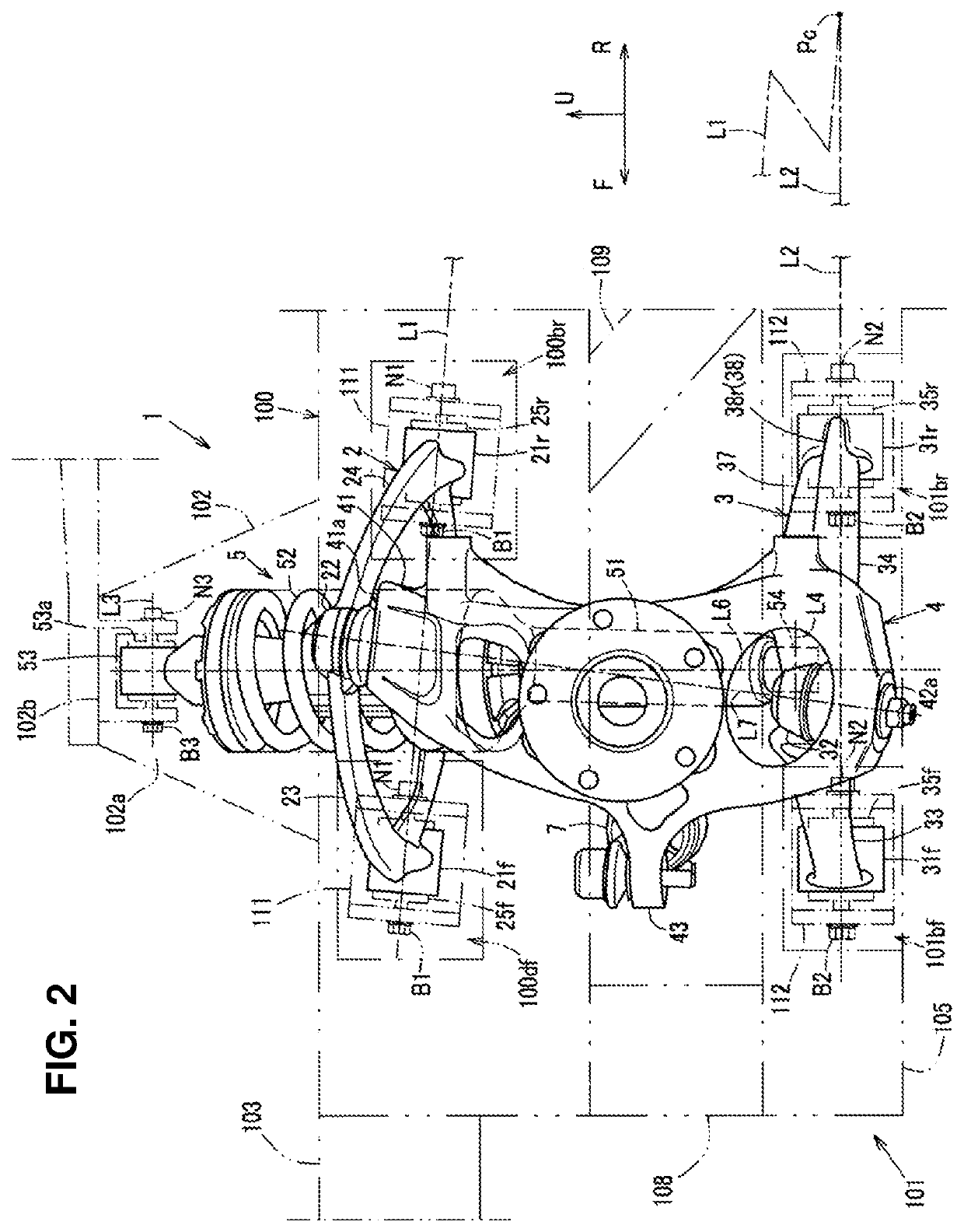
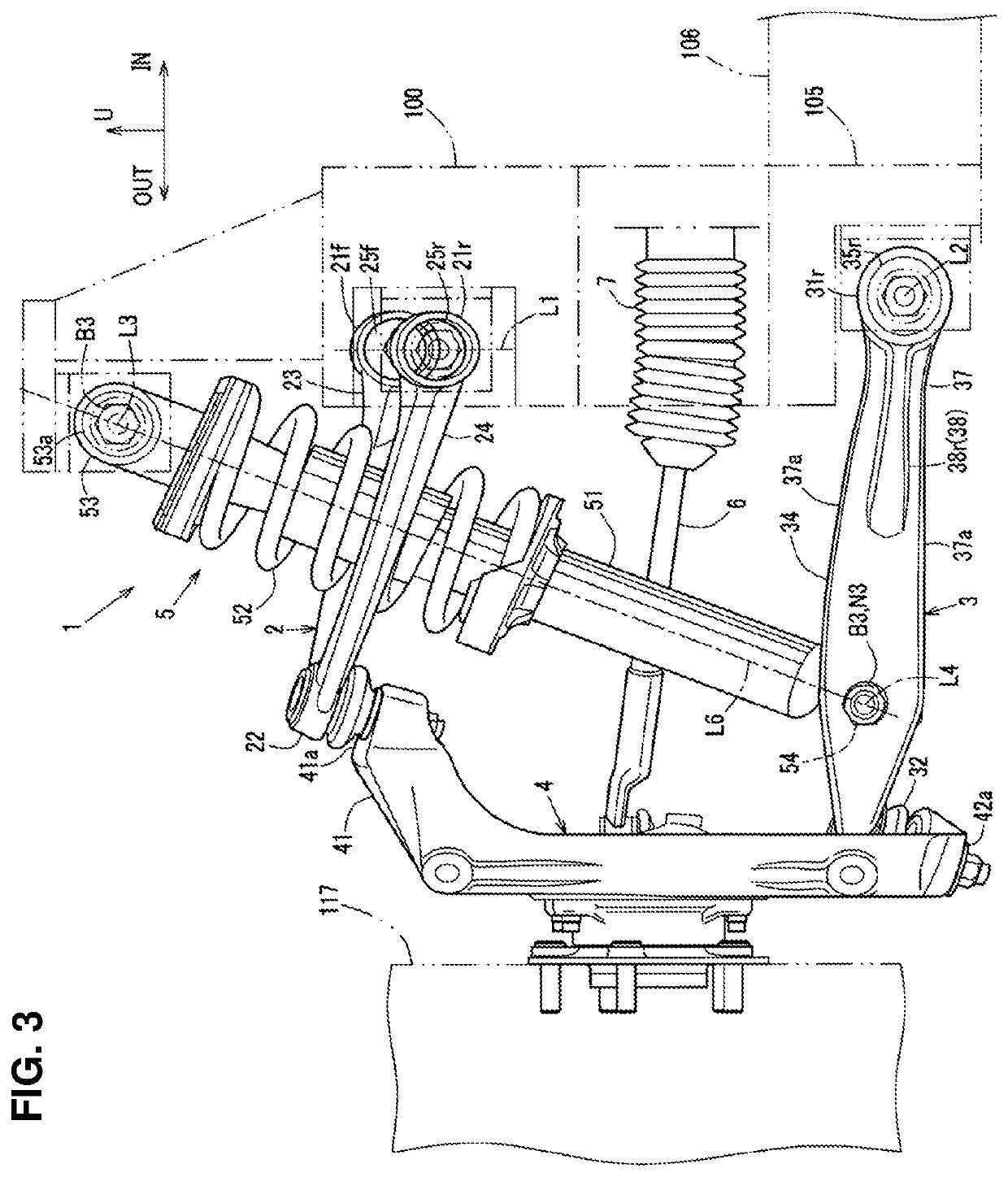
Front suspension structure of automotive vehicle
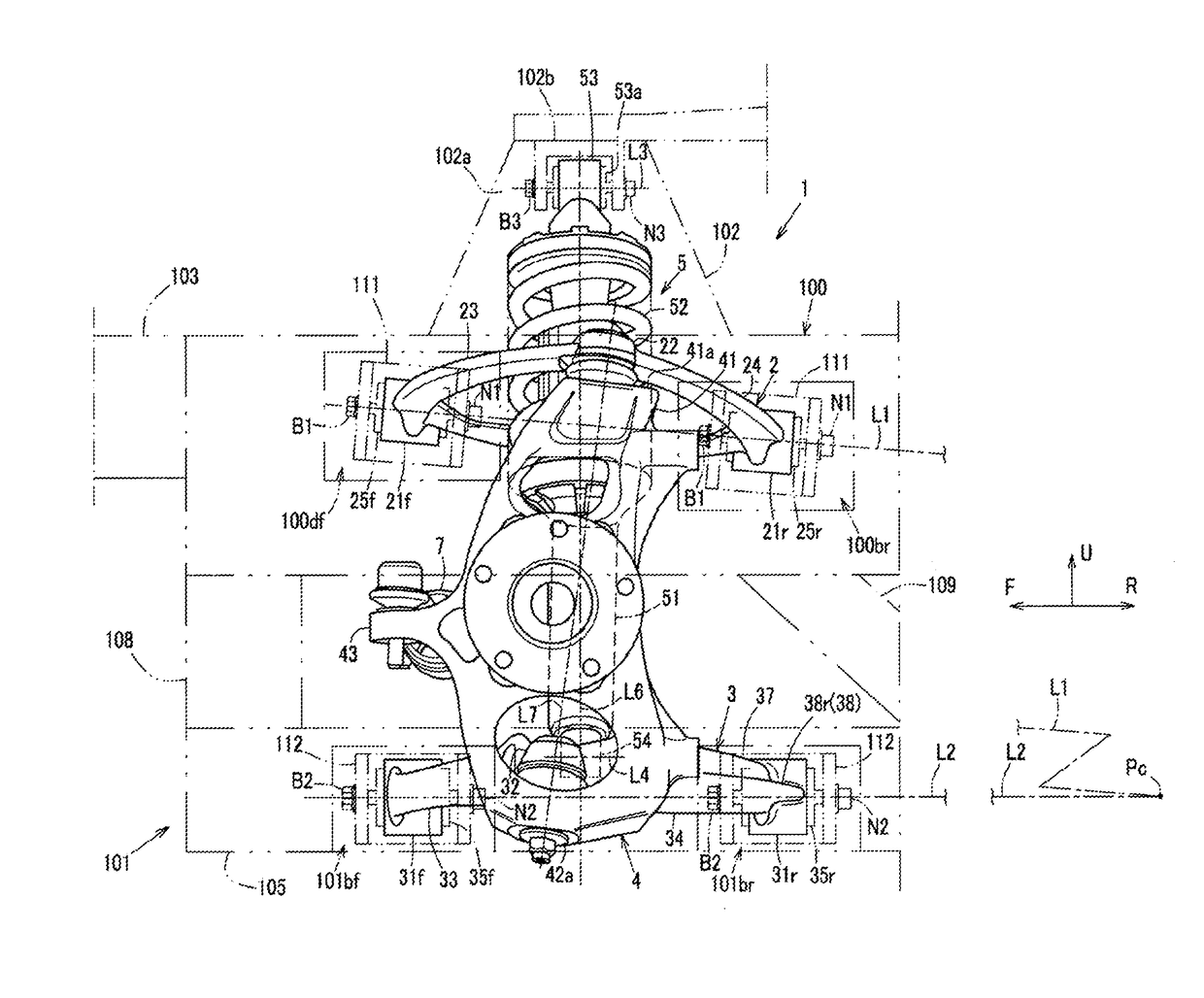
ActiveUS20180001723A1Improve vehicle handlingStable responseResilient suspensionsPivoted suspension armsRotational axisEngineering
In a double-wishbone type front suspension structure, upper and lower arms are pivotally supported at a vehicle-body side via front-and-rear pivotal portions, axial lines of resilient bushes of the front and rear pivotal portions of the arms extend in a longitudinal direction, a knuckle-side pivotal portion of the upper arm is positioned in back of a knuckle-side pivotal portion of the lower arm, and a lower end portion of a damper unit provided between a vehicle body and the lower arm is connected to the lower arm such that the damper unit is positioned perpendicularly to the axial lines of the lower arm in a side view and an upper end portion is pivotally supported at the vehicle body via a rotational axis extending in the longitudinal direction.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
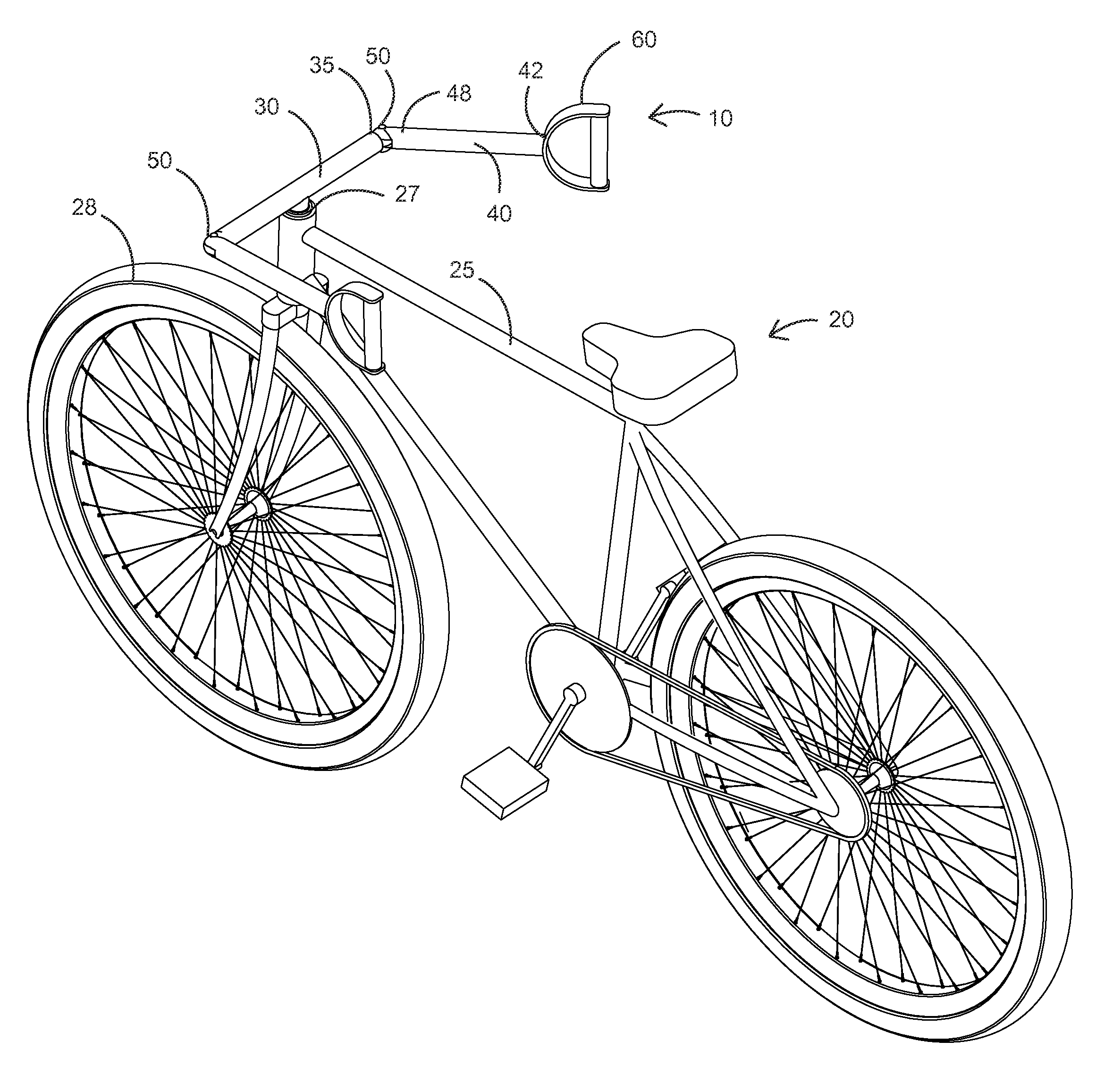
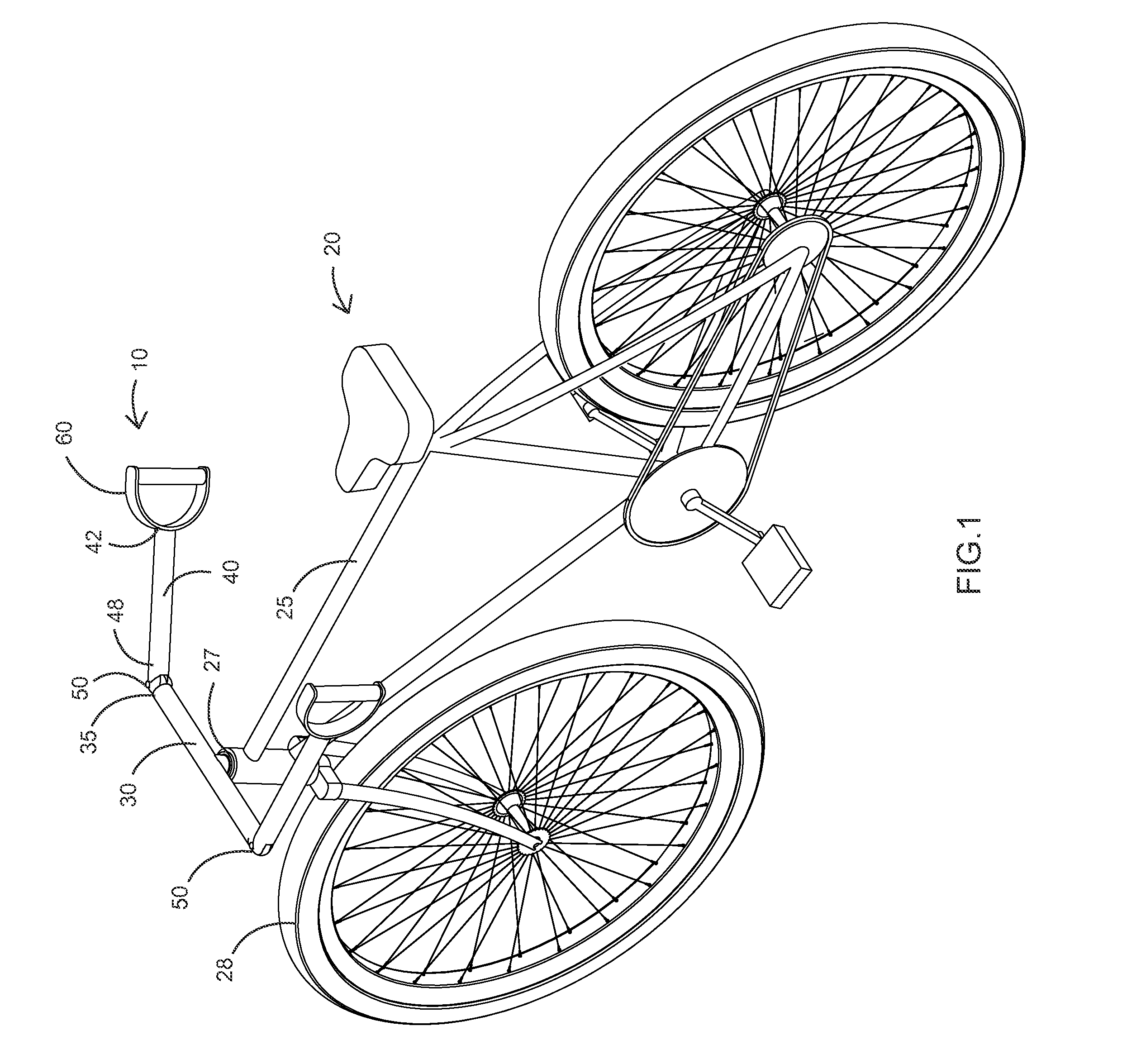
Handlebar arrangement
InactiveUS20130192411A1Reduce manufacturing costEasy to useMechanical apparatusSteering deviceEngineeringMechanical engineering
A handlebar arrangement for a bicycle or the like includes a handlebar having two opposing sides and adapted to turn a front wheel at a first pivot. Two tie rods are each pivotally attached at a forward end thereof proximate one of the ends of the handlebar at one of a pair of second pivots. Each tie rod terminates at a handle. In different embodiments, each handle is pivotally attached to the rearward end of one of the tie rods, or the handle of each tie rod includes a rotational bearing where connected to the tie rod, or each tie rod is pivoted to allow substantially 180 degrees of horizontal pivoting of the tie rod with the handlebar, and substantially 90 degrees of vertical upward pivoting of the tie rod with the handlebar, or each tie rod may be mutually pivotally connected with a connecting rod.
Owner:WONG JON
Rear wheel toe angle control system for a vehicle
ActiveUS8755972B2Improve vehicle handlingEasy to handleDigital data processing detailsAutomatic steering controlControl systemAxial force
In a rear wheel toe angle control system, the toe angle response properties of the right and left wheels are prevented from differing from each other depending on the operating condition of the vehicle, and the handling of the vehicle can be improved. The rear wheel toe angle control system (10) comprises a control command angle computing unit (83) for setting a target toe angel for each rear wheel (5) according to an operating condition of the vehicle (V), an angle-length conversion unit (87) for setting a target operating amount of each electric actuator (11) according to the target toe angle, a stroke sensor (17) for detecting an actual operating amount of each electric actuator (11), a motor position feed back duty computation unit (89) for setting a control value of each electric actuator (11) according to the difference between the actual operating amount and the target operating amount, and a compensating unit (90) for compensating the control value according to a value such as the lateral acceleration of the vehicle body (1) which is associated with the axial force of each electric actuator (11).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Front suspension structure of automotive vehicle
ActiveUS10556474B2Improve vehicle handlingStable responseResilient suspensionsPivoted suspension armsRotational axisSuspension (vehicle)
In a double-wishbone type front suspension structure, upper and lower arms are pivotally supported at a vehicle-body side via front-and-rear pivotal portions, axial lines of resilient bushes of the front and rear pivotal portions of the arms extend in a longitudinal direction, a knuckle-side pivotal portion of the upper arm is positioned in back of a knuckle-side pivotal portion of the lower arm, and a lower end portion of a damper unit provided between a vehicle body and the lower arm is connected to the lower arm such that the damper unit is positioned perpendicularly to the axial lines of the lower arm in a side view and an upper end portion is pivotally supported at the vehicle body via a rotational axis extending in the longitudinal direction.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Gearbox Mounting System
ActiveUS20190128398A1Easy to adaptImprove economyToothed gearingsGearing controlStructural loadEngineering
A combination of an engine, a gearbox clutch housing and a mounting system for mounting the combination to the structural load-bearing components of a vehicle, comprising an engine having a first contact surface; a gearbox clutch housing having a second contact surface, the first contact surface of the engine and the second contact surface of the gearbox clutch housing each being joined to the other by mechanical fastening means; and a first hanger, where the latter comprises a rigid plate positioned between the first contact surface of the engine and the second contact surface of the gearbox clutch housing, with the first hanger being securely fastened between the engine and the gearbox clutch housing. The first hanger has first and second opposed load-transferring surfaces of closed perimeter, with the first of the load-transferring surfaces being in pressing contact with the first contact surface of the engine and the second of the load-transferring surfaces being in pressing contact with the second contact surface of the gearbox clutch housing. The first hanger includes one or more load-supporting members extending beyond the perimeter of the opposed load-transferring surfaces; and the one or more load-supporting members include plural spaced-apart fastening elements adapted for coupling to one or more select structural load-bearing components of a vehicle.
Owner:AUTO IP LLC
Automated differential lock
ActiveUS9821780B2Improve vehicle handlingGreat tractionPropulsion unit safety devicesBraking systemsControl systemMechanical engineering
A differential locking axle control system that can cause the axle to automatically lock and unlock at any vehicle speed, up to a predetermined maximum speed, or any wheel spin rate up to a predetermined maximum, when a vehicle is being steered either in a straight line or around a curve while taking traction and global positioning factors into account.
Owner:INT TRUCK INTPROP LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com