Calculation method of microstructure family equivalent material properties, microstructure, system and medium
A technology of equivalent materials and calculation methods, applied in calculation, computer-aided design, computer material science, etc., can solve problems such as unsuitable material properties, high cost, slow speed, etc., to save time for physical experiments, control costs, and improve efficiency effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] refer to figure 1 , the calculation method of the equivalent material properties of the microstructure family in this embodiment, including:
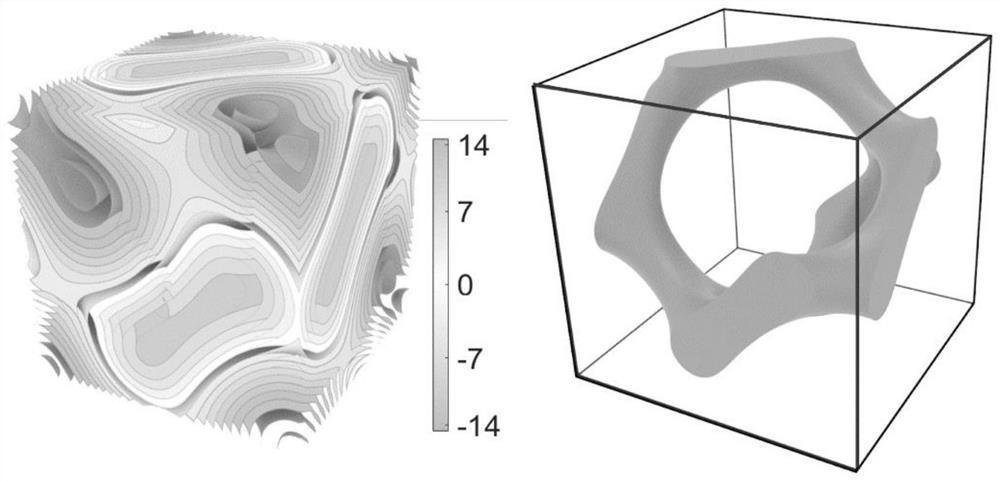
[0034] Step (1): Generate voxels in the unit space, and determine whether each voxel is filled according to the three-period minimal surface of TUBULAR GYROID type, so as to voxelize the three-period minimal surface.
[0035] Specifically, the definition and generation method of the TUBULAR GYROID type three-period minimal surface is as follows:
[0036] Use the following implicit function to represent the TUBULAR GYROID type three-period minimal surface:
[0037] φ(p,c)=10[cos(px)sin(py)+cos(py)sin(pz)+cos(pz)sin(px)]
[0038] -0.5[cos(2px)cos(2py)+cos(2py)cos(2pz)
[0039] +cos(2pz)cos(2px)]-c
[0040] Among them: p controls the period of the surface, c controls the isosurface of the surface, x, y, z represent a coordinate point in the three-dimensional space coordinate system.
[0041] Use the implicit function φ(p, c) to...
Embodiment 2
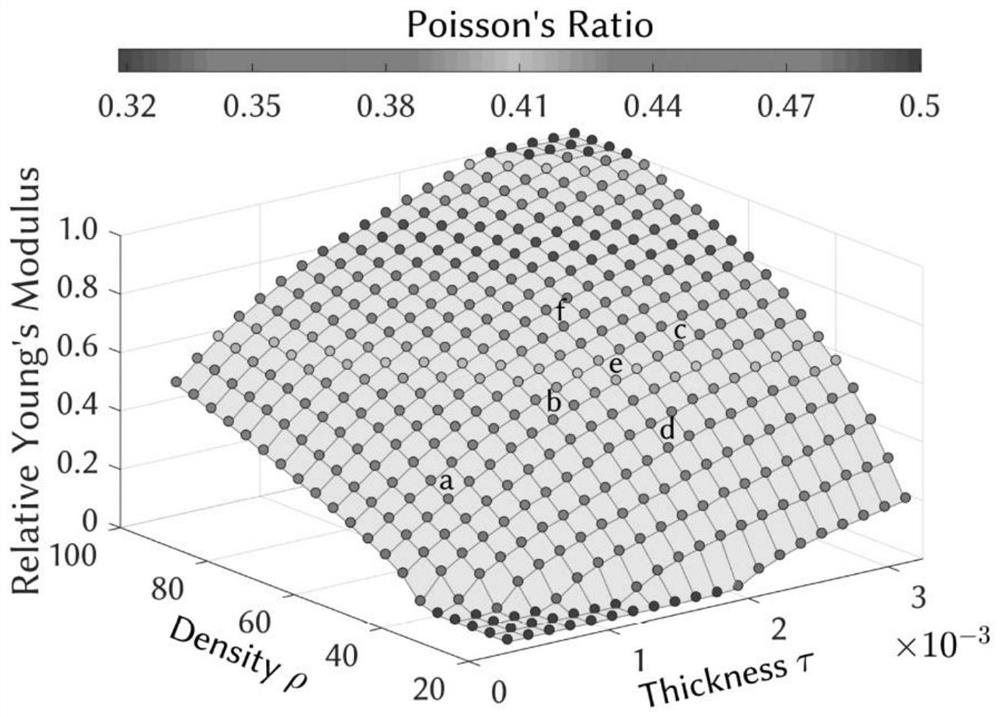
[0076] This embodiment provides a TUBULAR GYROID type microstructure, which is printed from equivalent materials with a certain Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio; the Young's modulus and Poisson are based on the microstructure described in the first embodiment above It is calculated by the calculation method of the equivalent material properties of the family.
Embodiment 3
[0078] This embodiment provides a calculation system for equivalent material properties of microstructure families, which includes:
[0079] A voxelization module, which is used to generate voxels in the unit space, and determine whether each voxel is filled according to the TUBULAR GYROID type three-period minimal surface, so as to voxelize the three-period minimal surface;
[0080] A homogenization module, which is used to calculate a homogenization matrix from the unit displacement of the voxel and the global displacement field, and the homogenization matrix represents the homogenization material properties corresponding to the current three-period minimal surface microstructure;
[0081] Interpolation fitting module, which is used to interpolate and fit the results of homogenized material properties, obtain interpolation functions about density and thickness, and obtain Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio to guide the preparation and printing of TUBULAR GYROID type microstr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Poisson's ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com