Fusion multiply-add operator with correctly rounded mixed precision floating-point number
An arithmetic unit and floating-point number technology, which is applied in the direction of instruments, calculations, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems that do not mention the specific size of the adder
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
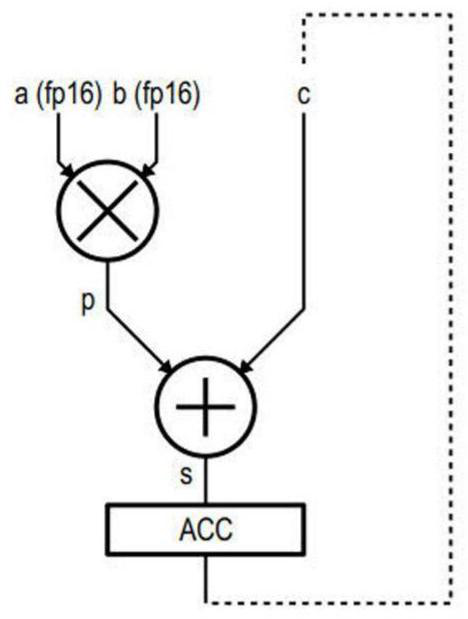
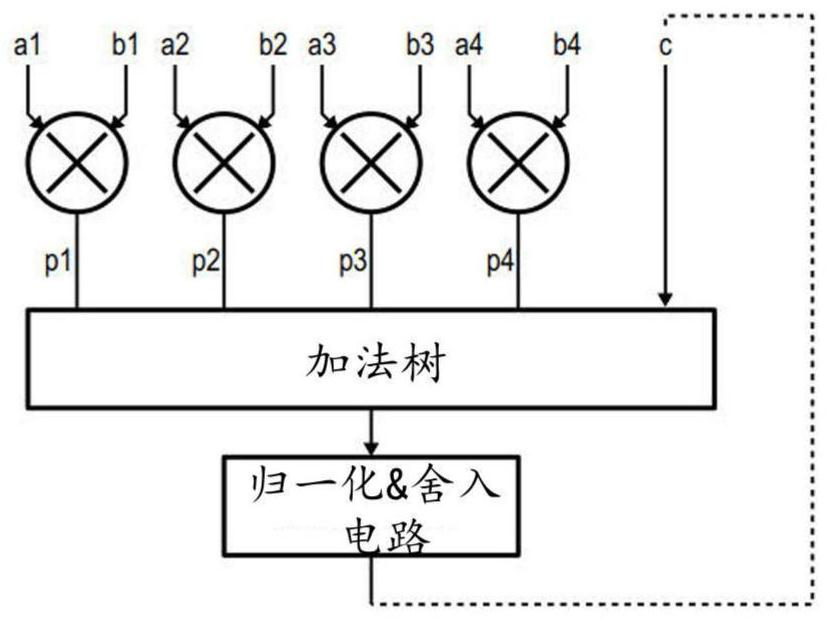
[0033] In order to improve computational accuracy during the multiple stages of accumulation of partial products, it is desirable to implement a mixed-precision FMA, ie, an addition operand with higher precision than the multiplicand. In fact, during repeated accumulation, the addition operands tend to increase continuously, while the partial products remain bounded.
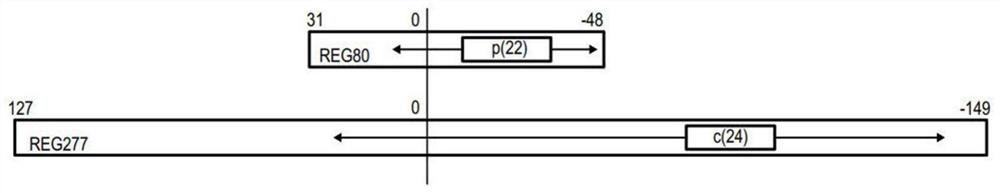
[0034] The above IEEE article by Nicolas Bruni proposes a solution that provides accurate computation of multiplicands suitable for binary 16 format, the product of which can be represented in an 80-bit fixed-point format, a format that is not difficult for processors to It is still acceptable for hardware processing within the core's processing unit.
[0035] However, the product of two binary 16s produces a non-standard floating point number with a sign bit, 6 exponent (exponent) bits, and 21+1 mantissa (mantissa) bits, encoded on 28 bits. This format is only used internally. Then, expect the addition operan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com