Autonomous avoidance maneuvering method for multiple interceptors by spacecraft based on reinforcement learning
A technology of reinforcement learning and spacecraft, applied in the field of anti-interception, can solve the problem of low success rate of evasion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
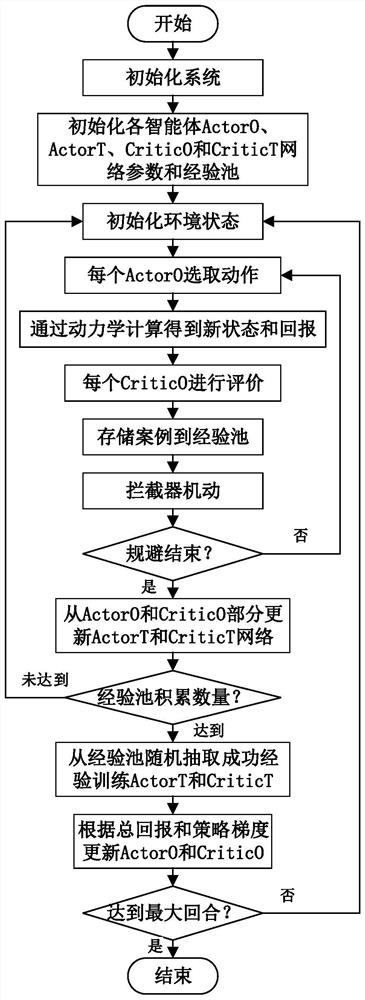
[0020] Specific implementation mode 1: A method for self-avoiding maneuvers of spacecraft to multiple interceptors based on reinforcement learning described in this implementation mode, the method is specifically implemented through the following steps:
[0021] Step 1: Establish the space dynamics models of the spacecraft and the interceptor respectively;
[0022] Step 2: Based on the space dynamics model of the spacecraft and interceptor established in Step 1, establish a true-scale guidance model for multiple interceptors;
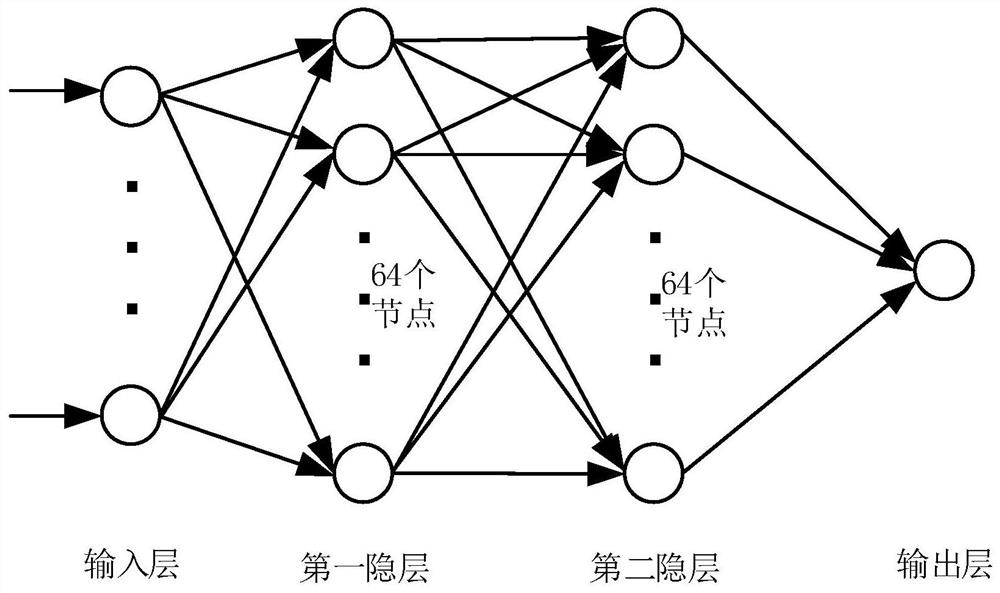
[0023] Step 3: Take each engine of the spacecraft as an agent to establish a decision-making model for spacecraft evasion maneuvers;
[0024] Step 4: Establish a multi-agent autonomous decision-making training system based on reinforcement learning theory;
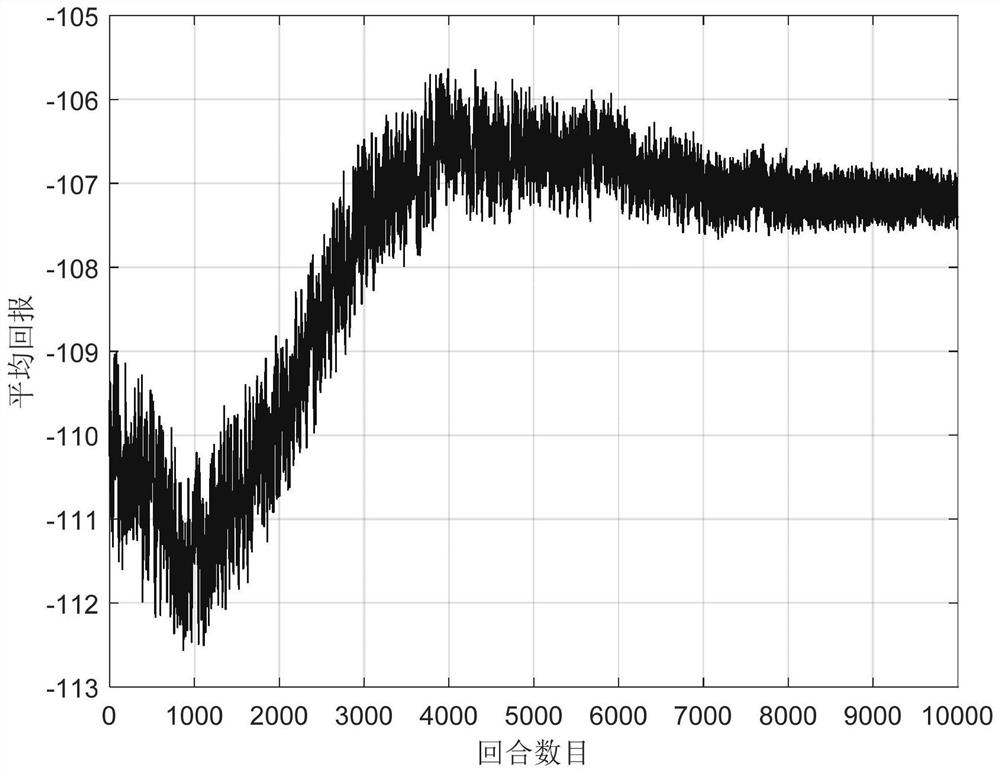
[0025] Step 5: Apply the model established in step 1, step 2 and step 3 to the system of step 4, and train the spacecraft evasive maneuver decision-making model offline;
[0026] Step 6: Apply the...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: said step one establishes the space dynamics model of spacecraft and interceptor respectively, and its specific process is:
[0029] In the geocentric inertial coordinate system, the space dynamics model of the spacecraft is:
[0030]
[0031] in, is the space position vector of the spacecraft, r M for Corresponding scalar, m M is the instantaneous mass of the spacecraft, T M is the total thrust of the spacecraft engine, is the unit vector of the thrust direction of the spacecraft engine, μ is the gravitational constant of the earth, and the value is 3.986×10 5 km 3 / s 2 ; for The second derivative of , Be the perturbation acceleration vector, set as a constant value in the present invention;
[0032] The mass change rate of the spacecraft is:
[0033]
[0034] in, is the rate of change of spacecraft mass, I sp,M is the specific impulse of the space...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0041] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment two is that: in the step two, according to the space dynamics model of the spacecraft and the interceptor established in the step one, a multi-interceptor true-scale guidance model is established, which The specific process is:
[0042] According to the space dynamics model of the spacecraft and the interceptor established in step 1, the relative motion model of the spacecraft and the interceptor is obtained as:
[0043]
[0044] in, is the combined thrust vector of the spacecraft engine, is the combined thrust vector of the interceptor engine;
[0045] In order to simplify the calculation, only the maximum sight angle and saturated maneuvering overload are constrained, and the noise and other disturbance problems are not considered. Decompose equation (5) along the direction of the projectile line of sight and the direction perpendicular to the direction of projectile line...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com