Camera lens with small head size
A lens and head technology, applied in the field of small head size lenses, can solve the problems of inability to reduce the size of the camera lens and the depth of the viewpoint, and achieve the effects of miniaturization, high cost performance, and small protrusions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
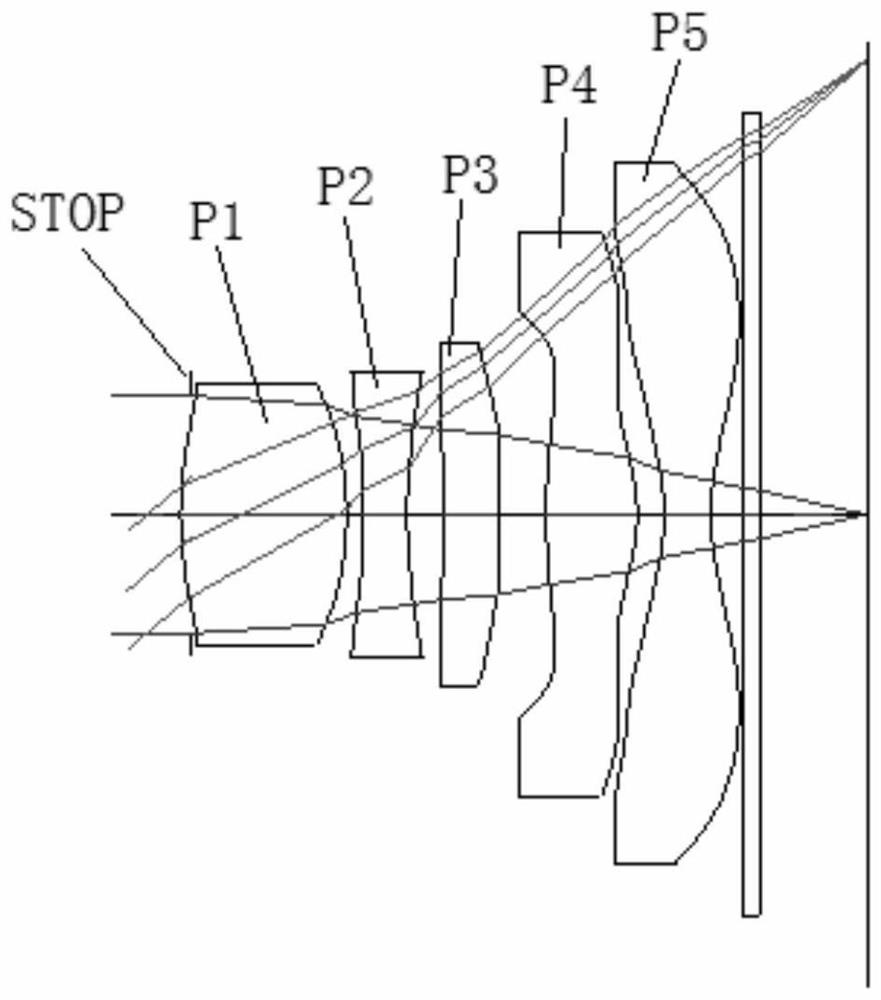
[0059] figure 1 It is a 2D diagram of the optical lens of Example 1 of the present application.
[0060] Such as figure 1 As shown, the optical lens of the present embodiment comprises in sequence from the object side to the image side along the optical axis: the first lens has positive refractive power; the second lens has negative refractive power; the third lens has positive refractive power; the fourth lens has Positive refractive power, the fifth lens has negative refractive power; the filter has object side and image side, and the aperture is set in front of the first lens. The incident light sequentially passes through the surfaces of each lens and is finally imaged on the imaging plane.
[0061] Tables 1(a), 1(b), and 1(c) show the surface type, curvature radius, thickness and material of each lens of the optical lens of Example 1. Wherein, the units of the radius of curvature and the thickness are both millimeters (mm).
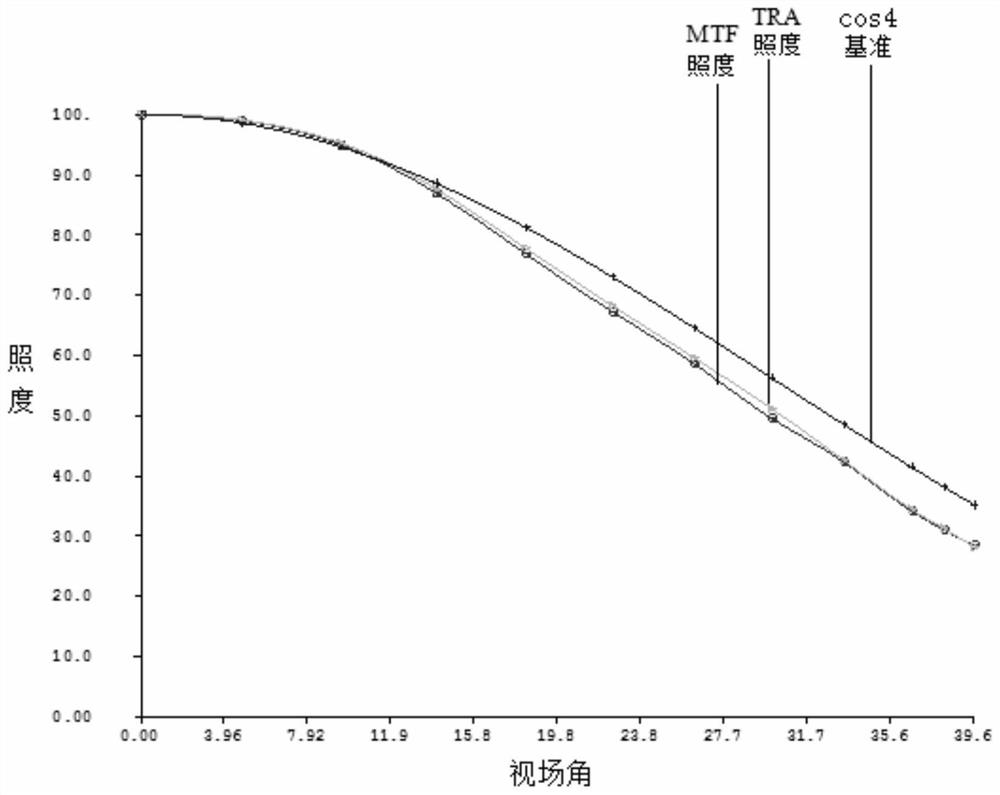
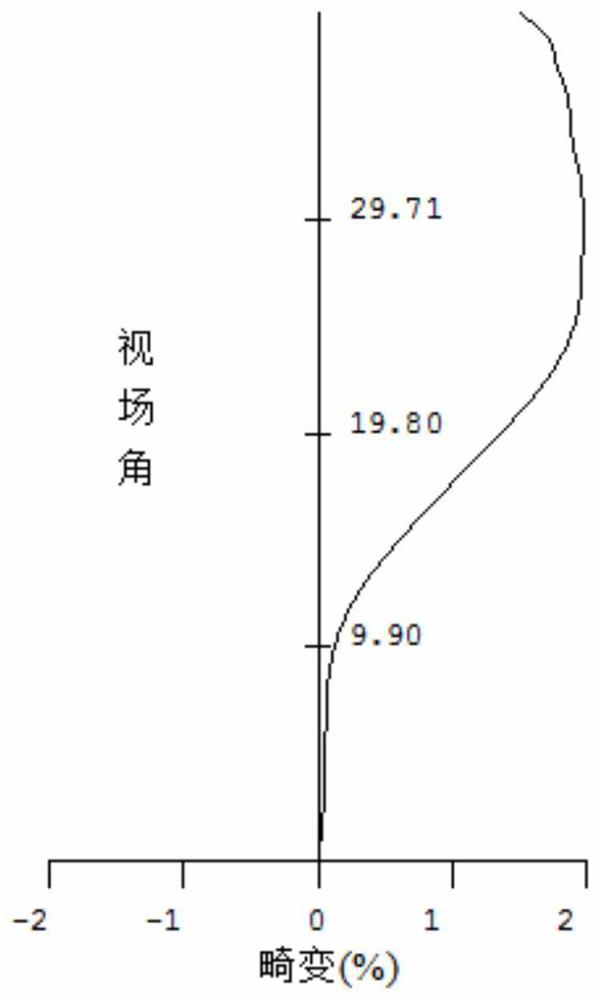
[0062] Please refer to the following table...
Embodiment 2
[0078] image 3 It is the 2D figure of the optical lens given in Embodiment 2 of the present application.
[0079] Such as image 3 As shown, the optical lens of the present embodiment comprises in sequence from the object side to the image side along the optical axis: the first lens has positive refractive power; the second lens has negative refractive power; the third lens has positive refractive power; the fourth lens has Positive refractive power, the fifth lens has negative refractive power; the filter has object side and image side, and the aperture is set in front of the first lens. The incident light sequentially passes through the surfaces of each lens and is finally imaged on the imaging plane.
[0080] 2(a), 2(b), and 2(c) show the surface type, radius of curvature, thickness and material of each lens of the optical lens of Embodiment 2. Wherein, the units of the radius of curvature and the thickness are both millimeters (mm).
[0081] Please refer to the follow...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Figure 5 Embodiment 3 of the present application provides a 2D diagram of the optical lens.
[0096] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the optical lens of the present embodiment comprises in sequence from the object side to the image side along the optical axis: the first lens has positive refractive power; the second lens has negative refractive power; the third lens has negative refractive power; the fourth lens has Positive refractive power, the fifth lens has negative refractive power; the filter has object side and image side, and the aperture is set in front of the first lens. The incident light sequentially passes through the surfaces of each lens and is finally imaged on the imaging surface.
[0097] Tables 3(a), 3(b), and 3(c) show the surface type, curvature radius, thickness and material of each lens of the optical lens of Example 3. Wherein, the units of the radius of curvature and the thickness are both millimeters (mm).
[0098] Please refer to the followin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com