Device and method for testing heat-conducting property of thin film material
A technology for thermal conductivity and thin-film materials, which is applied in the field of thermal conductivity testing devices for thin-film materials, can solve the problems of low thermal conductivity detection accuracy and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] Select the polyimide (PI) graphite film that comparative example 1 provides to carry out thermal conductivity test, including:
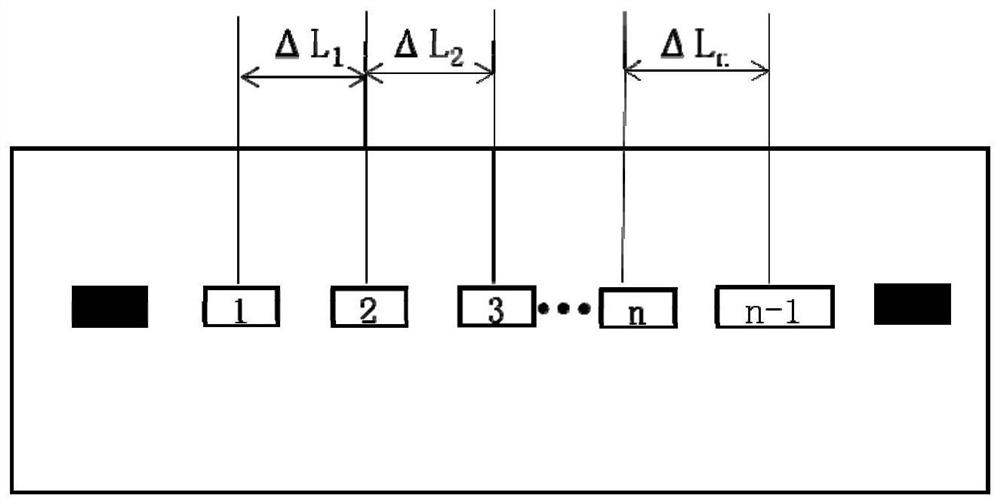
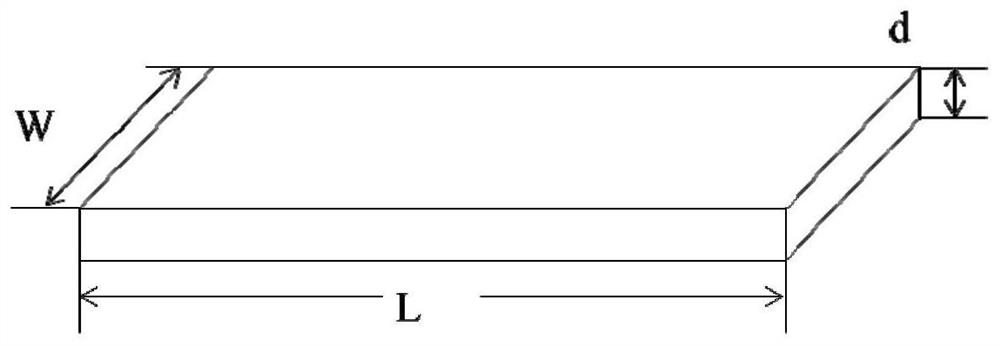
[0071] The PI film is tested by using the thermal conductivity testing device for thin film materials provided by the application, wherein the number of temperature measuring elements is three, and the distance between thermocouple temperature measuring points is ΔL=2cm. The polyimide graphite film has a thickness d of 73 μm and is cut into a rectangle with a width of 1 cm and a length of 10 cm.
[0072] Coat the surface of the heating element, the temperature measuring element and the cooling element with thermally conductive silicone grease, and the thermal conductivity of the thermally conductive silicone grease is 1.5W / (m·K).
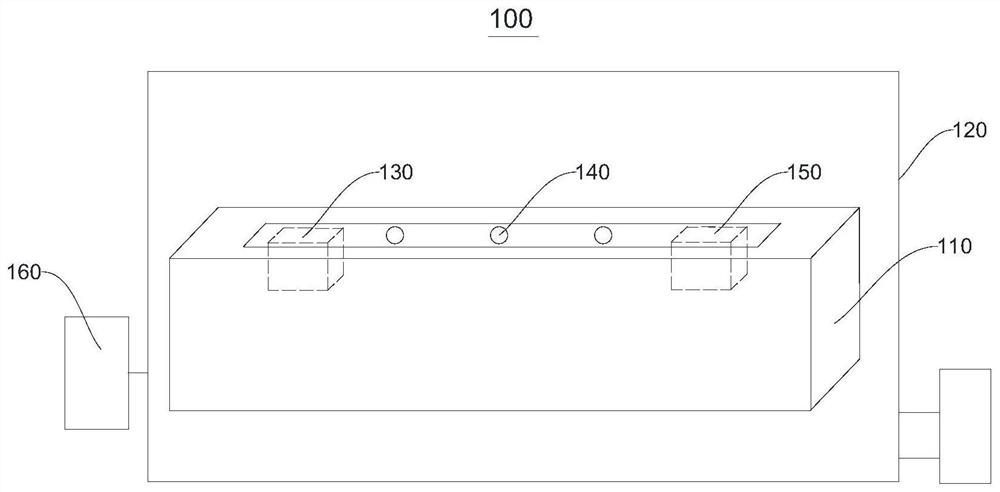
[0073] Please refer to Figure 4 , place the PI film on the test platform. Turn on the vacuum incubator, set the temperature to 25°C, and set the vacuum degree to 1000Pa.
[0074] When the constant temperature fl...
Embodiment 2
[0081] The graphene heat conduction film provided in Comparative Example 2 was selected for thermal conductivity test, and the same test method as in Example 1 was used for testing, the only difference being:
[0082] The thickness of the graphene heat conduction film is d=145μm, cut into a rectangle with a length of 10cm and a width of W=0.5cm. The temperature is set to 800Pa. When the temperature of each point is constant and reaches the steady-state heat flow, the voltage across the heating sheet is U=1.06V, the current I=0.693A, and the electric-thermal conversion rate of the heating sheet is η=80%. The test results in T 1 =37.8°C, T 2 =27.1°C, T 3 =16.8°C, calculated to get ΔT 1 =10.7°C, ΔT 2 =10.3°C, ΔT 平均 =10.5°C, substituted into the formula for calculation, the thermal conductivity λ=771.9W / (m·K).
Embodiment 3
[0086] The graphene heat-conducting film provided in Comparative Example 3 was selected for thermal conductivity testing, and the same test method as in Example 1 was used for testing, the only difference being:
[0087] The thickness of the graphene heat conduction film is d=130μm, cut into a rectangle with a length of 15cm and a width of W=1cm. Set to 500Pa. When the temperature of each point is constant and reaches the steady-state heat flow, the voltage across the heating sheet is U=0.75V, the current I=0.605A, and the electric-thermal conversion rate of the heating sheet is η=80%. The test results in T 1 =33.2°C, T 2 =26.8°C, T 3 =20.6°C, calculated to get ΔT 1 =6.4°C, ΔT 2 =6.3°C, ΔT 平均 =6.2°C, then substitute into the formula to calculate the thermal conductivity λ=886W / (m·K).
[0088] The laser flash method used in the comparative example is a non-steady-state method for testing thermal conductivity. The test principle of this method is that the thin disc sample ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com