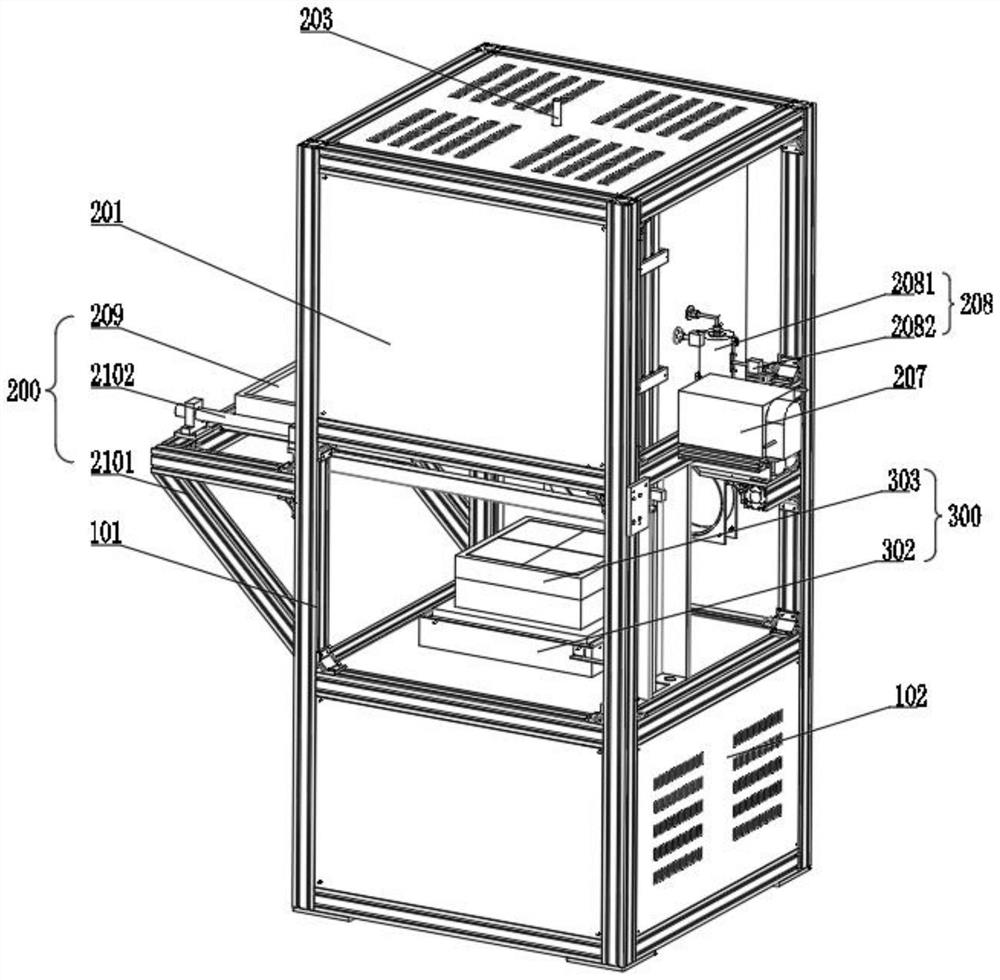
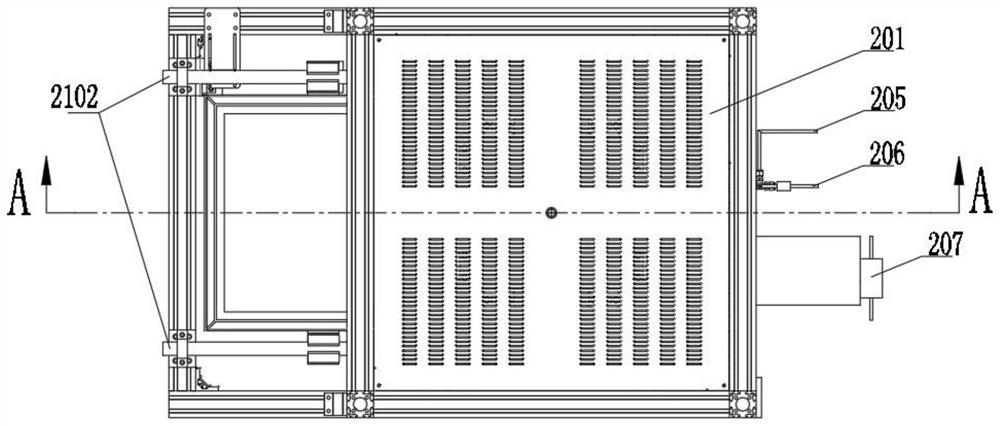
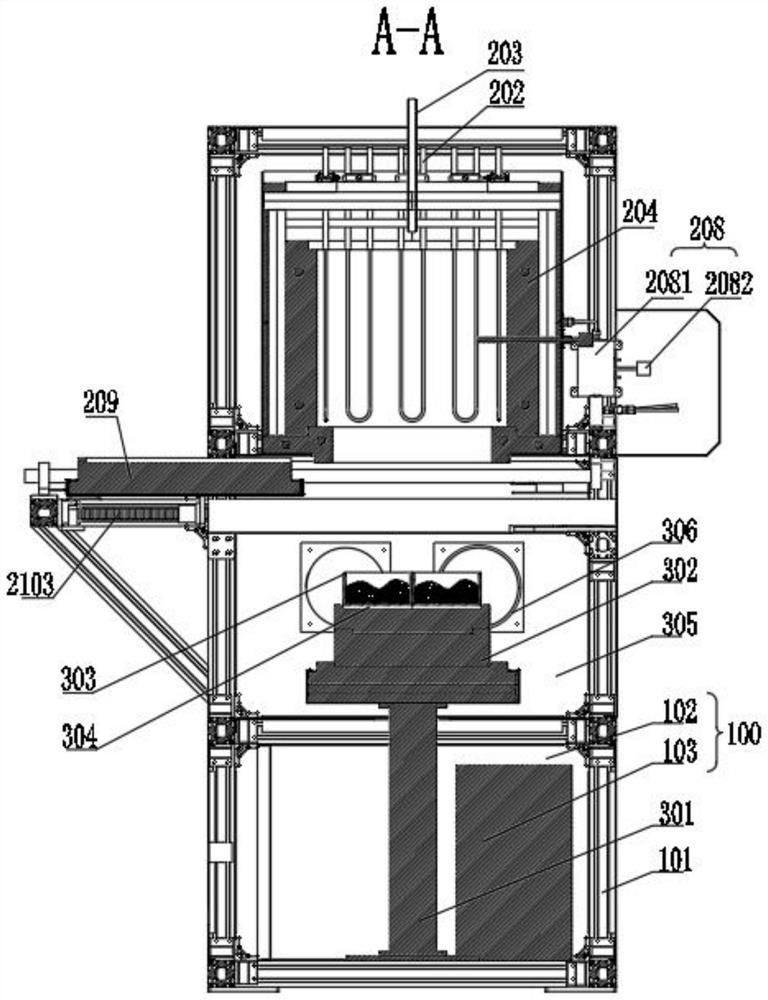
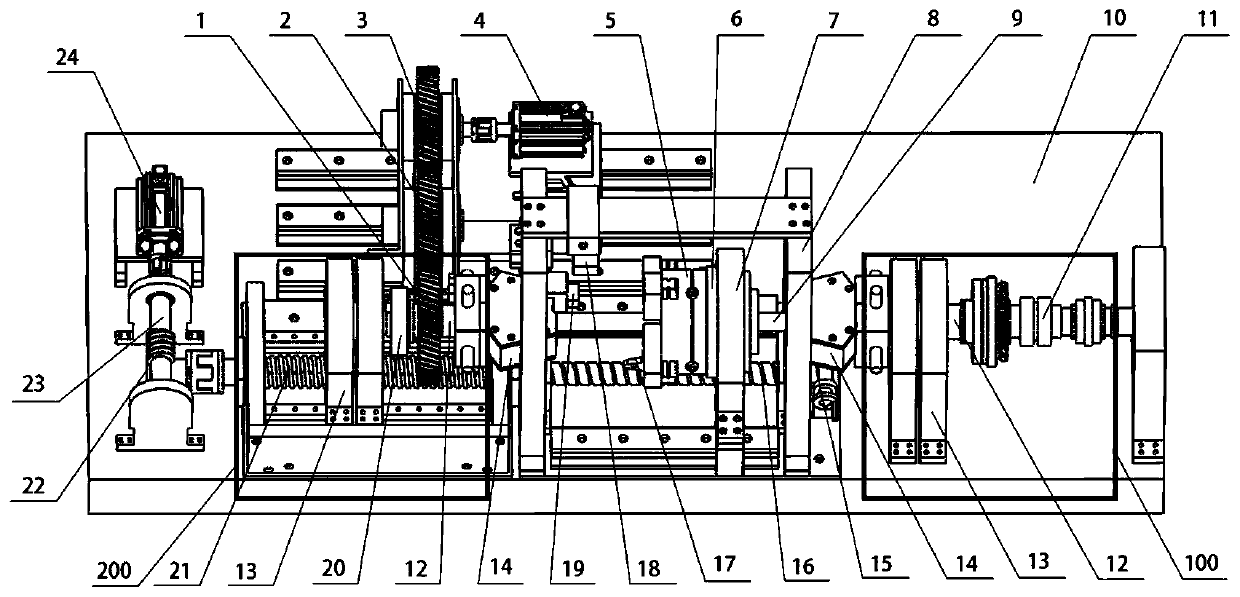
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Material properties" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The thermodynamic properties of materials are intensive thermodynamic parameters which are specific to a given material. Each is directly related to a second order differential of a thermodynamic potential. Examples for a simple 1-component system are: Compressibility (or its inverse, the bulk modulus) Isothermal compressibility βT=-1/V(∂V/∂P)T =-1/V ∂²G/∂P² Adiabatic compressibility βS=-1/V(∂V/∂P)S =-1/V ∂²H/∂P² Specific heat (Note - the extensive analog is the heat capacity) Specific heat at constant pressure cP=T/N(∂S/∂T)P =-T/N ∂²G/∂T² Specific heat at constant volume cV=T/N(∂S/∂T)V =-T/N ∂²A/∂T² Coefficient of thermal expansion α=1/V(∂V/∂T)P =1/V ∂²G/∂P∂T where P is pressure, V is volume, T is temperature, S is entropy, and N is the number of particles.
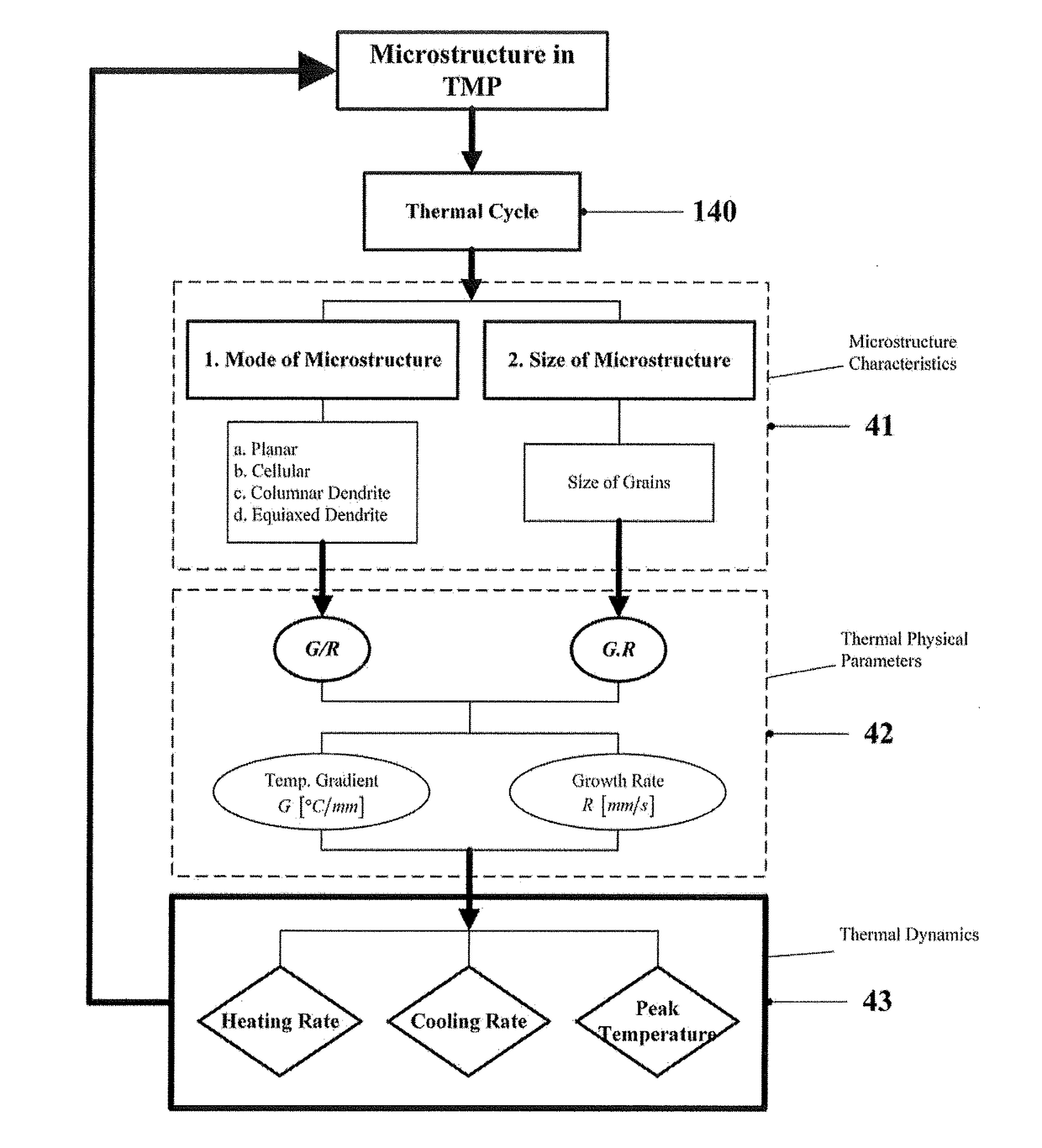
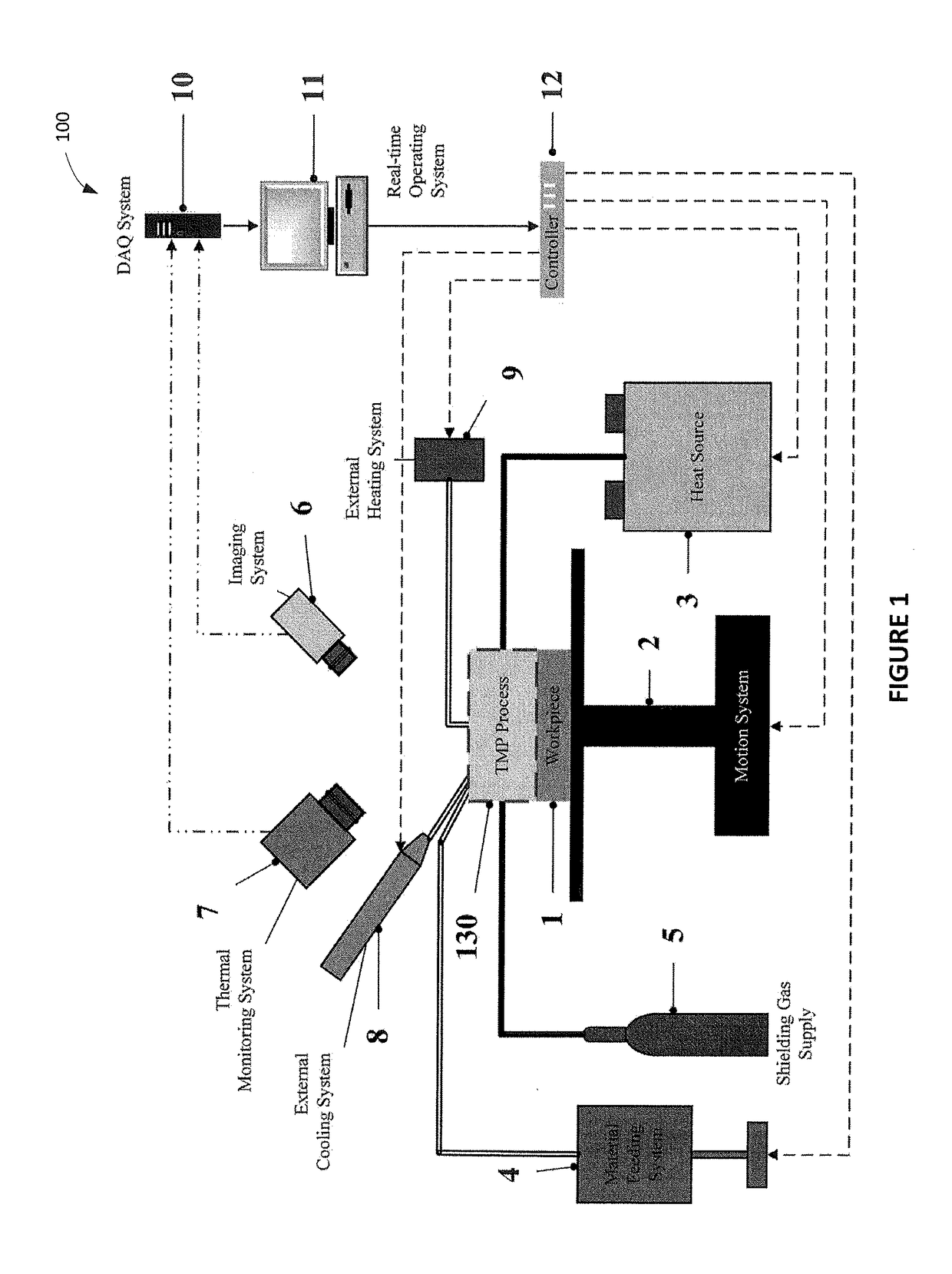
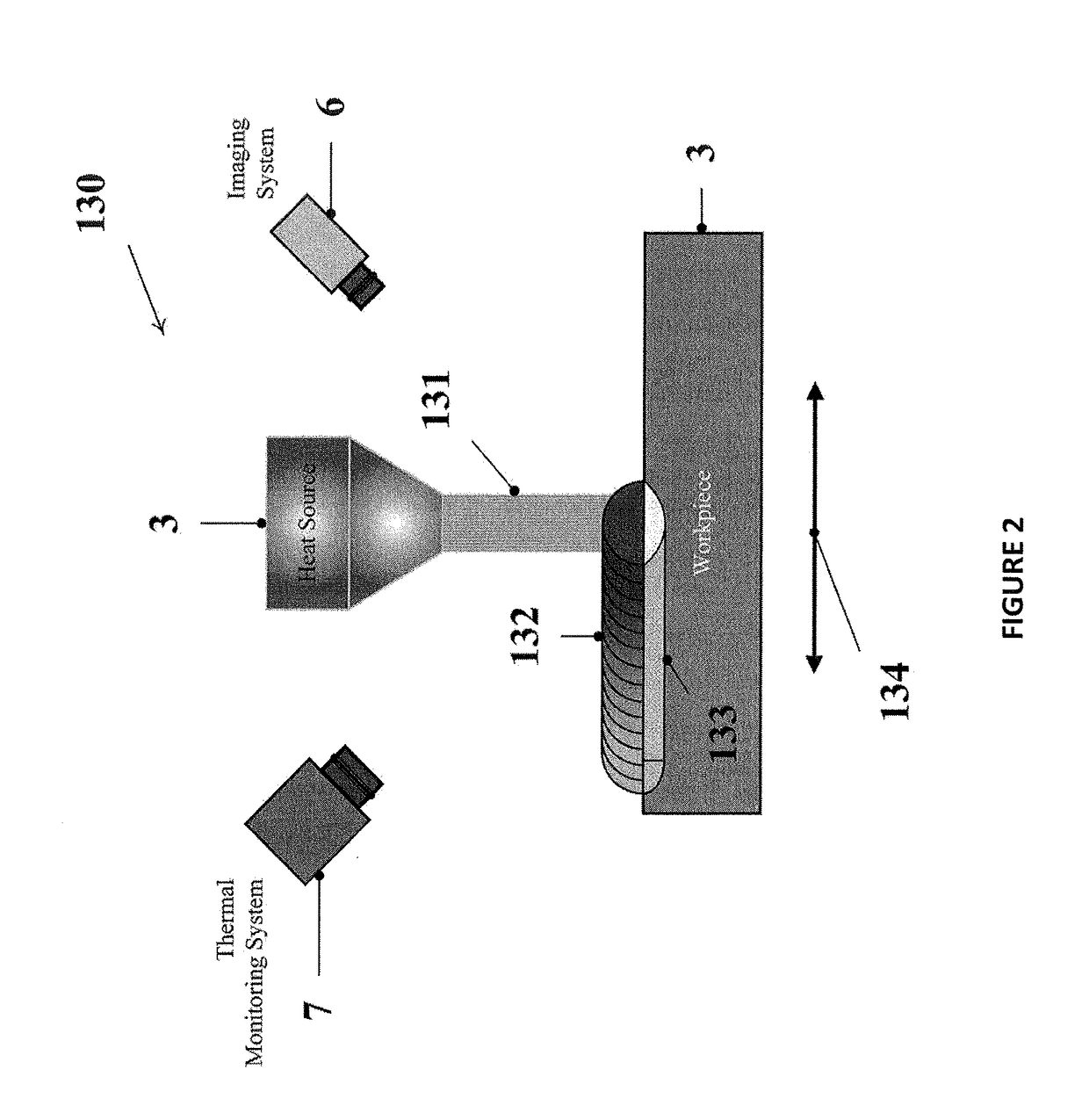
System and method for real time closed-loop monitoring and control of material properties in thermal material processing
ActiveUS20170102689A1Programme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusProcess engineeringMonitoring and control
The disclosure is directed at a method and apparatus for integrated real-time monitoring and control of microstructure and / or geometry in thermal material processing (TMP) technologies. The method includes obtaining real-time thermal dynamic variables, such as, but not limited to the cooling rate, peak temperature and heating rate, and geometry of the thermal material process. These real-time thermal variables are then analyzed along with a thermal model to determine a microstructure / geometry model. This microstructure / geometry model can then be used to provide the real-time monitoring and control of a finished state for the material being processed by the thermal material processing procedure.
Owner:KHAJEPOUR AMIR +2
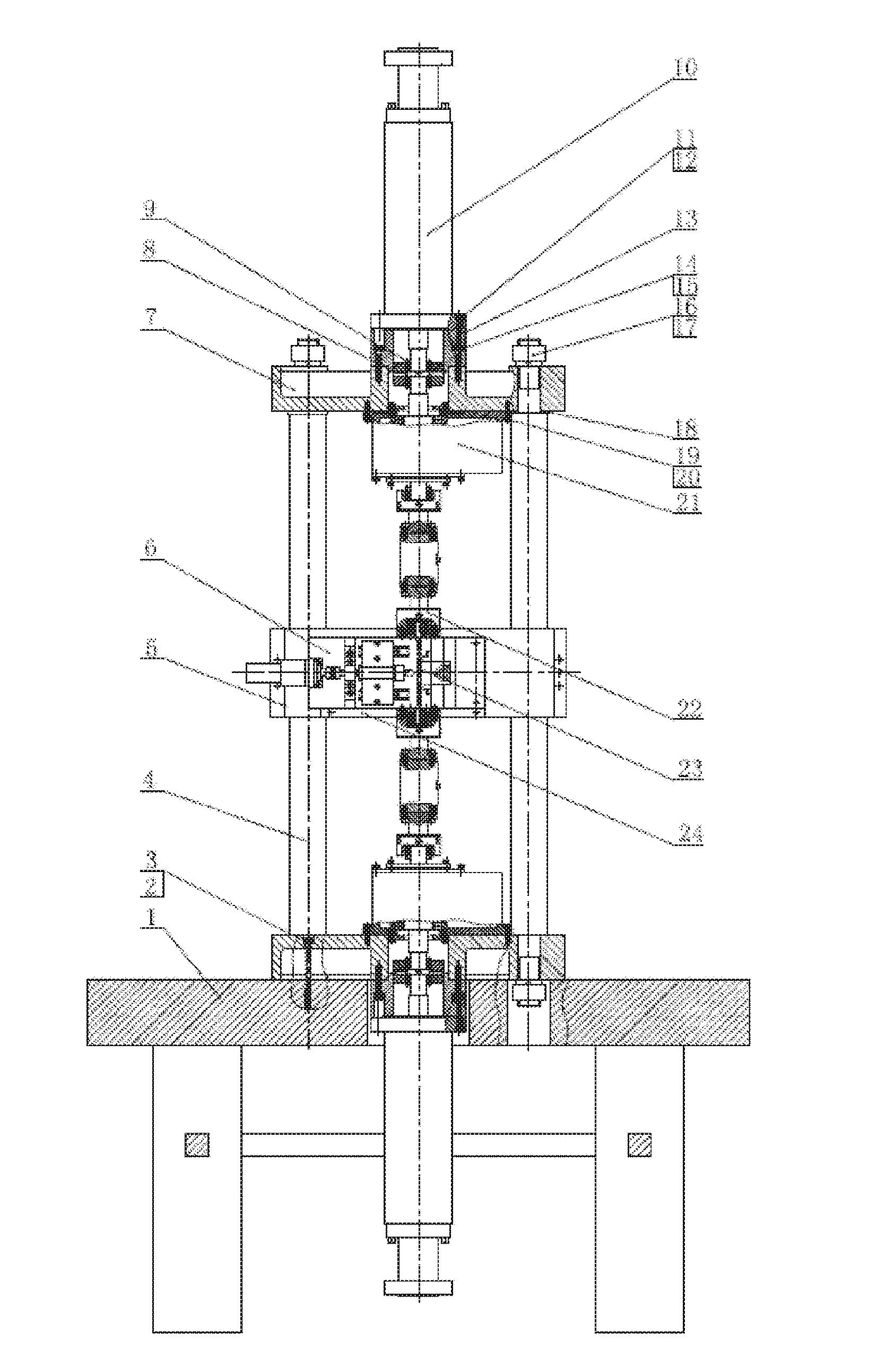
In-situ testing equipment for testing micromechanical properties of material in multi-load and multi-physical field coupled condition
ActiveUS20160216182A1Innovative structureEffective testingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady bending forcesTesting equipmentTest material
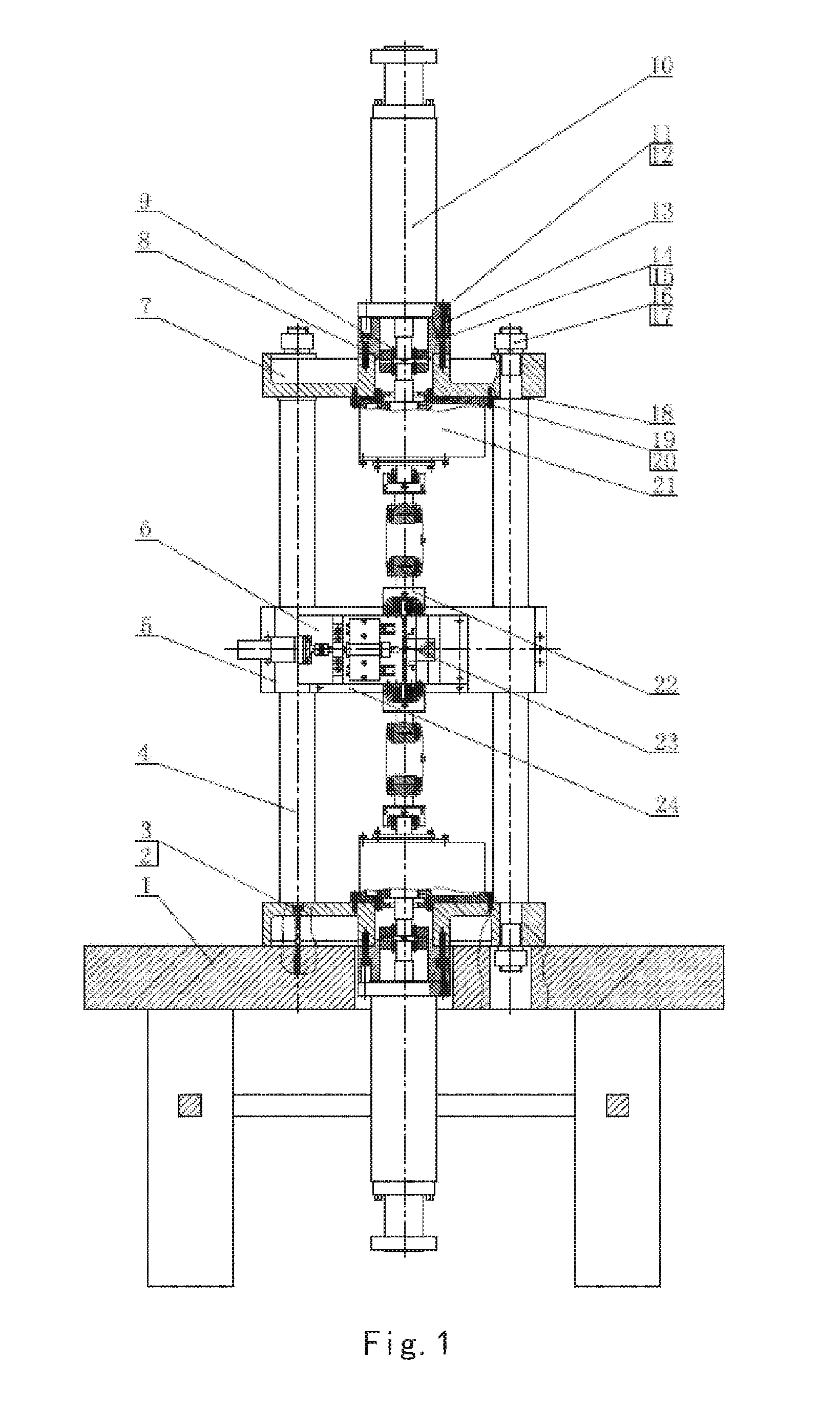
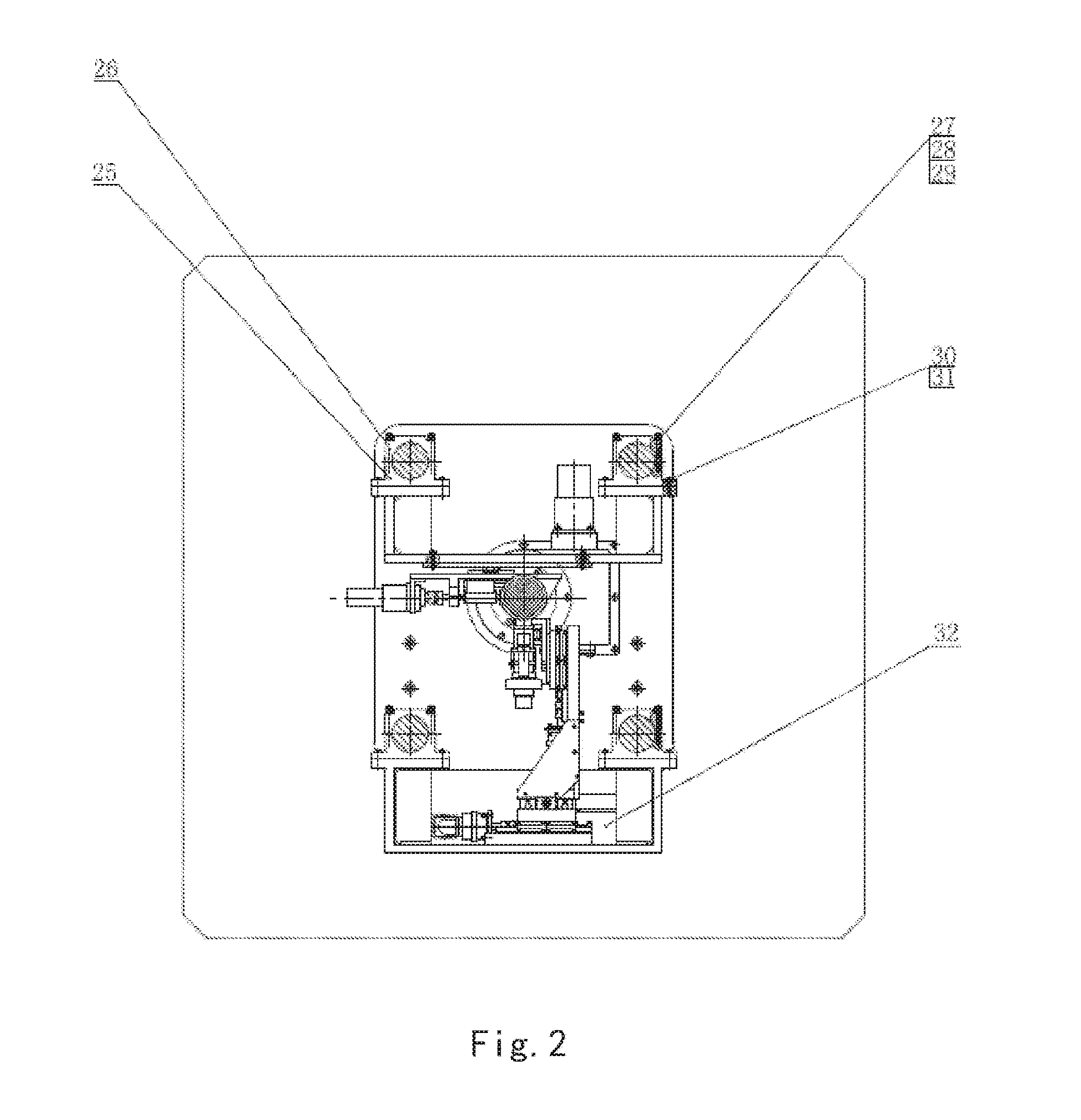
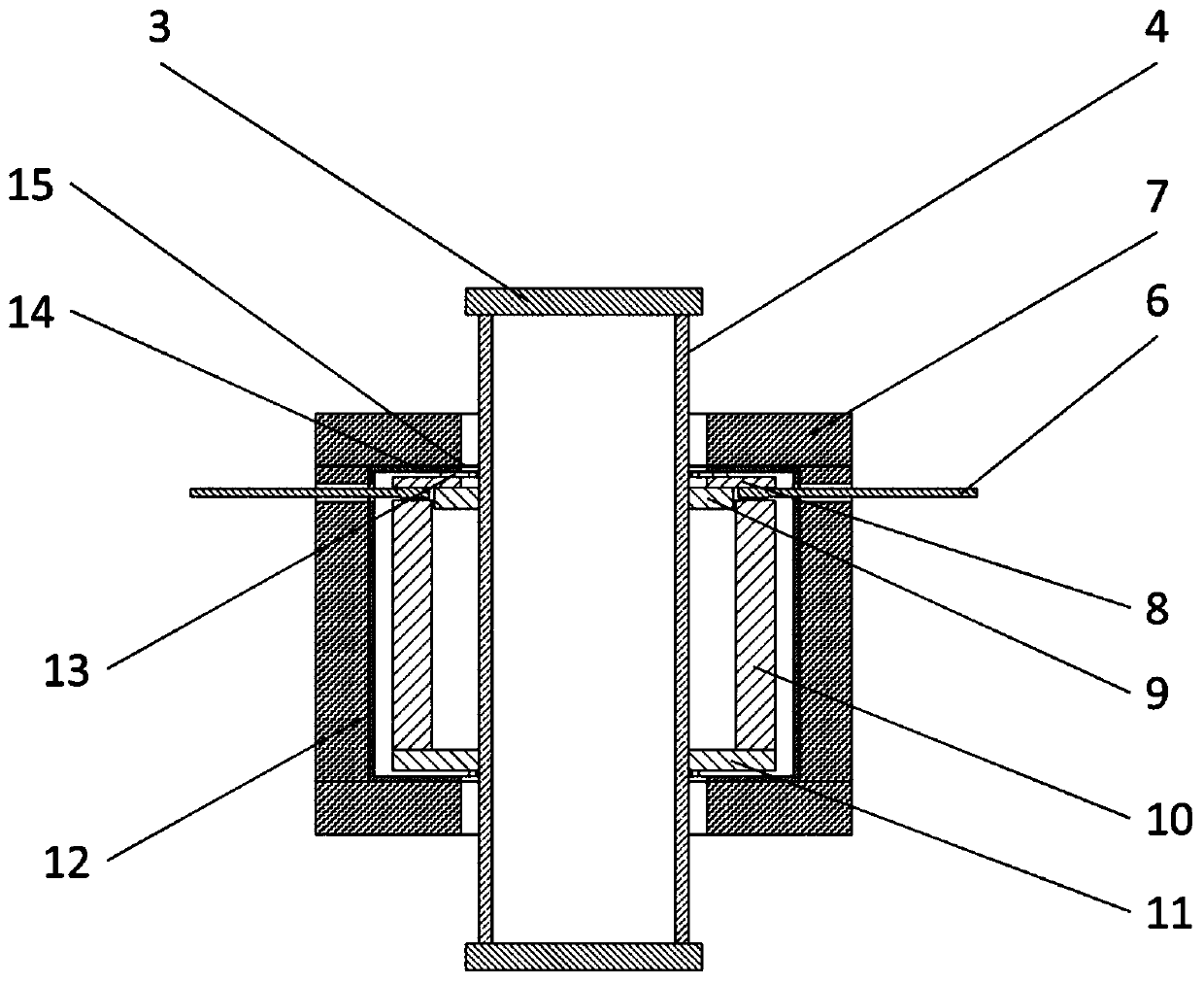
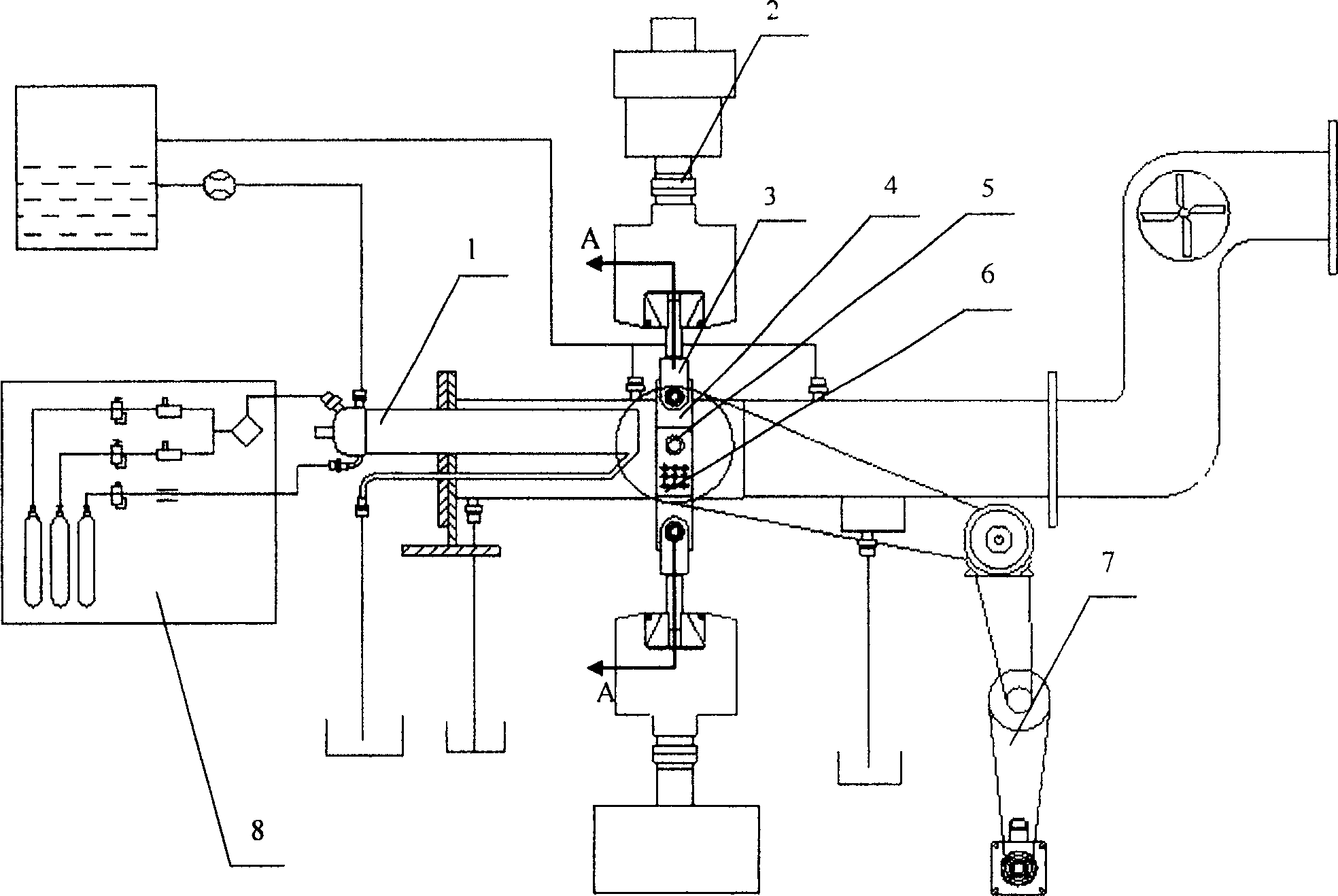
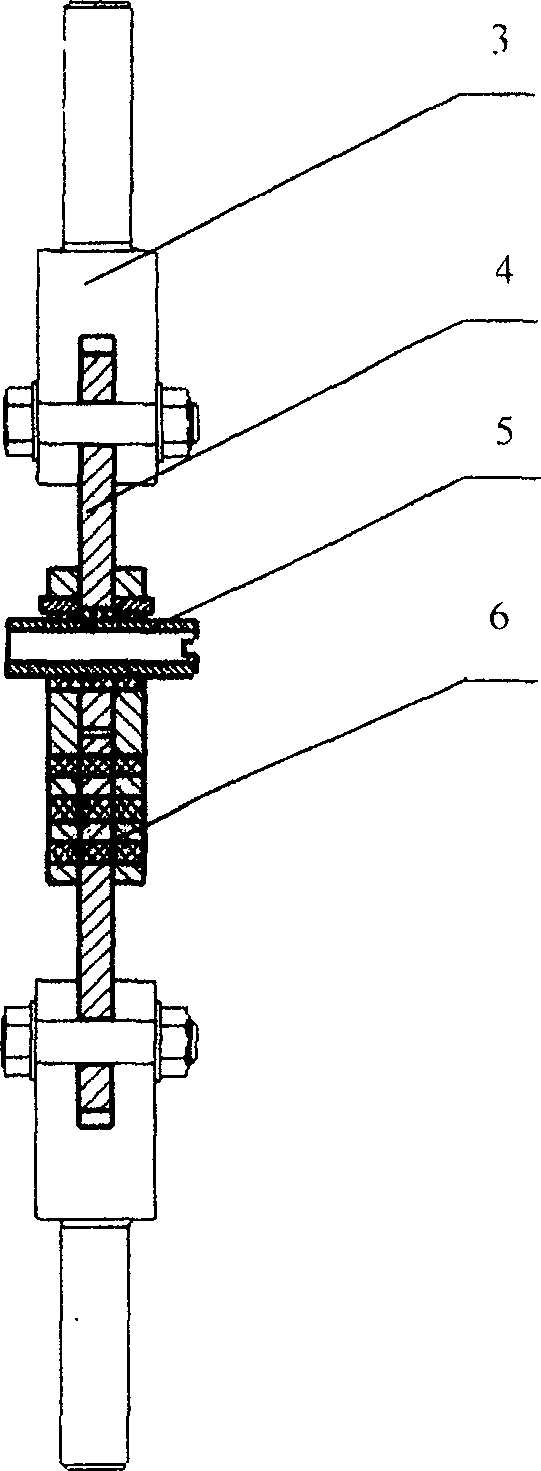
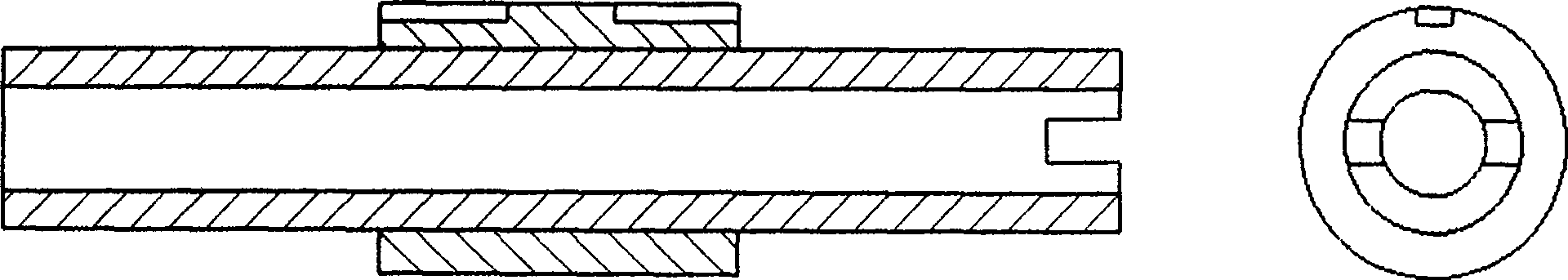
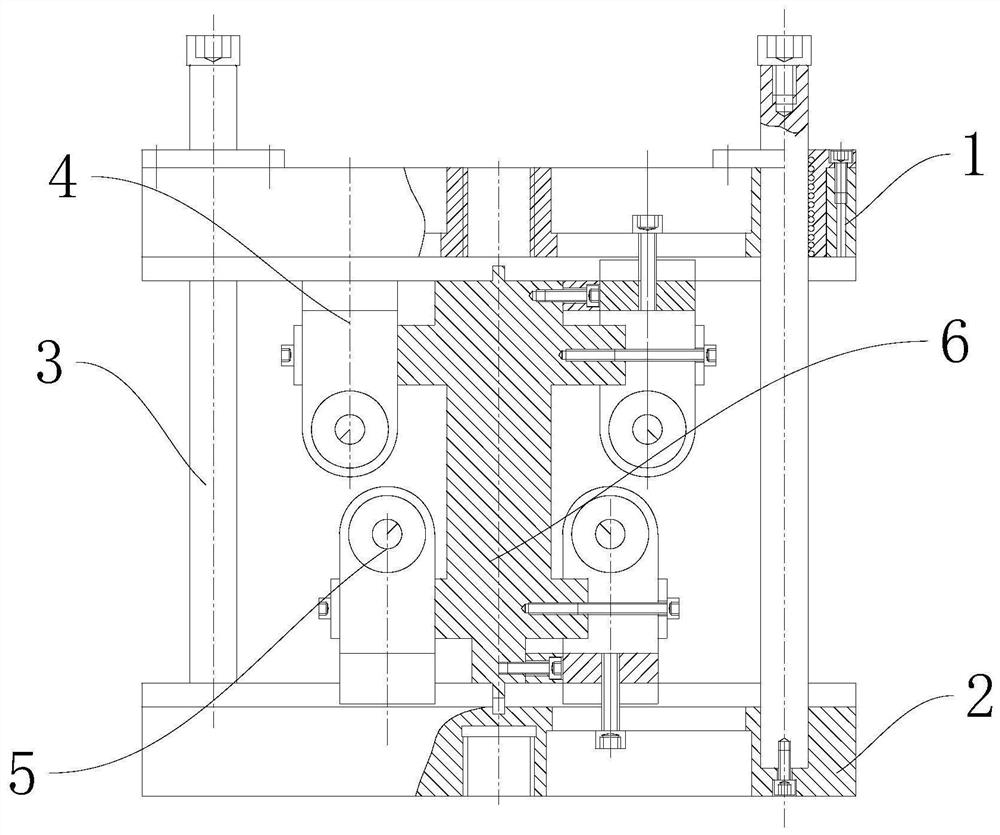
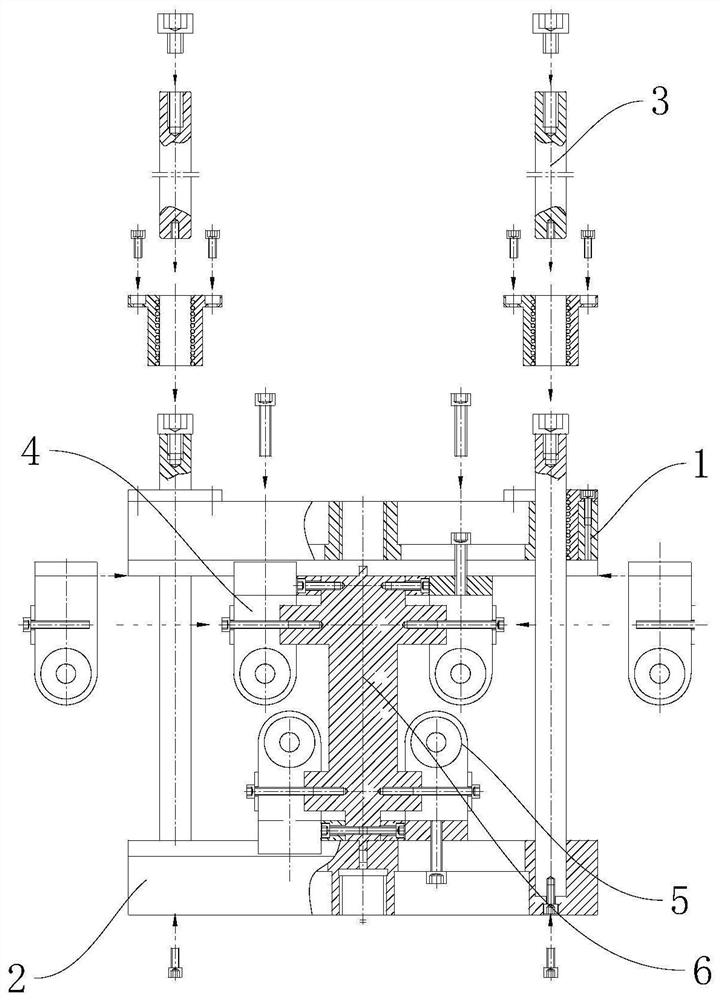
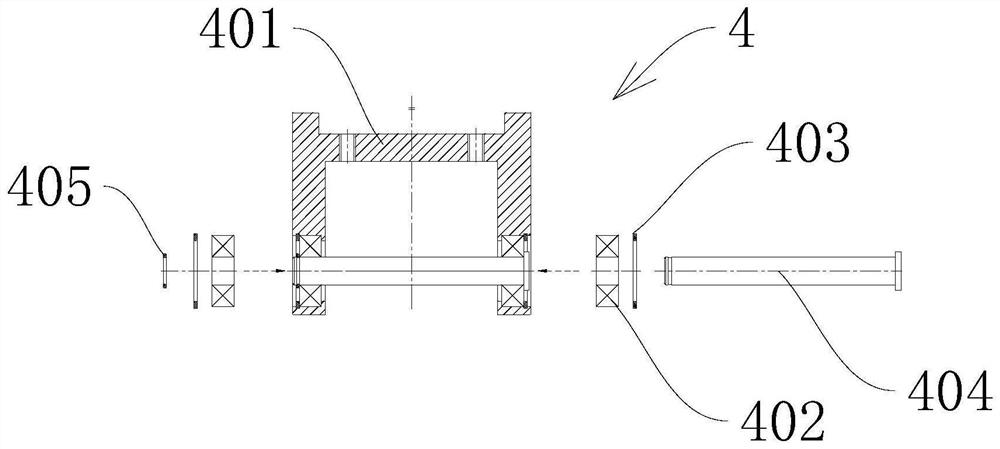
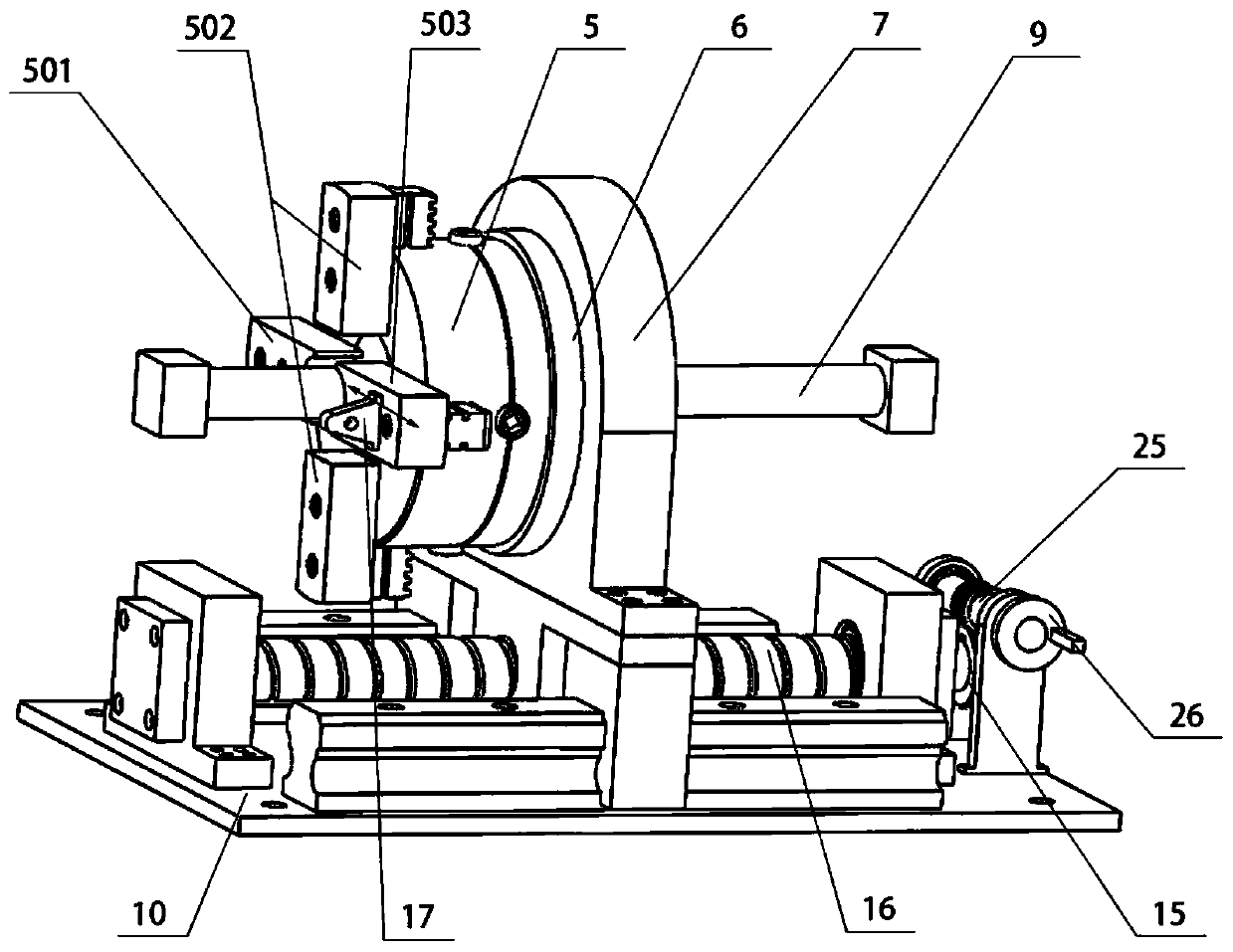
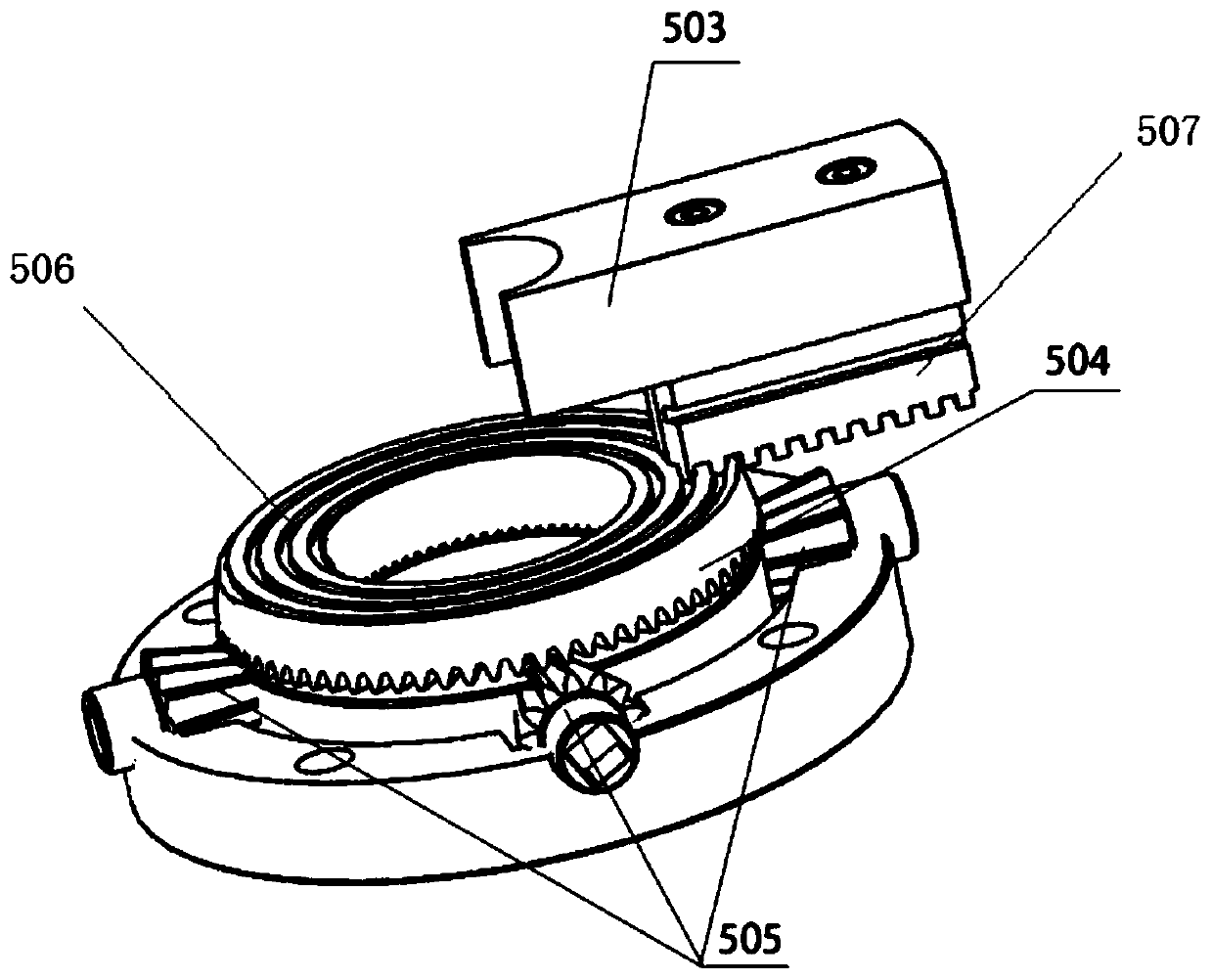
An in-situ testing equipment for testing micromechanical properties of a material in a multi-load and multi-physical field coupled condition is disclosed. The equipment comprises a frame supporting module, a tension / compression-low cycle fatigue module, a torsioning module (21), a three-point bending module (6), an impressing module (33), a thermal field and magnetic field application module (34), an in-situ observation module (32) and a clamp body module (22). The frame supporting module provides a structural support for the whole testing equipment, the tension / compression-low cycle fatigue module is arranged at upper and lower ends of the testing equipment, the torsioning module (21) is directly arranged at a front end of the tension / compression-low cycle fatigue module, the three-point bending module (6), the impressing module (33) and the thermal field and magnetic field application module (34) are disposed on a support post at one side of the whole testing equipment through a common replacing component, and the in-situ observation module is disposed on another support post at the other side of the testing equipment. The clamp body module is connected to a front segment of the torsioning module, so as to clamp a test piece. An overall structure of the testing equipment is configured in a vertically symmetrical arrangement achieved by using four support posts. Two identical servo hydraulic cylinders (10) and two torsioning modules (21) are located at the upper and the lower ends of the testing equipment respectively and are used to perform a symmetrical tension / compression test and a symmetrical torsion test on the test piece (23) positioned centrally. The testing equipment is capable of realizing applications of five different types of loads including tension / compression, low cycle fatigue, torsion, bending and impressing, performing an intensive study on micromechanical properties of the material in the multi-load and multi-physical field coupled condition by using built-in electric, thermal and magnetic application modules and the in-situ observation module, and acquiring relations between deformation behavior, mechanism of damage, performance weakening of the material, applied loads and material properties.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
In-situ testing equipment for testing micromechanical properties of material in multi-load and multi-physical field coupled condition
ActiveUS10012576B2Simple structureClosely arrangedMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady bending forcesPhysical fieldEngineering
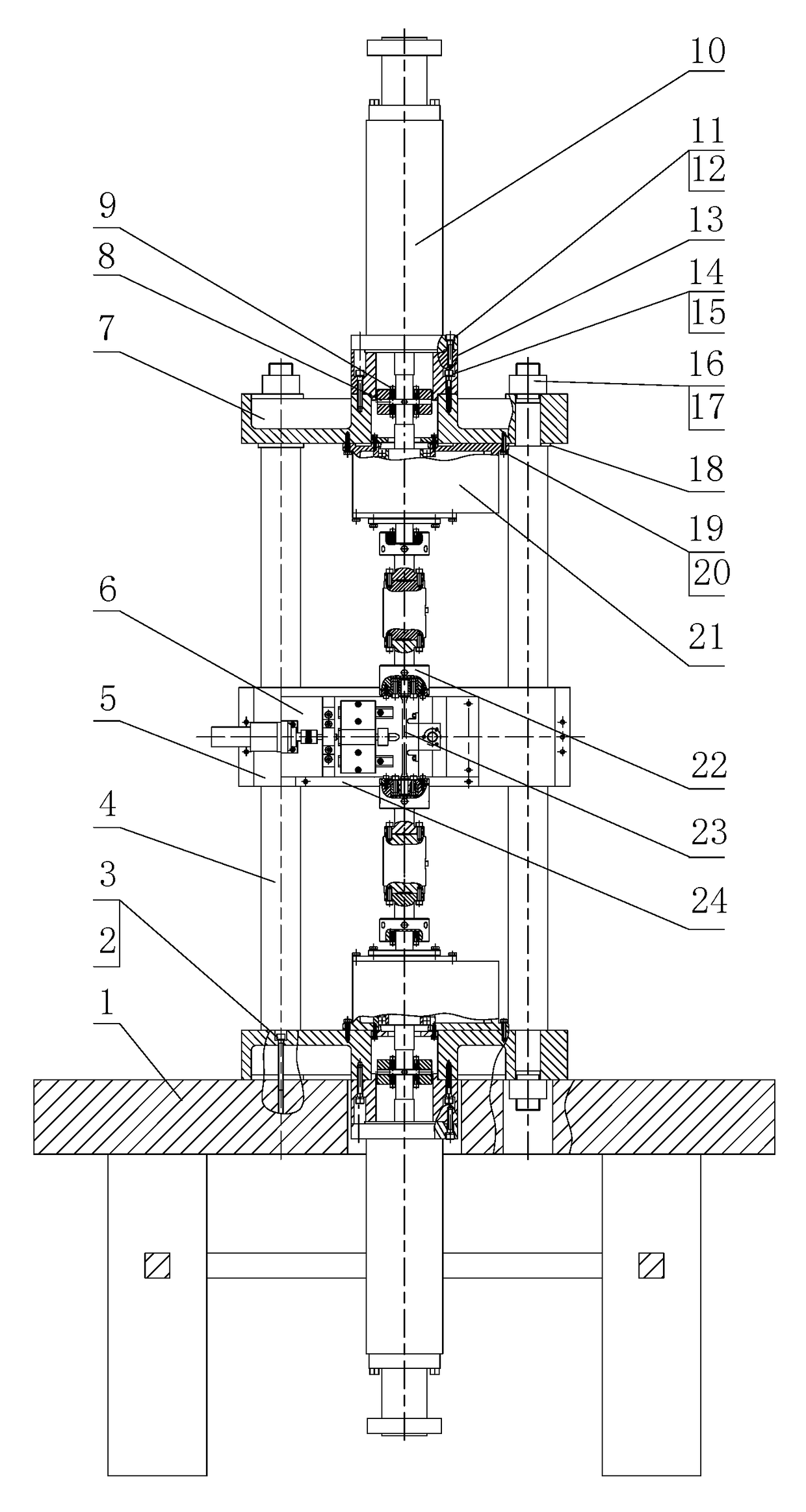
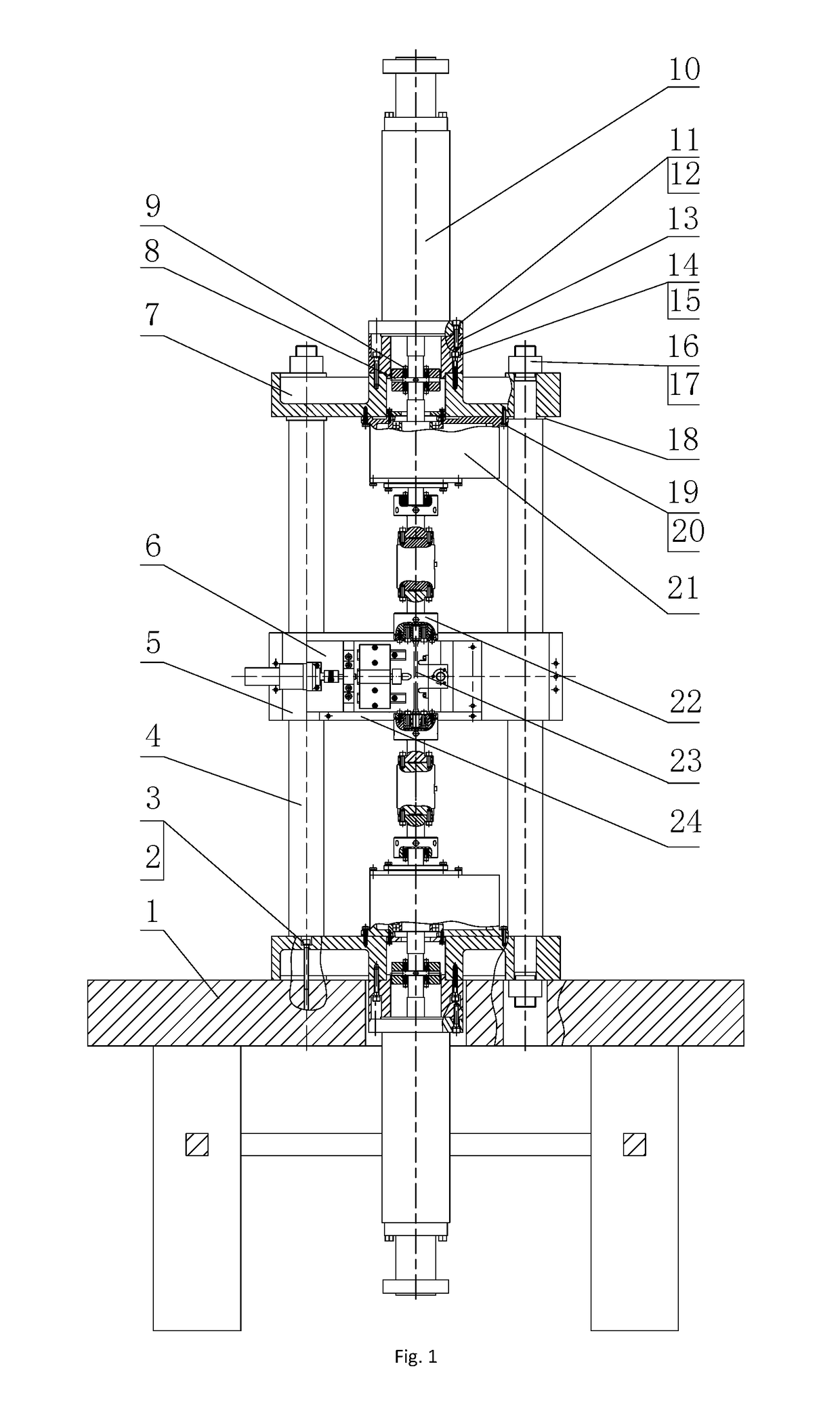
An in-situ testing equipment for testing micromechanical properties of a material in a multi-load and multi-physical field coupled condition is disclosed. The equipment comprises a frame supporting module, a tension / compression-low cycle fatigue module, a torsioning module (21), a three-point bending module (6), an impressing module (33), a thermal field and magnetic field application module (34), an in-situ observation module (32) and a clamp body module (22). The testing equipment is capable of realizing applications of five different types of loads including tension / compression, low cycle fatigue, torsion, bending and impressing, performing an intensive study on micromechanical properties of the material in the multi-load and multi-physical field coupled condition by using built-in electric, thermal and magnetic application modules and the in-situ observation module, and acquiring relations between deformation behavior, mechanism of damage, performance weakening of the material, applied loads and material properties.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
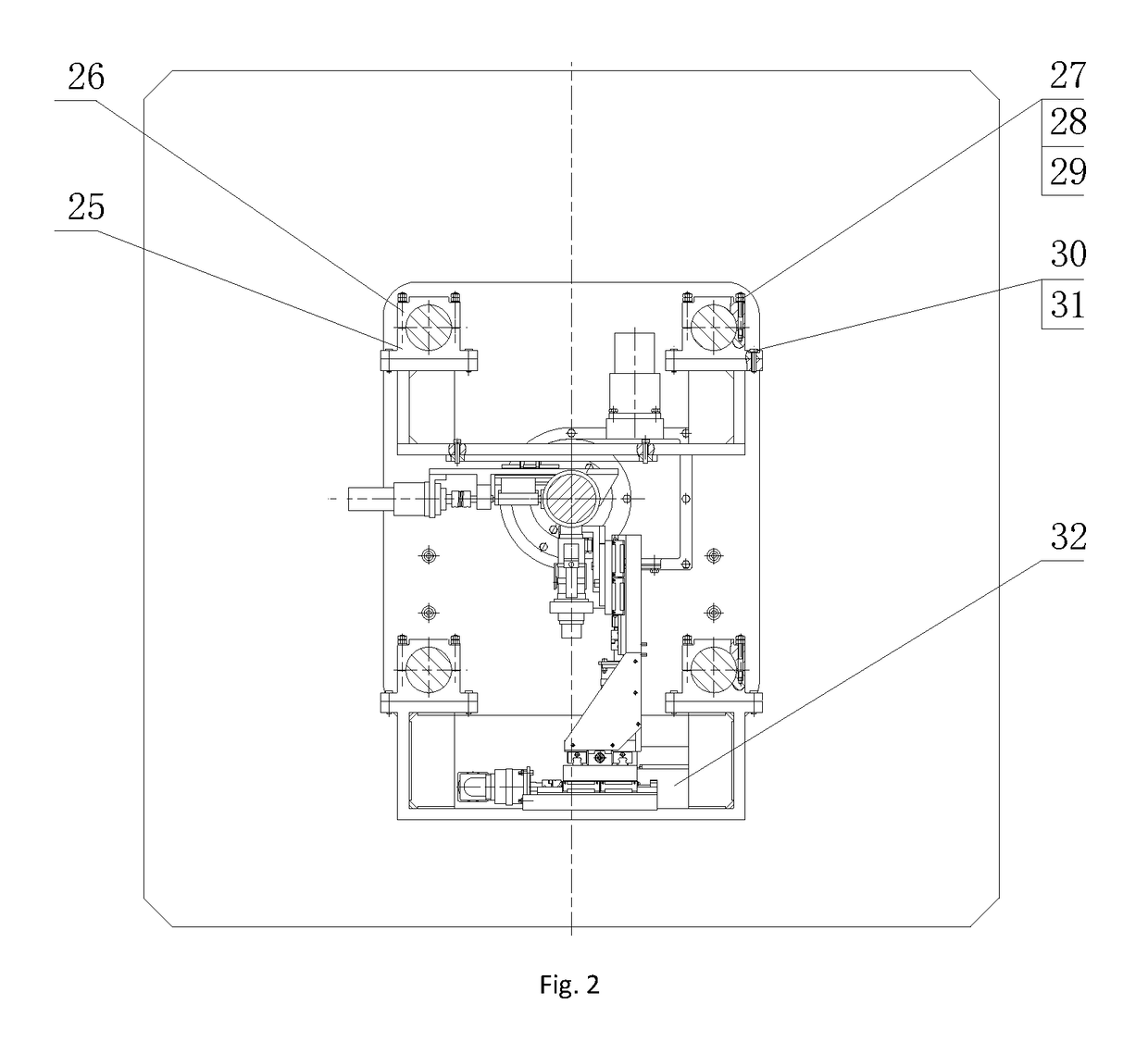
High fill compaction quality real-time evaluation method considering underlying surface influence
PendingCN111444560AImprove accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationPorosityQuality control
The invention belongs to the field of high fill engineering construction quality control. The objective of the invention is to realize comprehensive and real-time evaluation of the fill compaction quality under different underlying surface or boundary constraint conditions. According to the invention, the high fill compaction quality real-time evaluation method considering the underlying surface influence is provided; firstly, a compaction process real-time monitoring device is used for collecting rolling compaction parameters of a lower layer and an upper layer, and meanwhile, a PDA is used for collecting on-site test pit test results of the upper layer, and the on-site test pit test results comprise the water content w, the grading P and the compaction quality parameter compaction degreeD or the dry density rho or the porosity e which reflect the material property; secondly, a regression model of the compaction quality, the rolling compaction parameters, the material property parameters and the underlying surface, namely a fill compaction quality evaluation model considering the influence of the underlying surface is established; and finally, based on the model, the compaction quality of the corresponding position on the construction bin surface is calculatd by utilizing the rolling compaction parameters, the rolling wheel acceleration signals and the material property parameters which are acquired in real time. The method is mainly applied to high fill engineering construction quality control occasions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
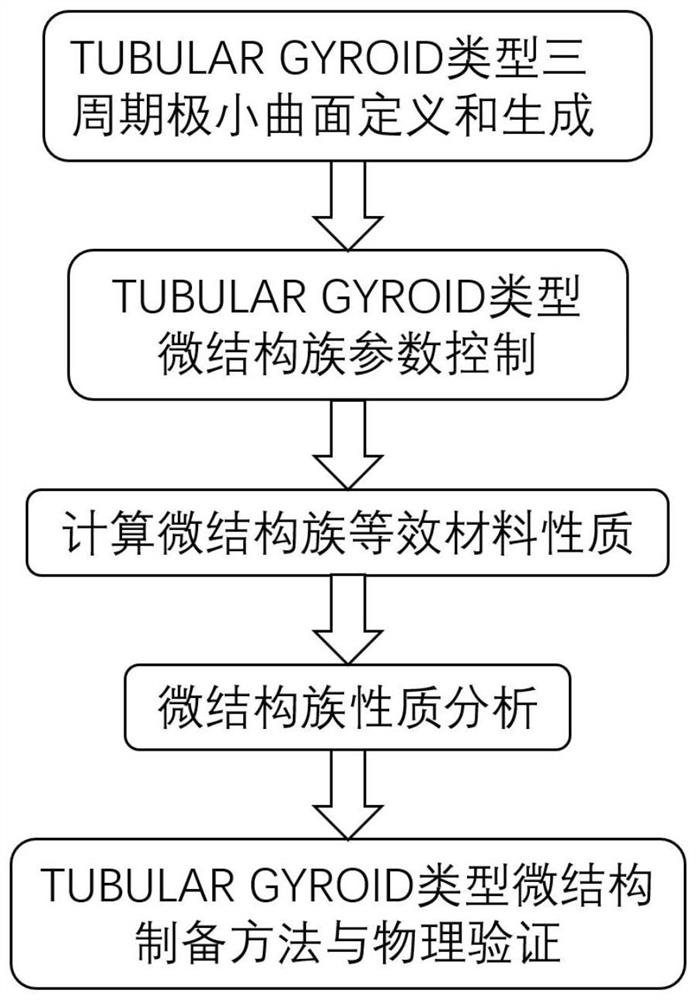
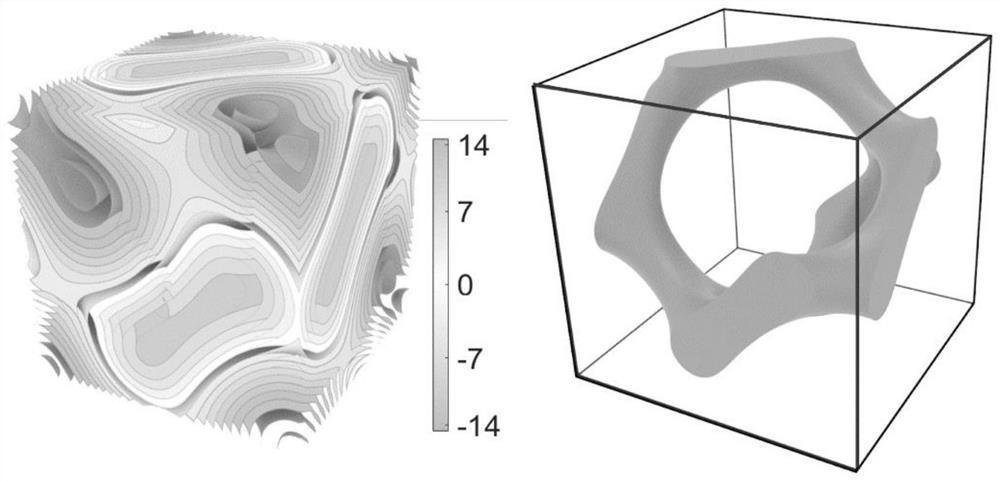
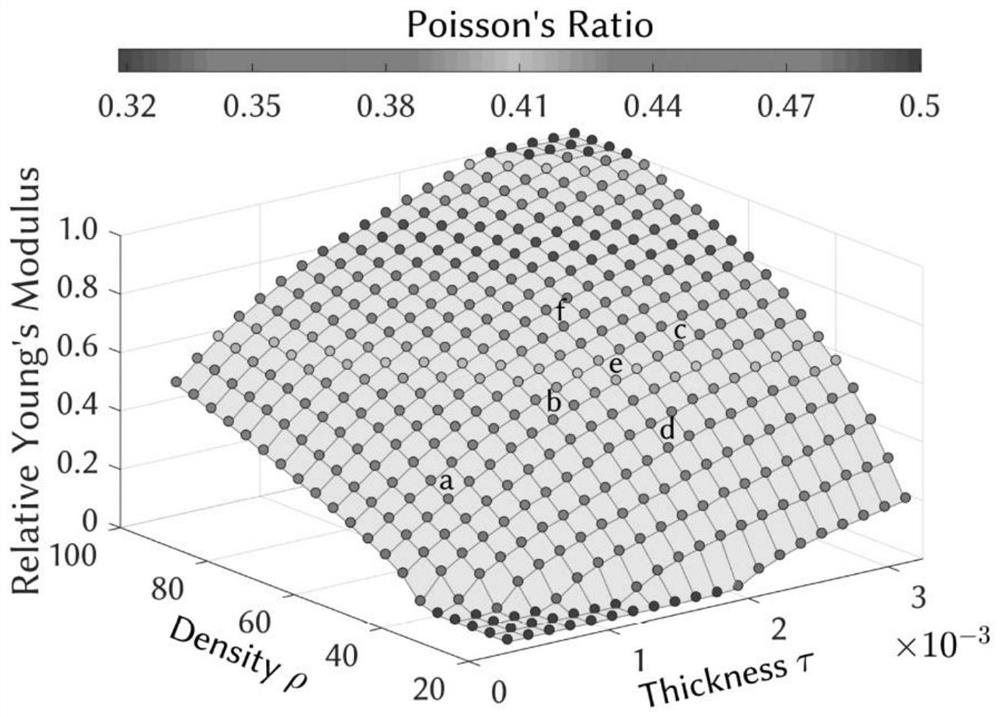
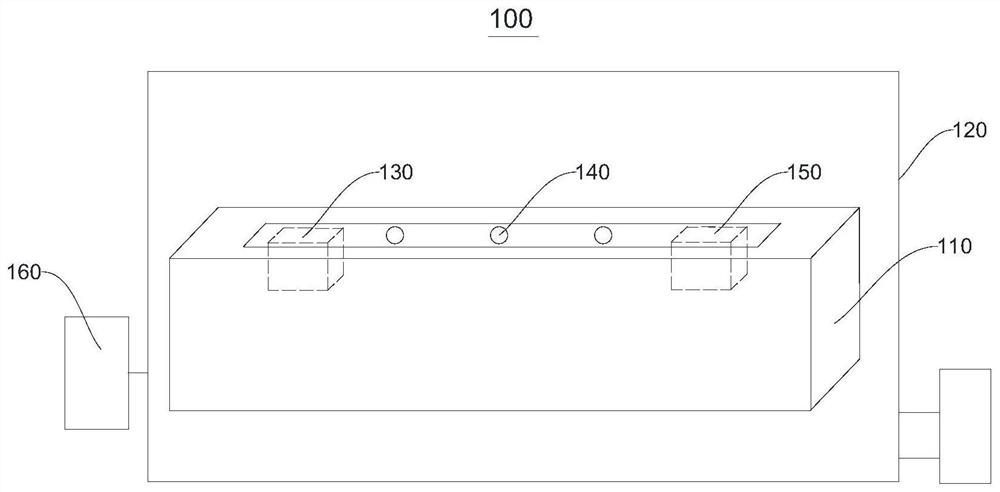
Calculation method of microstructure family equivalent material properties, microstructure, system and medium
PendingCN112395746AEfficient acquisitionImprove efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationGyroidVoxel
The invention belongs to the field of equivalent material property calculation, and provides a calculation method of microstructure family equivalent material properties and a system. The method for calculating the microstructure family equivalent material properties comprises the following steps: generating voxels in a unit space, and determining whether each voxel is filled or not according to aTUBULAR GYROID type three-period minimal curved surface so as to voxelize the three-period minimal curved surface; calculating homogenization by the unit displacement of the volume element and the global displacement field to form a matrix, wherein the homogenization matrix represents the attribute of the homogenization material corresponding to the current three-period minimum curved surface microstructure; and performing interpolation fitting on the homogenized material attribute result to obtain an interpolation function about density and thickness, and obtaining a Young modulus and a Poisson's ratio so as to guide the preparation of a TUBULAR GYROID type microstructure and print a corresponding model.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Device and method for testing heat-conducting property of thin film material
The invention provides a device and a method for testing the heat-conducting property of a thin-film material, and relates to the technical field of material property characterization. The thin film material heat-conducting property testing device comprises a testing platform, a heating element, a temperature measuring element and a cooling element. The thin film material heat-conducting property testing device is simple in structure and easy and convenient to operate, a temperature field which does not change along with time is established in a to-be-tested film material on a heat-insulating testing platform through the heating element and the cooling element, the to-be-tested film material reaches a one-dimensional steady-state conduction state, then the temperature gradient of the to-be-tested film material is measured through the temperature measuring element, and then the heat flow and the heat conductivity coefficient are calculated, and the test result precision is high.
Owner:NINGBO GRAPHENE INNOVATION CENT CO LTD
Device and method for measuring micro yield strength of composite material rod
InactiveCN111220477AReduce mistakesHigh precisionMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesThermal dilatationTemperature control
The invention provides a device for measuring the micro yield strength of a composite material rod. The device relates to the technical field of material performance testing, adopts a displacement sensor to perform non-contact length measurement, is free of abrasion, avoids influence of manual operation in a contact type length measuring process due to the fact that a probe does not apply a mechanical external force to a tested sample, is superior to 0.1 micrometer in length measuring precision, reaches dozens of nanometer magnitude, and is high in measuring precision. The device adopts a temperature control assembly to provide a stable thermal environment for the whole test system, reduces thermal expansion deformation of the sample due to environmental temperature fluctuation to the minimum, and reduces measurement errors to the minimum. The invention further provides a method for measuring micro yield strength of the composite material rod, and the method adopts the testing device for measurement. The device and the method for measuring the micro-yield strength of the composite material rod solve the technical problem that the bonding process and the environmental temperature fluctuation influence the measurement result in the prior art, and improve the measurement precision of the micro-yield strength of the composite material rod.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Analog device and method of material property testing
InactiveCN100538320CStudy friction and wear problemsImprove heating efficiencyAerodynamic testingInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceControl systemEngineering
The invention discloses a material performance test simulation device, which is used for the experimental simulation of stress oxidation ablation, high temperature connection, high temperature, high load and low speed friction and wear performance of materials under reentry atmosphere environment. Including the material mechanics testing machine (2), also includes the small atmospheric pressure subsonic gas flow wind tunnel (1), the servo transmission device (7) and the gas control system (8), the material mechanics testing machine (2) and the small atmospheric pressure subsonic The sonic gas flow wind tunnel (1) is placed vertically, the test piece (5) is placed in the test section of the small atmospheric pressure subsonic gas flow wind tunnel (1), and its shaft pin is fixedly connected with the servo transmission device (7). (7) Driven to rotate. The invention also discloses a method for simulating a material performance test by using the above-mentioned material performance test simulation device. A small atmospheric pressure subsonic gas flow wind tunnel, a material mechanics testing machine and a servo transmission device are used to realize the thermal physical and chemical environment of re-entry into the atmosphere, the aerodynamic Experimental simulation of load and rotational loads.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Dissimilar pipe joints under high temperature, high pressure transients and under cyclic loading
ActiveCN107110408BAvoid problems with joint descriptionsExtend your lifeFlanged jointsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingCouplingMetallic materials
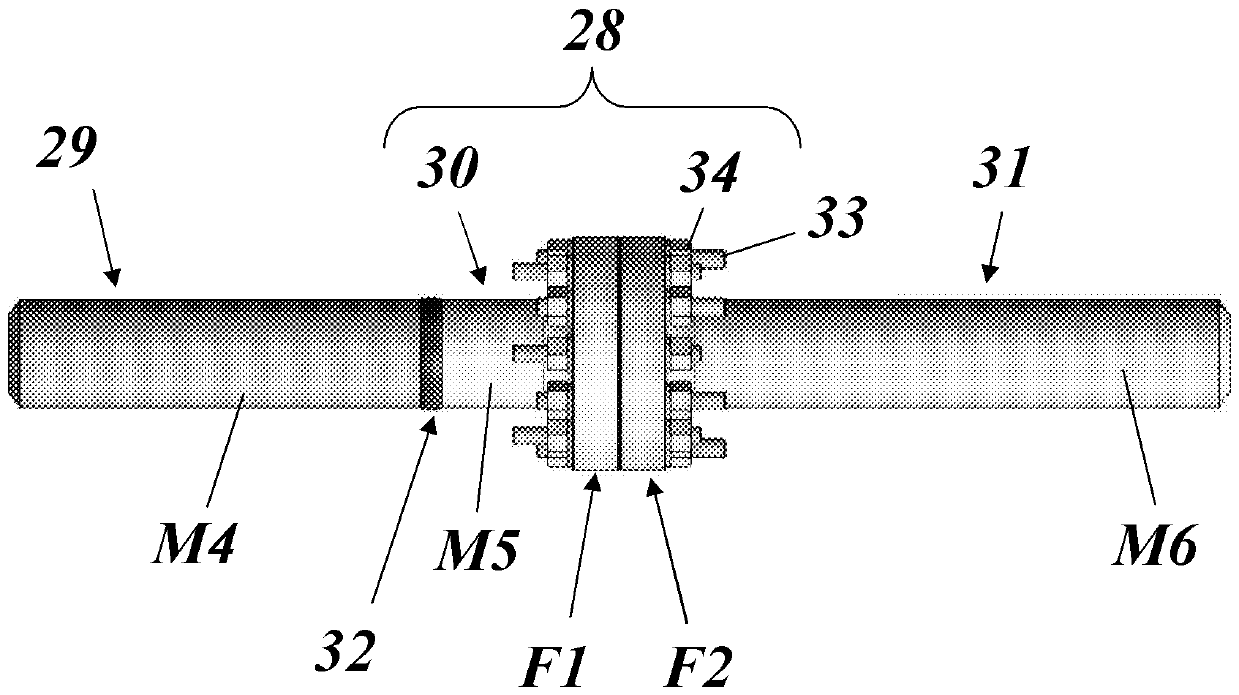
A dissimilar pipe joint arrangement (28) is described comprising a first pipe section (30) and a second pipe section (31), and a dissimilar pipe joint between the first pipe section and the second pipe section , the first and second continuous pipe sections (30, 31) are respectively made of first and second metallic materials (M5, M6) having different material characteristics and properties. Improved lifetime and extended applicability are achieved, wherein said dissimilar pipe joint (28) is a coupling joint (F1, F2), said first pipe section made of said first metallic material (M5) (30) At one end, there is a first coupling piece (F1) made of said first metal material (M5), said second pipe area made of said second metal material (M6) The segment (31) is provided at one end with a second coupling (F2) made of said second metallic material (M6), and the first coupling (F1) and the second coupling (F2) are bolted Together, whereby the first seal is established by direct metallic contact between the front faces of the first coupling ( F1 ) and the second coupling ( F2 ).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
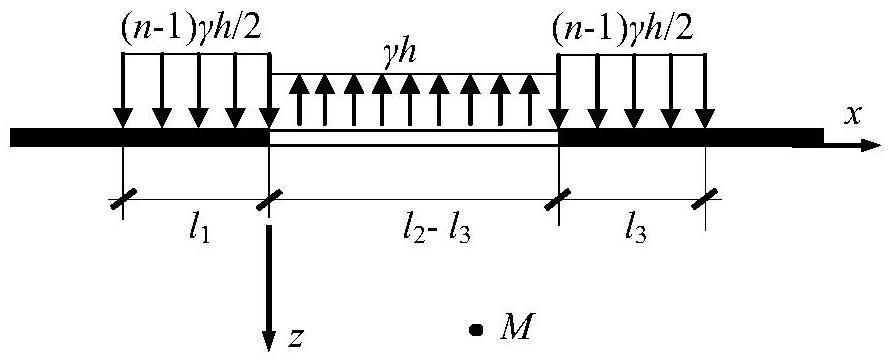
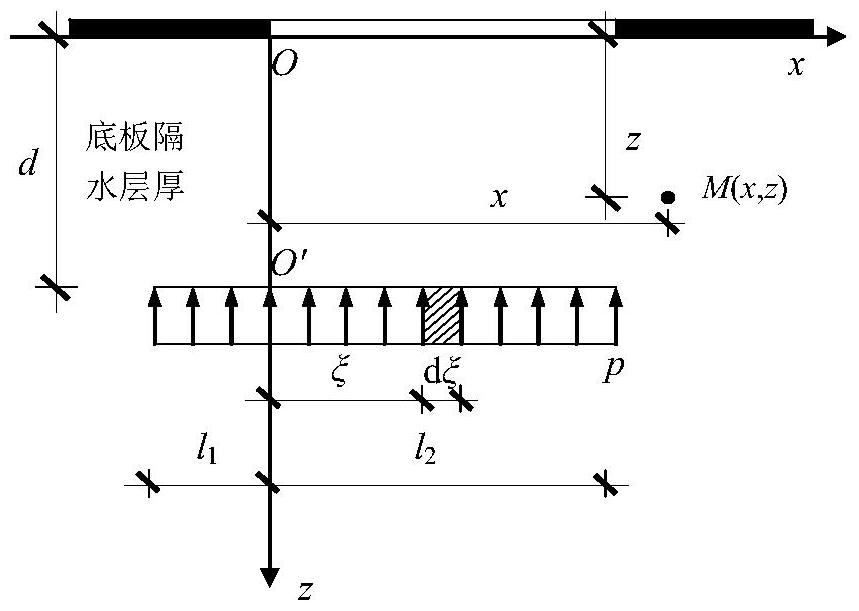
Calculation method of stope floor damage depth under the action of confined water pressure
The invention discloses a method for calculating the damage depth of the stope floor under the action of the confined water pressure, which comprises the following steps: 1) selecting the calculation range of the model; 2) defining the action ranges and loads of the supporting pressure and the water pressure of the floor distribution form; 3) Define the material properties of the floor rock mass within the calculation range; 4) Set the floor stress component to be the superposition of the additional stress caused by the mine pressure and water pressure and the original rock stress; 5) According to the elastic half-space theory Fu Laman solution and Mindlin’s solution deduced the additional stress components of the floor under the action of support pressure and water pressure; 6) According to the results of the stress solution, the mohr-coulomb criterion with tensile yield was selected to calculate the depth of floor failure, and the shear and Depth and extent of tensile failure. Compared with the existing analytical solution method, the present invention considers the effect of the bottom plate's confined water pressure, which is more in line with the actual situation.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of measuring method of uranium isotope ratio
ActiveCN109900771BShort cycleImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDerived DataUranium
The invention belongs to the technical field of material property determination, and in particular relates to a method for determining a uranium isotope ratio. The present invention includes the following steps: Step 1. Heating up: applying current to make the ionization zone and evaporation zone and the temperature of the evaporation zone where the ion current intensity of the control sample is less than 100mV; Step 2. Adjusting the focusing parameters: adjusting the focusing parameters at a low evaporation zone temperature , to stabilize the sample peak platform; Step 3. Data collection: refer to the pre-evaporation heating rate to raise the temperature of the evaporation zone to the set test ion current intensity; Step 4. Data fitting; Step 5. Data derivation: use the fitting result The equation calculates the data for 1-2 cycles; Step 6. Selection of the starting point of the derived data; Step 7. Calculation of the result: Calculate the mean value of the data between the starting point of fractionation correction and the end point of the calculation. The invention can solve the problem that the mass fractionation effect of the existing conventional measurement methods is inconsistent, and it is difficult to perform external standard correction, and the pervaporation method has good consistency of the mass fractionation effect, but the measurement process takes too long.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
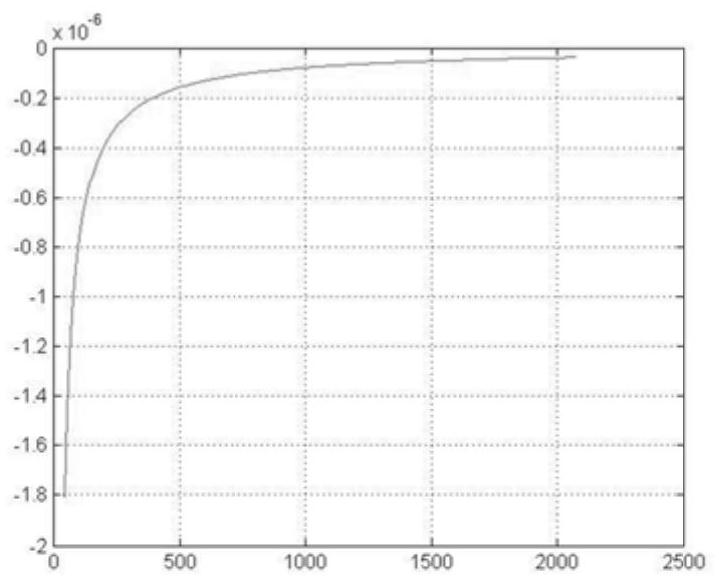
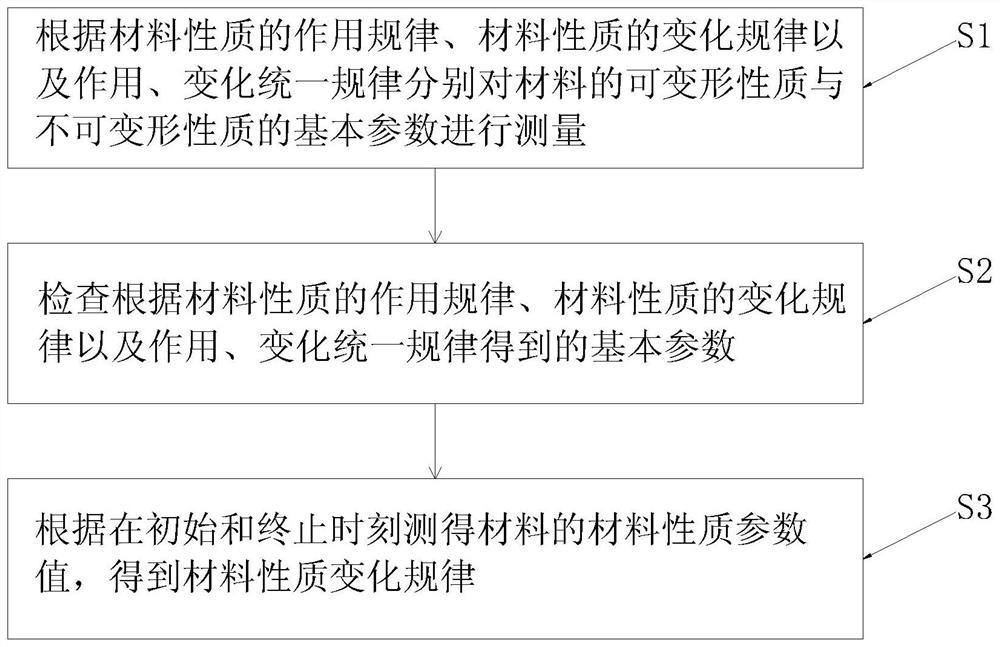
Material property testing method and testing device thereof
PendingCN114199678AMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringStructural engineering
The invention discloses a material property testing method and a testing device thereof. The method comprises the following steps: respectively measuring basic parameters of deformable property and non-deformable property of a material according to an action rule of the material property, a change rule of the material property and a unified rule of action and change; basic parameters obtained according to the action rule of the material properties, the change rule of the material properties and the unified rule of action and change are checked; and obtaining a material property change rule according to the material property parameter values of the material measured at the initial moment and the termination moment. The invention provides a new theoretical formula for researching the problems of material deformation resistance strength and material virtuality or compactness and a new scientific method determined by the new theoretical formula, so that the problem that application mechanics lacks a theoretical formula for researching material properties and ultimate bearing capacity and an experimental analysis calculation method is solved; a new space in the field of material property experimental test research is developed, and convenience is brought to material property test and scientific prediction.
Owner:王昌益
Method for non-intrusively determining the temperature of a fluid flowing through a conduit portion
ActiveCN111801556AThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsVolume/mass flow measurementMechanical engineeringMechanics
The invention relates to a method for determining the temperature of a fluid (12) flowing through a conduit portion (11), wherein: - the temperature of the conduit portion (11) is ascertained; a reference temperature at a distance (13) from a surface (14) of the conduit portion (11) is detected; - the heat-transfer behaviour, in particular the thermal resistance, of a boundary layer (15) of the fluid (12) at an inner wall (16) of the conduit portion (11) is determined on the basis of at least one material property and at least one value of a state variable of the fluid (12); and - the temperature of the fluid (12) is determined on the basis of the heat-transfer behaviour of the boundary layer (15), the heat-transfer behaviour, in particular the thermal resistance, of the conduit portion (11), the temperature of the conduit portion (11), and the reference temperature.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
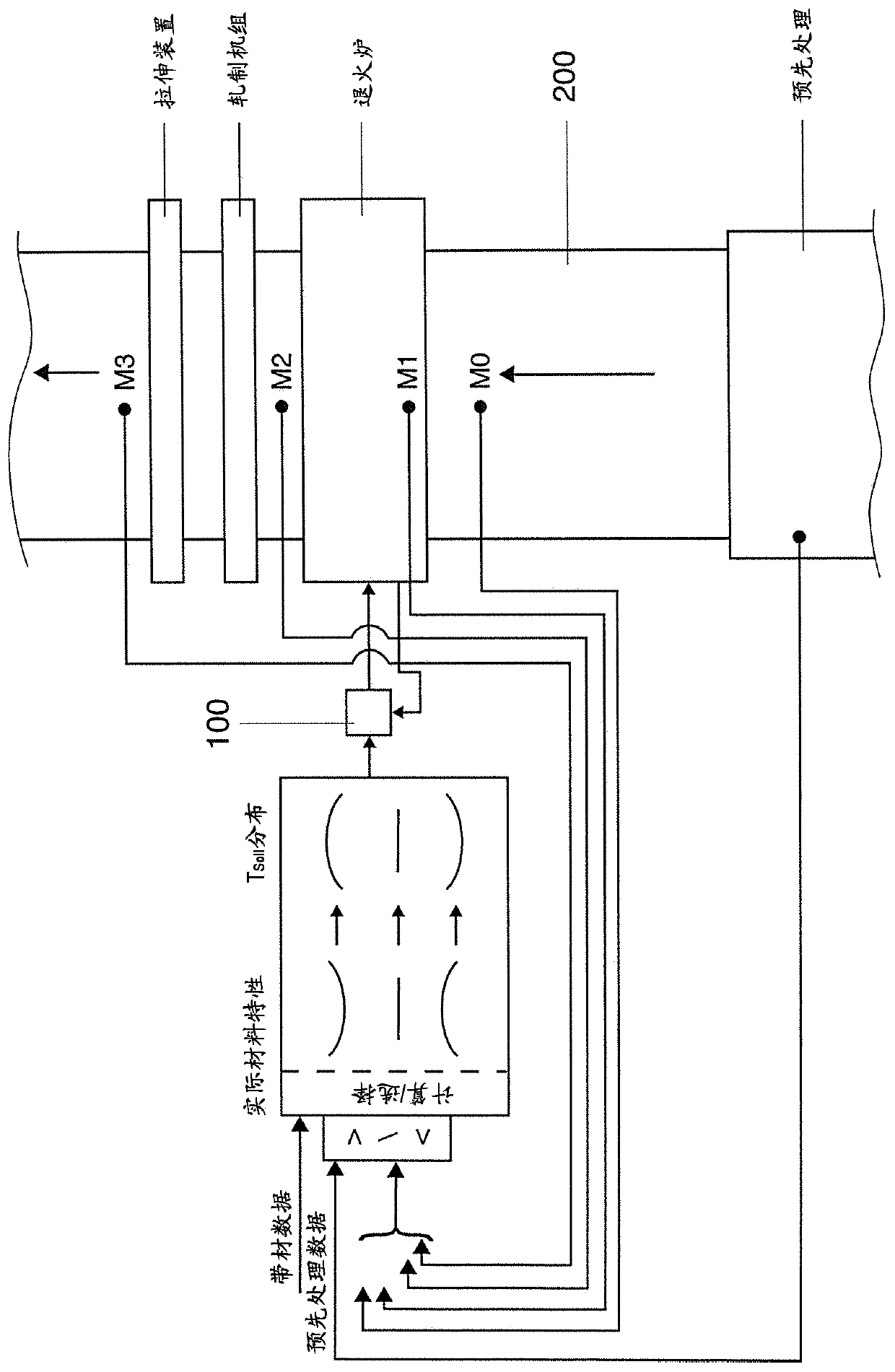
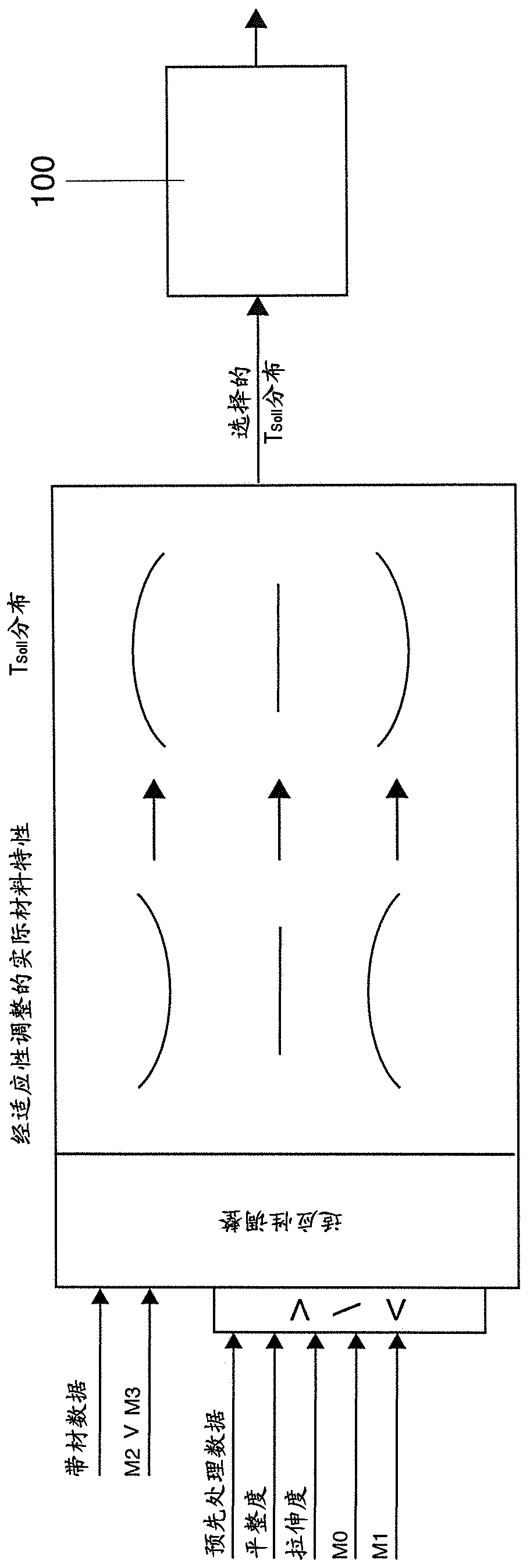
Method for operating an annealing furnace for annealing metal strip
ActiveCN109563559BCompensation for fluctuations in material propertiesAccurate distributionFurnace typesControl devices for furnacesMetal stripsMaterial properties
Owner:SMS GRP GMBH
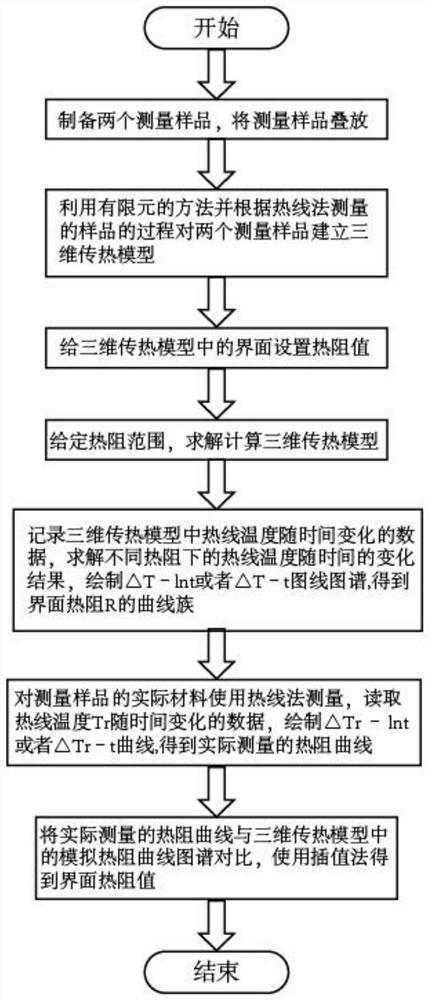
A Method of Measuring Interface Thermal Resistance Between Two Solids Using Hot Wire Method
ActiveCN108535313BFast measurementAccurateMaterial heat developmentEngineeringInterfacial thermal resistance
The invention discloses a method for measuring the thermal resistance of an interface between two solids by using a hot wire method. The material properties are assigned to the calculation model, and the interface in the model is set to have thermal resistance; (4) Given the range of thermal resistance values, traverse all the thermal resistance values R to solve the calculation model; (5) Draw the interface thermal resistance of the three-dimensional heat transfer model R curve family; (6) use the hot wire method to measure the actual material, and draw the actual measured thermal resistance curve; (7) compare the actual thermal resistance curve with the standard thermal resistance curve, and the range of the actual thermal resistance can be obtained . The interface thermal resistance can be measured more accurately, the cost of measuring the interface thermal resistance is reduced, the measurement time is reduced, and the rate of measuring the interface thermal resistance is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
System and method for real time closed-loop monitoring and control of material properties in thermal material processing
The disclosure is directed at a method and apparatus for integrated real-time monitoring and control of microstructure and / or geometry in thermal material processing (TMP) technologies. The method includes obtaining real-time thermal dynamic variables, such as, but not limited to the cooling rate, peak temperature and heating rate, and geometry of the thermal material process. These real-time thermal variables are then analyzed along with a thermal model to determine a microstructure / geometry model. This microstructure / geometry model can then be used to provide the real-time monitoring and control of a finished state for the material being processed by the thermal material processing procedure.
Owner:KHAJEPOUR AMIR +2
A Macroscopic and Mesoscopic Numerical Analysis Method of Explosive Cook-off
ActiveCN112818575BHigh precisionAccurate temperatureSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationExplosive AgentsEngineering
The invention discloses a macroscopic and microscopic numerical analysis method of explosive cook-off. Firstly, a three-dimensional macroscopic numerical calculation model of the cook-off test object is established; temperature boundary conditions, material properties of the cook-off test object and self-heating reaction source items are assigned to The three-dimensional macroscopic numerical calculation model performs numerical calculation; the mesoscopic numerical analysis area is selected at the macroscopic ignition position, and the temperature boundary conditions and the material properties of the cook-off test object are assigned to the three-dimensional macroscopic numerical calculation model to perform numerical calculation again and extract the mesoscopic values Analyze the boundary temperature of the region only under the effect of heat conduction; establish a three-dimensional von Lonei diagram mesoscopic numerical calculation model, and use the boundary temperature as the temperature boundary condition of the mesoscopic numerical calculation model; The thermal reaction source term is respectively assigned to the corresponding explosive component regions in the mesoscopic numerical calculation model, and the temperature distribution of each explosive component and the explosive component that first responds to ignition are obtained through numerical calculation.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
A processing method based on anisotropic homogenization of multiple isotropic materials
ActiveCN112578082BImprove accuracyImprove the efficiency of reliability testingMaterial thermal coefficient of expansionMaterial thermal conductivityBi-isotropic materialEngineering
The invention provides a processing method based on anisotropic homogenization of multiple isotropic materials, specifically selecting an equivalent volume element reasonably in a multi-embedded area of a complex structure, and each material in the volume element is an isotropic material , the equivalent volume element is a new structure, and the specific parameters of the structure in various directions can be reacquired through experiments or simulations. Specifically, it can be summarized as applying force / heat loads to this volume element, and collecting the equivalent volume element ( The displacement / heat / force result data of RVE) can be calculated by the formula to obtain the anisotropic material properties of the equivalent volume element. The invention solves the problems that the equivalent volume method ignores the anisotropy of the whole module in different directions, which leads to large deviations in experimental values and cannot simplify the processing of multi-layer nested packaging structures / materials in microelectronic products, and greatly improves the experimental value. The accuracy of the value can effectively improve the efficiency of reliability testing of microelectronic products and simplify the workflow.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
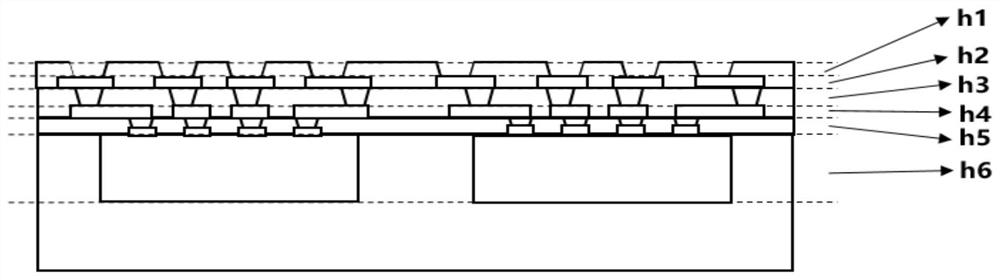
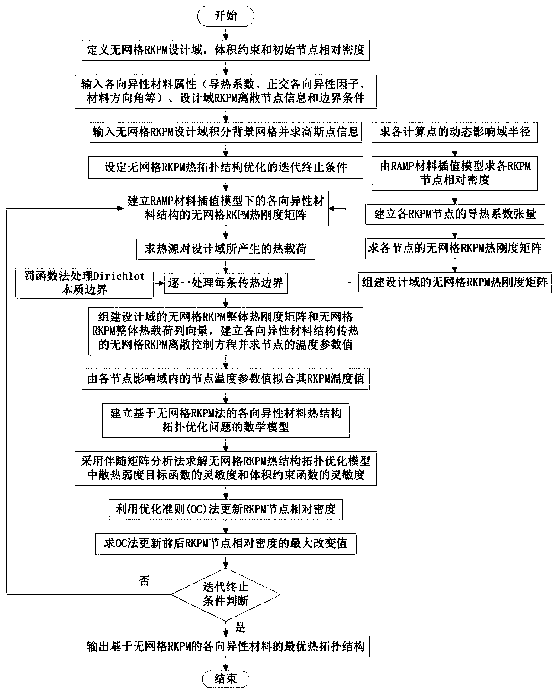
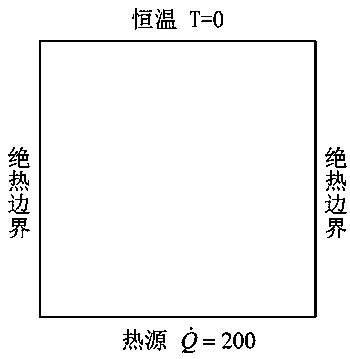
Topology optimization method for thermal structure of anisotropic materials based on meshless rkpm
ActiveCN106845021BImprove reliabilityFlexible handlingDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical stabilityGauss point
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
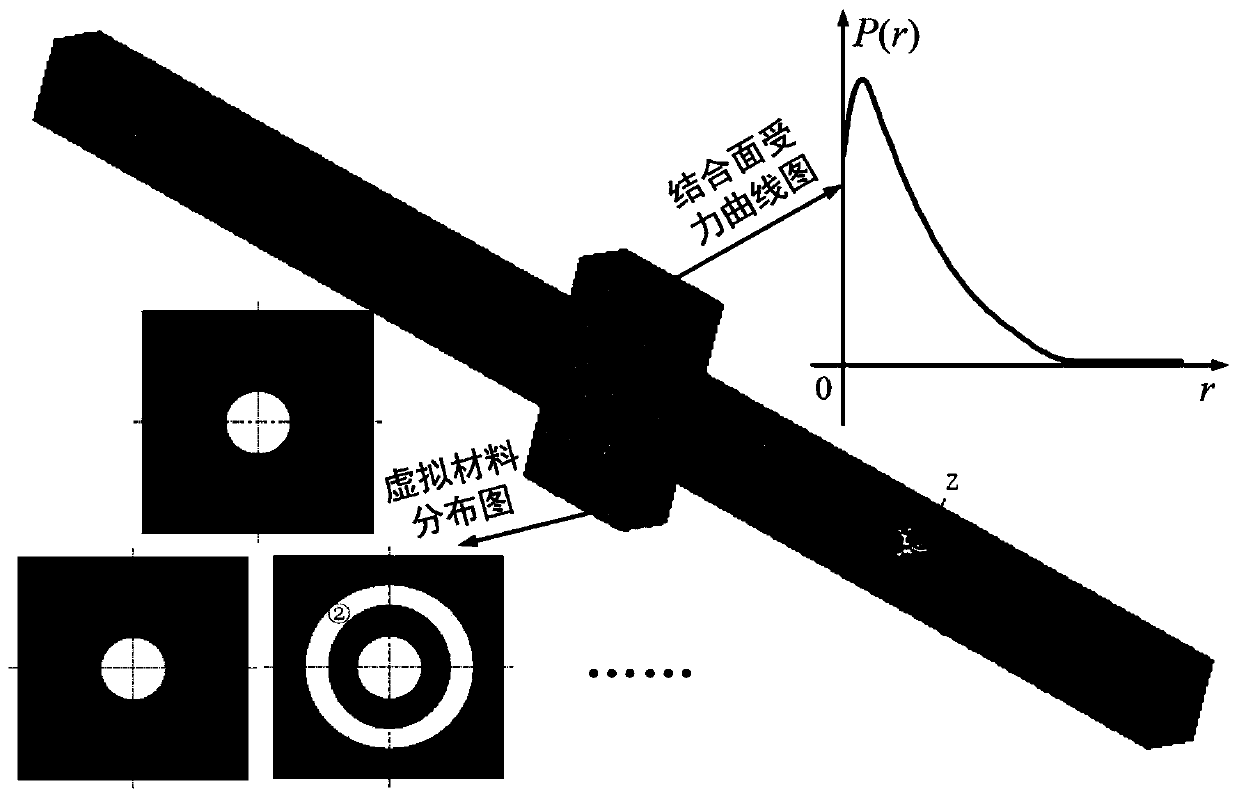
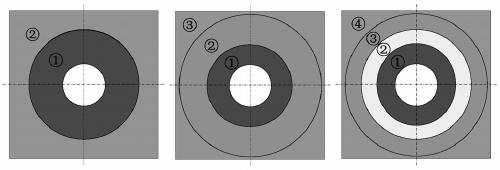
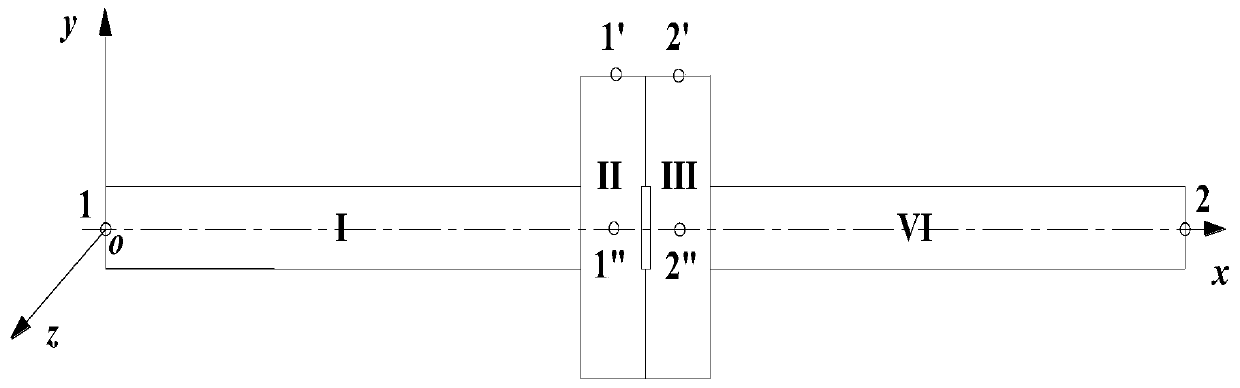
A METHOD OF DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS USING VIRTUAL MATERIAL EQUIVALENT BOLTED JOINTS
ActiveCN107491624BHigh precisionVerify correctnessGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelContact pressure
The invention discloses a method for utilizing a virtual material to perform equivalence of dynamic characteristic of a bolting joint part. The bolting joint part is regarded as a plurality of virtual material layers, a finite element method is utilized to simulate stress conditions of different of bolting joint part at the contact areas under different bolt pretightening forces, and the contact pressure distribution of the bolting joint part is equivalent to be a fourth-order polynomial function with respect to the contact radius; an equivalent virtual material model of the bolting joint part is established by utilizing material mechanics knowledge, to determine a function relationship between the contact radius in an effective contact area and virtual material properties (elastic modulus, shear modulus, Poisson's ratio, density and virtual layer thickness); by the finite element method, two-layer, three-layer or more-layer virtual materials coupled with each substructure to establish a finite element model of the whole structure, and dynamic response analysis is performed, an obtained frequency response function is compared with modal test data to verify the correctness of the model, and the novel idea and method are provided for studying the dynamic characteristics of the bolting joint part.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
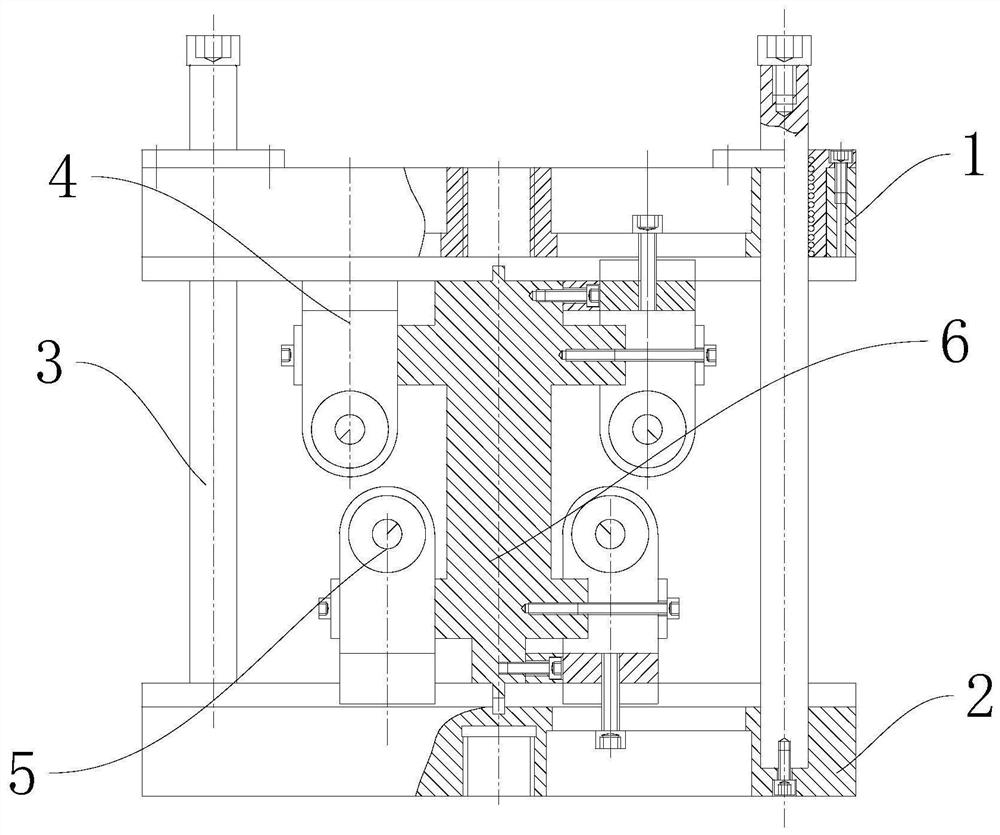
Device and method for measuring out-of-plane tensile mechanical property of composite material
ActiveCN113514333AStrong heat resistanceImprove rigidityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesPortal frameMechanical property
The invention discloses a device and a method for measuring out-of-plane tensile mechanical properties of a composite material, and belongs to the technical field of material performance detection. The device and method for measuring the out-of-plane tensile mechanical properties of the composite material comprises an upper beam and a lower beam, the lower beam is arranged at the bottom end of a device body, the upper beam and the lower beam are connected with guide columns, the bottom ends of the guide columns are fixedly connected with the lower beam, and the upper beam is connected to the guide columns in a sliding fit mode; the lower end of the upper beam is connected with a portal frame upper compression roller assembly, the upper end of the lower beam is connected with a portal frame lower compression roller assembly, and an accessory distance frame assembly is connected between the portal frame upper compression roller assembly and the portal frame lower compression roller assembly; and the problems that a metal clamp is low in rigidity and poor in centering performance at high temperature, and thermal stress matching exists between a compression roller and a sample are solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
A Method for Calculating the Temperature of Materials Bombarded by Ion Beams Using Computer Simulation
InactiveCN106951608BAvoid record analysisReduce processingDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsThermodynamic simulationNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a method for calculating the temperature of a material by ion beams through utilizing computer simulation, and aims to overcome the defect of inconvenience of measuring the temperature of the bombarded material through an artificial experiment. By utilizing a computer simulation technology, through thermodynamics simulation analysis, a curve, changed with time, of the temperature of the material bombarded by the ion beams is subjected to analog simulation, so that the temperature curve of the bombarded material can be obtained only by changing parameters of the bombarded material in practical use. According to the method, a conventional mode of measuring the temperature of the material bombarded by the ion beams through the experiment is changed; technical staffs are freed from the tedious actual temperature measurement experiment; preparation of actual temperature measurement experiments, recording and analysis of experiment data and processing of later experiment data are avoided; the working efficiency of scientific and research personnel in researching various material properties by utilizing the ion beams is greatly improved; and a space of prevention in advance can be provided for adverse conditions caused by increased temperature of the bombarded material more conveniently.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ASTRONOMICAL OPTICS & TECH NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSE
Action-logy method of material property measurement and measurement instrument therefor
InactiveCN105842079AEasy to measureFill in the Science Questions of the CenturyMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesResearch resultApplied mechanics
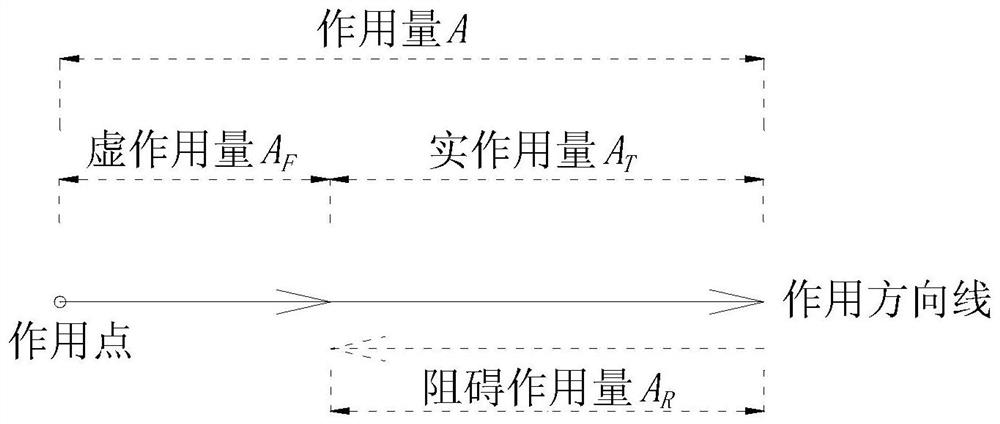
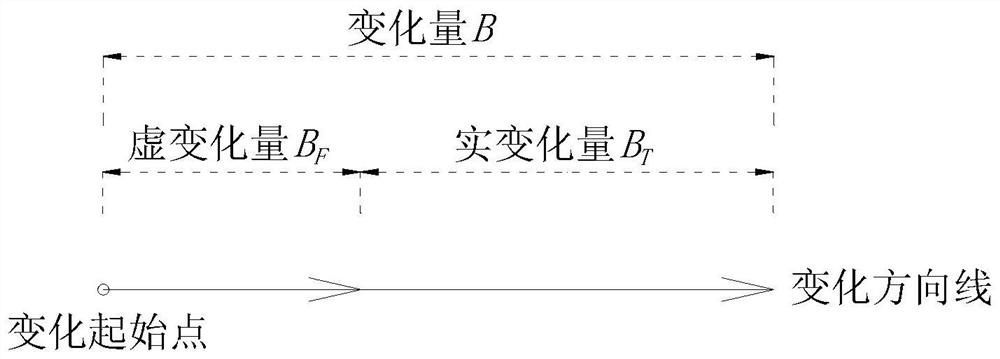
The invention relates to an action science method for measuring material properties and a measuring instrument thereof, belonging to the research fields of theoretical mechanics, applied mechanics and experimental mechanics. According to the theory of action, the deformation is not only related to the size of the force, but also related to the size of the action, and the basic law equation for studying the deformation is obtained as It can be obtained by measuring the value of each parameter: the general relationship law of stress-strain relationship, the unified relationship law between ultimate stress and stress, solidity, and void, the maximum action that the material can resist without deformation within a certain time limit, and the solidity of the material The value research method of the sum of emptiness and its change law, emptiness and solidity. The beneficial effects of the present invention are: based on the functional theory, a new theory and a new formula for the study of material variable strength and void or solidity are given; a new theory of the relationship between material strength, action stress and material solidity is used And new methods, suitable for solving various material strength tests, calculations and evaluation problems of various material properties.
Owner:王昌益
A device and method for measuring out-of-plane tensile mechanical properties of composite materials
ActiveCN113514333BStrong heat resistanceImprove rigidityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringStructural engineering
The invention discloses a device and a method for measuring out-of-plane tensile mechanical properties of composite materials, belonging to the technical field of material property detection. A device and method for measuring out-of-plane tensile mechanical properties of composite materials, comprising an upper beam and a lower beam, the lower beam is arranged at the bottom end of the device body, and a guide column is connected to the upper beam and the lower beam , the bottom end of the guide column is fixedly connected with the lower beam, the upper beam is slidably connected to the guide column; the lower end of the upper beam is connected with a gantry frame upper pressing roller assembly, and the upper end of the lower beam is connected with a gantry frame The lower pressing roller assembly, the attachment spacer frame assembly is connected between the gantry upper pressing roller assembly and the gantry lower pressing roller assembly; the invention solves the problem of low rigidity and poor neutrality of the metal fixture under high temperature , the thermal stress matching between the pressure roller and the sample, etc.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
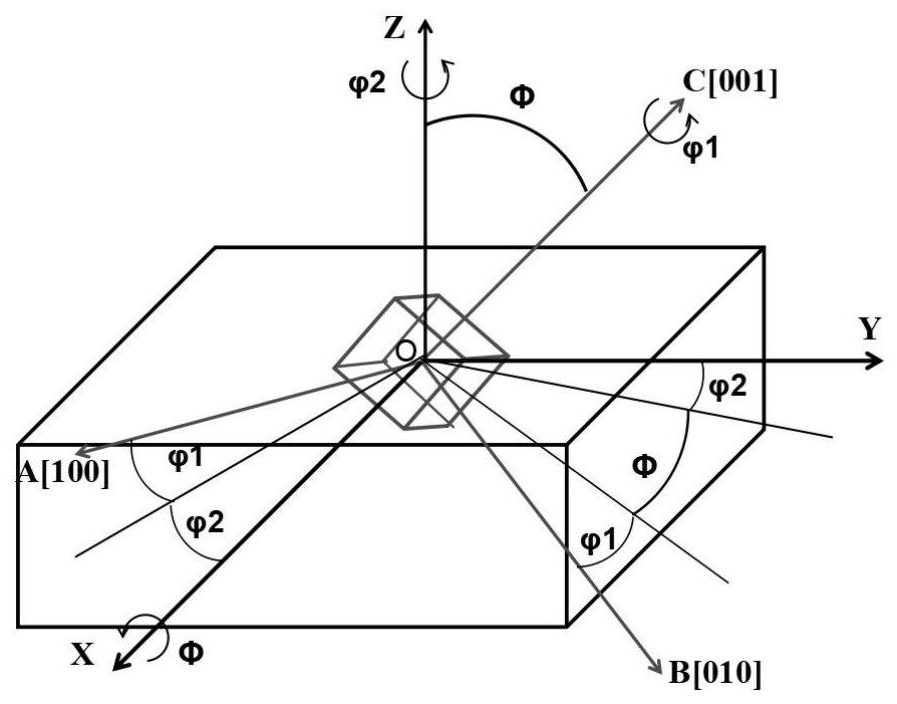
A method for quickly displaying the distribution characteristics of specific crystal planes in polycrystalline materials
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for quickly presenting the distribution characteristics of specific crystal planes of polycrystalline materials. This method has high efficiency, low cost, simple operation, and can accurately present the characteristics of multiple specific crystal plane orientations inside the polycrystalline material. The present invention mainly includes the steps of EBSD sample preparation, electron backscattering diffraction analysis technology to collect sample surface information, data processing and specific crystal face presentation; the present invention can be used for research on grain size, distribution and orientation relationship under specific crystal face characteristics , such as the study of the genetic orientation phenomenon of alloy materials during heat treatment and thermal processing; secondly, it can be used to explore the relationship between the oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance of materials and the distribution characteristics of specific crystal planes on the surface of materials; in addition, it can also be used to quantitatively study the The joint effects of different crystal planes and multiple specific crystal planes on material properties are used to guide the formulation of reasonable heat treatment and processing technology in actual production, so as to fully exert or improve the service performance of materials.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
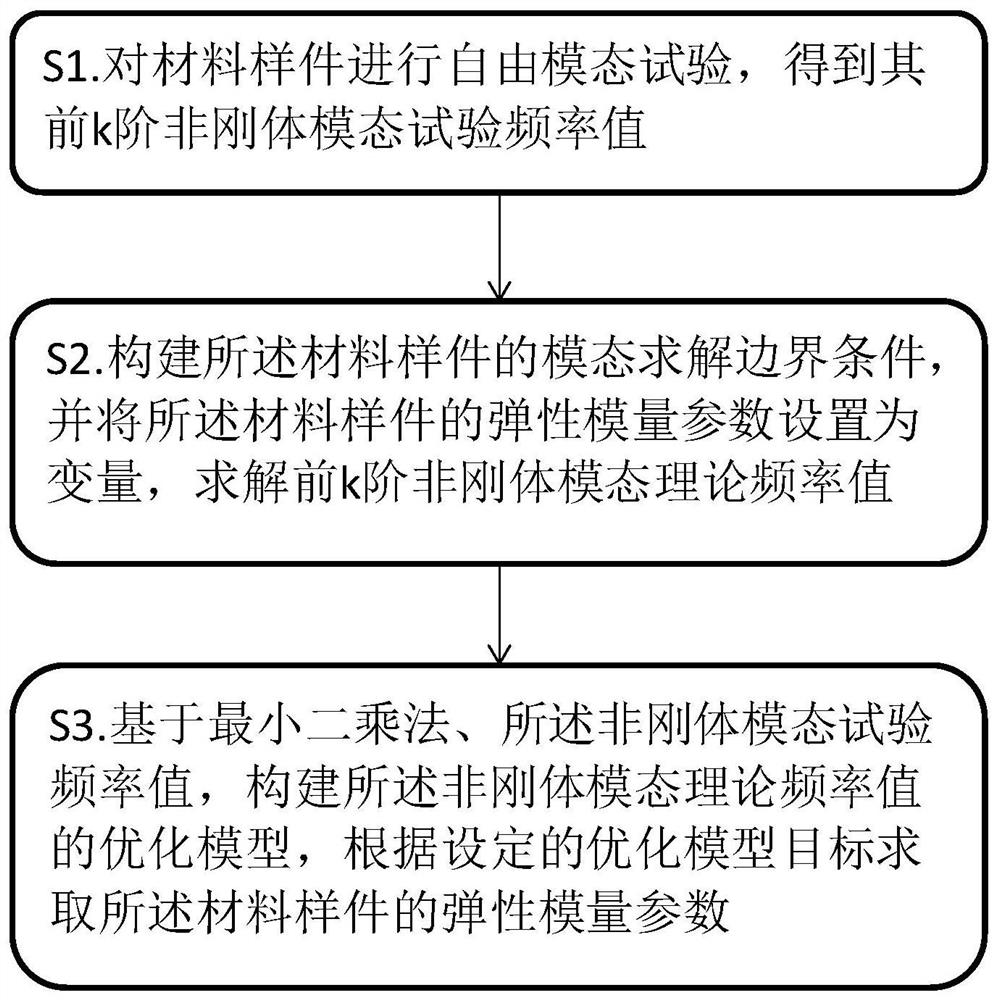
Method for solving material elastic modulus parameter based on least square method
PendingCN112861404ALow costDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsNoise, vibration, and harshnessAlgorithm
The invention relates to the field of NVH (Noise Vibration and Harshness) materials, and particularly discloses a method for solving a material elastic modulus parameter based on a least square method, which comprises the following steps of: performing a free modal test on a material sample to obtain a first k-order non-rigid modal test frequency value; constructing a modal solution boundary condition of the material sample, setting an elastic modulus parameter of the material sample as a variable, and solving a first k-order non-rigid modal theoretical frequency value; and based on a least square method and the non-rigid modal test frequency value, constructing an optimization model of the non-rigid modal theoretical frequency value, and solving an elastic modulus parameter of the material sample according to a set optimization model target. According to the method, the elastic modulus parameter of the material sample is solved by combining the modal test and the finite element analysis, so that special material performance testing equipment can be avoided, and the cost is saved; moreover, the scheme constructs the optimization model based on the least square method, and has the advantages of high fitting degree and easy implementation, so that the accuracy of the solved elastic modulus parameter is relatively high, and the solving process is simple.
Owner:CHINA AUTOMOTIVE ENG RES INST
Method for rolling and/or heat treating metal products
ActiveCN108779508BMonitor qualityReduce manufacturing costProgramme controlHot-dipping/immersion processesMechanical engineeringMaterial properties
Owner:SMS GRP GMBH
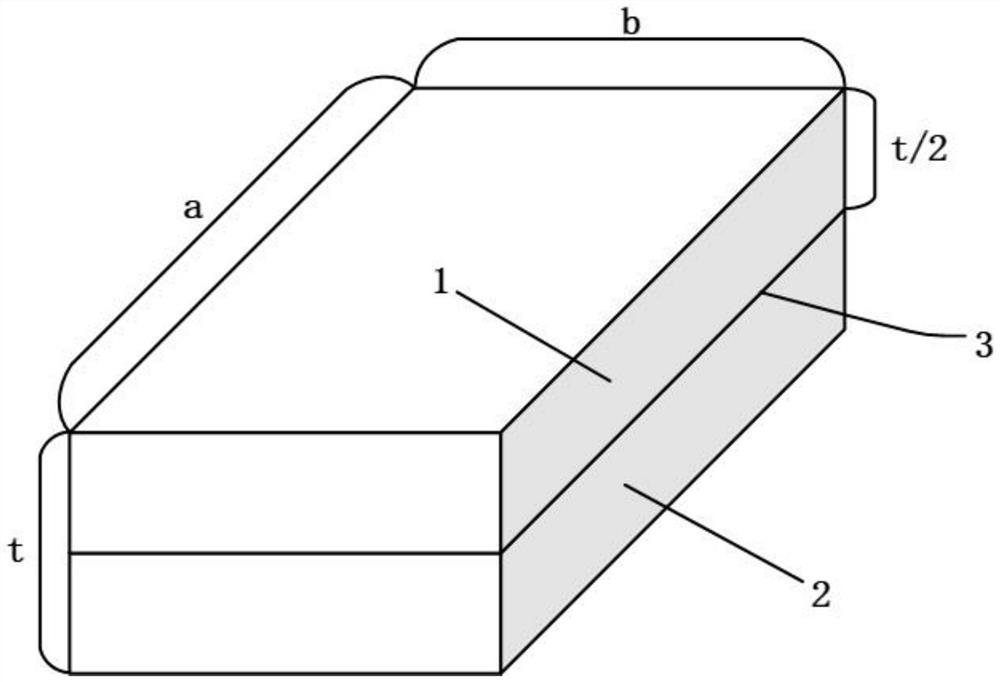
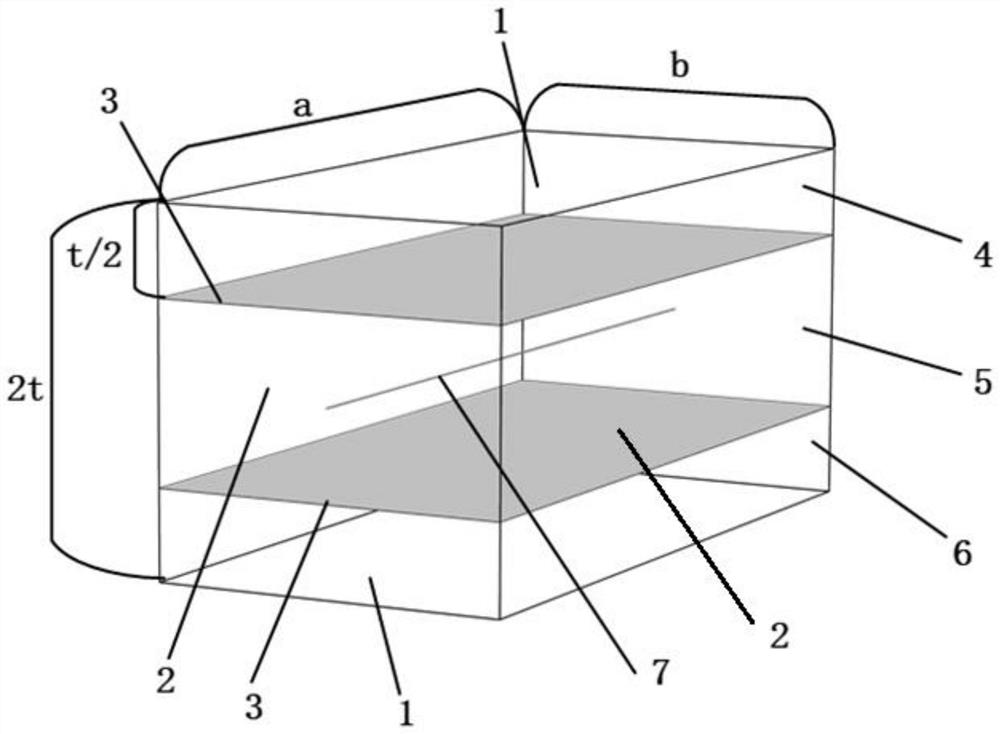
A heterogeneous material gradient structure connection joint and its preparation method
ActiveCN113280022BOverrealizedAvoid mutationAdditive manufacturing apparatusSecuring devicesStructural engineeringUltimate tensile strength
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
System for researching rapid cooling and rapid heating properties of material
The invention discloses a system for researching rapid cooling and rapid heating properties of a material, and relates to the technical field of material property testing. The system for studying the rapid cooling and rapid heating properties of the material comprises a testing mechanism, a heating mechanism and a cooling mechanism are arranged on the testing mechanism, and the testing mechanism comprises a supporting frame, an electric appliance box fixed to the lower portion of the supporting frame, a transformer arranged in the electric appliance box and a control screen fixed to the supporting frame. Through the structures such as the heating box, the silicon molybdenum rod and the preheating assembly, materials can be rapidly heated, the materials can be rapidly cooled through the arranged draught fan, the materials can be rapidly switched between the heating state and the cooling state by starting an electric lifting column to move up and down, repeated rapid cooling and rapid heating operation can be conveniently carried out on the materials, and the heating efficiency of the materials is improved. Various tests such as thermo-oxidative aging and thermal shock circulation can be carried out on materials, the number of circulation times of rapid cooling and rapid heating can be set through the control screen, and continuous operation is carried out.
Owner:合肥科晶材料技术有限公司
A comprehensive performance test platform for composite shaft tension, compression, bending, torsion, and vibration
InactiveCN108982212BEasy to operateHighly integratedAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFlexural torsionalCurrent technology
The invention discloses a comprehensive performance testing platform for composite shaft tension, compression, bending, torsion and vibration, which includes a tension and compression unit, a bending unit, a torsion unit, and a vibration unit; the fixed end of the clamping device is fixed on the workbench; the invention integrates The static test of three single loads of tension, compression, bending, and torsion and the multi-load composite loading are integrated, and the rotation movement can be realized under any combination of tension, compression, bending, and torsion, so as to perform vibration tests and simulate the differences in actual production. Working conditions, the load space coupling model of composite load loading is established, which provides an effective test platform for studying the influence of various loads on material properties and the variation rules of other performance parameters, and promotes the research on actual complex working conditions to a certain extent. The exploration of the deformation and damage mechanism of materials solves the problems of complex operation and poor compatibility in current technology, and has the characteristics of simple operation, high integration, compact structure, diversified test modes, and rich test content.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com