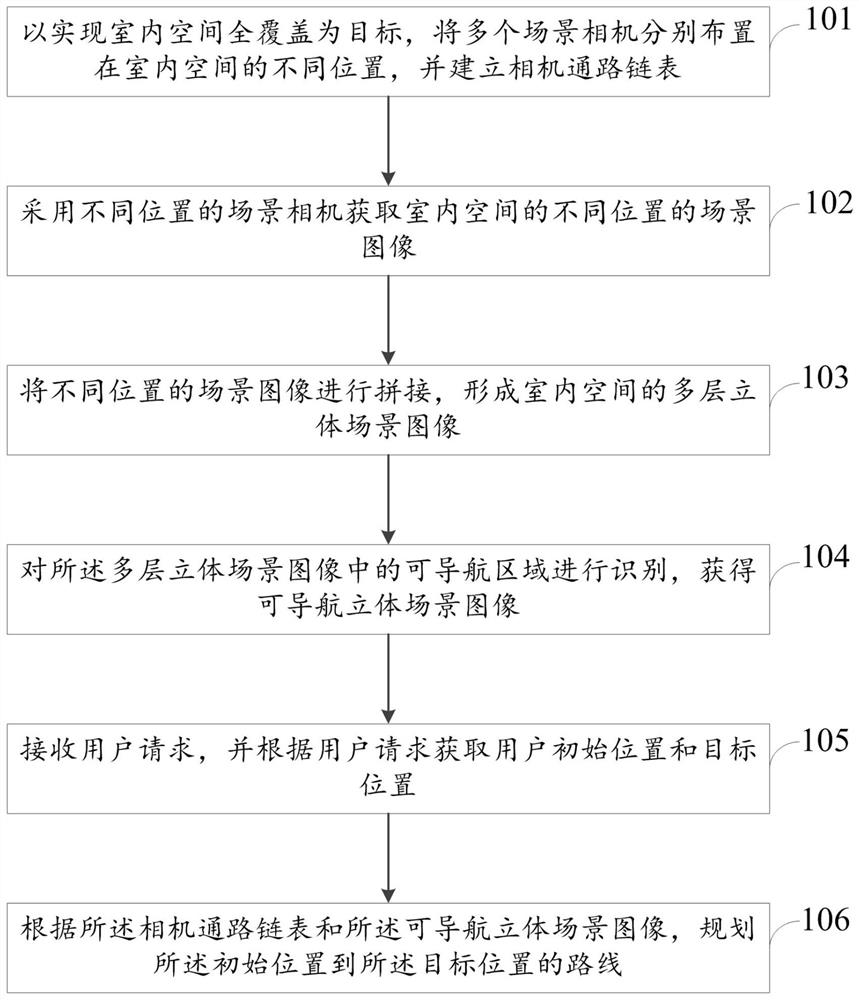
Indoor positioning and navigation method and system based on computer vision
A computer vision and indoor positioning technology, applied in the field of indoor navigation, can solve problems such as inability to accurately distinguish between different floors, satellite signal blocking, and inability to achieve positioning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] The present invention takes the navigation object as a car, and describes the navigation method when the navigation object of the present invention is a robot. Specifically include the following steps:
[0090] Step 1: First install the camera in the indoor area where navigation is required, and the camera should be installed as high as possible. The installation of the camera can be mixed with the dome camera and the bolt camera to ensure that the field of view of all cameras can cover the navigation area, and there is a certain overlapping coverage area between two cameras. When an area is full of guns, directional positioning and navigation is used; when an area is mixed with guns and ball machines, omnidirectional positioning and navigation is used. All cameras are numbered.
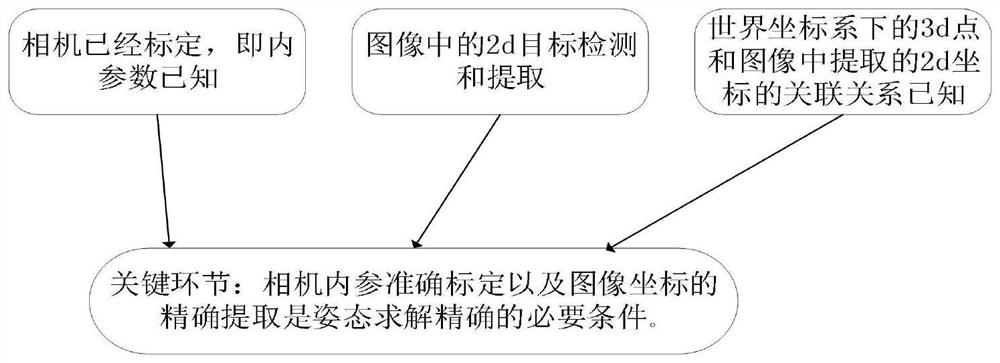
[0091] Step 2: After installing all cameras, use Zhang Zhengyou calibration method to calibrate the cameras. Obtain the internal and external parameters of the camera, and correct the image...
Embodiment 2
[0128] Embodiment 2: Orientation positioning navigation
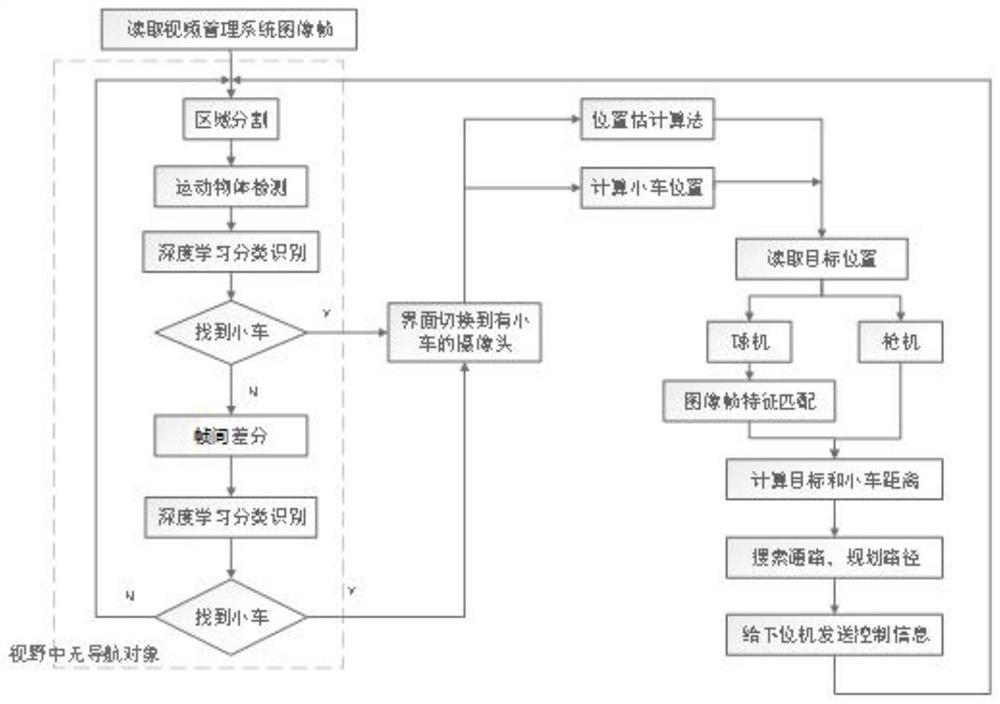
[0129] Orientation and positioning navigation, its mode is mainly to install the camera with a fixed angle of view such as Image 6 , the viewing angles of different cameras are intersected or there are connection points where the two viewing angles do not intersect, such as Figure 7 The interior of the room: from the perspective of the corridor and the perspective of the door, the door is a connection point. V1-V9 indicates the number of the camera, the field of view of the camera can cover the area that may be navigated indoors, and D1-D9 indicates the connection point between the cameras. In this mode, builds such as Figure 8 The linked list of cameras. All cameras are fixed, by retrieving the navigation object in all camera views, and then positioning.
[0130] like Figure 5 It is a flow chart of the navigation method based on orientation and positioning provided by the embodiment of the present application....
Embodiment 3
[0142] Embodiment 3: Omni-directional positioning and navigation
[0143] The difference between omnidirectional positioning navigation and directional positioning navigation is that: the angle of view of the omnidirectional positioning navigation camera is not fixed, but can be controlled to rotate; the angle of view of the directional positioning navigation camera cannot be rotated. Omni-directional positioning and directional positioning can complement each other. Under omni-directional positioning navigation, when the camera detects the navigation object, it will adjust the camera's field of view, that is, it will rotate with the movement of the navigation object, so that the navigation object is always in the best position in the field of view. For example in Figure 4 In the corridor, install a dome camera at the center of the corridor, the schematic diagram is as follows Figure 14 ;When the car appears at the end of the corridor, through the detection of the navigati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com