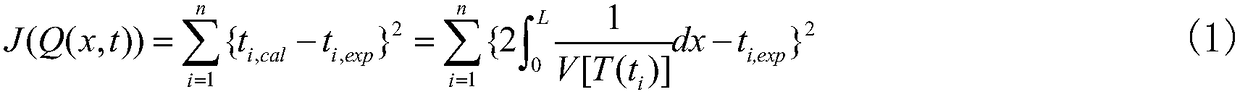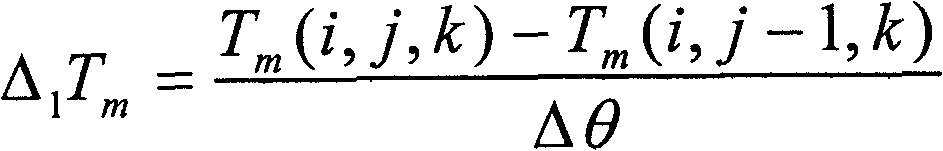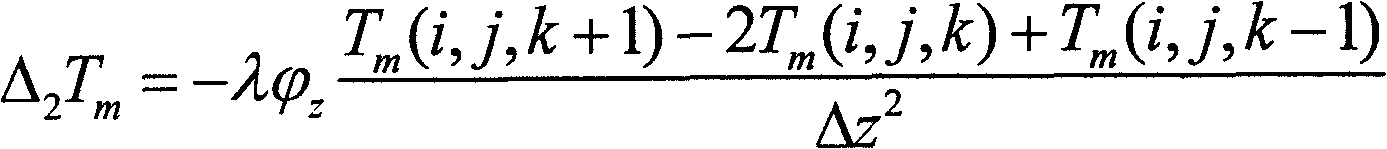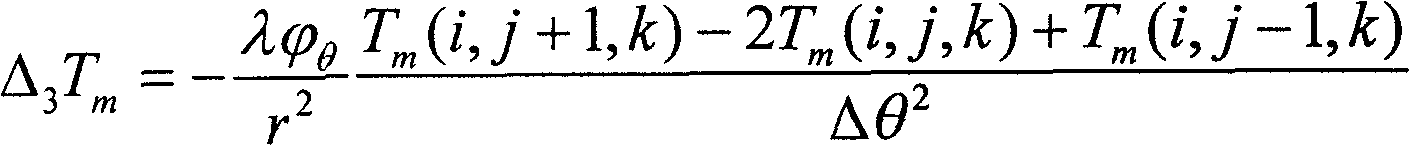Patents
Literature
62 results about "Boundary temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
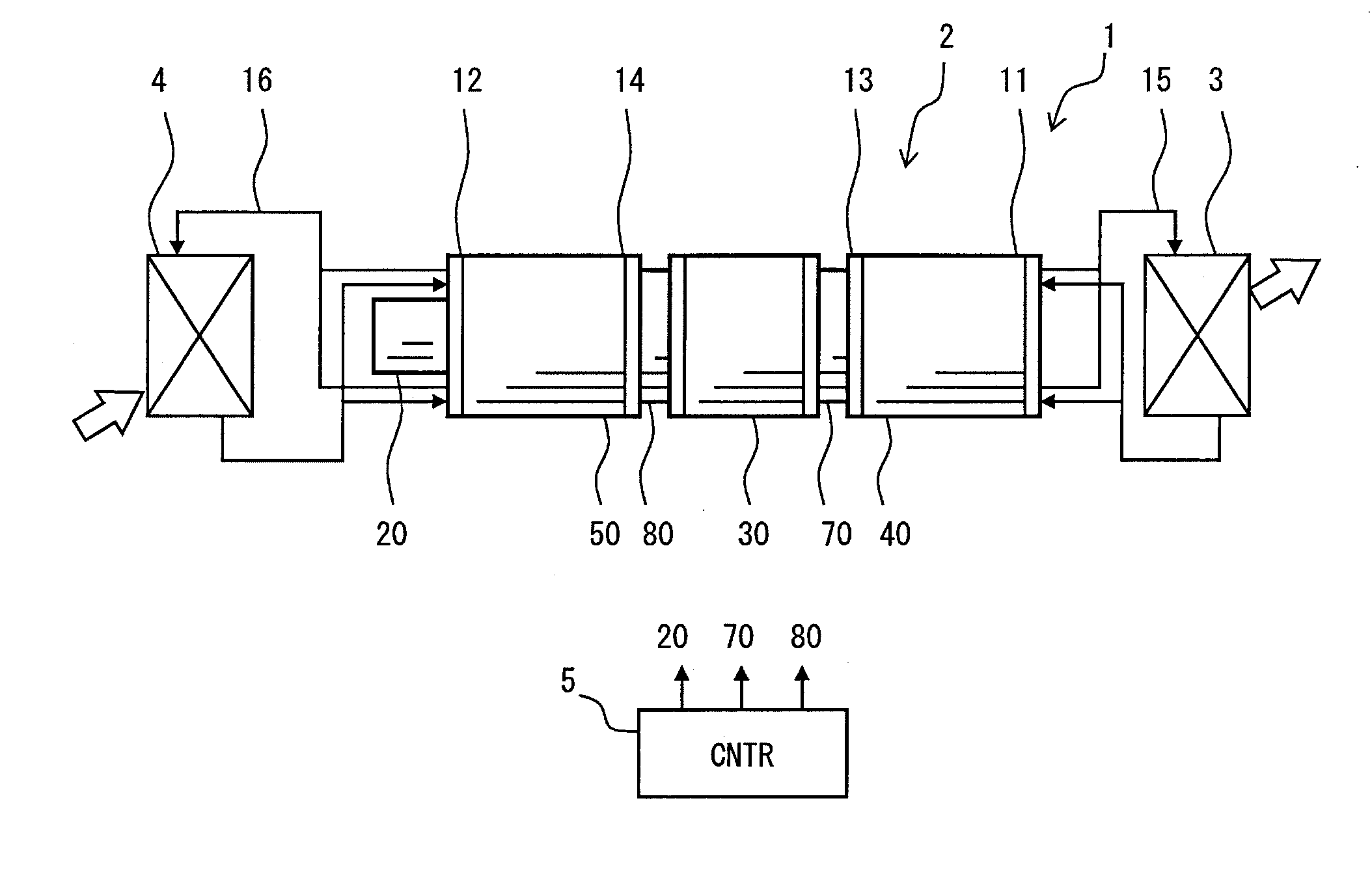
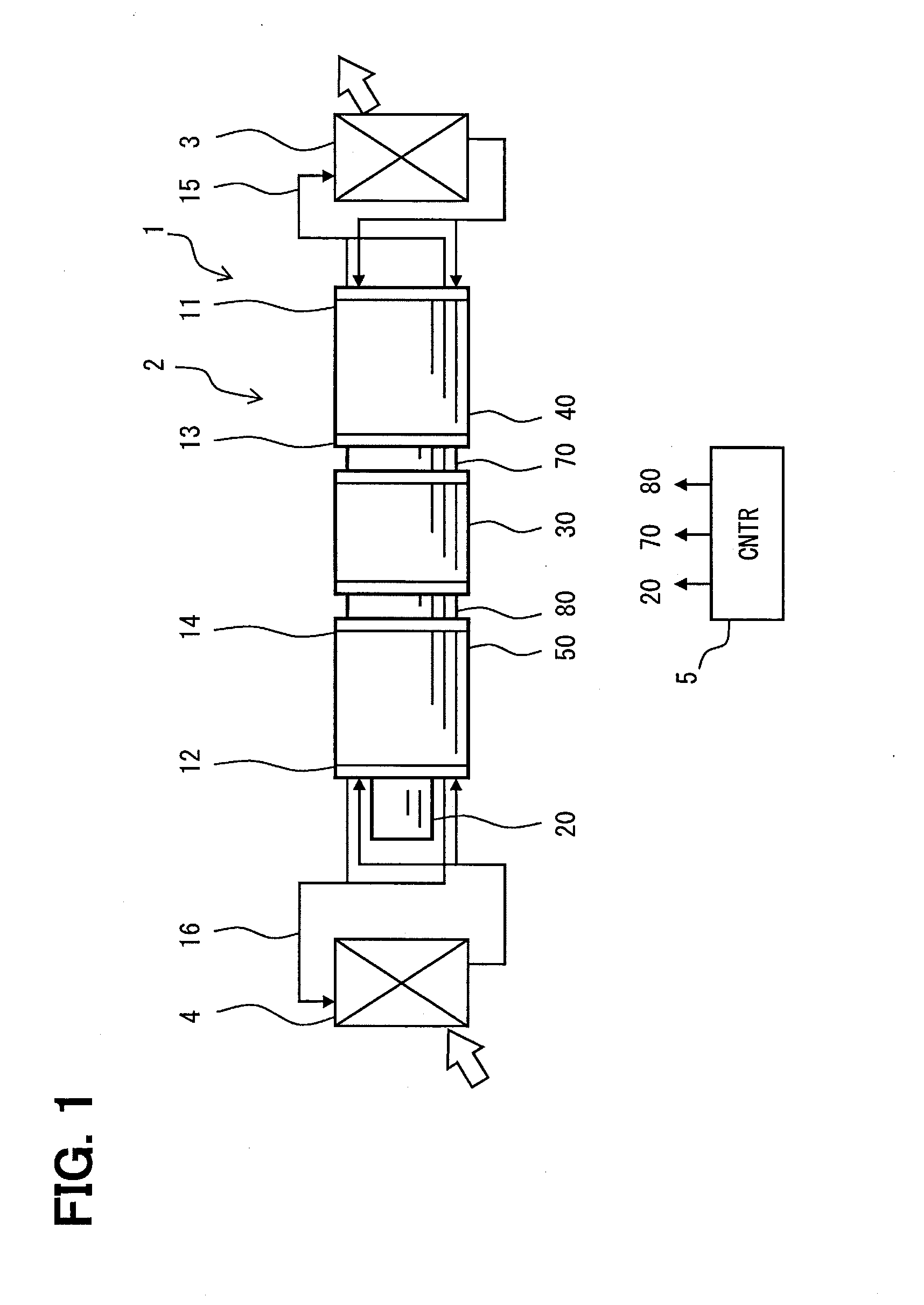
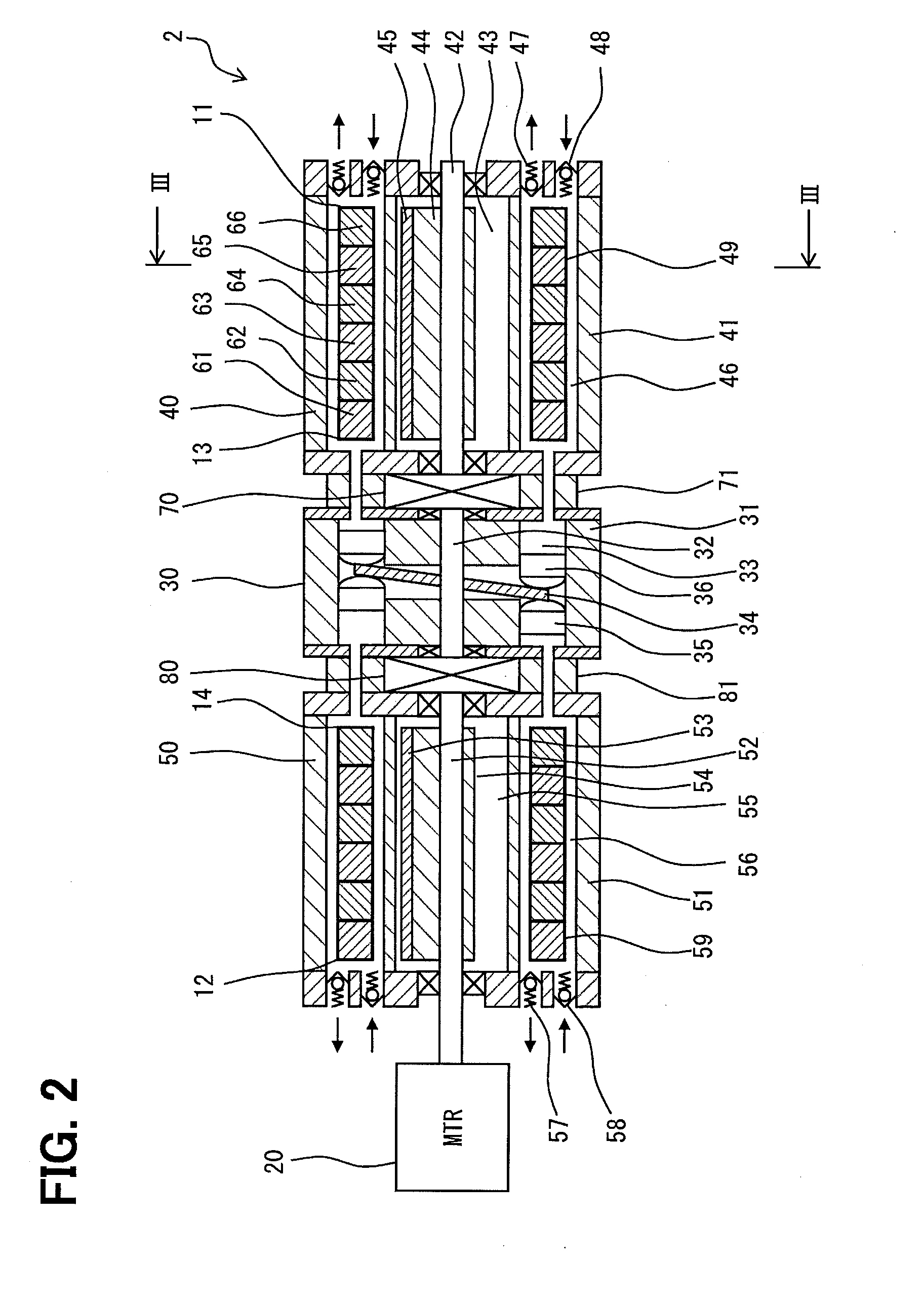
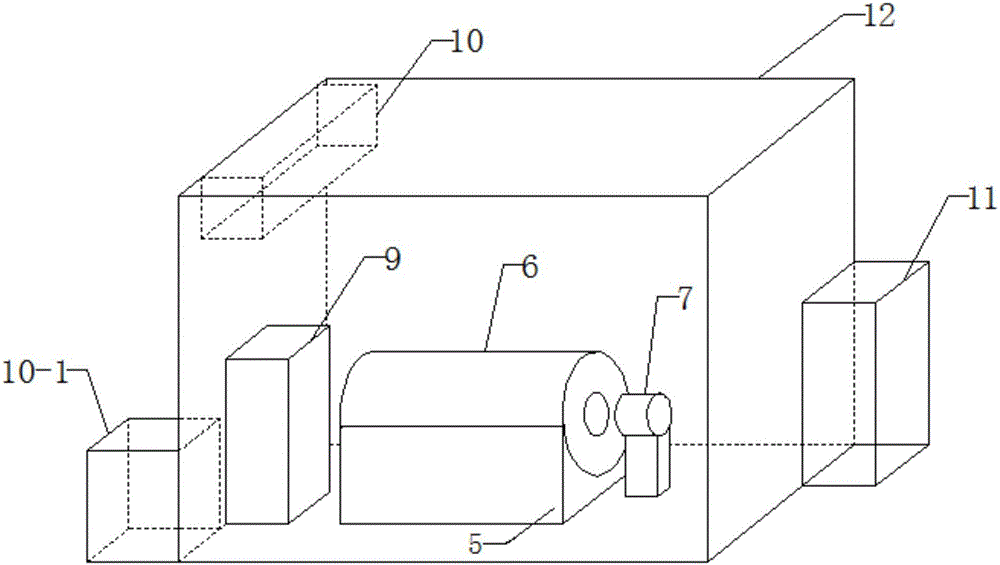
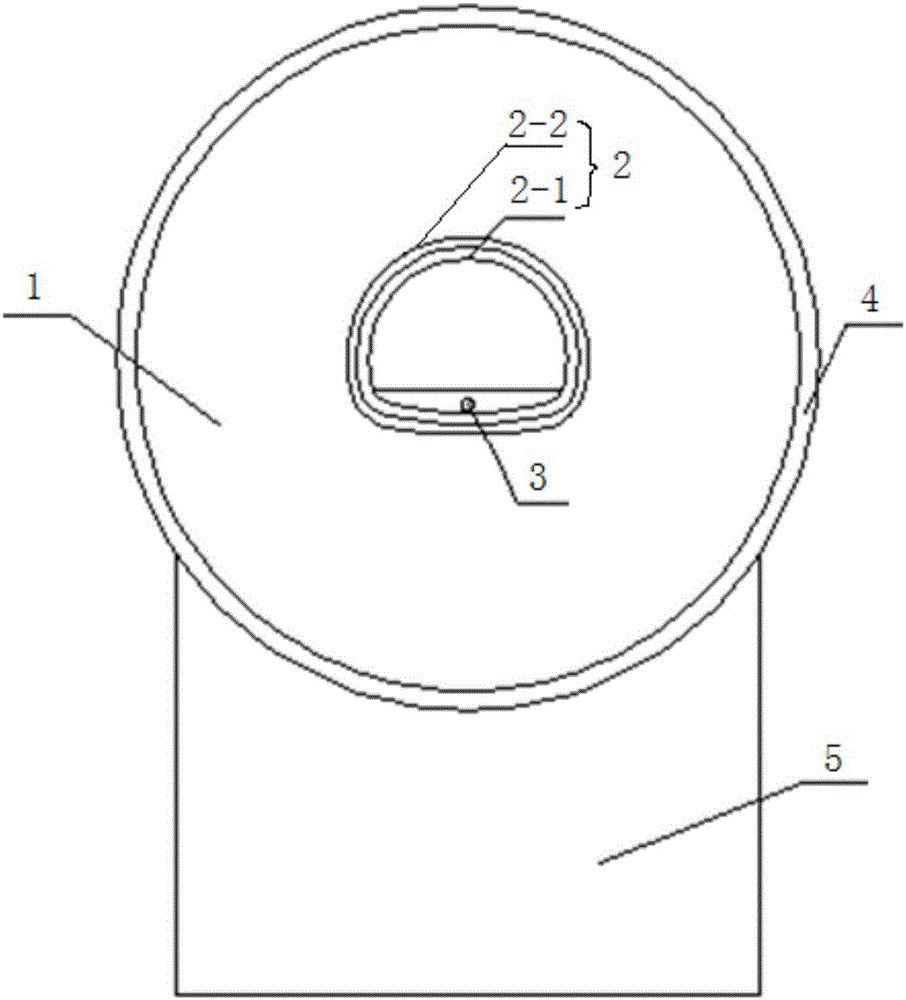
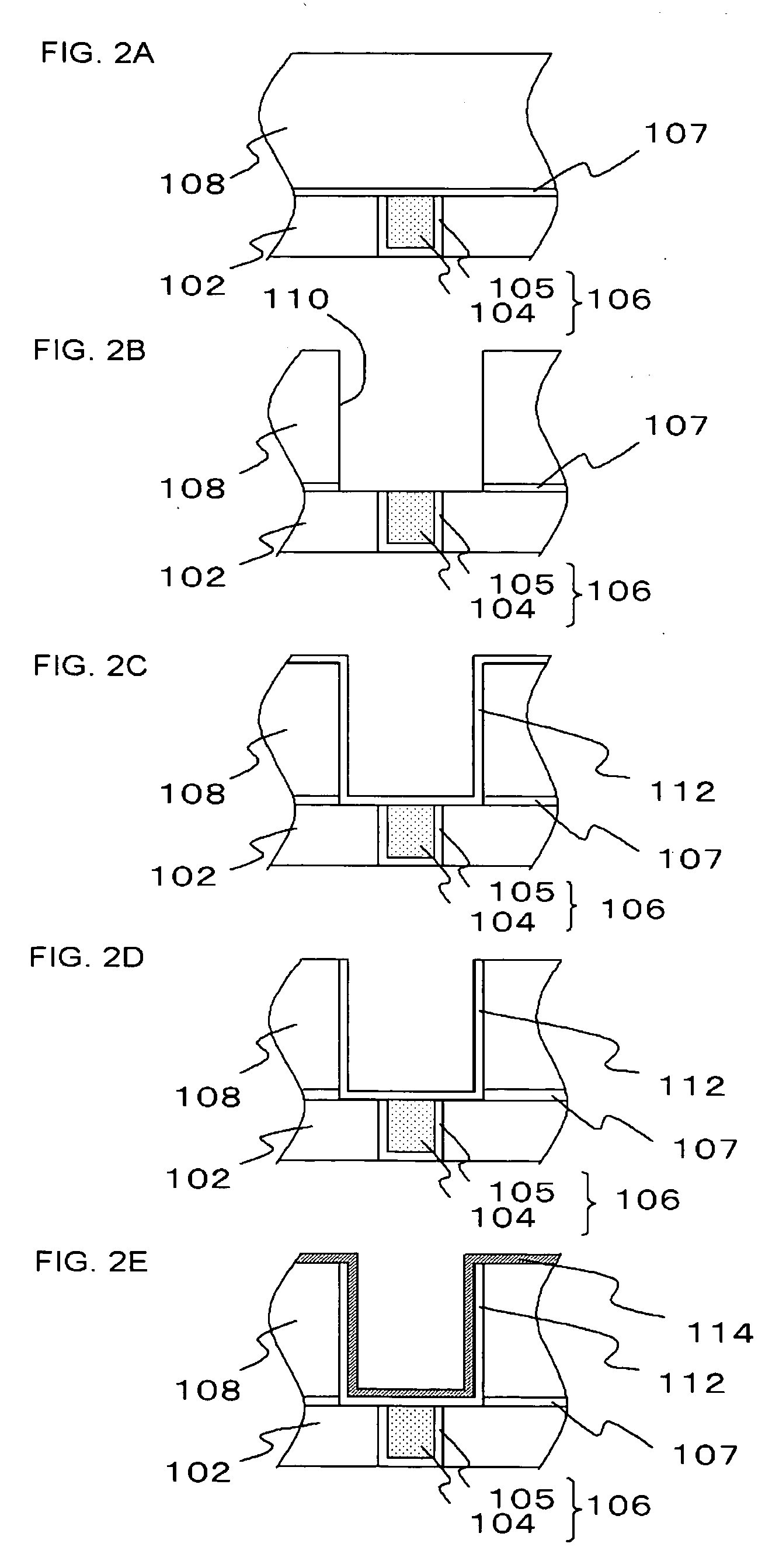
High energy beam area-selecting fusing method and device capable of controlling temperature gradient in shaping area
ActiveCN104959604AEnsure directional solidification conditionsReal-time monitoring of temperature gradientsAdditive manufacturing apparatusTemperature controlHeat flow
The invention discloses a high energy beam area-selecting fusing method and device capable of controlling temperature gradient in a shaping area, and a temperature measurement module and a temperature control module are added to a shaping assembly of the device. When the device is used for manufacturing high-energy beam additive, the temperature gradient interval in a molten pool can be calculated in real time utilizing the boundary temperature, acquired by the temperature measurement module, of a shaping area, proper hot-fluid conditions can be applied to the shaping area through the temperature control module to control temperature gradient intervals of the molten pool and the shaping area, so the molten pool can always satisfy conditions of directional solidification, high precision and performance directional solidified metal members and monocrystalline metal members having different sizes and structures can be efficiently manufactured. By adopting the high energy beam area-selecting fusing method and device capable of controlling the temperature gradient in a shaping area, not only the temperature gradient of the shaping area can always satisfy directional solidification conditions, but also the temperature gradient distribution in stages of a shaping process can be flexibly changed according to actual process needs, so various of functional / structural gradient members can be manufactured.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
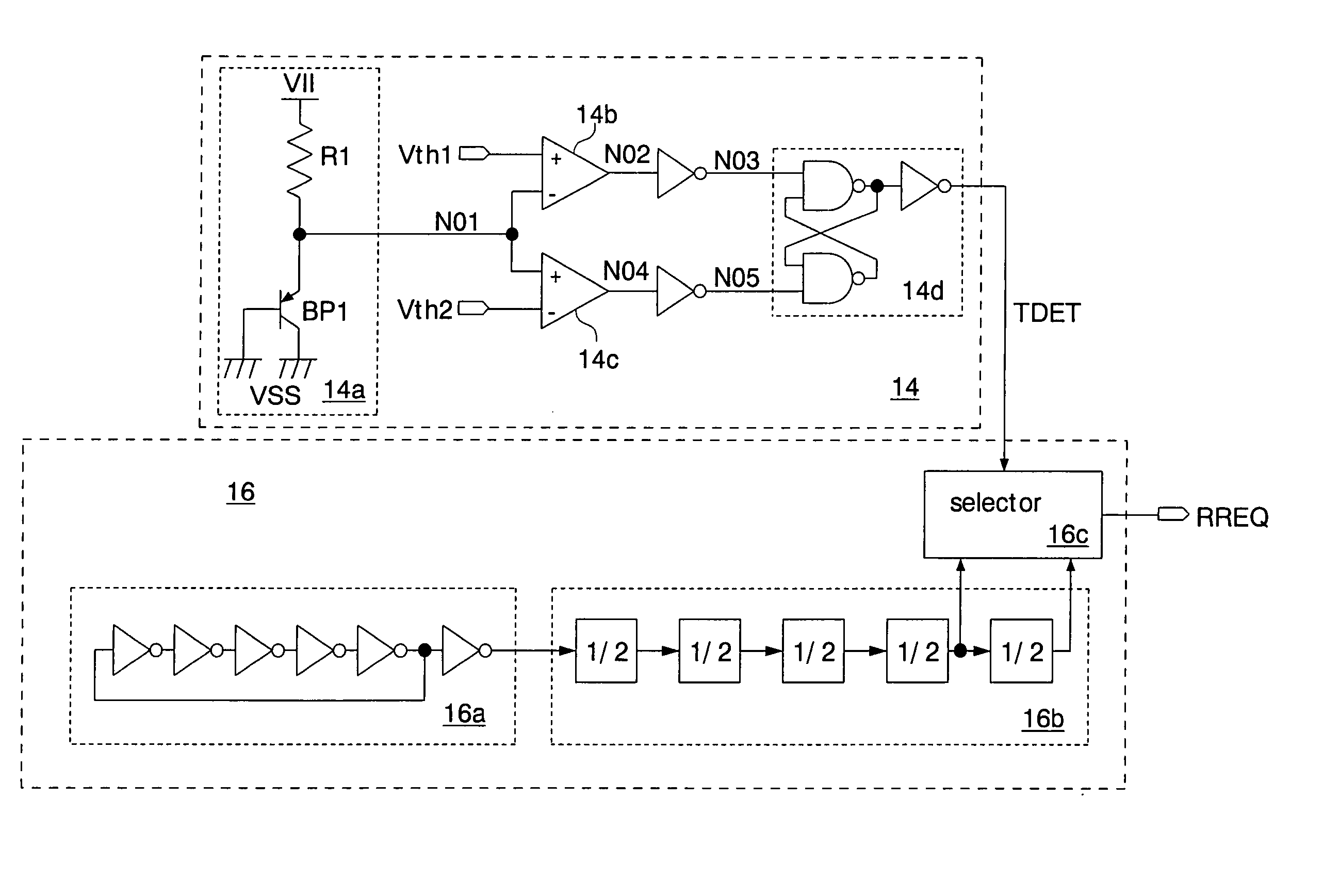
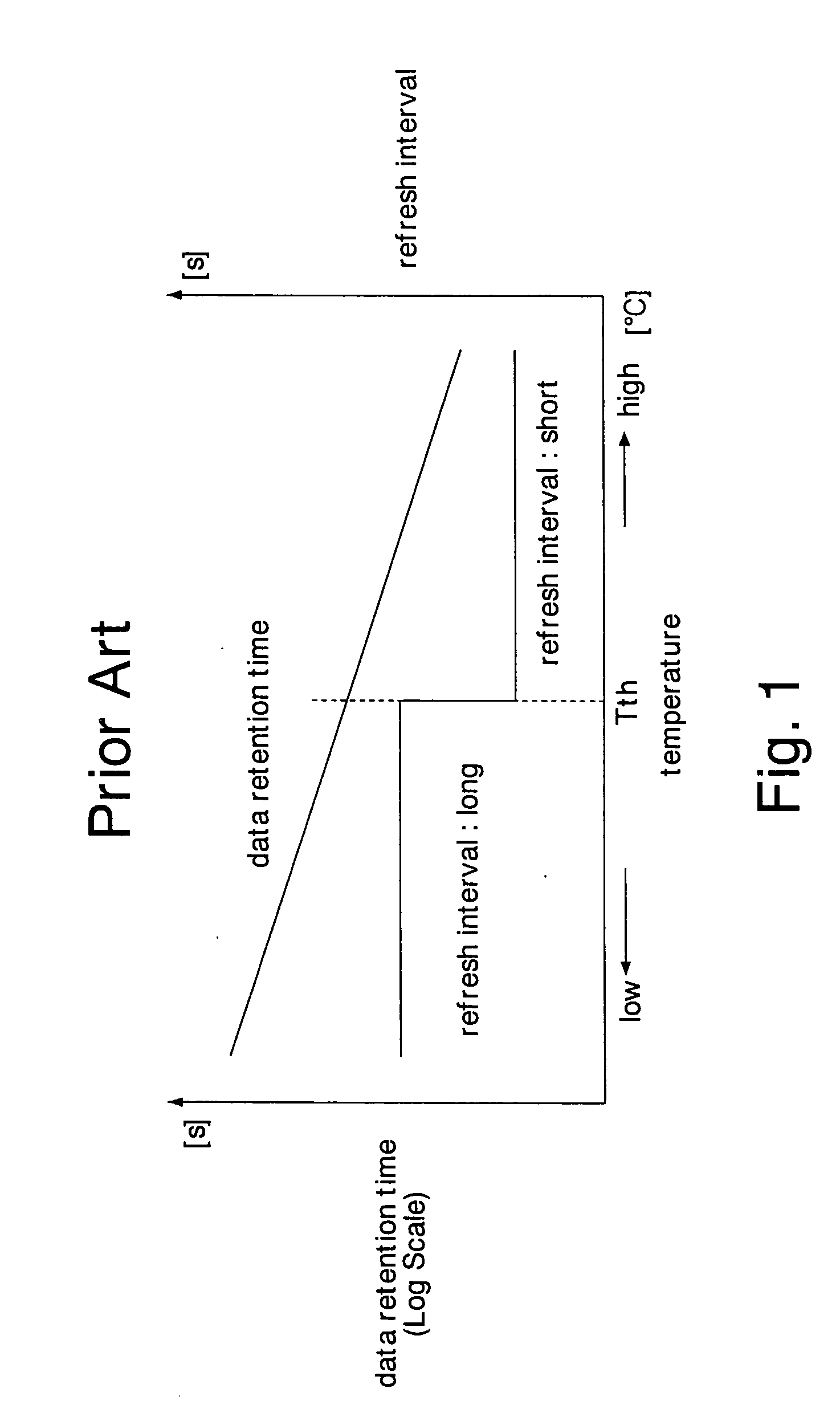
Semiconductor integrated circuit
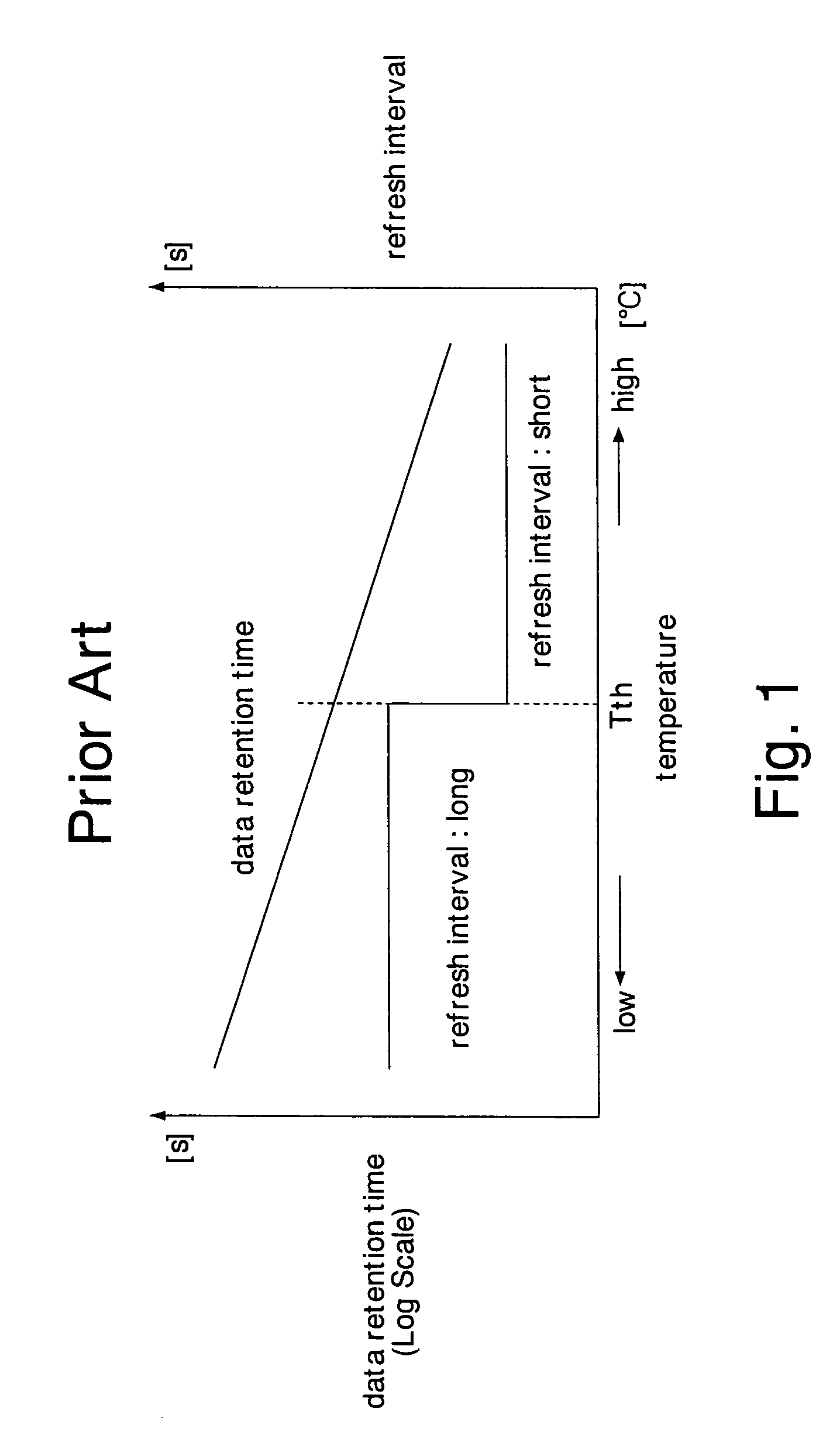
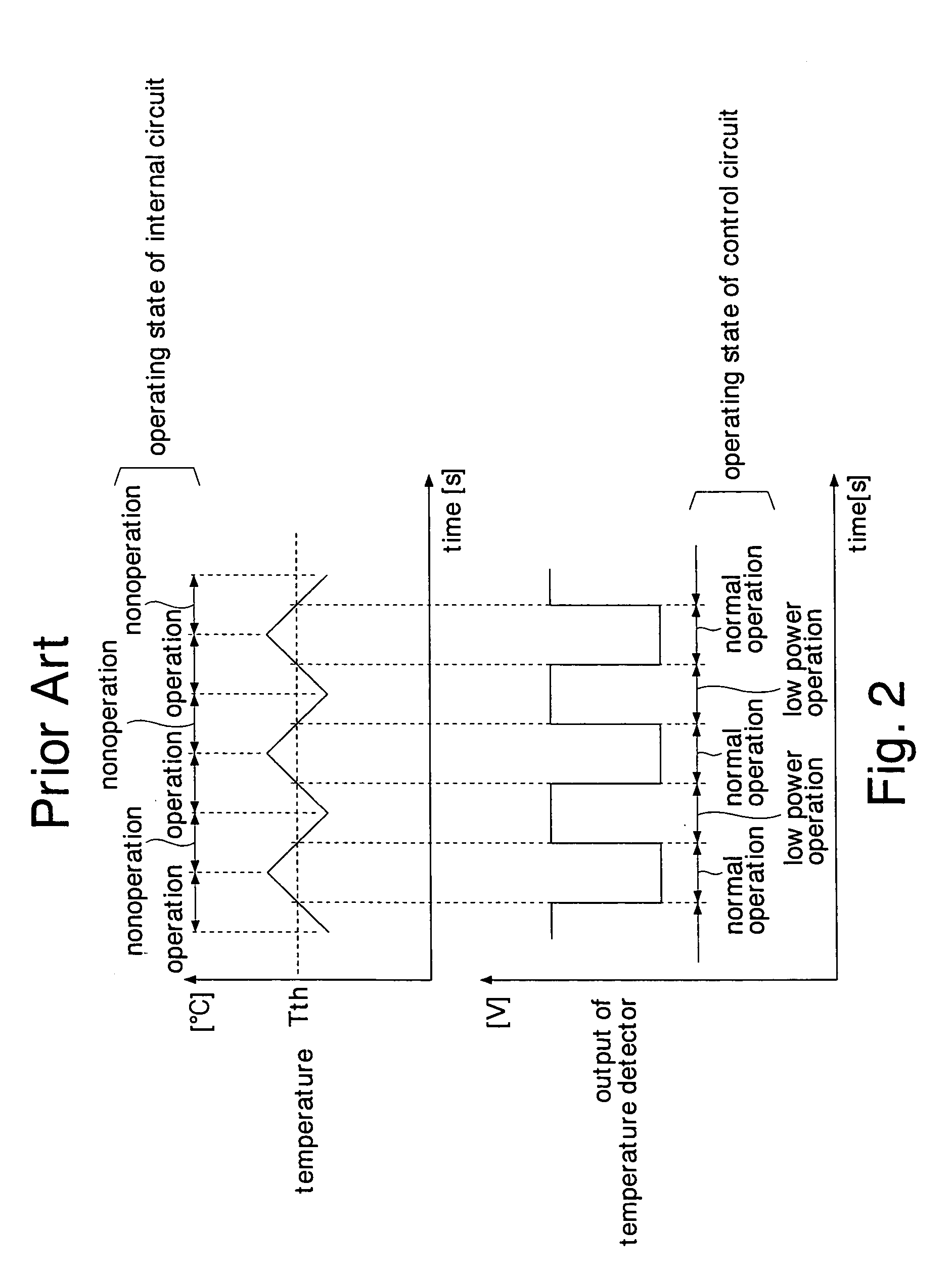
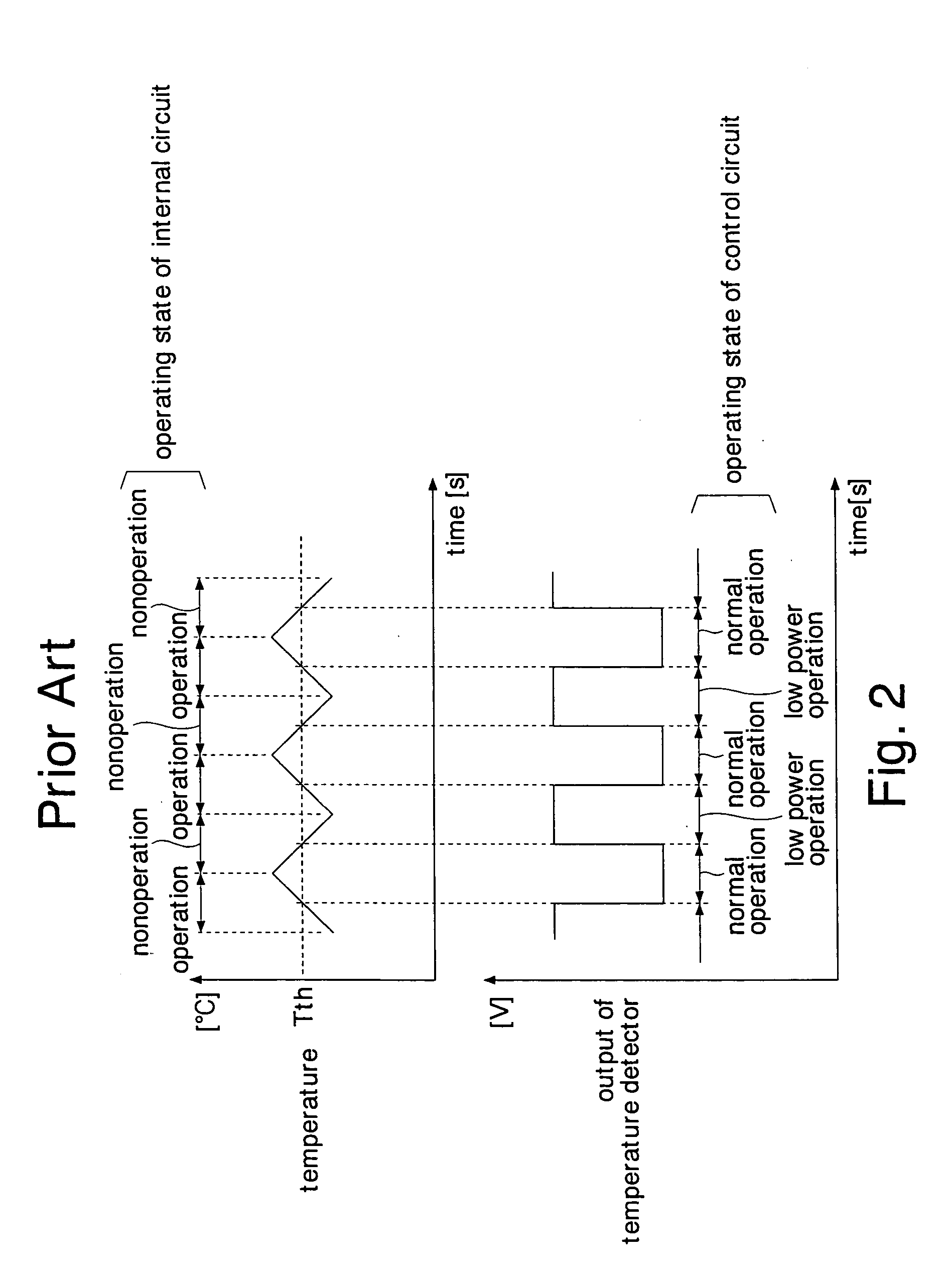
ActiveUS7149644B2Reduce current consumptionAvoid failureThermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionHandoff controlBoundary temperature
A temperature detector sets the level of a temperature detecting signal to a level indicating a high temperature state, detecting that the chip temperature is higher than a first boundary temperature. The temperature detector sets the level of thereof to a level indicating a low temperature state, detecting that the chip temperature is lower than a second boundary temperature. A control circuit changes its operating state according to the level of the temperature detecting signal. This prevents the operating state of the control circuit from frequently switched even when the chip temperature fluctuates around the boundary temperatures, and accordingly reduces current consumption of the control circuit due to the switching operation. Further, the first and second boundary temperatures set a buffer zone, so that the temperature detector does not detect power supply noises as temperature variation. This can prevent malfunction of the temperature detector and the semiconductor integrated circuit.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Device for testing performance of low-temperature vacuum multilayer heat-insulation material based on thermal protection
The invention discloses a device for testing performance of a low-temperature vacuum multilayer heat-insulation material based on thermal protection. The device comprises a vacuum outer cover, a blind plate end cover flange, an upper protective cavity, a testing cavity, a lower protective cavity, a back pressure stabilizing device, a controllable electric heating system, a temperature and flow-rate sensing system, a liquid nitrogen filling system, a data collecting-processing system and a vacuum pumping system, wherein the upper protective cavity and the lower protective cavity are used for insulating heat leakage in the vertical direction and connected with the blind plate end cover flange of the vacuum outer cover through thin-wall steel tubes; the testing cavity is connected with the blind plate end cover flange through the same thin-wall steel tube structure as the protective cavities. An insulating material testing sample of the device can be replaced at will, the temperature distribution inside the insulating material and the evaporation rate of stored liquid under different thermal boundary temperature conditions can be measured, and the heat leakage percentage and the material apparent thermal conductivity can be further obtained by the evaporation rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Magneto-caloric effect element and thermo-magnetic cycle apparatus
ActiveUS20150096307A1Improve efficiencyVehicle heating/cooling devicesMachines using electric/magnetic effectsBoundary temperatureEngineering
A magneto-caloric-effect element has a plurality of element units. The element units have lengths, respectively. The element units have different Curie temperatures, respectively. The element units demonstrate magneto-caloric effects. Two adjoining performance distribution crosses at a cross temperature. A temperature in the rated operational status between two adjoining element units is called a boundary temperature. The lengths and / or Curie temperatures are set so that the boundary temperatures and the cross temperatures coincide each other. Thereby, a plurality of element units can function at high effectiveness in the rated operational status.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Multi-layer low-temperature heat insulation structure arranged in density-variable mode
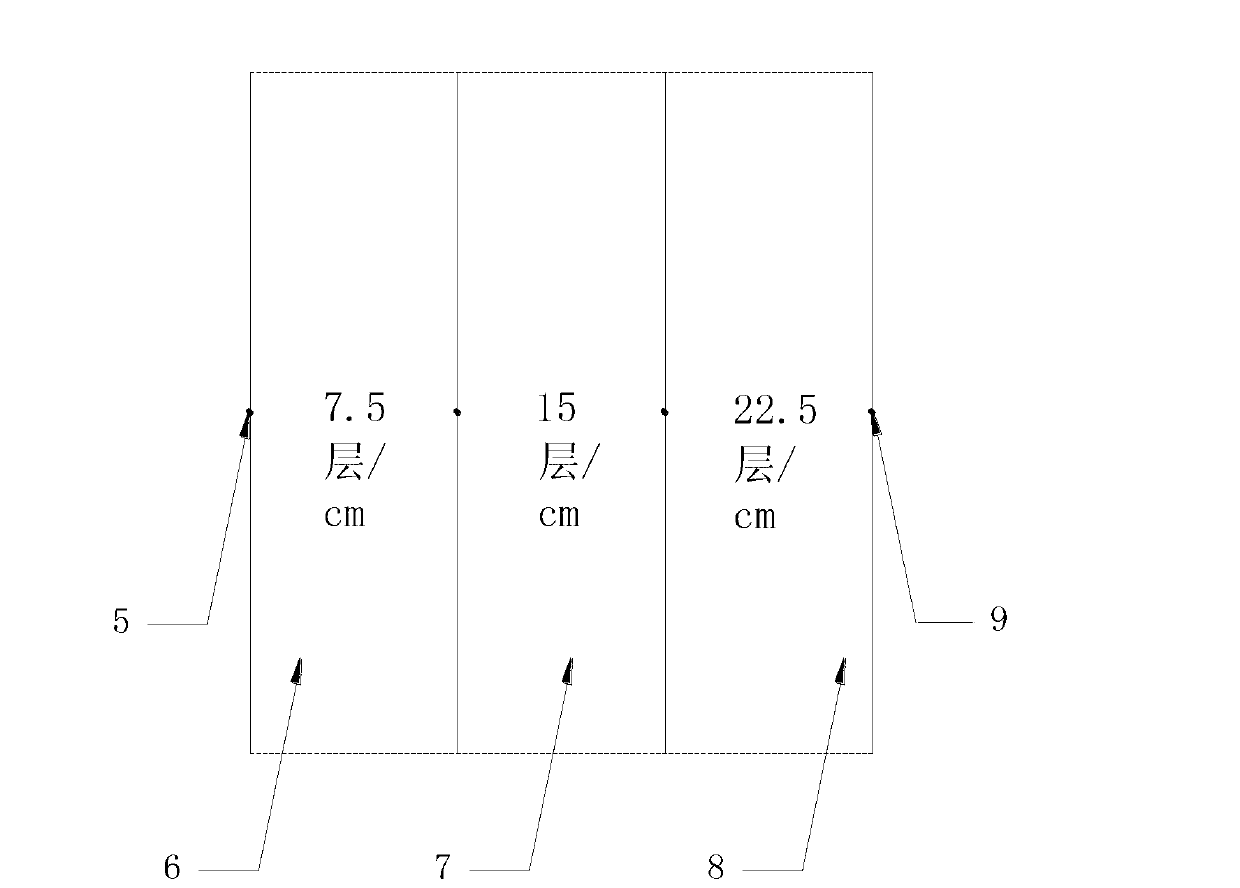
InactiveCN103277630AGood insulation performanceThermal insulationPipe protection by thermal insulationLiquid nitrogen containerBoundary temperature
The invention discloses a multi-layer low-temperature heat insulation structure arranged in a density-variable mode. The multi-layer low-temperature heat insulation structure arranged in the density-variable mode comprises multiple reflecting layers which are evenly separated into three parts in the thickness directions of the reflecting layers. Different layers of isolating materials are filled among adjacent reflecting layers of each part, wherein the layer density of the multi-layer low-temperature heat insulation structure close to a cold-boundary part is 7.5 layers per centimeter, the layer density of the middle part of the multi-layer low-temperature heat insulation structure is 15 layers per centimeter, the layer density of the multi-layer low-temperature heat insulation structure close to a hot-boundary part is 22.5 layers per centimeter. Compared with the traditional multi-layer heat insulation arrangement mode that the density of the whole structure is 15 layers per centimeter, the arrangement mode of the multi-layer low-temperature heat insulation structure arranged in the density-variable mode ensures that heat insulation performance is improved by 14.3% when being applied to a liquid nitrogen container with the hot-boundary temperature of 353K and the cold-boundary temperature of 77K for heat preservation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
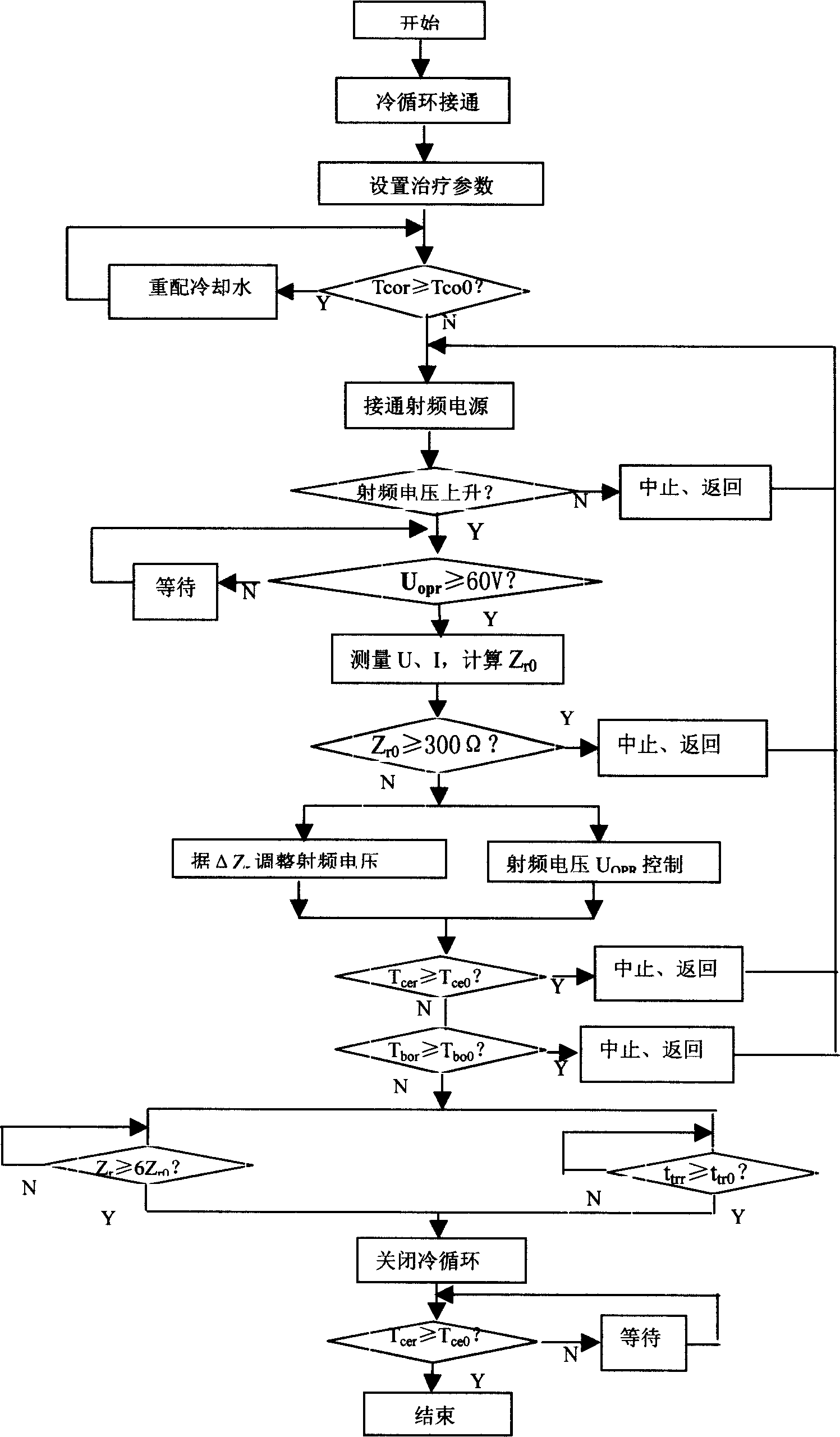
Intelligentized controlling means of water-cooled radio frequency tumour ablation treating system
InactiveCN1631327AAvoid bleedingAvoid plantingComputer controlSurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringRadio frequency
The invention provides an intelligent controlling means of water-cooled radio frequency tumour ablation treating system which consists of, determining radio frequency voltage output magnitude according to tissue impedance and its variation increment measured real-time, monitoring needle electrode front end temperature and boundary temperature of focus tissue and normal tissue, immediately disconnecting radio frequency source automatically when abnormal condition is found, when the real time monitored tissue impedance in operation is the initialized times of the initial impedance, or when the therapeutic time reaches initialized therapeutic time, then deciding that the fusion is finished, then closing recirculated cooling water, making the front end temperature of the needle electrode rise steeply, carrying out needle passage cauterization until the set temperature value is reached.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
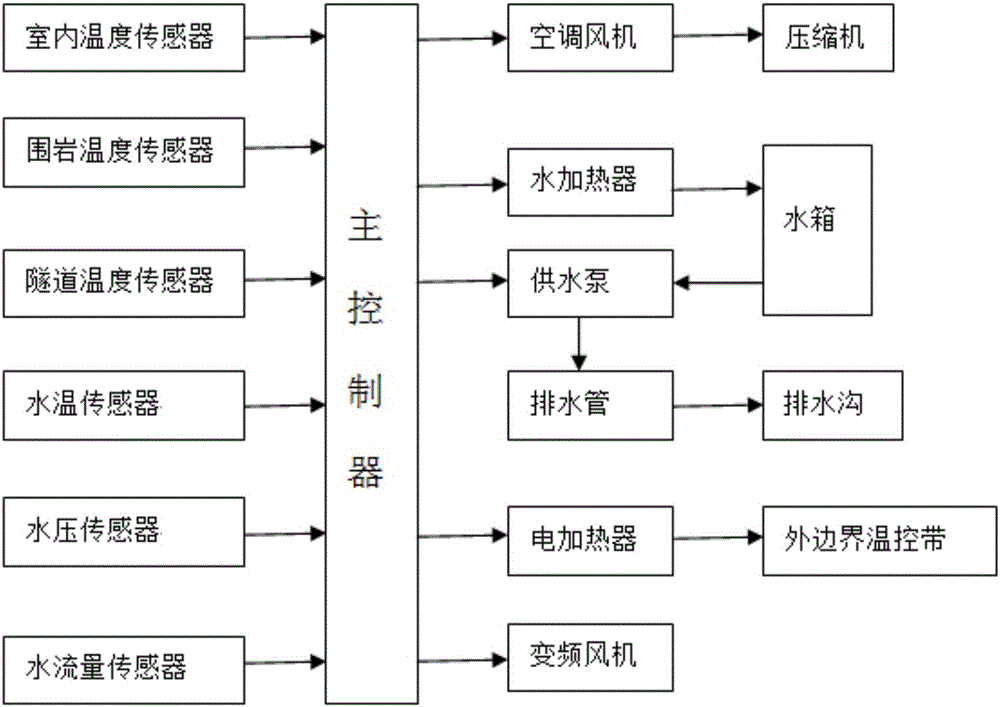
Cold region tunnel temperature field indoor experiment system
ActiveCN106485975AReal-time monitoring and control of temperature changesFacilitate experimental analysisCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsEngineeringAir blower
The invention provides a cold region tunnel temperature field indoor experiment system which comprises a main controller and a tunnel model. The tunnel model is arranged in a freezing chamber. The main controller is outside the freezing chamber. The outer boundary temperature control belt of the tunnel model is provided with an electric heater. A surrounding rock temperature sensor is distributed in a surrounding rock. The lower part of a tunnel body is provided with a drainage ditch with the distribution of a water temperature sensor and a water flow sensor. The freezing chamber is also internally provided with a heat insulation water tank, a variable frequency air blower, an air conditioner fan and a room temperature sensor. The heat insulation water tank communicates with the drainage ditch via a water supply pump and a water supply pipe. The variable frequency air blower is at the opening of the tunnel model and faces the tunnel model. The surrounding rock temperature sensor, the water temperature sensor, the water flow sensor, the room temperature sensor, the variable frequency air blower, the air conditioner fan, the electric heater, the water heater and the power supply pump are connected to the main controller. The simulation test of the three-dimensional temperature field of outer air temperature, underground water temperature and surrounding rock temperature of a cold region tunnel is simulated.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS20050093618A1Easy to operateReduce standby currentThermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionTemperature controlBoundary temperature
A temperature detector sets the level of a temperature detecting signal to a level indicating a high temperature state, detecting that the chip temperature is higher than a first boundary temperature. The temperature detector sets the level of thereof to a level indicating a low temperature state, detecting that the chip temperature is lower than a second boundary temperature. A control circuit changes its operating state according to the level of the temperature detecting signal. This prevents the operating state of the control circuit from frequently switched even when the chip temperature fluctuates around the boundary temperatures, and accordingly reduces current consumption of the control circuit due to the switching operation. Further, the first and second boundary temperatures set a buffer zone, so that the temperature detector does not detect power supply noises as temperature variation. This can prevent malfunction of the temperature detector and the semiconductor integrated circuit.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Meshless-method-based numerical algorithm of FG-GRC (functionally-graded graphene-reinforced composite) laminate buckling load factor
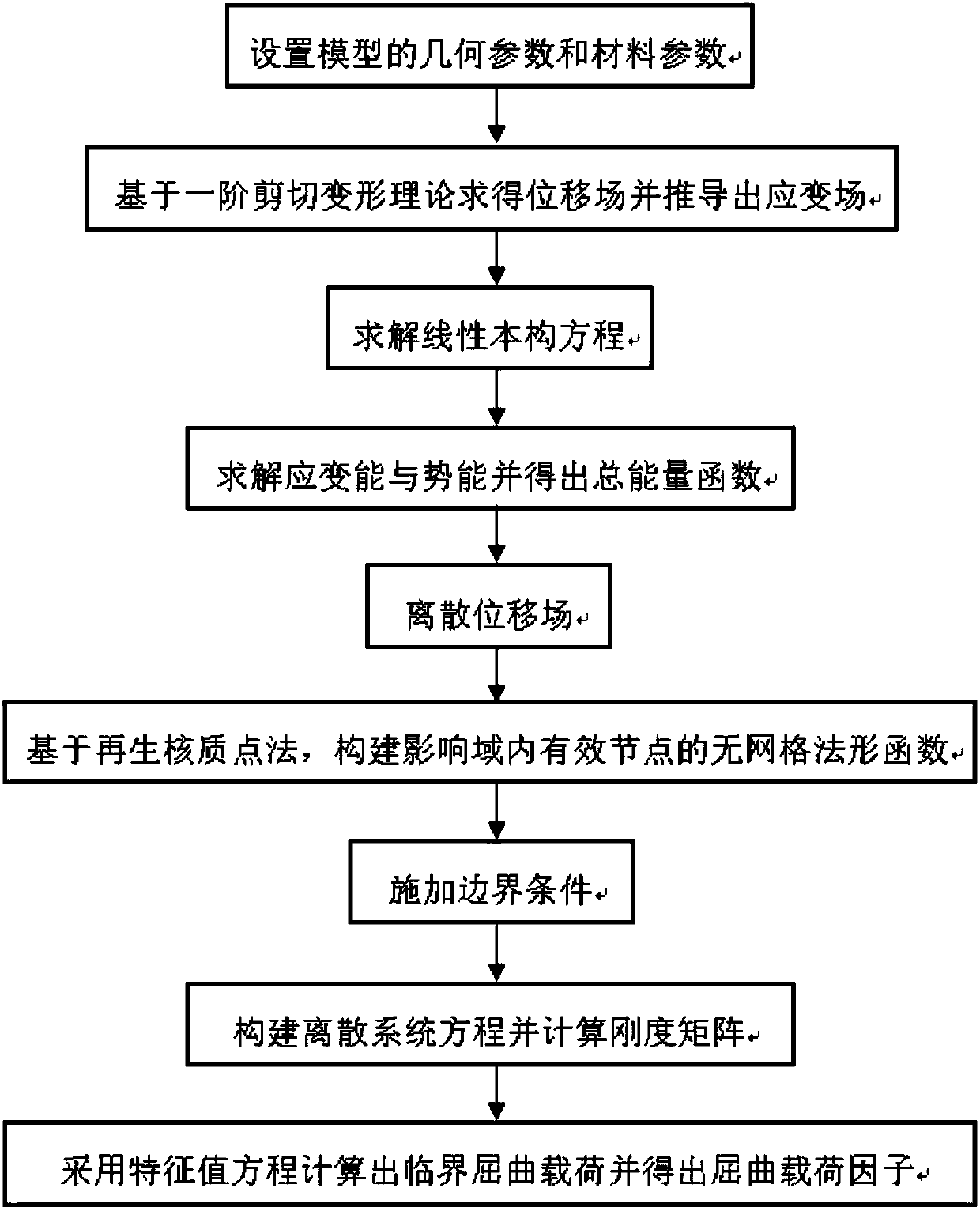
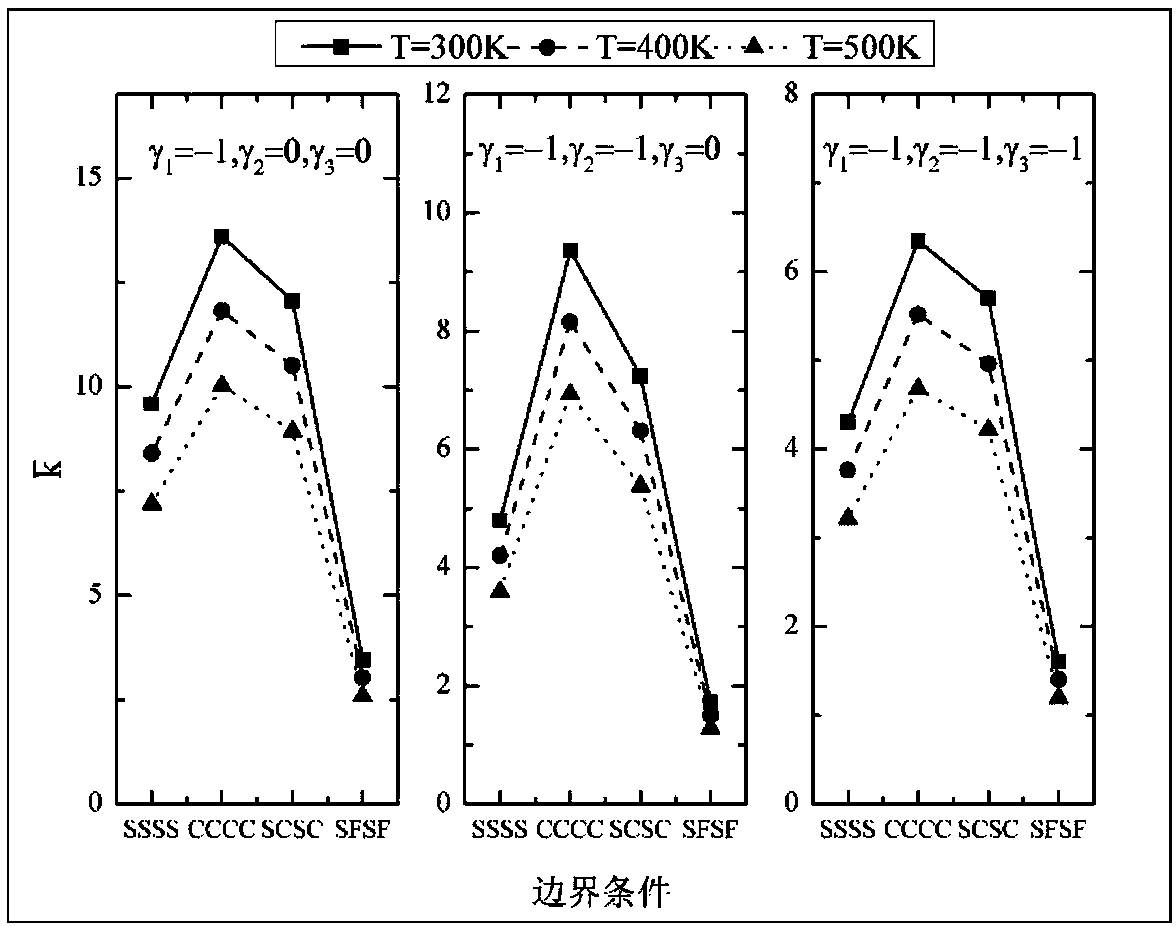
InactiveCN108108578AImprove accuracyImprove smoothnessGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAxial pressureBoundary temperature
The invention discloses a meshless-method-based numerical algorithm of FG-GRC (functionally-graded graphene-reinforced composite) laminate buckling load factor, comprising the steps of constructing amodel to determine geometric parameter and material parameters; solving a linear constitutive equation and a total energy function; constructing a meshless method shape function and applying boundaryconditions; calculating a stiffness matrix, and acquiring buckling load factor through an eigenvalue equation. The buckling load factor of an FG-GRC laminate under external thermal load and axial pressure can be accurately calculated through the algorithm. The algorithm is significant to the researches on the impact of boundary temperature, graphene distribution form, laminate length-width ratio and width-height ratio, number of laminas and the like upon buckling characteristics of FG-GRC laminates.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Phase miss match compensation heater of high power internal cavity freguency multiplier laser and its method
InactiveCN1794521AEasy temperature controlStable temperatureLaser constructional detailsProcess dynamicsInstability
This invention discloses a phase mismatch compensation heater and a method for a high power inner cavity multiple frequency laser including a KTP multiple crystal set in a closed metallic box inserted with a temperature sensor and a heating tube, the bottom is set with a semiconductor refrigerator and the box is set with a solid relay of a control box. The method includes: designing a KTP crystal boundary temperature value, increasing power of the heating pipe at low temperature to reduce voltage of the refrigerator to let the temperature approach to the designed value so as to keep the boundary temperature of the KTP multiple crystal at a stable state during the process dynamic balance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
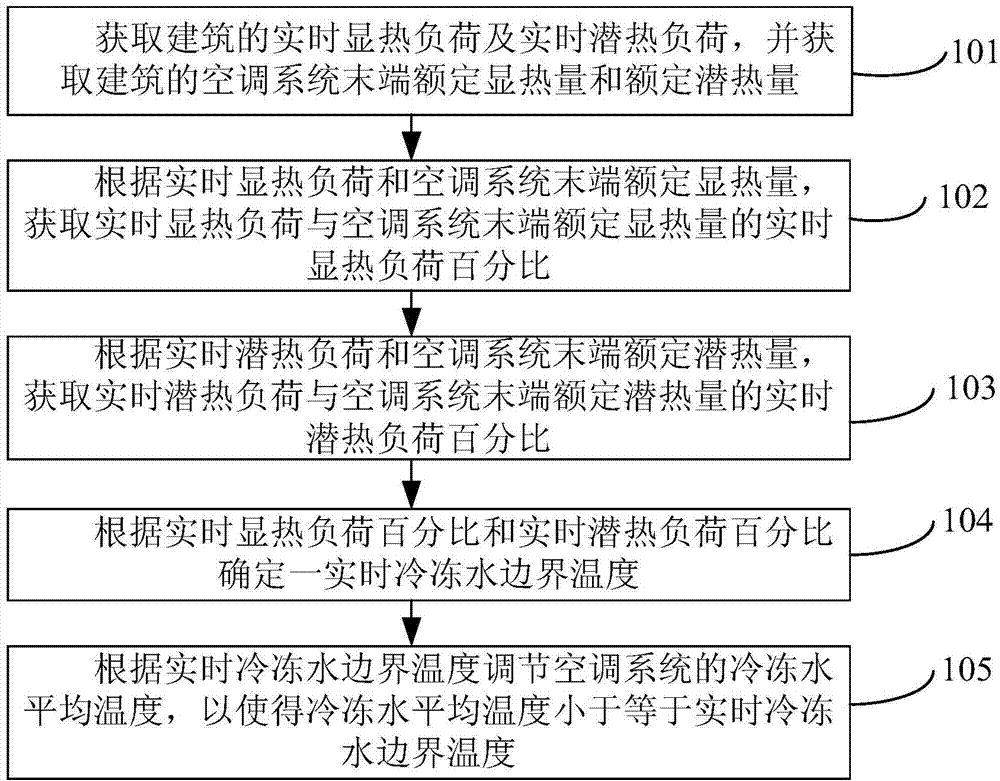
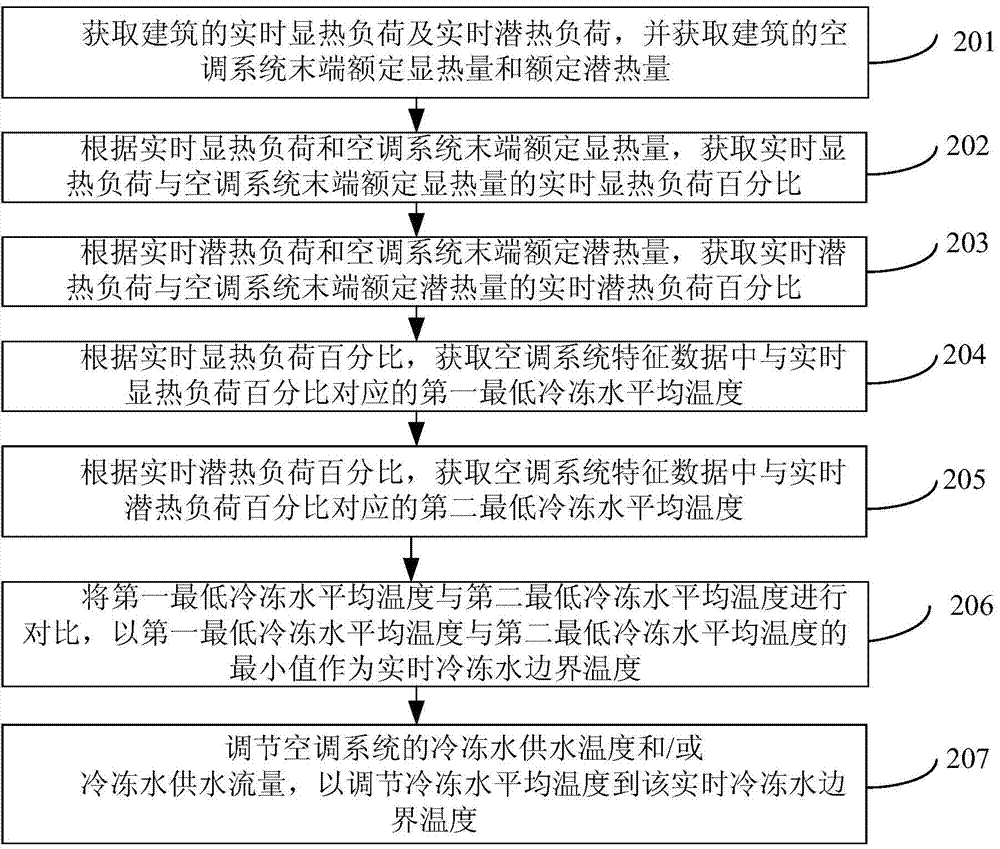
Method and device for controlling air conditioning system
InactiveCN104236020ASpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusBoundary temperatureEngineering
The invention provides a method and device for controlling an air conditioning system and relates to the technical field of air conditioners. The method includes the steps that the real-time sensible heat load and the real-time latent heat load of a building are acquired and the rated sensible heat and the rated latent heat of the tail end of the air conditioning system of the building are acquired; according to the real-time sensible heat load and the rated sensible heat, the sensible heat load percent of the real-time sensible heat load to the rated sensible heat is acquired; according to the real-time latent heat load and the rated latent heat, the latent heat load percent of the real-time latent heat load to the rated latent heat is acquired; according to the real-time sensible heat load percent and the real-time latent heat load percent, real-time chilled water boundary temperature is determined; according to the real-time chilled water boundary temperature, the chilled water average temperature of the air conditioning system is adjusted, so that the chilled water average temperature is smaller than or equal to the real-time chilled water boundary temperature. According to the method and device, the problems that the refrigeration capacity and the dehumidification capacity of the air conditioning system are affected and energy consumption is large due to an existing control strategy of the air conditioning system can be solved.
Owner:张迎春
Method for operating a laser as an ignition device of an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20100282196A1Simple and cost-effective implementationEasy to implementAnalogue computers for vehiclesLaser detailsBoundary temperatureEngineering
A method for operating a laser as an ignition device of an internal combustion engine, the laser including at least one laser crystal, a passive Q-switch and at least one pump device, particularly a laser diode, which optically pumps the laser crystal using pump radiation; at a temperature of the laser crystal below an operating boundary temperature, the pump radiation being changed, compared to a normal operation, in such a way that, compared to the normal operation, a greater radiation energy is converted to heat in the laser crystal.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
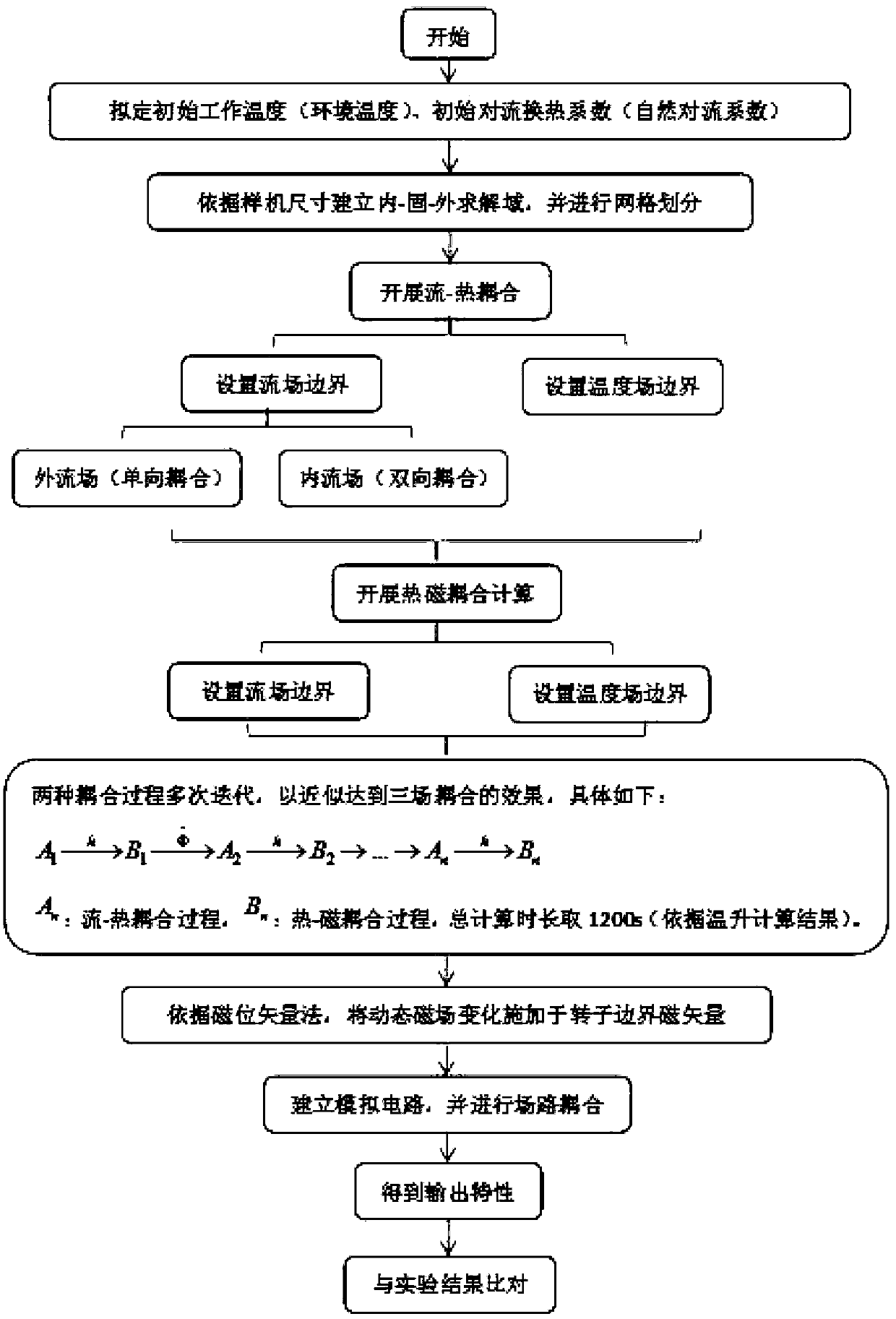
Multi-Field-Circuit Coupling Simulation Method for Permanent Magnet Wind Turbine
ActiveCN109063337AIncrease credibilityRealize flow-heat two-way couplingDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMulti fieldEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of a permanent magnet generator, in particular to a permanent magnet wind generator with multiple fields. Road coupling simulation method to establish theinner watershed-solid domain-outer watershed solving domain model, unstructured mesh partitioning; Applying material attributes according to the actual physical properties of each component; the initial constraint conditions of numerical simulation are collected, and the results are applied in the form of inlet conditions and rotating mechanical excitation. The initial boundary temperature and IHGinternal heat source are applied to compute and analyze the flow field and temperature field, and the flow is completed. The two-way exchange process of heat transfer, wall temperature and heat transfer coefficient on the solid contact surface realizes the generator flow. Thermal bi-directional coupling; The temperature distribution is applied to the electromagnetic field calculation, and the dynamic magnetic field variation is obtained by simulating the alternating magnetic field. The electromagnetic loss is returned to the heat source in the IHG. Numerical simulation results are obtained byrepeated iterations in the coupled flow field. The invention has the advantages of accurate and intuitive results, and can make up the limitation of the existing experimental means.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
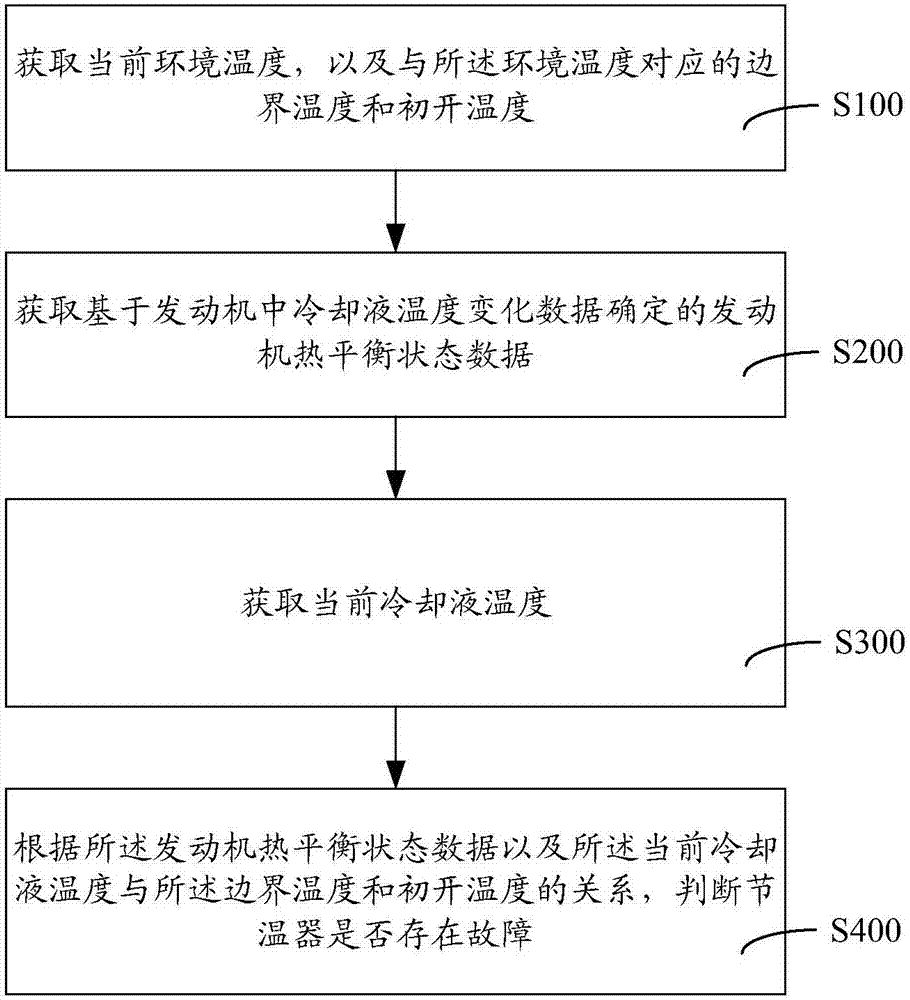
Thermostat fault diagnosis method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN107956573AThe judgment result is accurateReduce labor costsCoolant flow controlFail safeLiquid temperatureDiagnosis methods
The invention relates to a thermostat fault diagnosis method. The thermostat fault diagnosis method comprises the steps that the current environment temperature and the boundary temperature and initial starting temperature corresponding to the current environment temperature are obtained; engine heat balance state data determined based on cooling liquid temperature change data in an engine are obtained; the current cooling liquid temperature is obtained; and according to the relationship between the engine heat balance state data and current cooling liquid temperature and the boundary temperature and initial starting temperature, whether a thermostat has faults or not is judged. By means of the above method, whether the thermostat has the faults or not can be judged without building a water temperature model, the judgment result is accurate, needs of a large amount of standardization work is avoided, and manpower and resource cost can be reduced. In addition, a device, computer equipment and a storage medium are further included.
Owner:GUANGZHOU AUTOMOBILE GROUP CO LTD
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20060046421A1Improve reliabilityImprove equipment reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricDeposition temperature
In the process for manufacturing a semiconductor device of the present invention, a capacitor dielectric film is deposited via an atomic layer deposition employing an organic source material containing one or more metallic element(s) selected from the group consisting of Zr, Hf, La and Y as a deposition gas. The process for manufacturing a capacitor of the present invention includes obtaining a boundary temperature T (degree C.), at which an increase in a deposition rate for depositing the capacitor dielectric film as increasing the temperature is detected, on the basis of a correlation data of a deposition temperature in the atomic layer deposition employing the deposition gas with a deposition rate for depositing the capacitor dielectric film at the deposition temperature (S100 and S102); and depositing the capacitor dielectric film via the atomic layer deposition employing the deposition gas at a temperature within a range of from (T−20) (degree C.) to (T+20) (degree C.) (S104 to S112).
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Process for hot rolling steel strips and hot rolling train
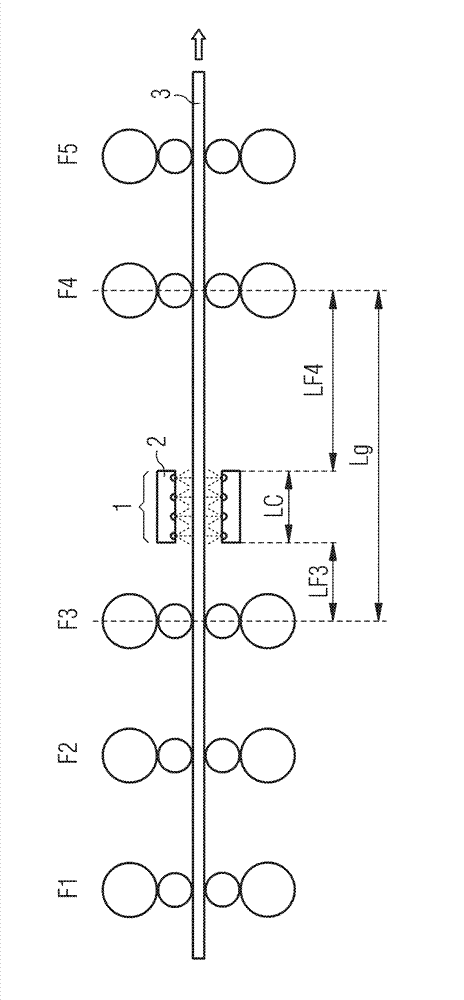
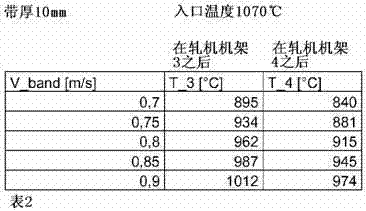
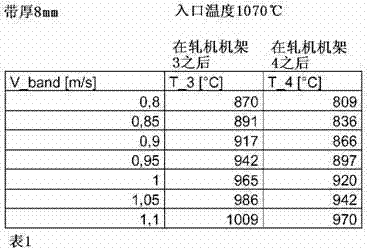
ActiveCN102859009AAchieve intercoolingPrevent rollingTemperature control deviceFurnace typesStrip millBoundary temperature
The invention relates to an apparatus and a process for hot rolling steel strips (3) in a plurality of successive roll stands (F1-F5), wherein the steel strips are finish-rolled to the end thickness in one or more roll stands firstly in the austenitic state and then, after liquid cooling, in the ferritic state. In order to ensure that the steel strip actually reaches the ferritic state after cooling, it is provided that the end thickness of the steel strip (3) is less than 3 mm, that the difference between the outlet temperature of the steel strip from the last roll stand (F3) before liquid cooling and the equilibrium austenite boundary temperature is set by the pilot control or regulation of the outlet temperature to no more than 70 K, preferably no more than 50 K, preferably less than 25 K, and that the liquid cooling takes place between two roll stands depending on the length (Lc) of a cooling section (1) by the application, in the cooling section and on both sides of the steel strip (3), of at least in each case a quantity of liquid Qu > 284 / (Lc1.42) litres per minute and per metre of strip width, in particular Qu > 2*284 / (Lc1.42) litres per minute and per metre of strip width, but not more than Qu = 7*284 / (Lc1.42) litres per minute and per metre of strip width, preferably Qu < 4*284 / (Lc1.42) litres per minute and per metre of strip width.
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH AUSTRIA GMBH
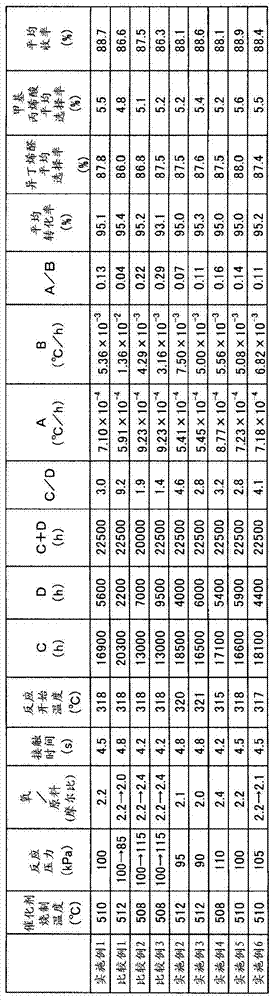
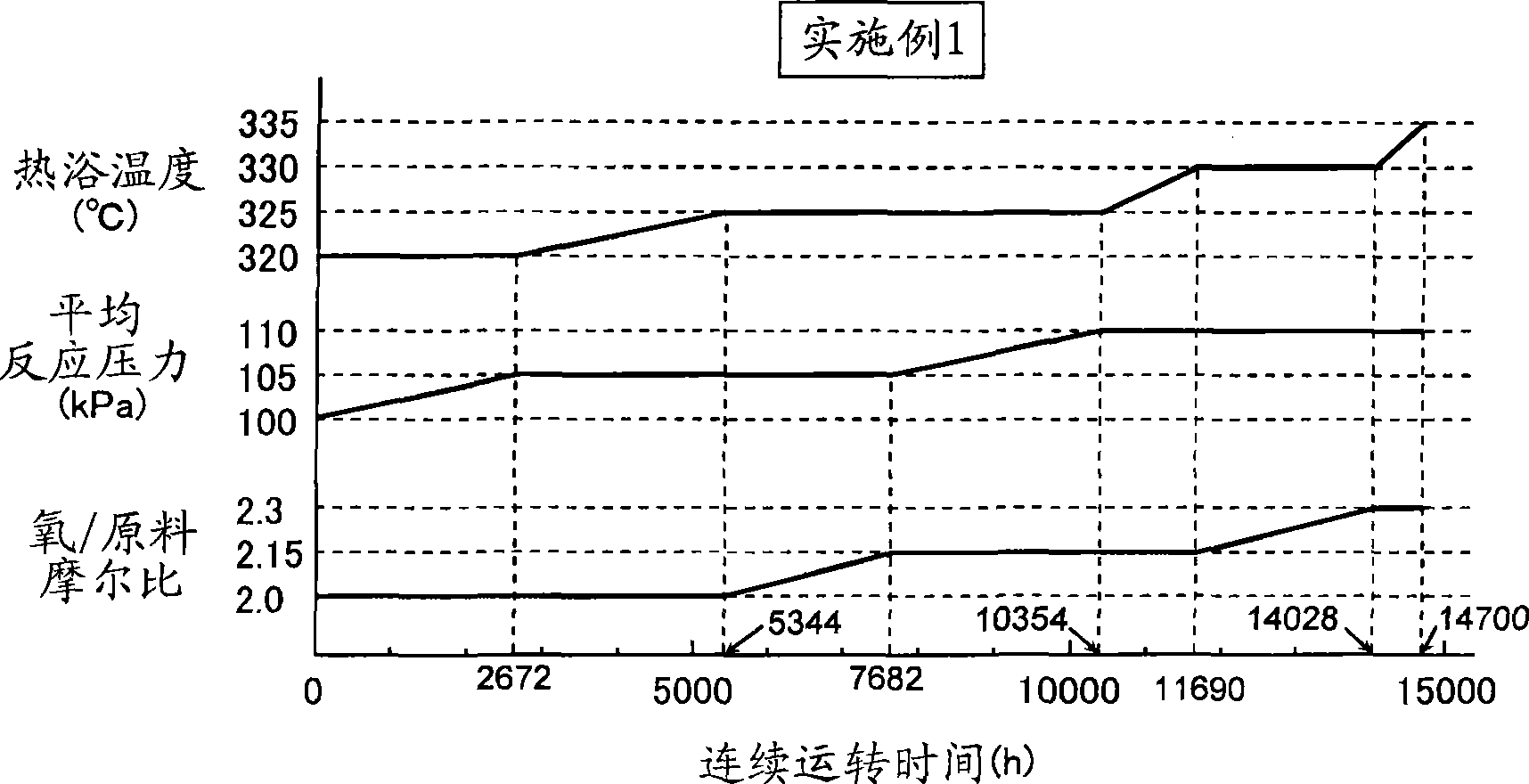
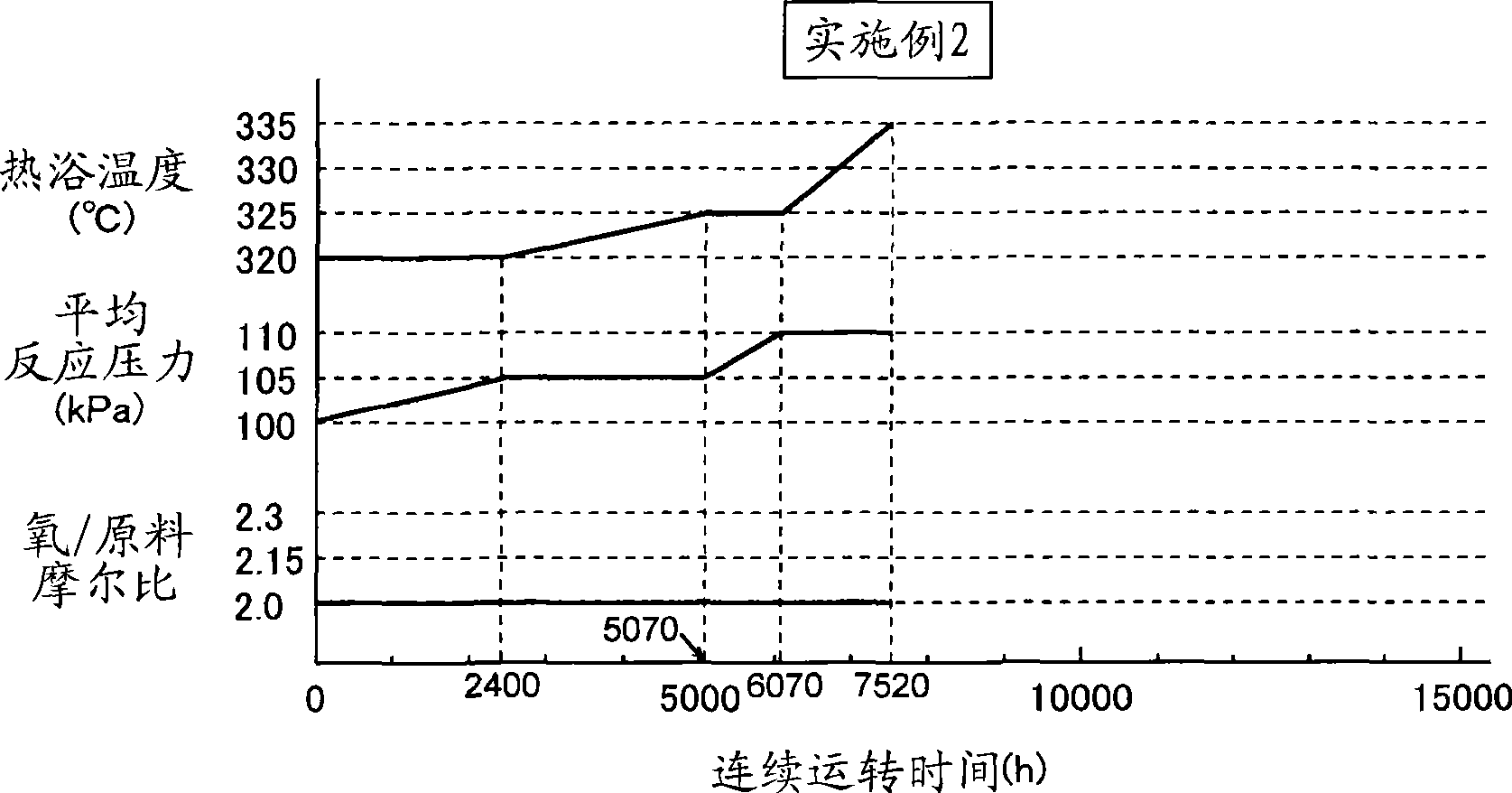
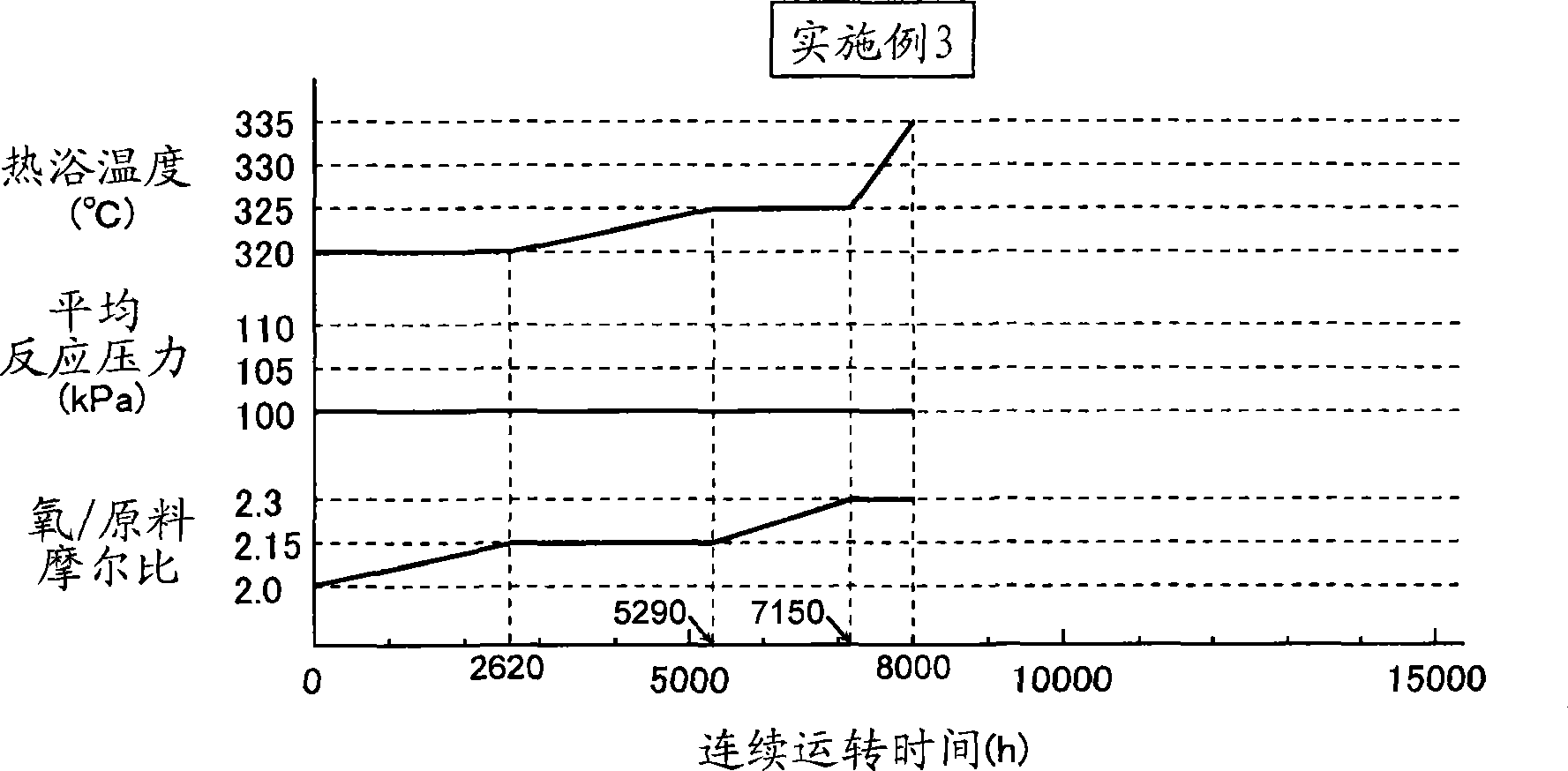
Method for producing methacrolein and methacrylic acid
ActiveCN104781221AHigh yieldOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationGas phaseReaction rate
Provided is a method for producing methacrolein and methacrylic acid, whereby it becomes possible to improve the yields of methacrolein and methacrylic acid. A method for producing methacrolein and methacrylic acid by carrying out the gas-phase catalytic oxidation of at least one raw material selected from the group consisting of isobutylene, TBA and MTBE with molecular oxygen in the presence of a catalyst comprising molybdenum, bismuth and iron using a fixed bed reactor, wherein the reaction starts at a temperature lower than a reaction temperature TA (˚C), the reaction temperature is so controlled that the reaction rate of the raw material can become constant while rising the reaction temperature, and the reaction is terminated at a temperature higher than TA (˚C) in which TA (˚C) represents the boundary temperature of the activation energy of the oxidation reaction, and wherein the ratio of A to B (i.e., A / B) is 0.05 to 0.18 in which A (˚C / hr) represents the average value of the temperature-rising rates employed until the reaction temperature reaches TA and B (˚C / hr) represents the average value of the temperature-rising rates employed at reaction temperatures higher than TA.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Heat field border displaying method ofr microwave interventional therapy of tumor
InactiveCN101088474AAvoid permutationsSimple processSurgical instrument detailsMicrowave therapyAbnormal tissue growthMicrowave
The heat field boundary displaying method for microwave interventional therapy of tumor includes the following steps: 1. measuring and calculating SAR distribution function of real-time 3D solidification heat field of single microwave antenna under different radiation power; 2. establishing mathematic model of heat field distribution under the action of over one microwave antenna based on the SAR distribution function; and 3. substituting the boundary temperature of the heat solidification region, the treating time and the tumor perfusing coefficient into the mathematic model of heat field distribution to find out the coordinate points meeting the requirement of the mathematic model and to find out the 3D display of the coordinate point set through software treatment. The present invention has continuous regulation of treating parameters, simple process, fast calculation speed and real-time display.
Owner:广东世荣兆业股份有限公司
Method and system for controlling brake circuit of wind power converter
ActiveCN109449995ARefined outputEfficient way of workingSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc-ac conversionControl signalBoundary temperature
The invention provides a method and system for controlling a brake circuit of a wind power converter. The method comprises the following steps: assigning the duty ratio of a control signal of each brake circuit for each of the at least one brake circuit according to total brake power; calculating real-time temperature of a brake resistor in each brake circuit and real-time brake power of each brake circuit; according to the real-time temperature of the brake resistor in each brake circuit, calculating braking energy that can be absorbed by each brake circuit in the case of reaching safety boundary temperature of each brake resistor; and calculating allowable running time of each brake circuit. The allowable running time of any one of the brake circuits is a specific value between the braking energy that can be absorbed by any one of the brake circuits and the real-time brake power of any one of the brake circuits; the duty ratio of the control signal of each brake circuit is adjusted based on the allowable running time of each brake circuit so as to ensure safe operation of each brake circuit and invariability of the total brake power.
Owner:BEIJING ETECHWIN ELECTRIC
Power cable connector construction normalization detection method based on temperature measurement
ActiveCN103644884AEasy to detectSmall amount of calculationMeasurement devicesCorrelation coefficientProcess quality
The invention relates to the field of power cable connector construction normalization detection, and particularly relates to a power cable connector construction normalization detection method based on temperature measurement. According to the power cable connector construction normalization detection method, a cable connector temperature measurement dot matrix is arranged and the temperature of each point is measured through a sensor with the accuracy meeting certain requirement so that the temperature distribution condition of the surface of a cable connector is obtained, and correlation coefficients which represents the temperature distribution uniformity degree of various sections, such as the relative deviation and k-order error norm of the temperature of the boundary temperature-measuring points of the sections, are further calculated; the relation between the correlation coefficients and cable connector construction process quality is obtained according to simulating calculation or experience. The power cable connector construction normalization detection method disclosed by the invention can be used for judging the defect condition of the cable connector in the aspect of the normalization of a construction process and providing the reference for the service life forecast of the cable connector through the detection of the temperature distribution of the cable connector and has the advantages of simple detection process, small calculated amount and high practicability.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Method for acquiring transient state temperature rise of single circuit cable core without depending on skin temperature
ActiveCN106294966AEasy to calculateThe principle is simpleDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTransient stateHeat flow
The invention relates to a method for acquiring the transient state temperature rise of a single circuit cable core without depending on the skin temperature. The method comprises the following steps: 1) acquiring the heat flow carrying capacity, the boundary temperature, the cable density, the specific heat harmonic heat conductivity coefficient of a cable, as well as the soil density, the soil specific heat and the soil heat transfer coefficient of soil related to the single circuit cable, to obtain a relation of the dissipated heat flow of the single circuit cable and the transient state temperature rise of the core; 2) respectively acquiring the parameters of a transient state temperature rise model, independent of the skin temperature, of the single circuit cable according to the relation of the dissipated heat flow and the transient state temperature rise of the core; 3) constructing the transient state temperature rise model, independent of the skin temperature, of the single circuit cable; 4) acquiring the environment temperature of the single circuit cable, and calculating the transient state temperature rise of the single circuit cable core. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of convenience in computation, simple principle, advanced method and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Overvoltage protection element
InactiveUS20100328829A1Reliable and good connectionAvoid disadvantagesSpark gap detailsCurrent responsive resistorsOvervoltageElectricity
An overvoltage protection element with a housing, at least one overvoltage limiting component in the housing, especially a varistor, and two connecting elements for electrically connecting the overvoltage protection element to a current or signal path in a normal state, the connecting elements being in electrically conductive contact with a respective pole of the overvoltage limiting component. In the normal state of the overvoltage protection element, at least one pole is connected to a connecting element via a plug-and-socket connection, and at least one spring is located between the housing and the overvoltage limiting component such that, when the overvoltage limiting component is thermally overloaded, it is turned by the spring separating the at least one pole from the assigned connecting element, and creating a thermally separating connection between the overvoltage limiting component and the housing when the temperature of the overvoltage limiting component exceeds a given boundary temperature.
Owner:PHOENIX CONTACT GMBH & CO KG
Thermal analysis apparatus
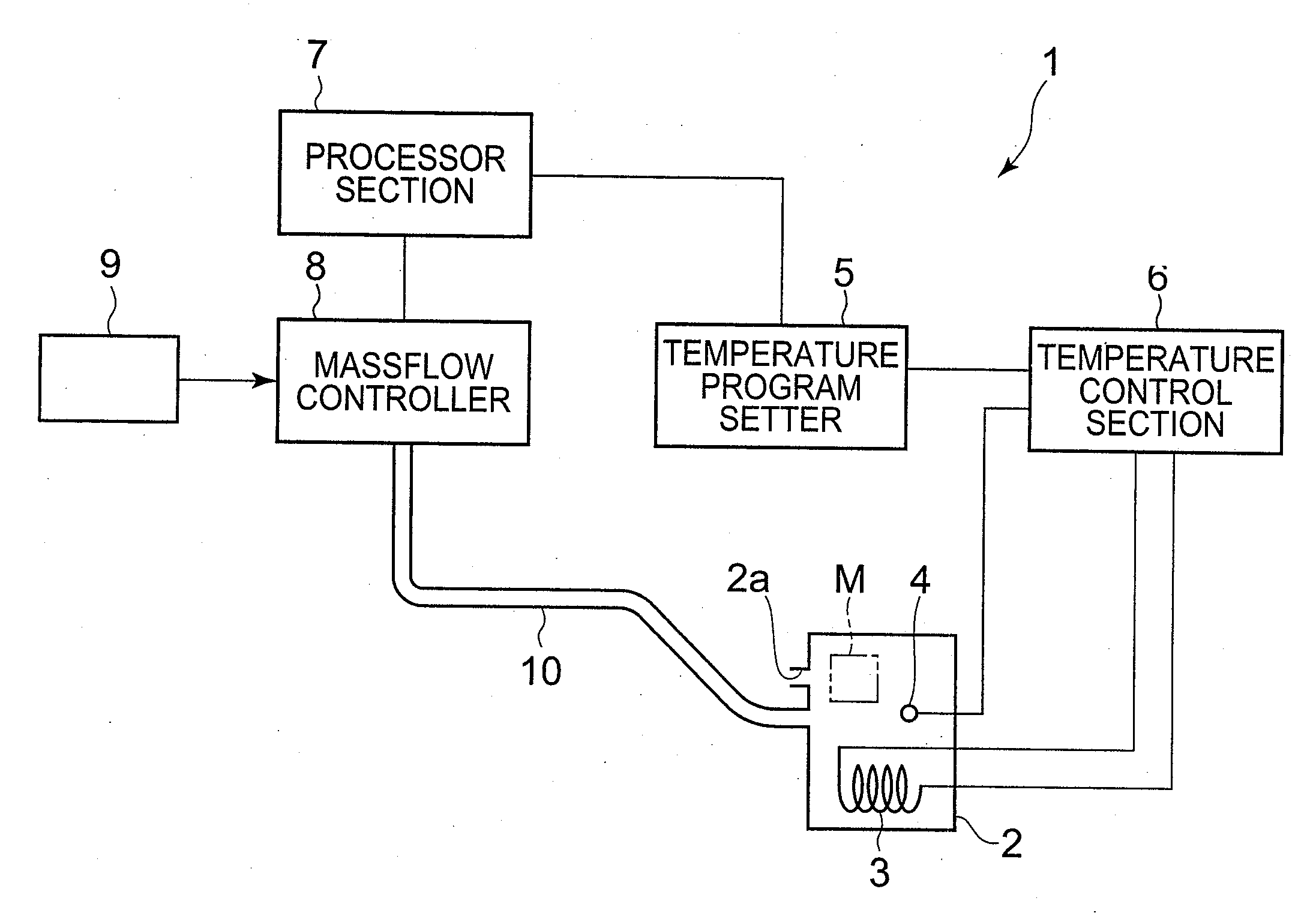
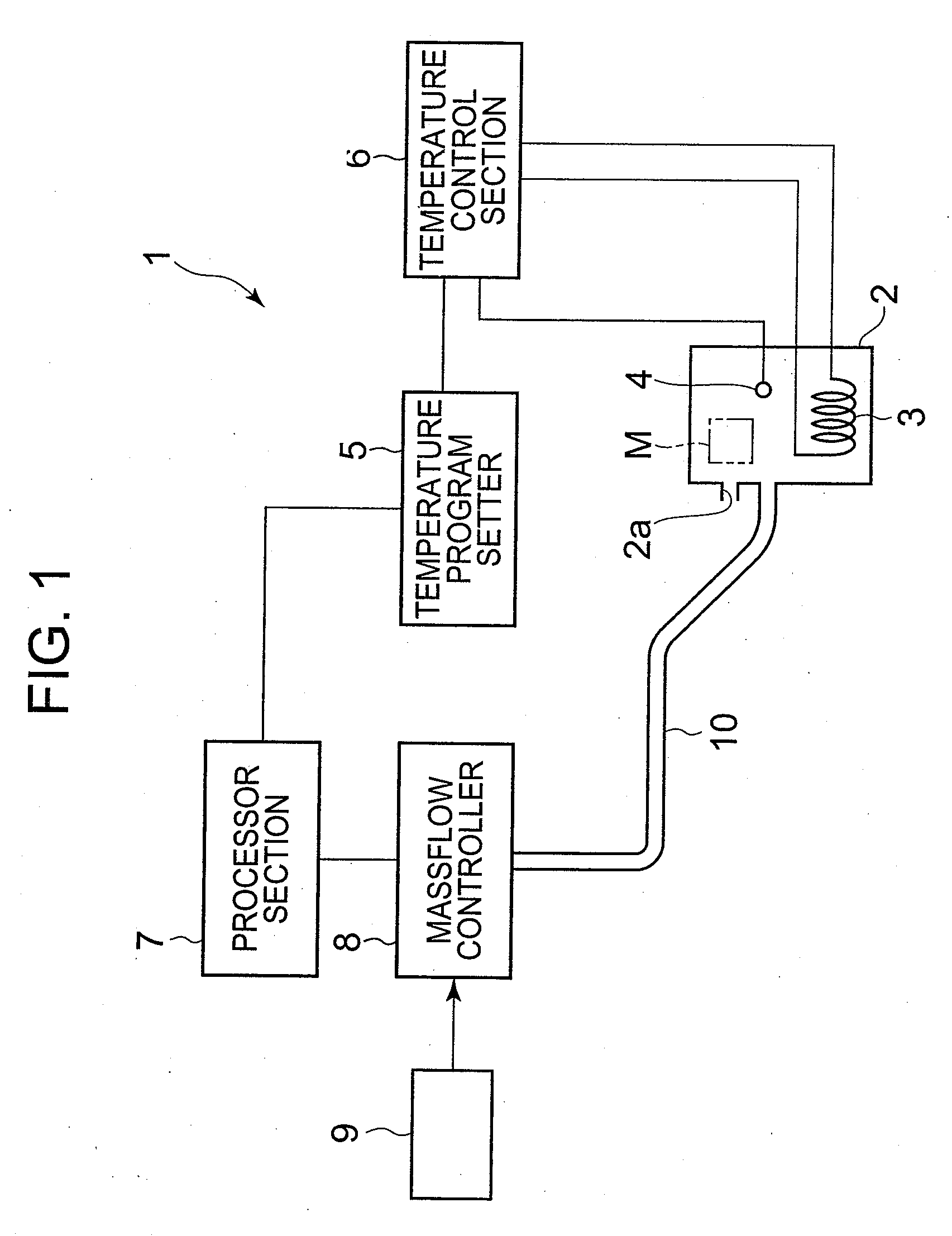
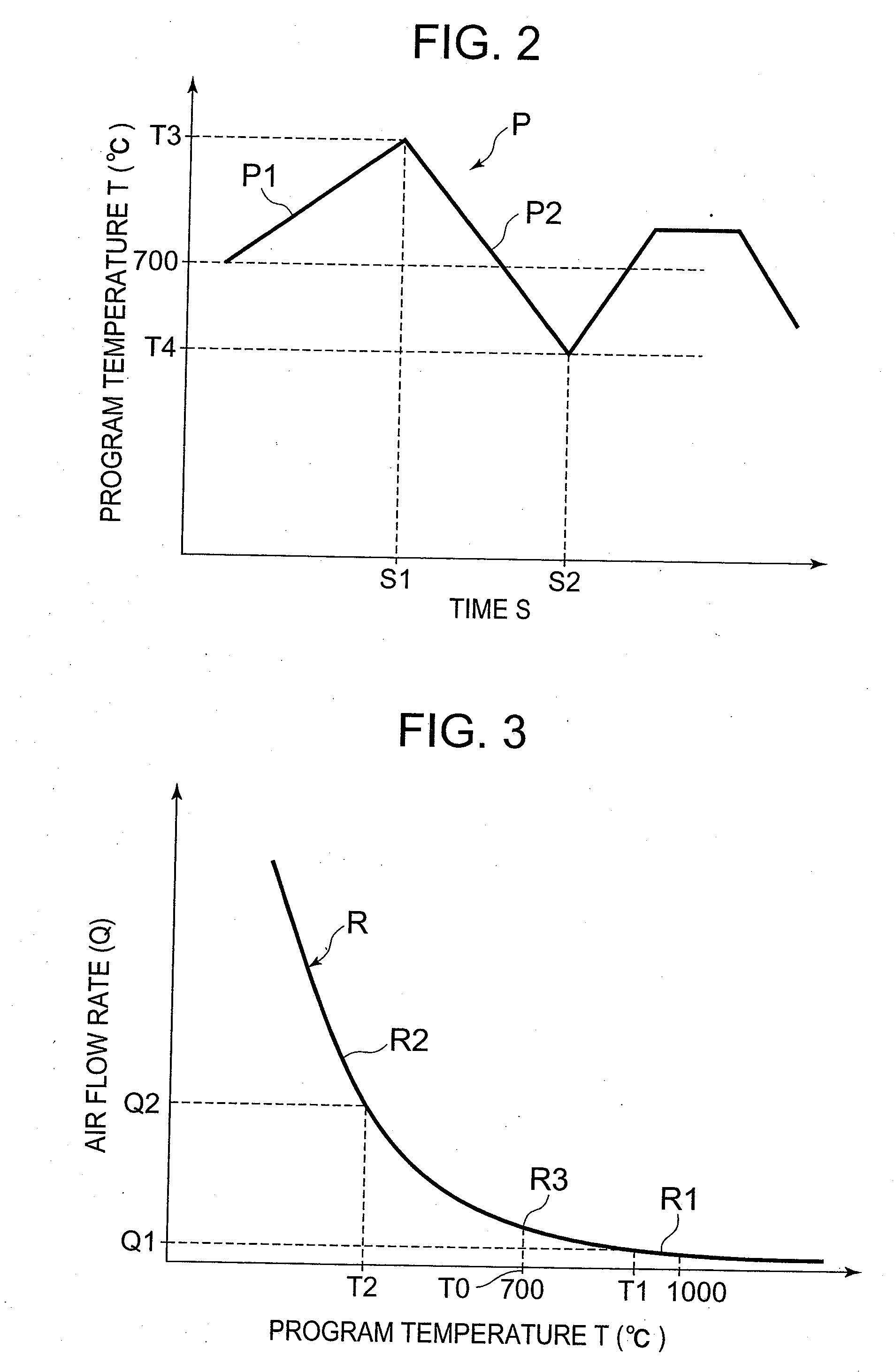
ActiveUS20080279249A1Precise temperature controlRapid coolingThermometer detailsRadiation pyrometryTemperature controlBoundary temperature
A thermal analysis apparatus possesses a temperature sensor measuring a temperature of a heating furnace inside, a temperature program setter which can set a temperature program and outputs a temperature program signal, a temperature control section adjusting a supply electric power to a heater in compliance with a difference between the temperature program signal and a detection signal of the temperature sensor, a processor section calculating an air flow rate corresponding to a program temperature, and a mass flow controller which adjusts an air flow rate supplied to the heating furnace inside in compliance with a signal of the air flow rate calculated by the processor section. In the processor section, operation expressions calculating the air flow rate are set so as to differ respectively in a higher temperature side and a lower temperature side than a predetermined boundary temperature.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH SCI CORP
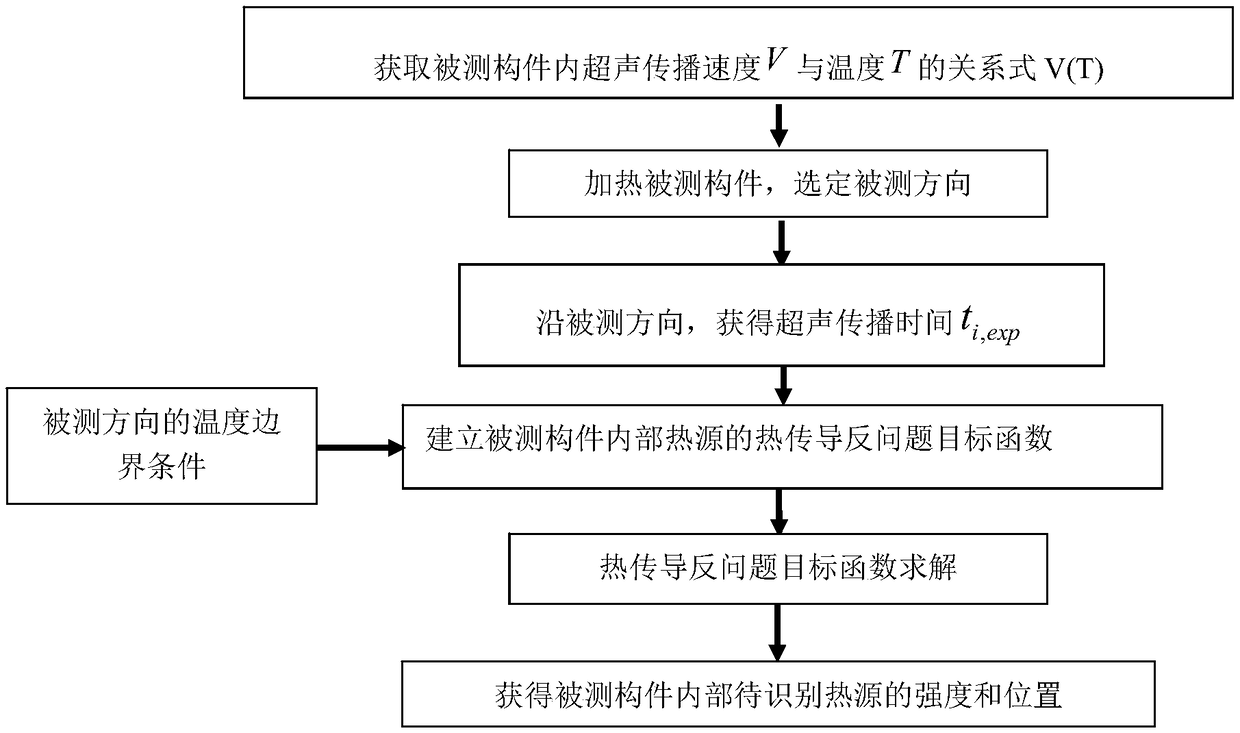
Ultrasound-based non-destructive measurement method of intensity and position of internal heat source
ActiveCN109470772ASimple measuring deviceSimple and fast operationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveTemporal change
The invention provides an ultrasound-based non-destructive measurement method of the intensity and position of an internal heat source. The method is characterized in that the time delay characteristic and the boundary temperature variation of ultrasonic waves during the internal propagation in a structure are simultaneously considered, and the solution is performed combining with inverse heat conduction problems, so as to perform non-destructive and fast measurement on the intensity and position of the heat source, which can change along with time in the structure. In the invention, no temperature information of internal points of the structure is needed to be acquired, so that measuring devices are simplified, and the operation is easy and convenient; and compared with an infrared detection technique of the internal heat source, the method disclosed by the invention can more effectively detect the intensity and position of the internal heat source of the structure, and has the advantages of high measuring speed, large measuring range and the like.
Owner:CHINA SPECIAL EQUIP INSPECTION & RES INST
Station boiler air preheater hot spot detecting method based on analog computation of rotor temperature field
InactiveCN101382458BSafe and stable operationImprove reliabilityThermometer applicationsAir preheaterPower station
The invention discloses a power station boiler air preheater heat spot detecting method based on rotor temperature field analog computation. The method is implemented according to the following steps: parameters of the air preheater needing to be monitored are determined and a temperature reference value is set; various parameters are collected in real time and the obtained parameters are input into a computation module; a boundary temperature value is initialized, and boundary conditions are determined; the temperature of the section, the interior of the sub-bin and a fluid and a heating surface on the exit boundary is obtained by using a difference equation; if temperature error obtained before and after an interactive process is in accordance with the set temperature reference value requirement, the computation is over, otherwise, the boundary temperature value is renewed to carry out interaction again. When fault happens to an infrared heat spot sensor or an executing mechanism ofan existing heat spot detecting system, the system sends out a switching command, by using the temperature field parameters obtained by the analog computation of the method of the invention as the reference value for control, the reliability of the air preheater heat spot detector is improved and the safe and stable operation of the detecting system is guaranteed.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Overvoltage protection element
InactiveUS8482896B2Reliable and good connectionAvoid disadvantagesSpark gap detailsCurrent responsive resistorsOvervoltageElectricity
An overvoltage protection element with a housing, at least one overvoltage limiting component in the housing, especially a varistor, and two connecting elements for electrically connecting the overvoltage protection element to a current or signal path in a normal state, the connecting elements being in electrically conductive contact with a respective pole of the overvoltage limiting component. In the normal state of the overvoltage protection element, at least one pole is connected to a connecting element via a plug-and-socket connection, and at least one spring is located between the housing and the overvoltage limiting component such that, when the overvoltage limiting component is thermally overloaded, it is turned by the spring separating the at least one pole from the assigned connecting element, and creating a thermally separating connection between the overvoltage limiting component and the housing when the temperature of the overvoltage limiting component exceeds a given boundary temperature.
Owner:PHOENIX CONTACT GMBH & CO KG
Method for producing unsaturated aldehyde and unsaturated carboxylic acid
ActiveCN101437782AAchieve long-term useOrganic compound preparationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsReaction rateCatalytic oxidation
Disclosed is a method wherein propylene, isobutylene or a tertiary butanol is catalytically oxidized with molecular oxygen in a vapor phase for producing corresponding unsaturated aldehyde and unsaturated carboxylic acid. This method enables to use a catalyst for a long time. Specifically disclosed is a method wherein propylene, isobutylene or a tertiary butanol as a raw material is catalytically oxidized with molecular oxygen in a vapor phase in the presence of a catalyst, which is composed of a complex oxide essentially containing molybdenum, bismuth and iron, for producing corresponding unsaturated aldehyde and unsaturated carboxylic acid. In this method, the reaction pressure and / or the molar ratio between oxygen and the raw material are controlled so that the reaction rate of the raw material is kept constant at a certain level within a temperature range of not less than (TA - 15) DEG C and not more than TA DEG C with TA DEG C being the boundary temperature of the activation energy of the catalyst.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
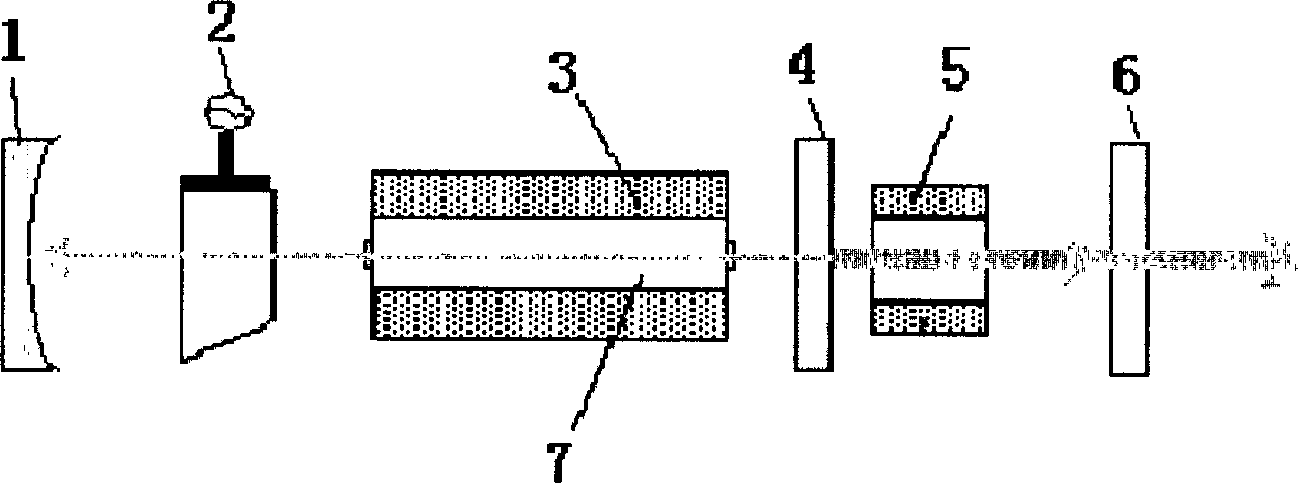
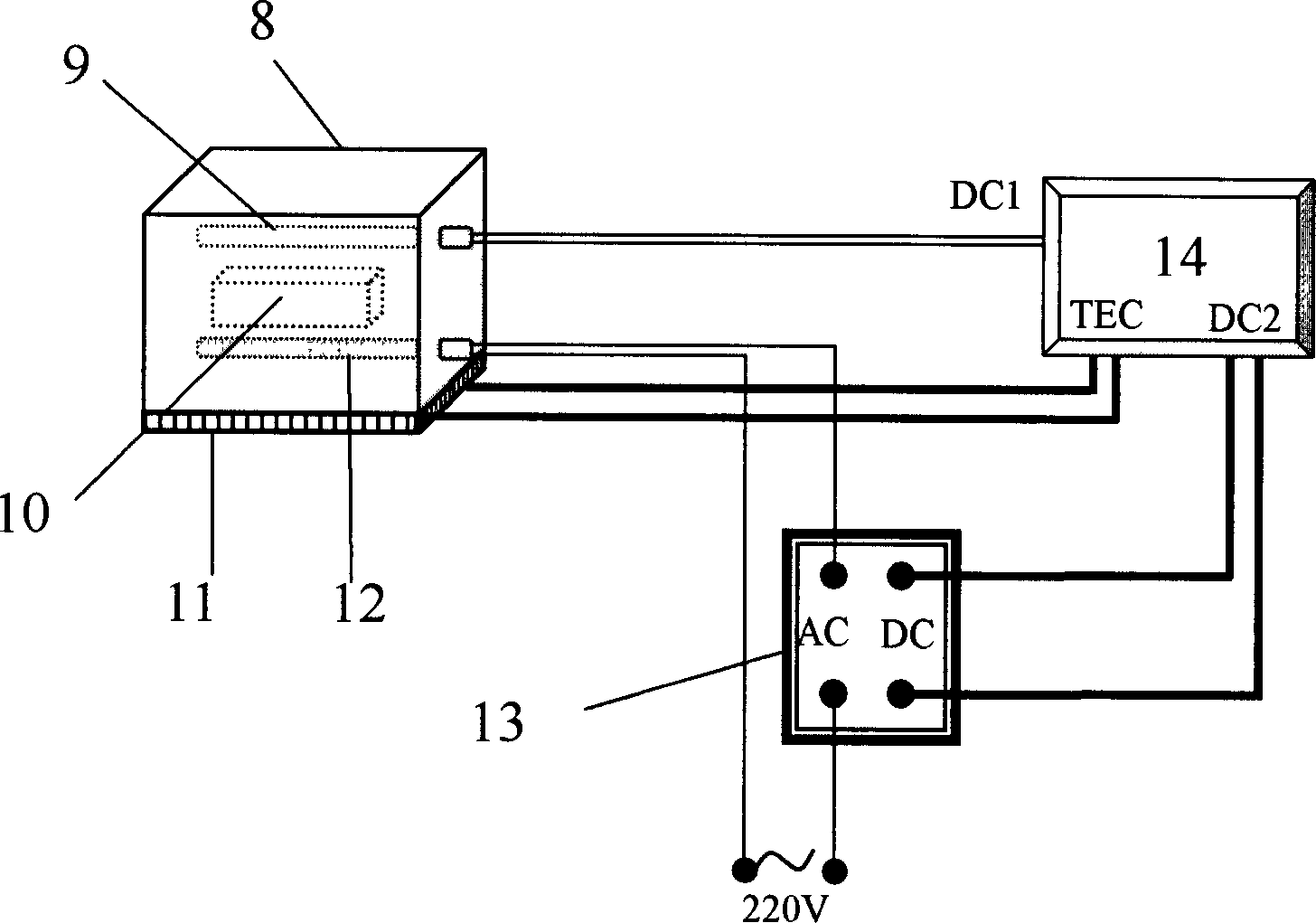
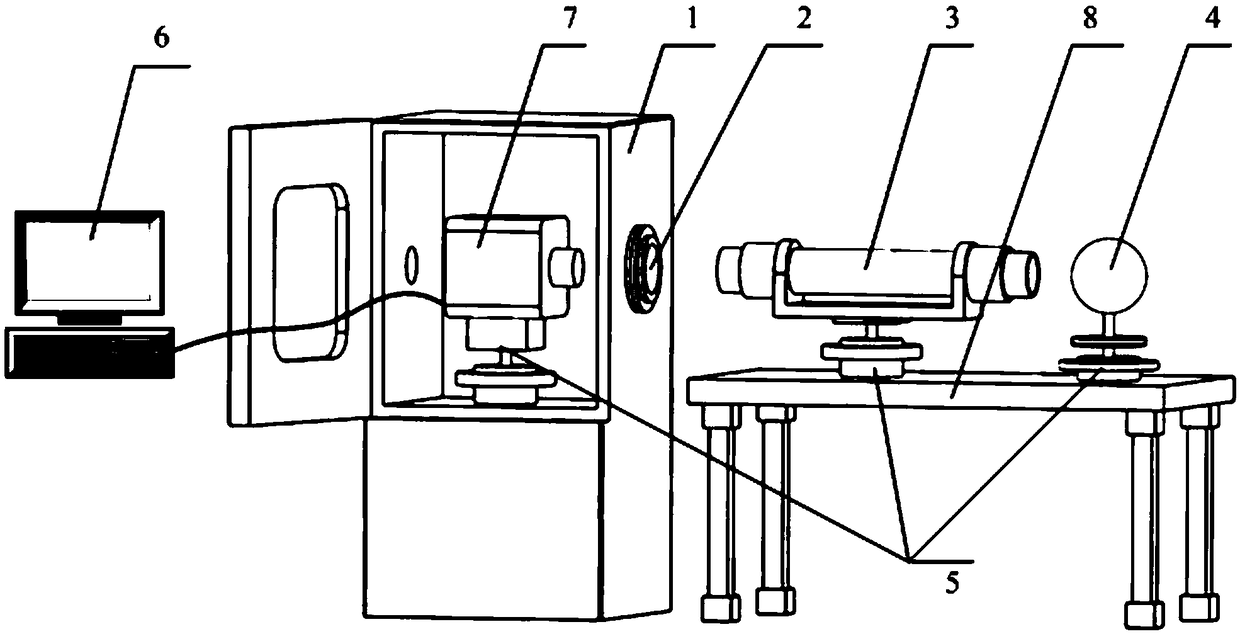
Device for quantitatively evaluating image quality of photoelectric imaging system under boundary temperature condition
PendingCN108801594ASimple structureReduce test errorOptical apparatus testingImaging qualitySystem under test
The invention relates to a device for quantitatively evaluating the image quality of a photoelectric imaging system under a boundary temperature condition and belongs to the optical detection field. In order to meet the needs of the prior art, the device mainly comprises a temperature simulation device, an optical window, a collimator, an integrating sphere, three mechanical adjustment devices, acomputer processing system and a test bench; the temperature simulation device is a high- and low-temperature test chamber with a dehumidification function; a photoelectric imaging system under test is arranged in the temperature simulator; the optical window is fixed at a through hole in the side wall of the temperature simulation device; the photoelectric imaging system under test, the optical window, the collimator and the integrating sphere are arranged coaxially in sequence; the photometric imaging system under test, the collimator and the integrating sphere are respectively arranged on the three mechanical adjustment devices; the mechanical adjustment devices where the collimator and the integrating sphere are located are mounted on the test bench; and the computer processing systemis connected with the photoelectric imaging system under test. With the device adopted, the image quality of a typical photoelectric imaging system can be quantitatively evaluated under the boundary temperature condition.
Owner:中国人民解放军陆军沈阳军事代表局驻长春地区军事代表室
Phase miss match compensation heater of high power internal cavity freguency multiplier laser and its method
This invention discloses a phase mismatch compensation heater and a method for a high power inner cavity multiple frequency laser including a KTP multiple crystal set in a closed metallic box inserted with a temperature sensor and a heating tube, the bottom is set with a semiconductor refrigerator and the box is set with a solid relay of a control box. The method includes: designing a KTP crystal boundary temperature value, increasing power of the heating pipe at low temperature to reduce voltage of the refrigerator to let the temperature approach to the designed value so as to keep the boundary temperature of the KTP multiple crystal at a stable state during the process dynamic balance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
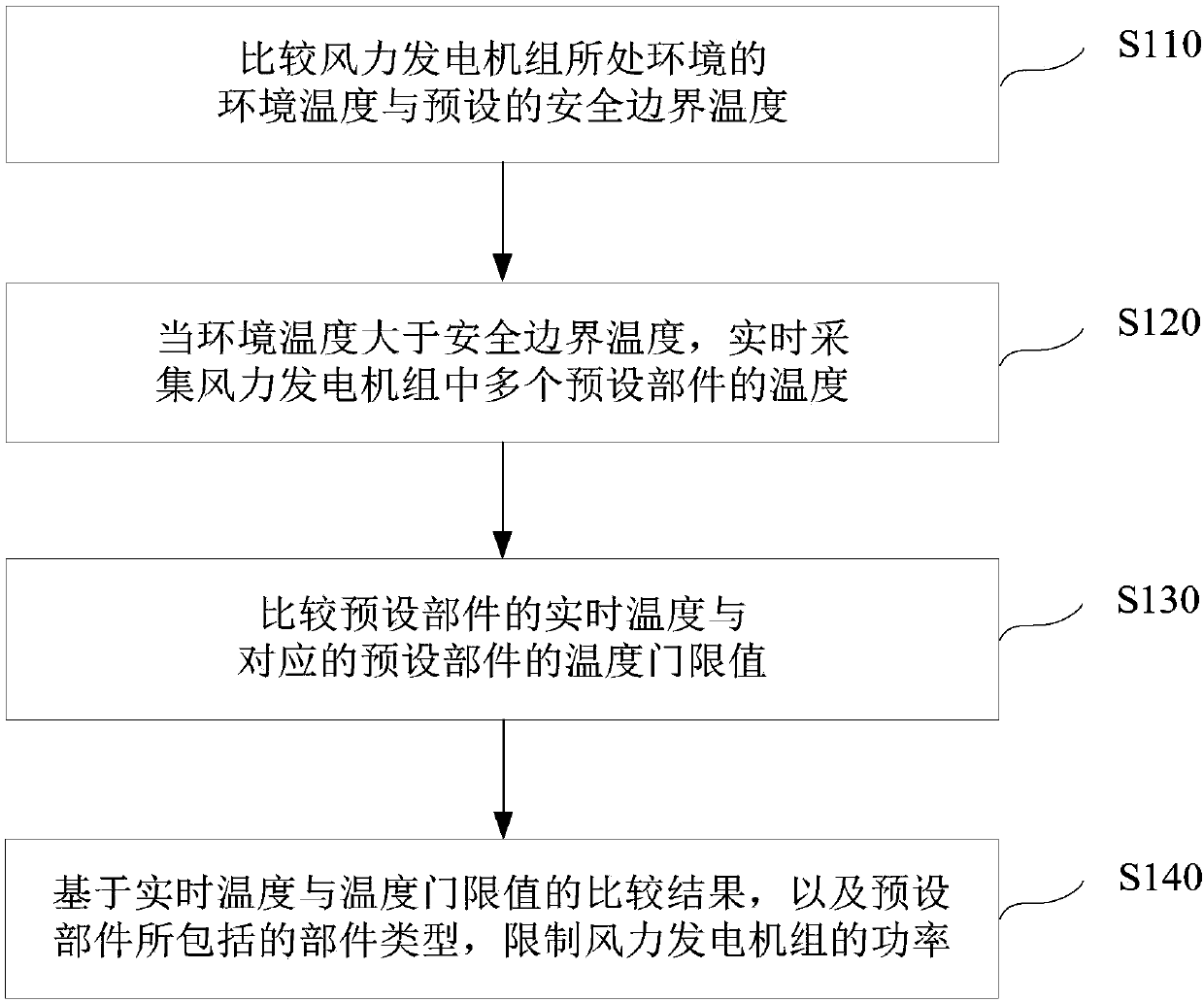
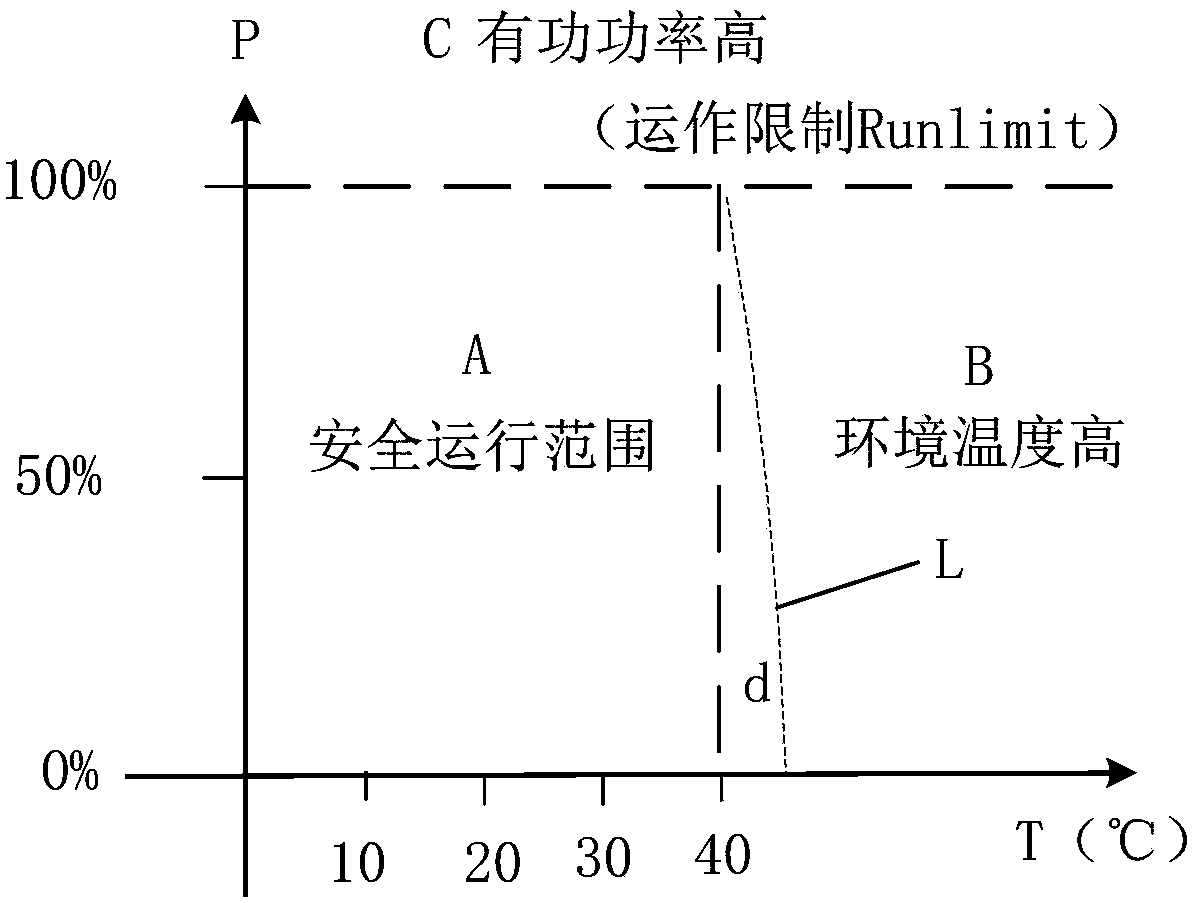
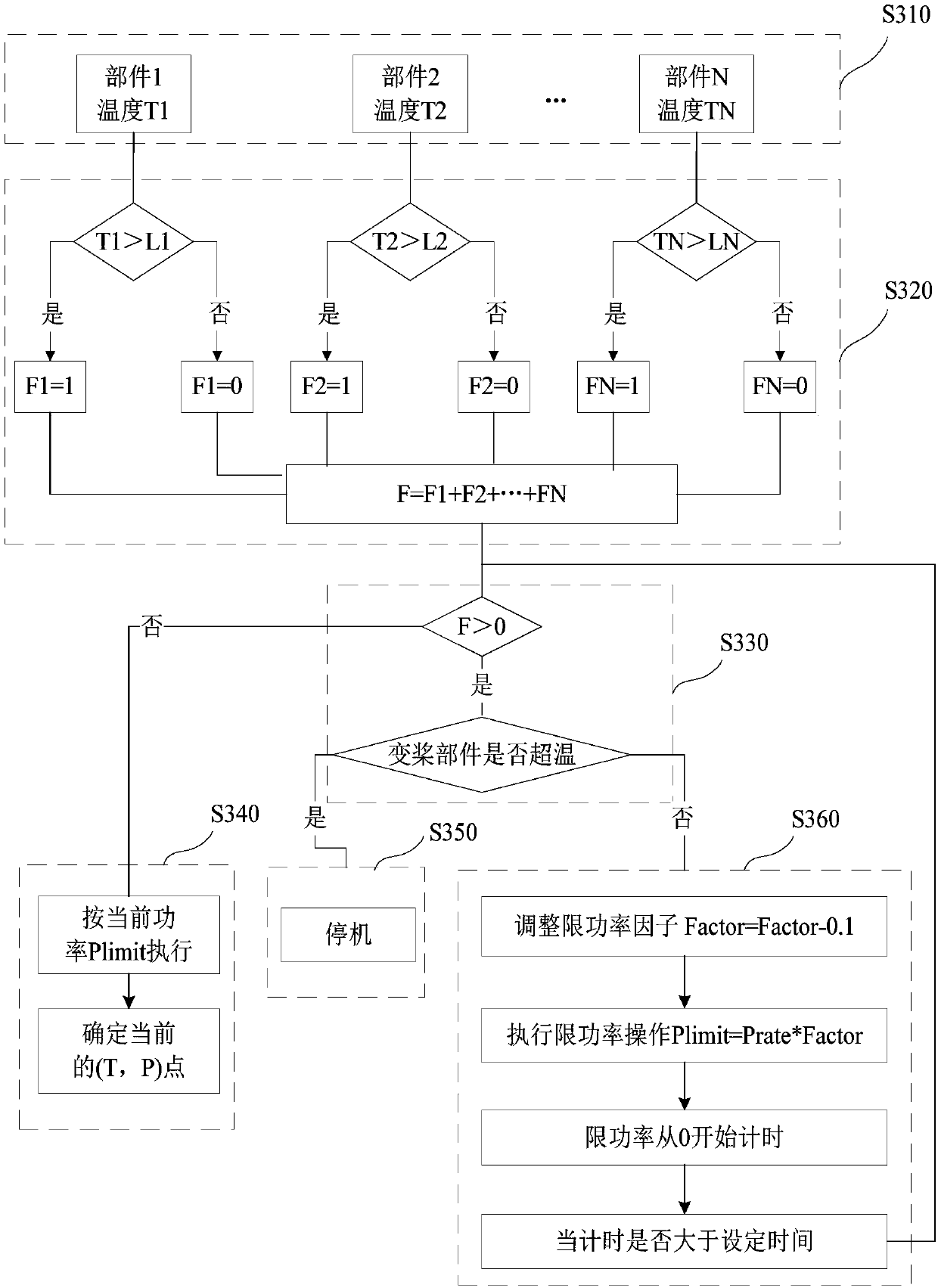
Power control method and device for wind turbine generator system
ActiveCN109779835AMaintain high temperature power generationReduce huge lossesWind motor controlFinal product manufactureBoundary temperatureEngineering
The invention discloses a power control method and device for a wind turbine generator system. The method comprises the steps of comparing the environment temperature of the environment in which the wind turbine generator system is located with a preset safety boundary temperature; collecting the temperatures of multiple preset components in the wind turbine generator system in real time when theenvironment temperature is higher than the safety boundary temperature; comparing the real-time temperatures of the preset components with temperature threshold values of the corresponding preset components; and limiting the power of the wind turbine generator system based on comparison results of the real-time temperatures and the temperature threshold values and the types of the preset components. According to the power control method and device, the wind turbine generator system can keep working when the temperature is beyond the safety boundary temperature, and maintain high-temperature electricity generation, thereby expanding the safe operation range, and reducing huge loss caused by a shutdown.
Owner:XINJIANG GOLDWIND SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com