Electroencephalogram emotion recognition method based on parallel sequence channel mapping network
An emotion recognition and network technology, applied in the field of EEG emotion recognition, can solve problems such as insufficient spatiotemporal information and low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
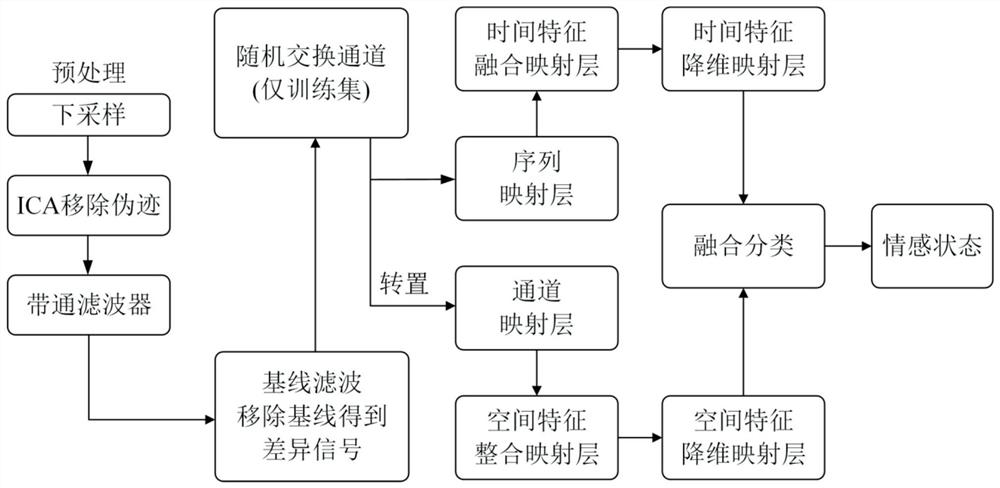
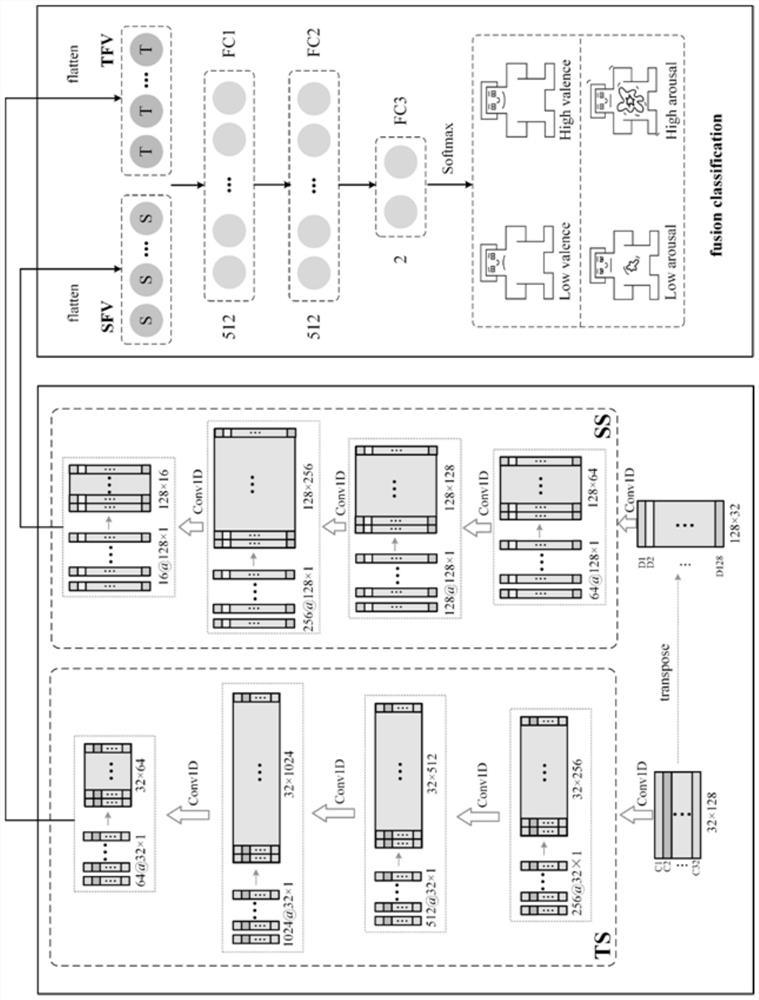
[0030] Embodiments of the present invention provide a method for EEG emotion recognition based on a parallel sequence channel mapping network, such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0031] 101: Preprocessing
[0032] The sampling frequency was reduced from 512Hz to 128Hz, and EOG artifacts were removed with ICA (Independent Component Analysis). Use a 4.0-45.0Hz band-pass filter to filter out noise. The preprocessed EEG data for each subject consisted of 40 trials with corresponding labels. Each trial contained 60 s of the emotional signal and 3 s of the pre-trial baseline signal.
[0033] 102: Baseline filtering
[0034] The embodiment of the present invention provides a baseline filter, which can filter out the baseline signal with relatively severe fluctuations, and retain the stable baseline signal for baseline removal (use the emotion signal to subtract the baseline signal to obtain a difference signal, and use it as network input) .
...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The scheme in embodiment 1 is further introduced below in conjunction with specific calculation formulas and examples, see the following description for details:
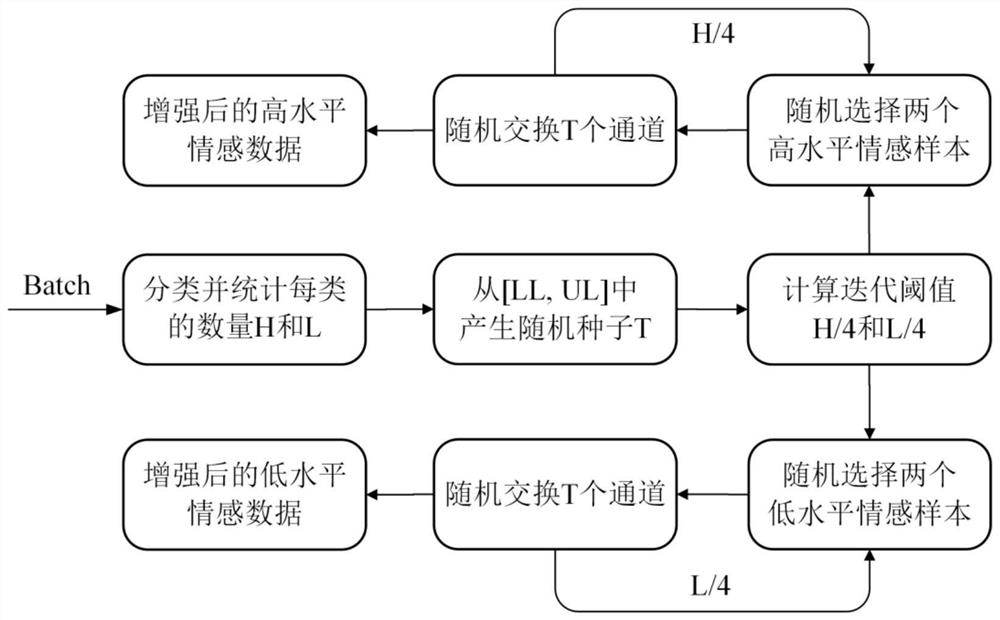
[0046] 201: Baseline filtering
[0047] Baselining the data can help the network to fit better. The DEAP database (well known to those skilled in the art, which will not be described in detail in the embodiment of the present invention) each trial contains a 3-second baseline signal, a 60-second emotional signal, and 32 EEG channels. The model takes the difference signal between the emotion signal and the baseline signal instead of the emotion signal as input. In order to amplify this difference, a baseline noise filter is designed to remove the volatile baseline signal. The specific working principle is as follows:
[0048] First, take the 3-second baseline signal from the first EEG channel and convert it into a key-value pair (Key, Value). Key is used to record the initial sequence of sampling points, and...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Below in conjunction with concrete experiment, the scheme in embodiment 1 and 2 is carried out feasibility verification, see the following description for details:
[0088] In this experiment, EEG data from the DEAP dataset were used for analysis. The DEAP dataset consists of data from 32 healthy participants (50% female) with an average age of 26.9 years. Each subject watched 40 60-second music videos. At the end of each video, a self-assessment of the degree of valence, arousal, dominance and liking is given on a continuous scale between 1 and 9. This experiment only uses the data of valence and arousal. Each video contained 60 s of the emotional signal and 3 s of the pre-trial baseline signal. Set 5 as the threshold and classify the videos into 2 categories according to the scores. The task is then transformed into two binary classification problems, high / low valence and high / low arousal.
[0089] As shown in Table 1, the average accuracy of this method on valen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com