A low carbon number light color sulfur-free chlorine-free ash-free polymerization inhibitor and its application
A technology of polymerization inhibitor and carbon number, which is applied in the field of low-carbon number, light-colored, sulfur-free, chlorine-free, ash-free polymerization inhibitors, can solve the problems of few reports, achieve the effect of reducing scaling and coking substances, and protecting human health
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0058] The present invention does not specifically limit the preparation method of the polymerization inhibitor, which can be prepared by a mixing method.
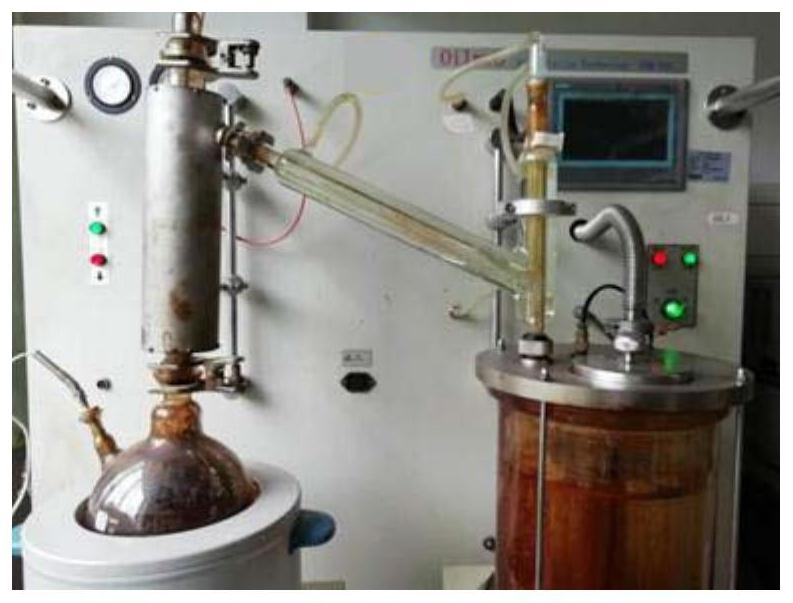
[0059] The second aspect of the present invention provides an application of the above-mentioned low-carbon number, light-colored, sulfur-free, chlorine-free, and ashless polymerization inhibitor for the high-temperature distillation and separation process of light mixed oil.
[0060] The light mixed oil of the present invention is a mixture of gasoline and diesel. The high-temperature distillation of the present invention is the distillation and separation of light mixed oil under the condition of normal pressure and ≤250°C.
Embodiment 1
[0064] This example provides a polymerization inhibitor. The preparation raw materials of the polymerization inhibitor include, in parts by weight, 15 parts of diphenylamine derivatives, 30 parts of p-phenylenediamine derivatives, 15 parts of succinimide and 30 parts of carbon Nine aromatic hydrocarbons; the diphenylamine derivative is 4-hydroxydiphenylamine, and the succinimide is N-methylsuccinimide;
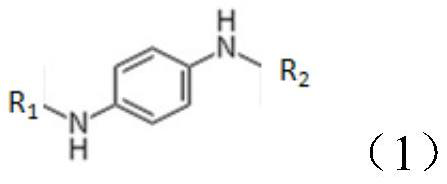
[0065] The structural formula of the p-phenylenediamine derivative is shown in formula (1):
[0066]
[0067] R 1 , R 2 Both are sec-butyl groups.
[0068] The N-methylsuccinimide was purchased from Nanjing Kangmanlin Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.
[0069] This example also provides the above-mentioned preparation method of the polymerization inhibitor, which includes the following steps: mixing the preparation raw materials of the polymerization inhibitor to obtain the polymerization inhibitor.
Embodiment 2
[0071] This example provides a polymerization inhibitor. The preparation raw materials of the polymerization inhibitor include, in parts by weight, 25 parts of diphenylamine derivatives, 40 parts of p-phenylenediamine derivatives, 20 parts of succinimide and 35 parts of carbon Nine aromatic hydrocarbons; the diphenylamine derivative is 4-hydroxydiphenylamine, and the succinimide is N-ethylsuccinimide;
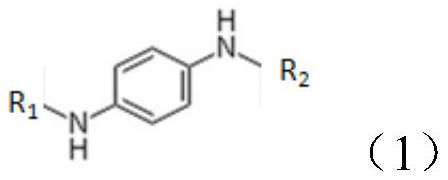
[0072] The structural formula of the p-phenylenediamine derivative is shown in formula (1):
[0073]
[0074] R 1 , R 2 Both are sec-butyl groups.
[0075] The N-ethylsuccinimide was purchased from Nanjing Kangmanlin Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.
[0076] This example also provides the above-mentioned preparation method of the polymerization inhibitor, which includes the following steps: mixing the preparation raw materials of the polymerization inhibitor to obtain the polymerization inhibitor.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com