Streptomyces albidoflavus and application thereof in production of epsilon-polylysine
A technology of Streptomyces albicans and polylysine, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, bacteria, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of general screening effect, high price, unsuitable for large-scale application in breeding work, etc., to avoid The effects of bacterial contamination, strong product tolerance, and excellent passage stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
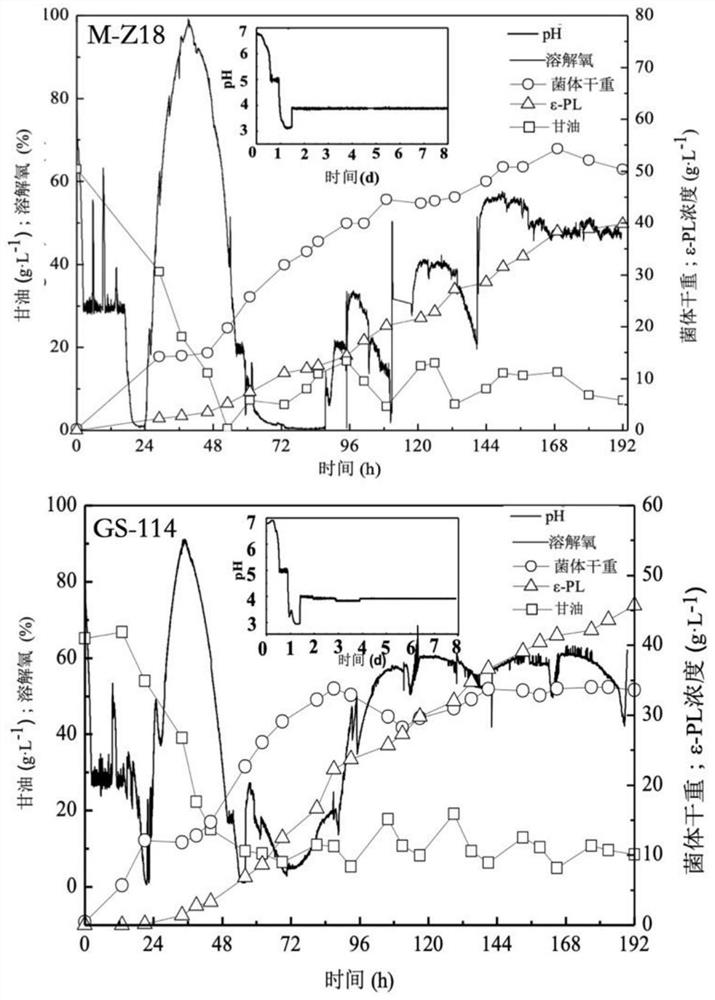
[0072] Embodiment 1: Breeding of Streptomyces parvus GS114
[0073] Bethner solid medium (g / 100mL): glucose 2, yeast extract 0.2, peptone 0.4, agar 2, pH 7.5, sterilized at 115°C for 20 minutes.
[0074] Antibiotic resistance medium (g / 100mL): glucose 2, yeast extract 0.2, peptone 0.4, agar 2, pH 7.5, sterilized at 115°C for 20 minutes. When the temperature of the culture medium dropped to 60°C, the stock solutions of streptomycin, gentamicin and rifamycin prepared in advance and sterilized by filtration through a 0.22 μm membrane were added thereto.
[0075] Specific steps are as follows:
[0076] (1) Construction of mutation library: 2% (v / v) DES was used to test the spores of Streptomyces albicans M-Z18 (the deposit number is CCTCC NO: M 2019589, and the strain is recorded in the patent application with application number 201911020454.4) The suspension was treated for 30min (28°C water bath), and NaS was added 2 o 3 Terminate the reaction, dilute and smear on a Bethner-...
Embodiment 2
[0078]Example 2: Morphological analysis of the starting bacterium M-Z18 and the high-yielding bacterium GS114
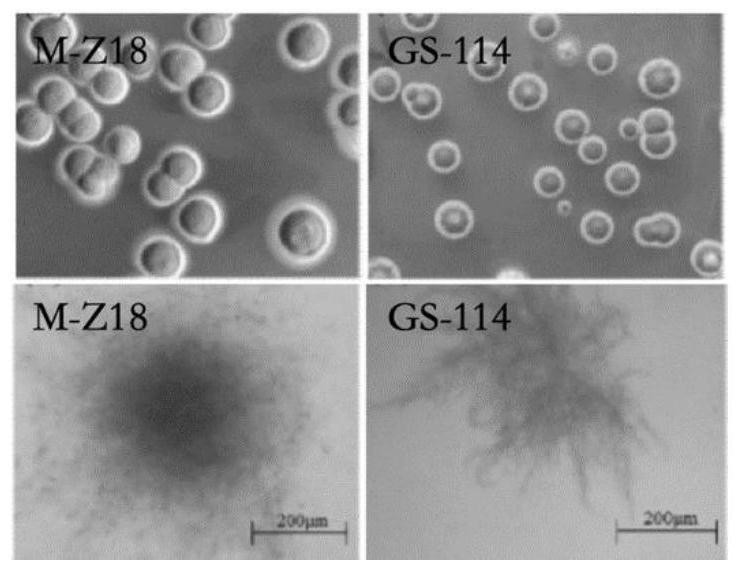
[0079] The morphology of the strains was observed with naked eyes and microscopic analysis.
[0080] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that there are obvious differences in morphology between the two strains. On the peptone yeast extract medium, the colony of the starting strain M-Z18 was larger, the aerial hyphae grew well, and the colony and its back were yellow or tan. In YP liquid medium, the mycelium of M-Z18 intertwined to form larger solid balls.
[0081] The colonies of the strain GS114 are small. On the peptone yeast extract medium, the aerial hyphae grow well, and the spores form gray-green chains, which are oval under the microscope; the colonies and their backs are yellow-green or yellow-brown. In YP liquid medium, the hyphae of GS114 were relatively loose and the balls were small.
Embodiment 3
[0082] Example 3: Resistance of Streptomyces parvus GS114 to a single antibiotic
[0083] Bettner solid medium: glucose 20g / L, yeast extract 2g / L, peptone 4g / L, agar 20g / L, pH7.5, sterilized at 115°C for 20min.
[0084] Preparation of single spore suspension: Streptomyces albicans GS114 was streak-inoculated on Bethner's medium, cultured at 30°C for 8 days, and after the spores matured, the spores were placed in an Erlenmeyer flask containing glass beads and sterile water. Shake at 200r / min on a shaker at 30°C for 20min, filter through 8 layers of sterile gauze to obtain a single spore suspension, and count with a hemocytometer under an optical microscope to determine the concentration of the prepared single spore suspension, using an order of magnitude of 10 8 ~10 9 cells / mL was used as the spore suspension.
[0085] Streptomycin and gentamicin can bind to the ribosomal S12 protein and L6 protein, respectively, and the strain will die due to the inhibition of protein transl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com