Blast furnace-rotary kiln co-processing method for dust containing zinc and iron
A collaborative processing and rotary kiln technology, applied in the field of iron and steel metallurgy and environmental protection, can solve the problems of low amount of blast furnace gas and mud, adverse effects of material application, etc., and achieve the effect of efficient utilization and recycling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
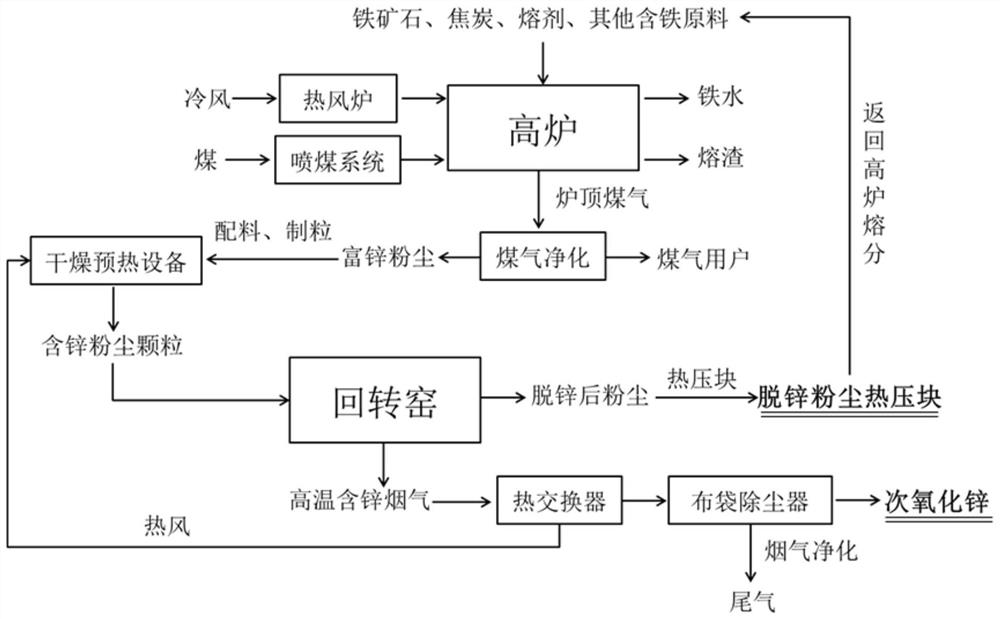
[0050] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a method for co-processing blast furnace-rotary kiln dust containing zinc and iron, comprising the following steps:
[0051] S1, using the zinc-containing and iron-containing dust produced by the blast furnace as the main raw material, then adding the flux quicklime and reducing agent coke powder to fully stir to obtain a mixed material; in the zinc-containing and iron-containing dust of the blast furnace, the zinc content is 9.0%; among them, according to Blast furnace zinc and iron dust: quicklime: coke powder: water are batched in a mass ratio of 70:15:15:12. In order to ensure the full reduction of zinc oxide in the dust, it should be ensured that the C / O in the mixed material should be kept at 1.1-1.3.
[0052] S2. Since the particle size of iron and steel zinc-containing iron dust is generally 2-50 μm, and the particle size diameter is relatively small, it is easy to cause ring formation in the rotary kiln. Therefore,...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a method for co-processing blast furnace-rotary kiln dust containing zinc and iron, comprising the following steps:
[0060] S1, using zinc and iron dust produced by blast furnace as the main raw material, then adding electric furnace dust, flux quicklime and reducing agent coke powder to fully stir to obtain a mixed material; among them, according to blast furnace zinc and iron dust: electric furnace dust: quicklime: Coke powder: water is batched in a mass ratio of 50:25:15:10:12.
[0061] S2, making the mixed material into zinc-containing iron dust particles with a particle size diameter of 3-5 mm.
[0062] S3. Drying and preheating the zinc-iron dust particles prepared in step S2 to obtain dried zinc-iron dust particles; the drying and preheating time is 40 minutes.
[0063] S4, sending the dried zinc-iron dust particles prepared in step S3 into a rotary kiln through a feeding device, and performing high-temperature red...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Embodiment 3 of the present invention provides a method for co-processing blast furnace-rotary kiln dust containing zinc and iron, comprising the following steps:
[0069] S1, using the zinc and iron dust produced by the blast furnace as the main raw material, then adding electric furnace dust, iron oxide scale, flux quicklime and reducing agent coke powder to fully stir to obtain the mixed material; among them, according to blast furnace zinc and iron dust: electric furnace dust : iron oxide scale: quicklime: coke powder: water is the mass ratio of 30:25:20:15:10:12 for batching.
[0070] S2, making the mixed material into zinc-containing iron dust particles with a particle size diameter of 3-5 mm.
[0071] S3. Drying and preheating the zinc-iron dust particles prepared in step S2 to obtain dried zinc-iron dust particles; the drying and preheating time is 40 minutes.
[0072] S4, sending the dried zinc-iron dust particles prepared in step S3 into a rotary kiln through...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com